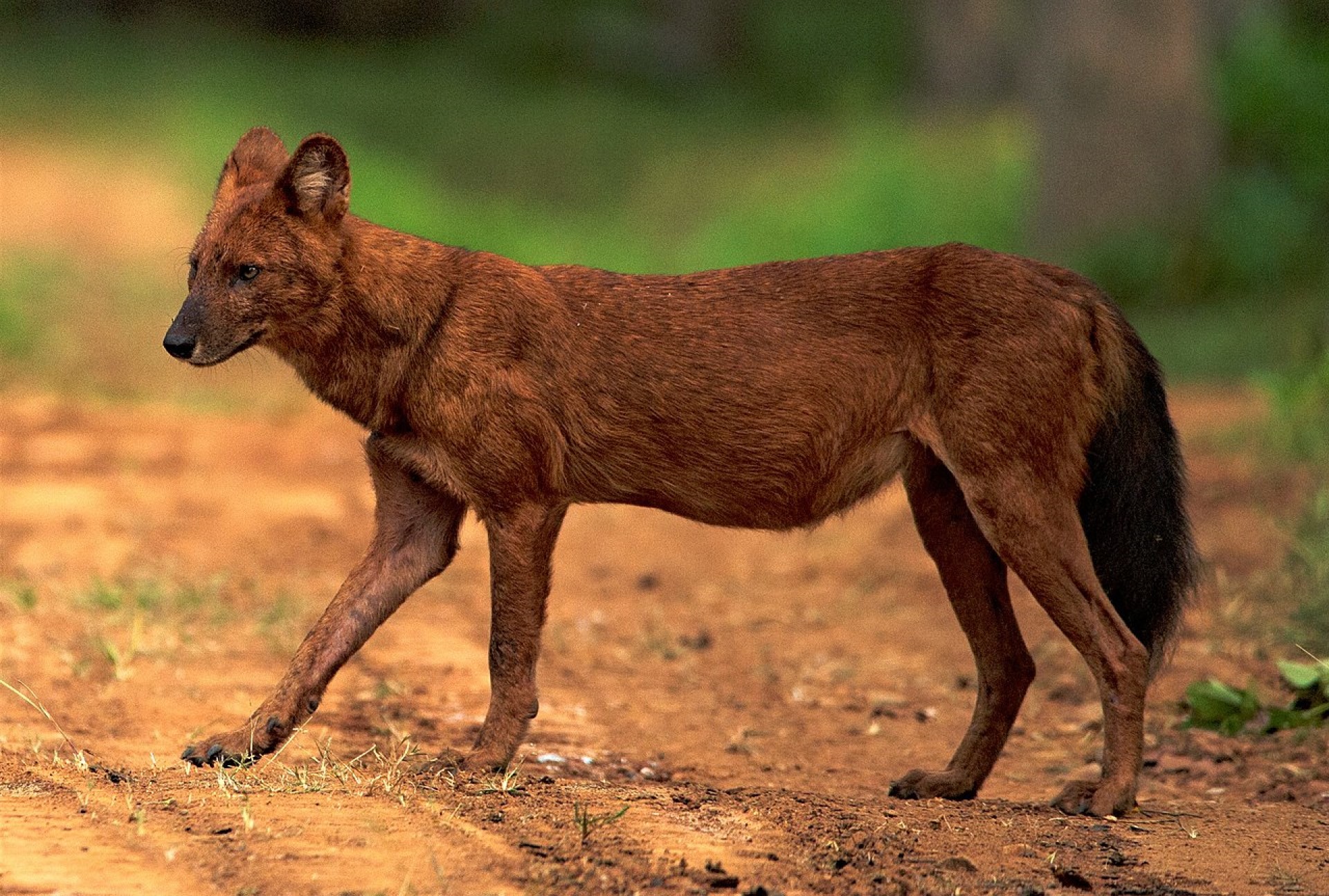
Dhole
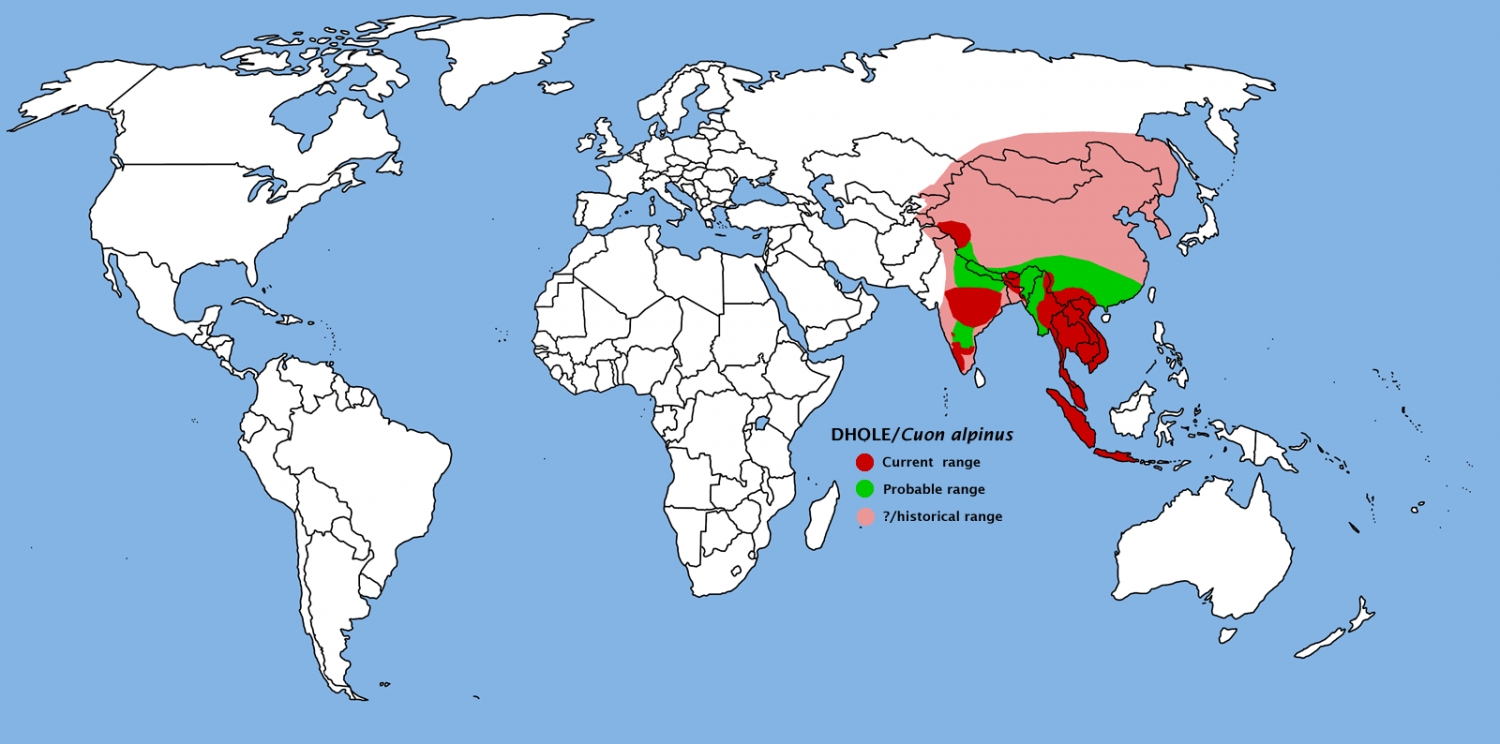 The Dhole is an ancient species of dog, It split from the rest of the dog family 5.2-7.6 million years ago.
The Dhole is an ancient species of dog, It split from the rest of the dog family 5.2-7.6 million years ago.
While it is related to the family of canis, it is different. It was once found throughout Europe, Asia and North America, but its range decreased down to its current range 12,000-18,000 years ago. In more recent times, this area has shrunk significantly, as a result of human changes.
Even with the dramatic reduction in range, it is still a large area, given the current population is thought to be around 2500 individuals, which means that it has to be a rare species, and likely there are areas with little or none of the species still found.
There are a variety of factors, from loss of habitat, persecution for livestock predation, competition from other species and diseases caught from closely related species. There are currently 7 subspecies of dhole recognized, though in the past that number has been as high as 10.
It is protected in parts of its range, but is still at threat.