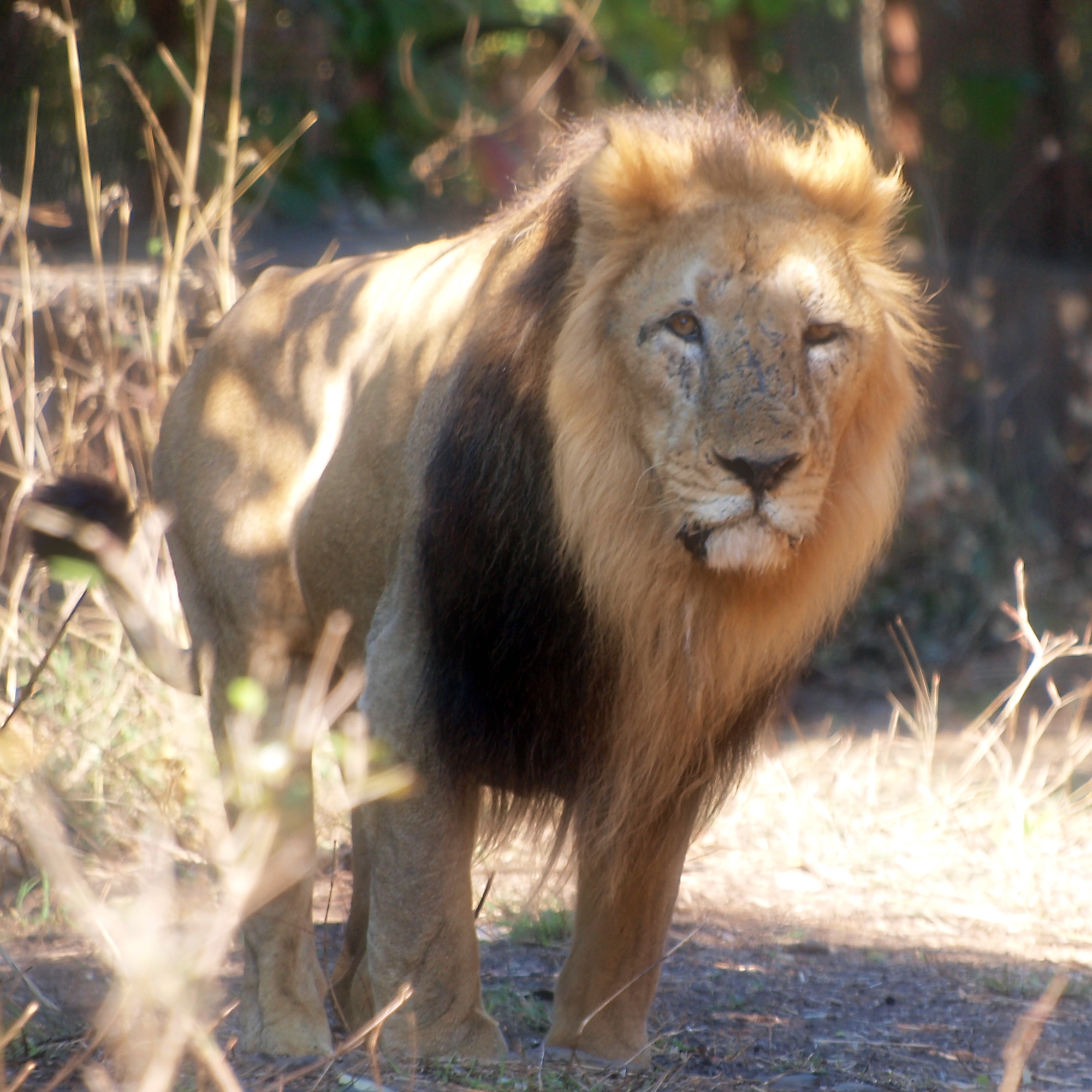
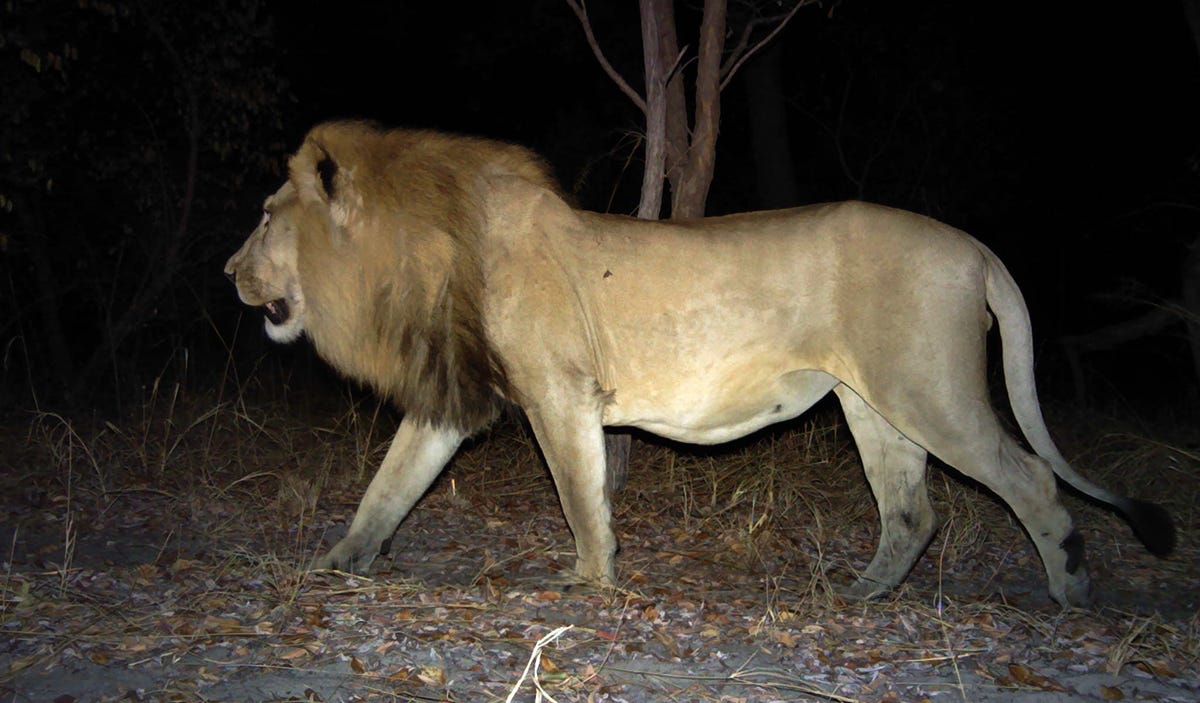
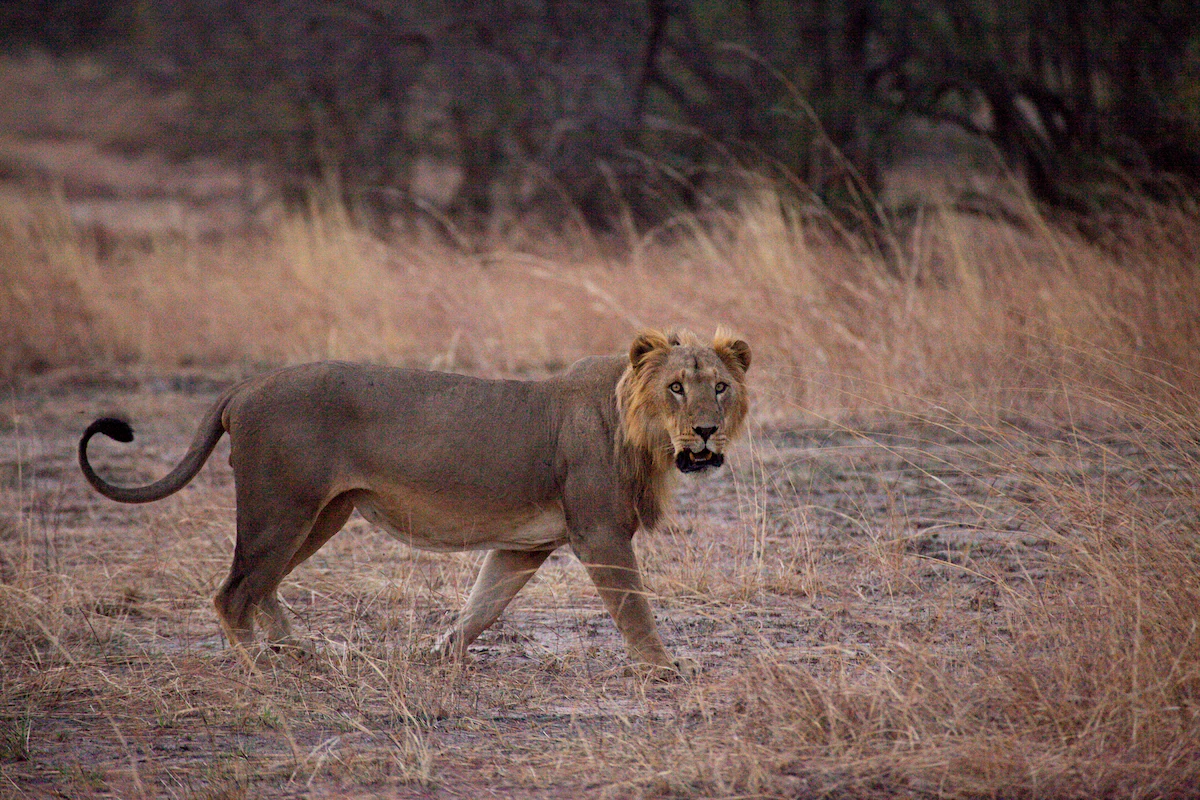
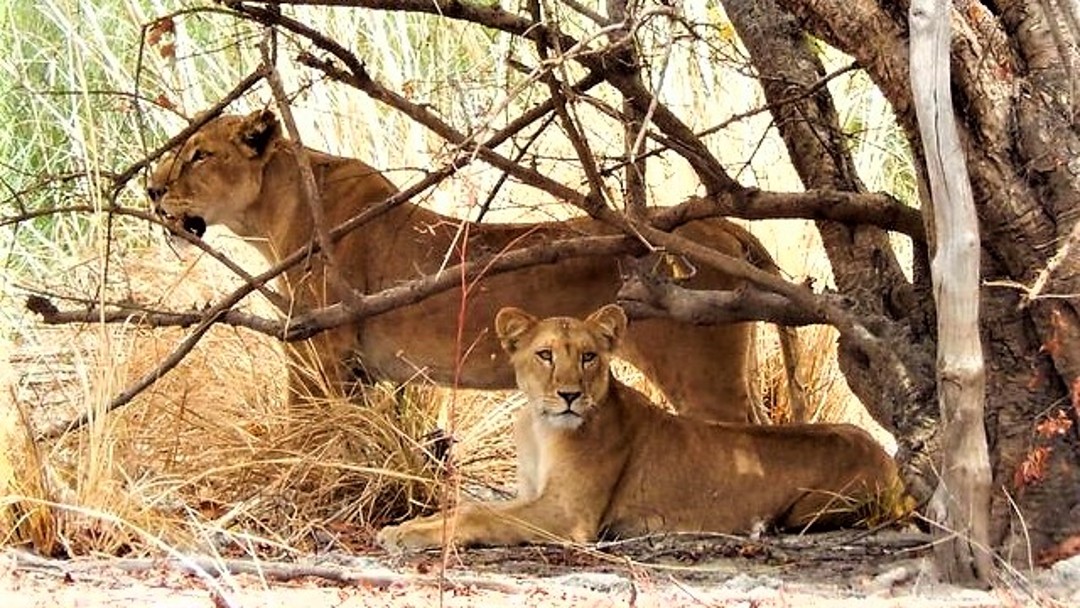
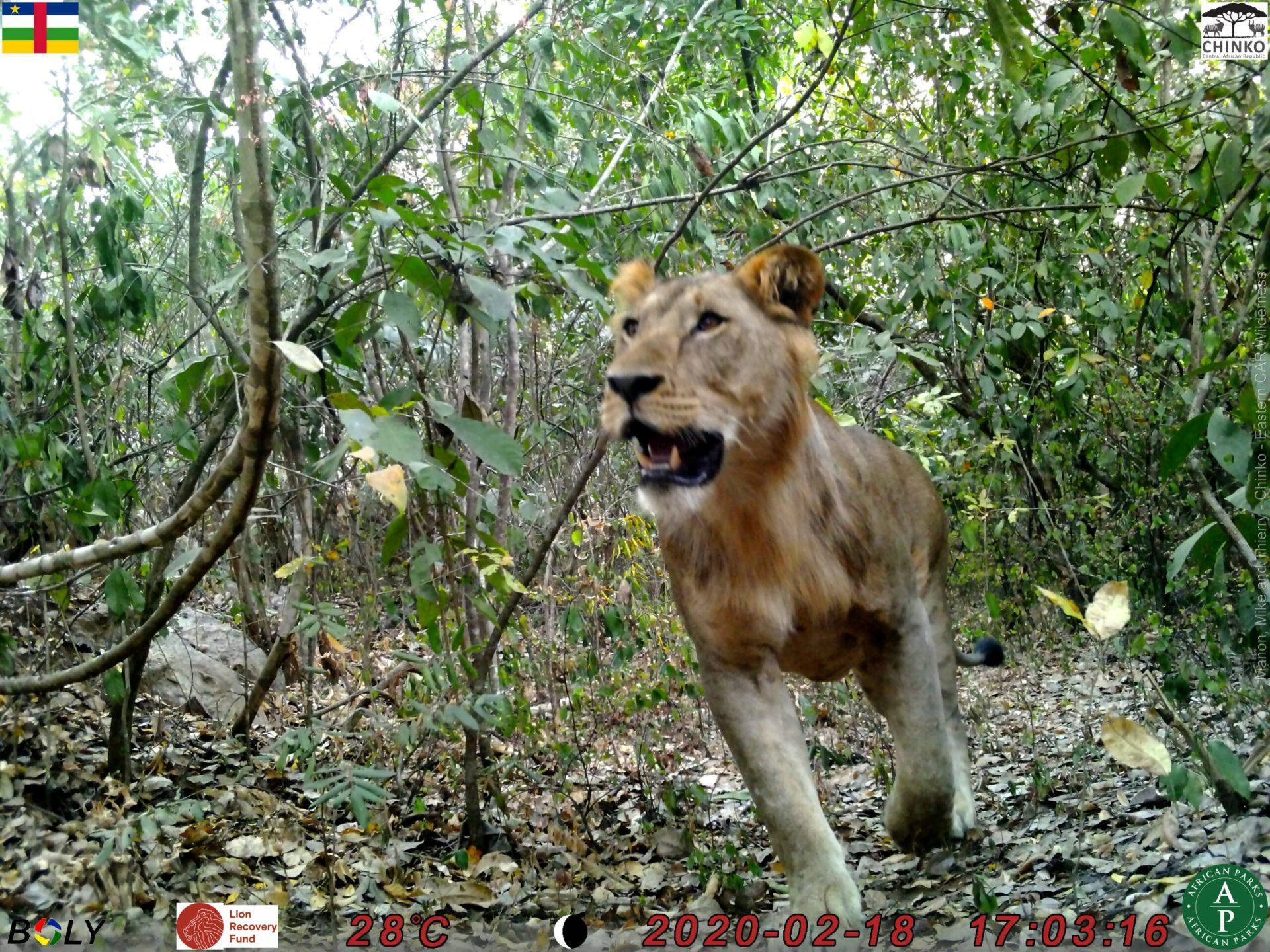
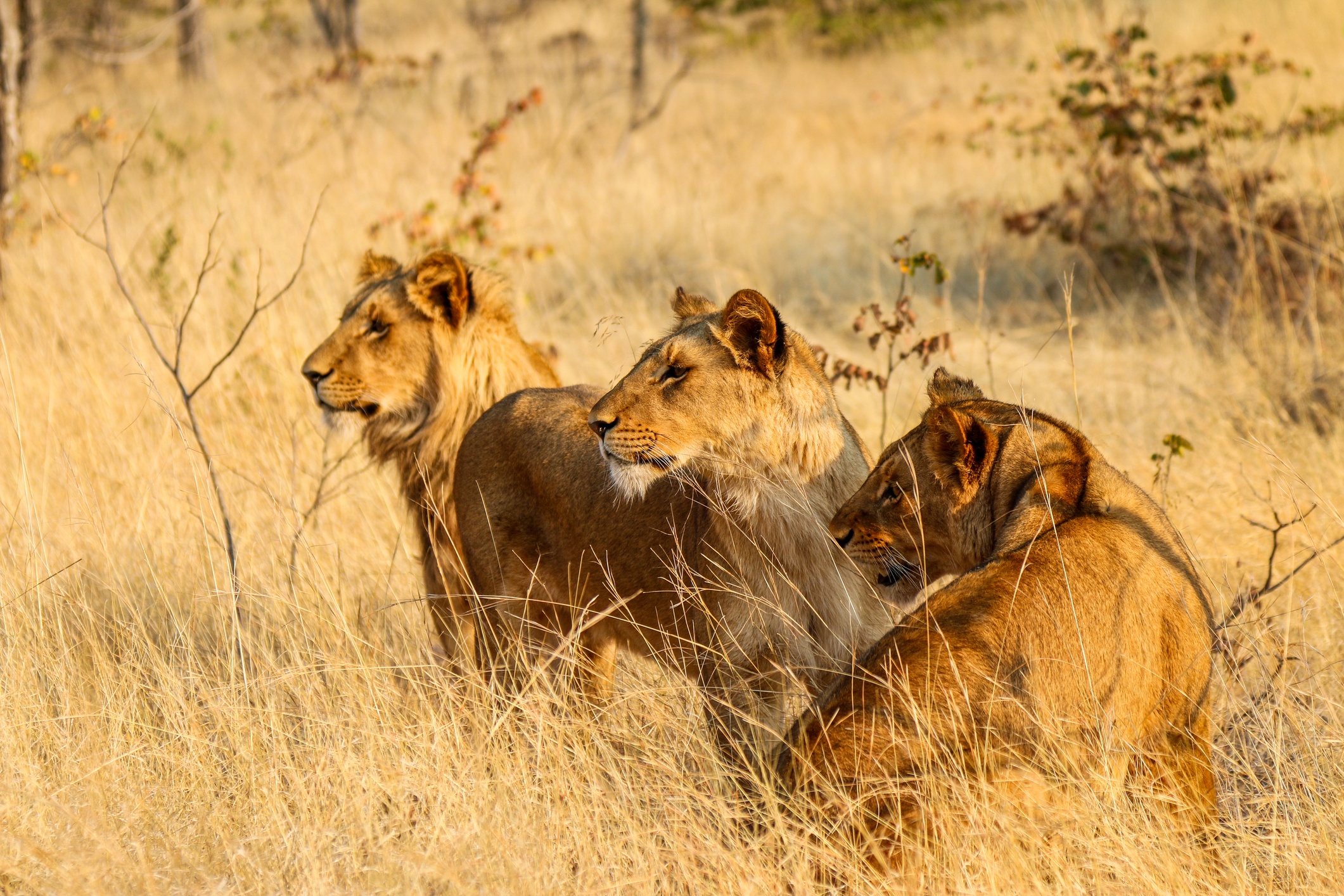
In 2021, Kenya did a survey of its wild area, and estimates that there is 2589 lions (this is around 74 lions more than the list I have been using for most of these numbers)
So, where are the Kenyan lions?
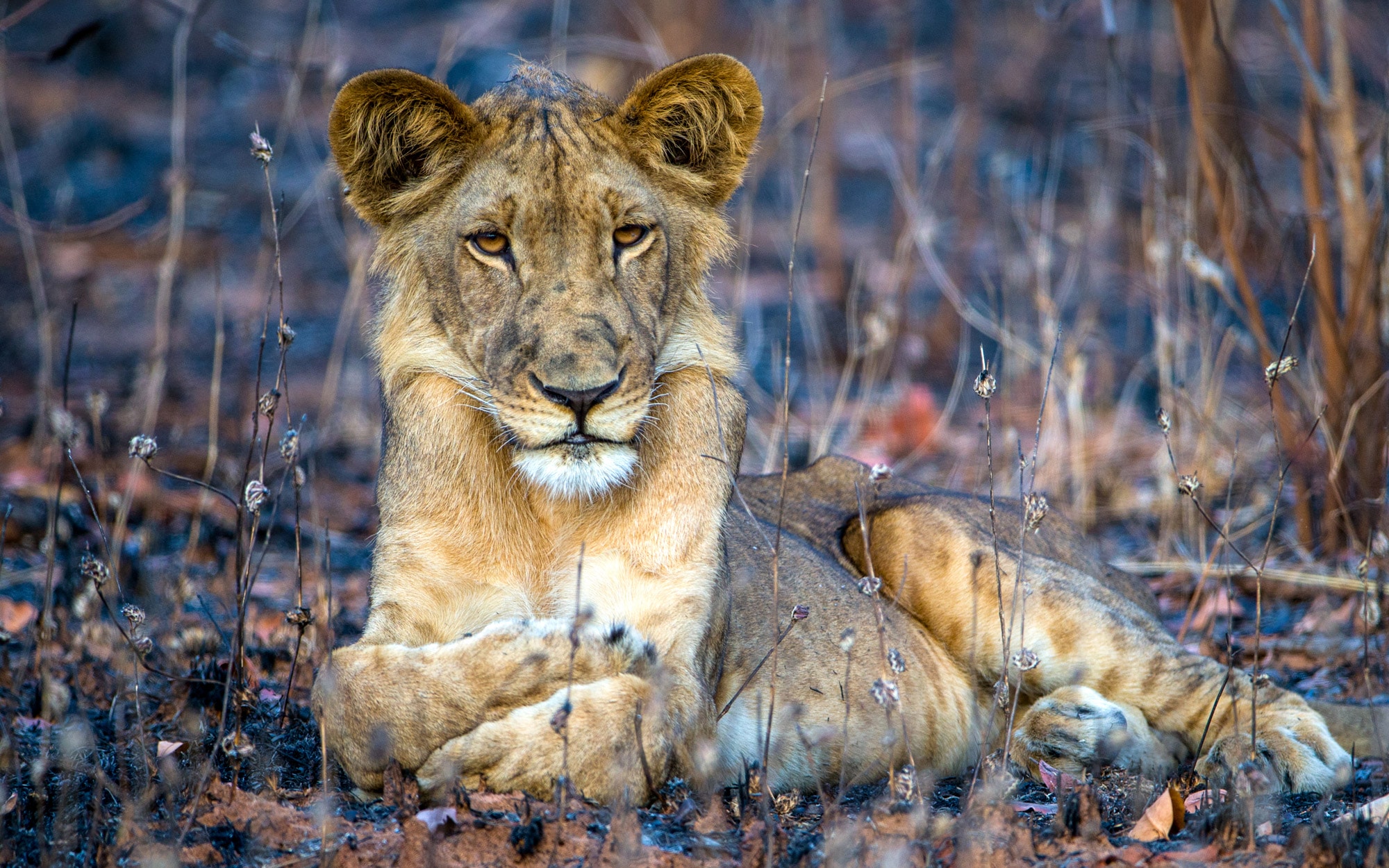
The Massai Mara national park is found in Kenya. It has an estimated population of 850-900 (this is a lifetime dream location for many people interested in wildlife). Look up the Serengeti ecosystem, for links in this ecosystem. We hope to add far more over time.
Ambosseli national park hosts roughly 100 wild lions. It is a big 5 reserve, and even has cheetah and a few wild dog, making it an ecotourism big 7 reserve (something that many larger reserves cannot claim). This reserve is only 392 square km. The Tsavo Amboselli ecosystem is thought to have roughly 675, thought these numbers are estimates, and it is unclear how accurate they are. While this whole ecosystem is very large, parts like Tsavo West are not good for animals like lion, which means that their density is likely to be higher than these numbers would suggest.
Niarobi national park has roughly 35 lions. It should be noted, that the range of the lions is thought to be around 400 square km, which is almost 3 times the size of the park at 140 square km. This park is odd. Once opening to the open savannah, the suburbs have expanded, and now largely completely surround it. Never-the-less, there is few other places in Africa where you can see lions with skyscrappers in the background. This reserve has 4 of the big 5 (missing elephants)
Hells gate national park is tiny, at half the size of the Niarobi national park. It was a big 5 reserve in the 1950s, and there is a suggestion that there are still a handful of lions, but not more than this. It is one of quite a few national parks, split by relatively short distances of human settlement, but it might as well be the other side of the moon, for the abillity for most small animals to move between.
The Abadares mountains national park still has a few lions, though it is unclear how many. In 2000 100-200 lions were killed to help a local antelope on the verge of extinction to survive.
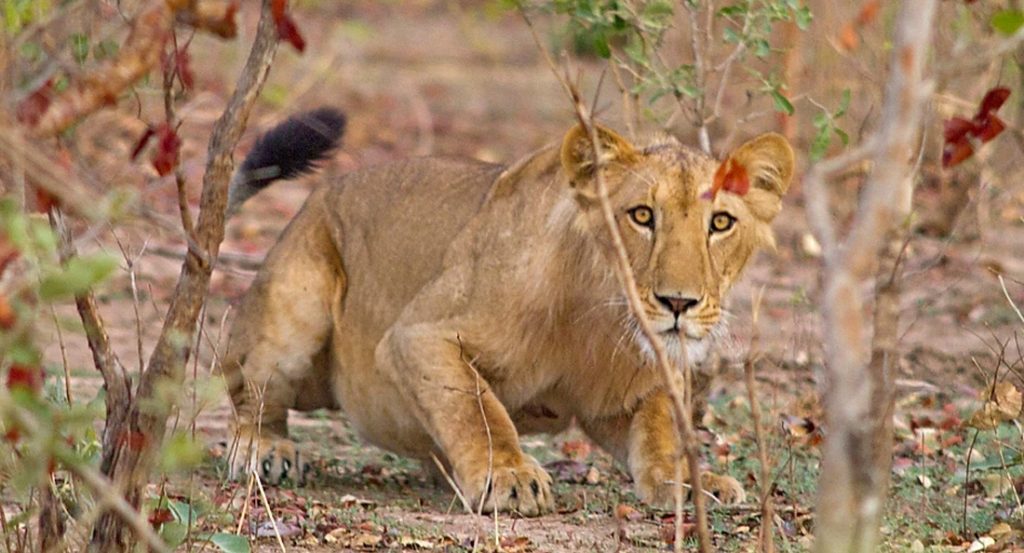
Lake nakuru national park has a small lion population. A 2018 survey counted just 16, even though earlier surveys had counted 60. I have personal history here, as this was the first African wilderness that I visited.
Meru national park has an estimated 76 wild lions. It covers 870 square km (340 square miles)
Mount Kenya National Park is 715 square kilometers (276 square miles) in size. Despite its relatively small size, it is a big 5 reserve, though leopard and rhino are both rarely seen.
Samburu Nature reserve has a population of 40-50 lions, alongside all of the big 5 (and both species of African rhino). Cheetah are found, and even wild dog.
Ruma National park has lions leopards and cheetah (though the lion and leopard are very hard to see) the last roan of Kenya survive in this national park, but only 19 or so are still there.
Kora national park is another ecotourism big 7 reserve. While the number of lion is hard to ascertain is the place where George Adamson worked in the 1970s. George Adamson, (husband of Joy Adamson – author of Born free along with many other books) his brother Terence, and Tony Fitzjohn worked together to rehabilitate lions and leopards in the park from 1971–1988. How easy it is too see wild lions is unclear, but well worth a visit.
Shimba hills nature reserve
Buffalo Springs National Reserve
Mount Elgon National Park
Shaba National Reserve
Chyulu Hills 250 lions
Marsabit National Park
Sibiloi National Park claims to have lions (though a survey from 2020 found none)
Malka Mari National Park has lions in its 1500 square km area this is another Ecotourism big 7
There are also likely a wide array of private reserves that are linked to these above, and perhaps even private reserves off on their own that are likely to host lions. I hope to grow the links as fast as possible
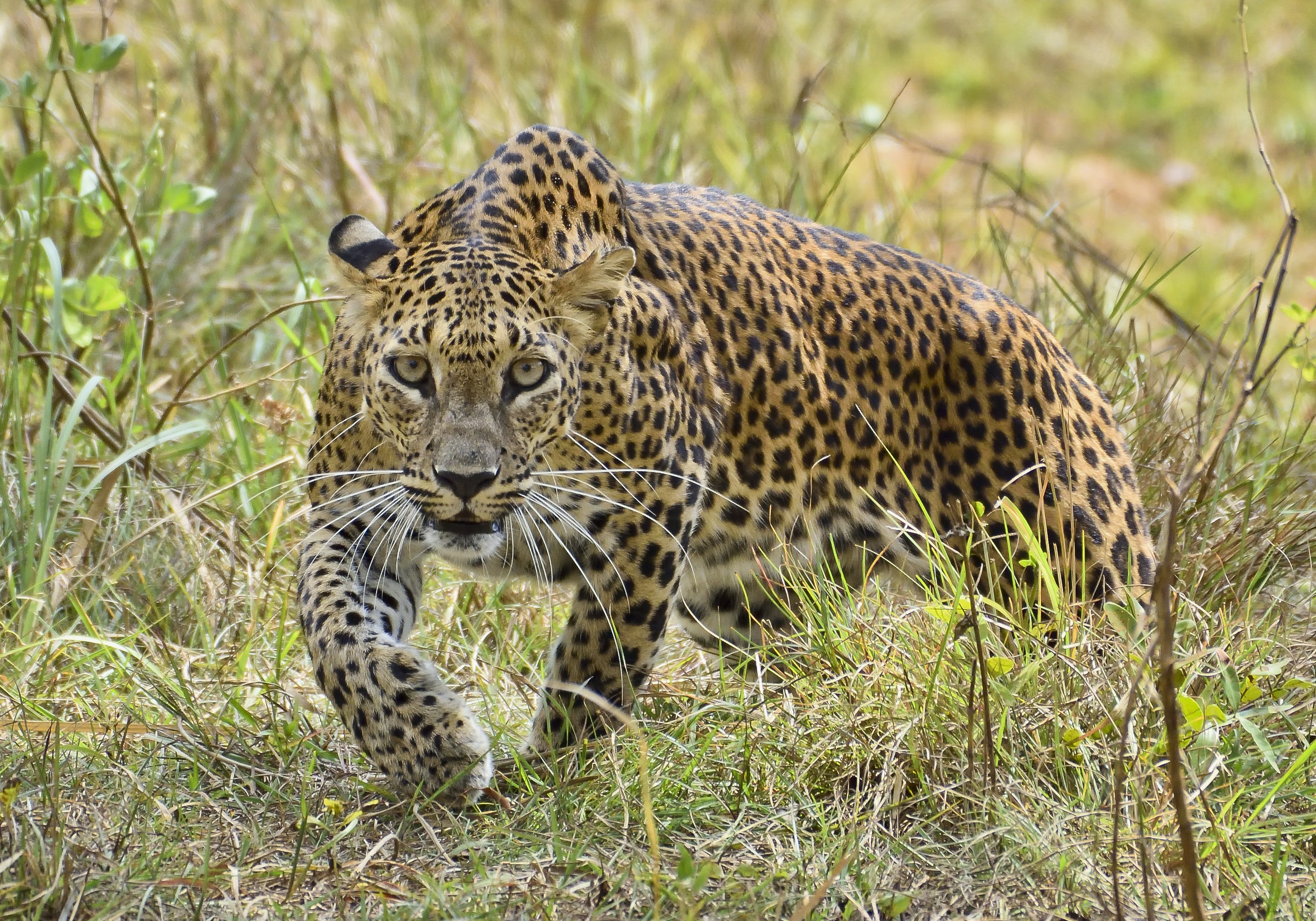






 As you can see from the map above, the name African lion is not particularly accurate, given that half of Africa was inhabited by the Asian Lion. Still, even taking into account this number of African lions which belong to the Asiatic lion subspecies, still the population of African lion subspecies account for the majority of lions left in the world. It should be noted, that while
As you can see from the map above, the name African lion is not particularly accurate, given that half of Africa was inhabited by the Asian Lion. Still, even taking into account this number of African lions which belong to the Asiatic lion subspecies, still the population of African lion subspecies account for the majority of lions left in the world. It should be noted, that while 
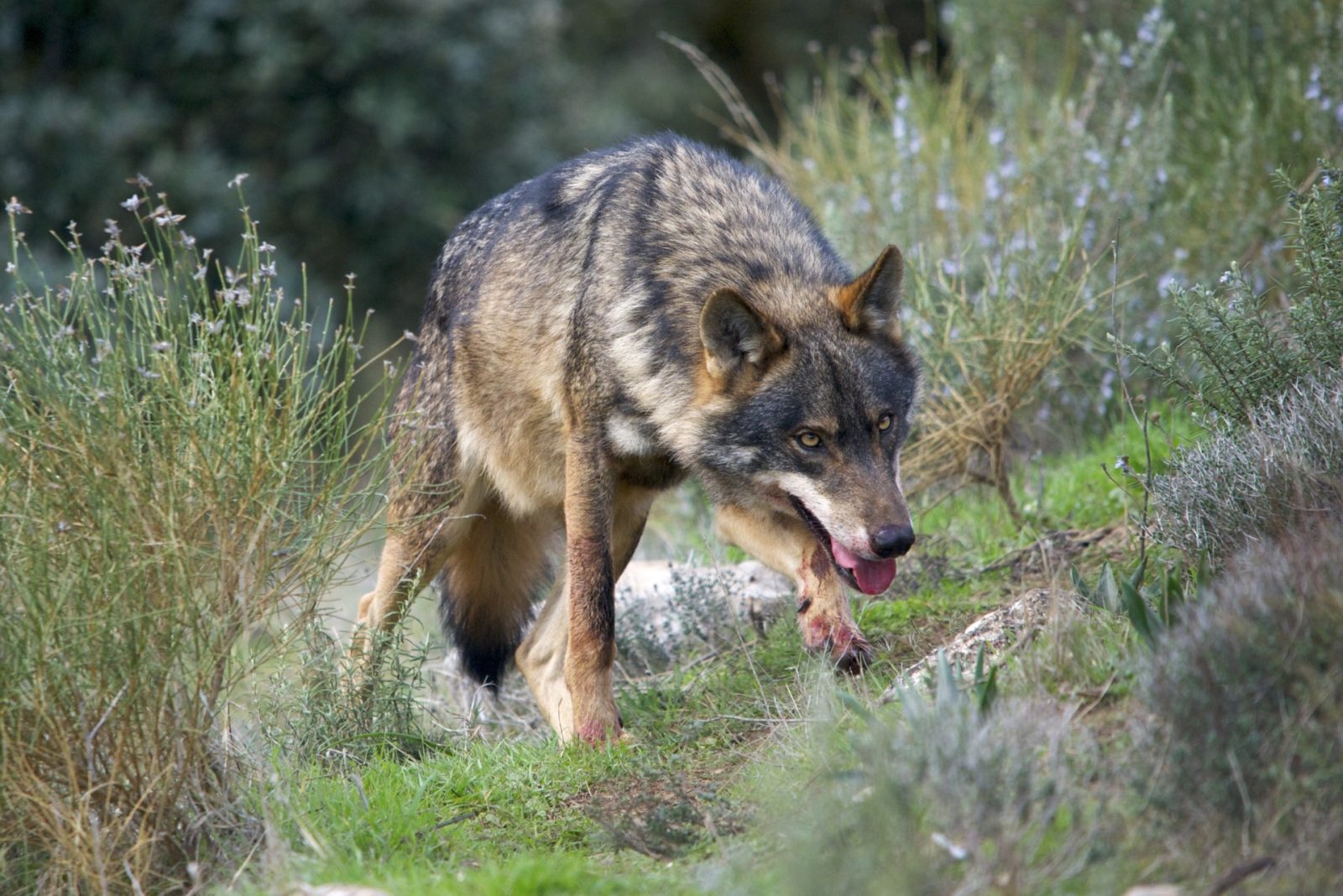
































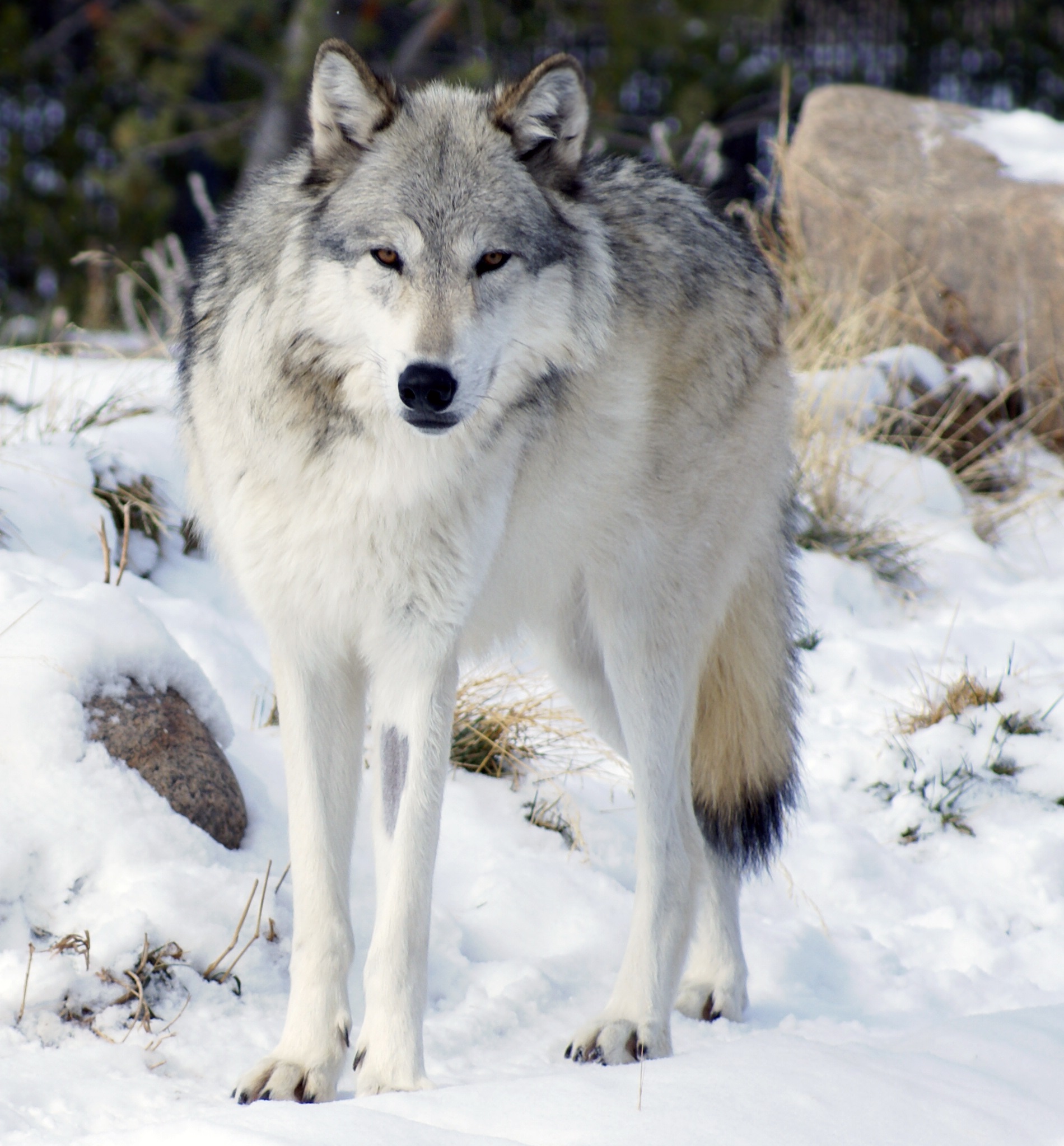
 The Iberian wolf is a subspecies of the grey wolf found on the Iberian peninsular. It reached its minimum in the 1970s with 500-700 iindividuals living in the wild. Until the middle of the 19th century, it was widespread, throughout the Iberian peninsular. It should be noted, that wolves have never had high densities, and the wolves of western Europe are not thought to have ever had a population much above 848–26 774 (depending on which end of the estimate you rely – but is the founding population of both the Iberian and Apennine population).
The Iberian wolf is a subspecies of the grey wolf found on the Iberian peninsular. It reached its minimum in the 1970s with 500-700 iindividuals living in the wild. Until the middle of the 19th century, it was widespread, throughout the Iberian peninsular. It should be noted, that wolves have never had high densities, and the wolves of western Europe are not thought to have ever had a population much above 848–26 774 (depending on which end of the estimate you rely – but is the founding population of both the Iberian and Apennine population).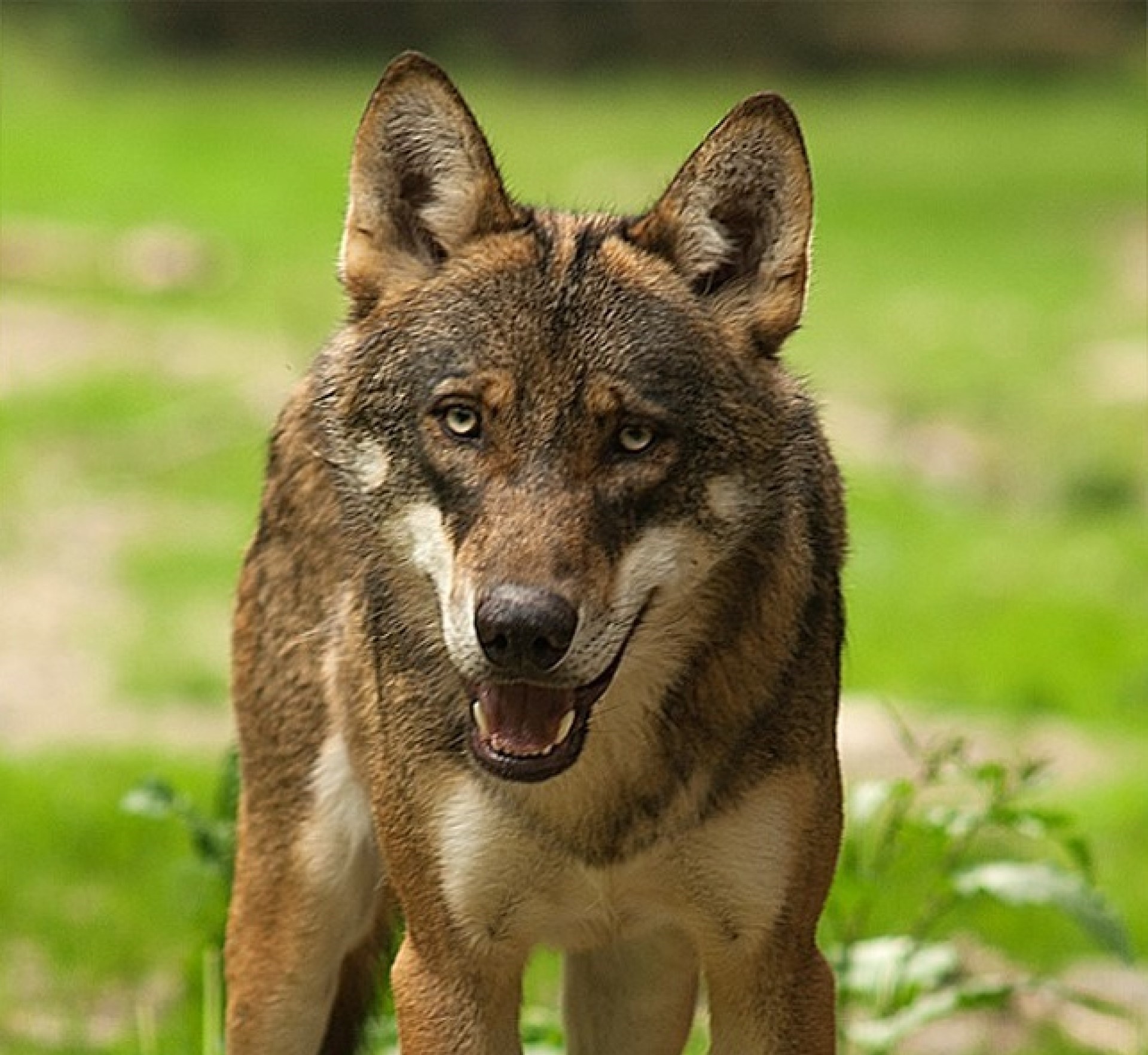
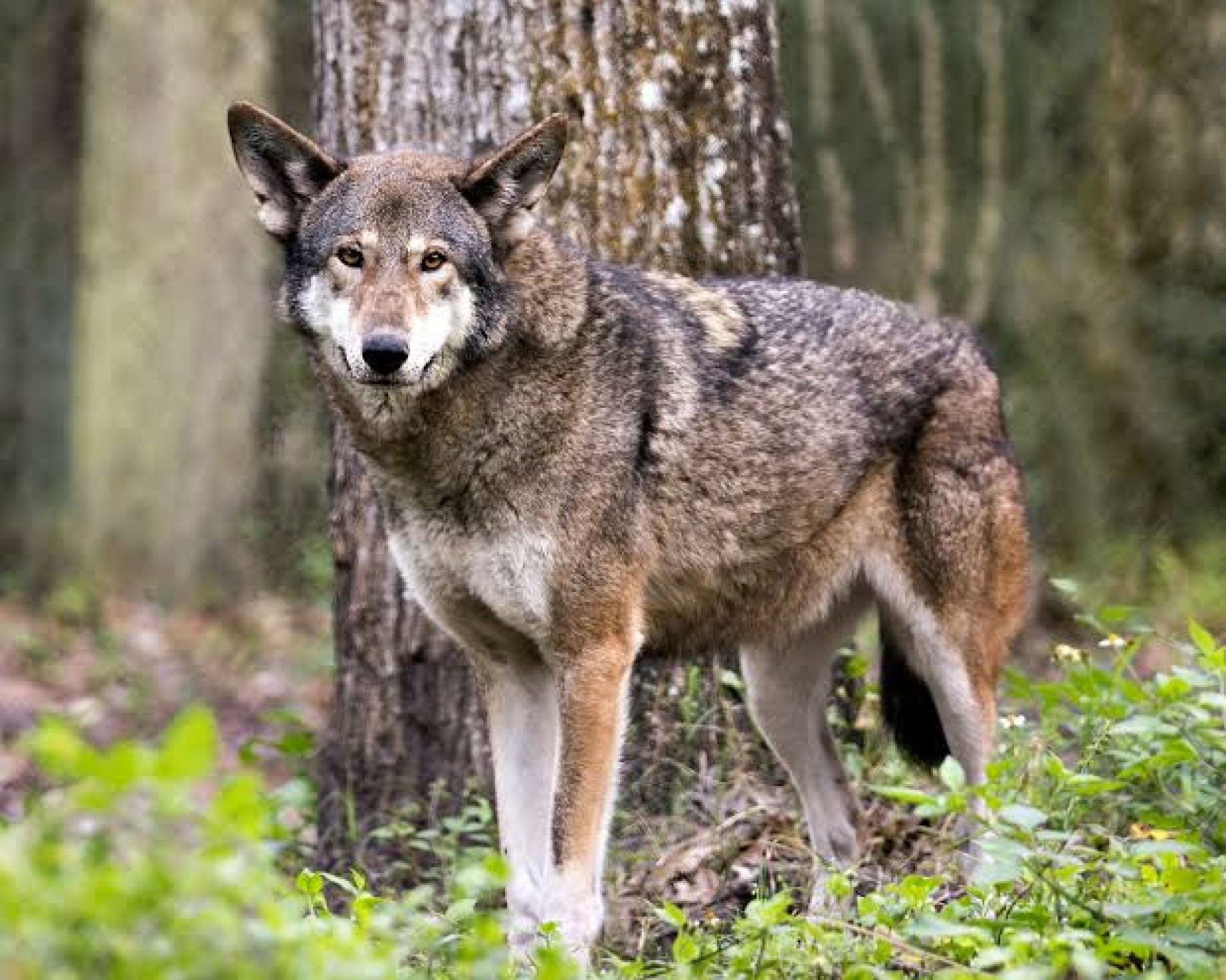
 The Apennine wolf is also known as the Italian wolf. Back in the 1970s the population reached its minimum, where the population reached 70-100 individuals. It has recovered well since then, with an Italian population of roughly 3300. However, since the early 1990s, this subspecies has been gradually moving into France. As such, at the end of 2022 the number was estimated at 1104 wolves in France.
The Apennine wolf is also known as the Italian wolf. Back in the 1970s the population reached its minimum, where the population reached 70-100 individuals. It has recovered well since then, with an Italian population of roughly 3300. However, since the early 1990s, this subspecies has been gradually moving into France. As such, at the end of 2022 the number was estimated at 1104 wolves in France.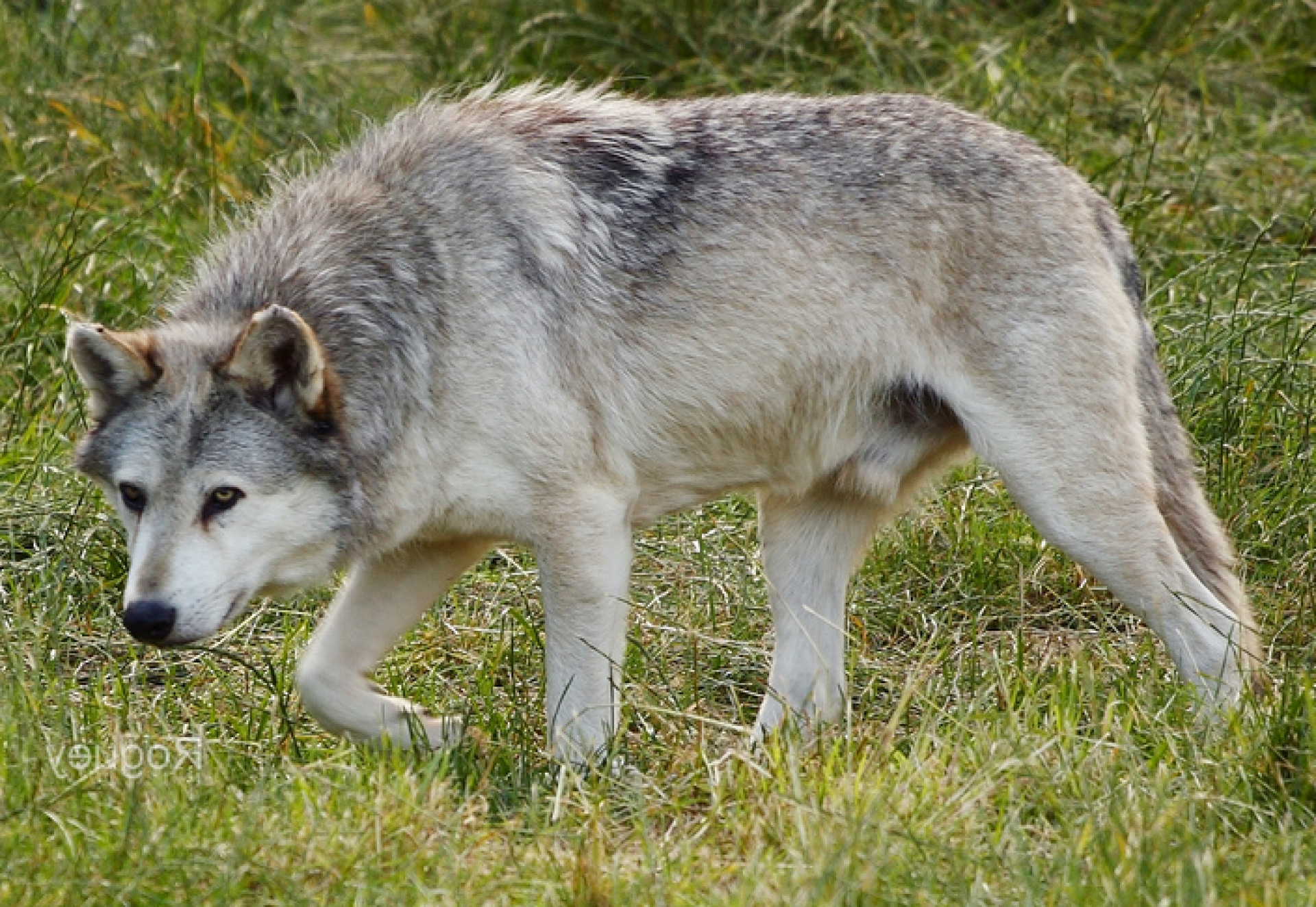
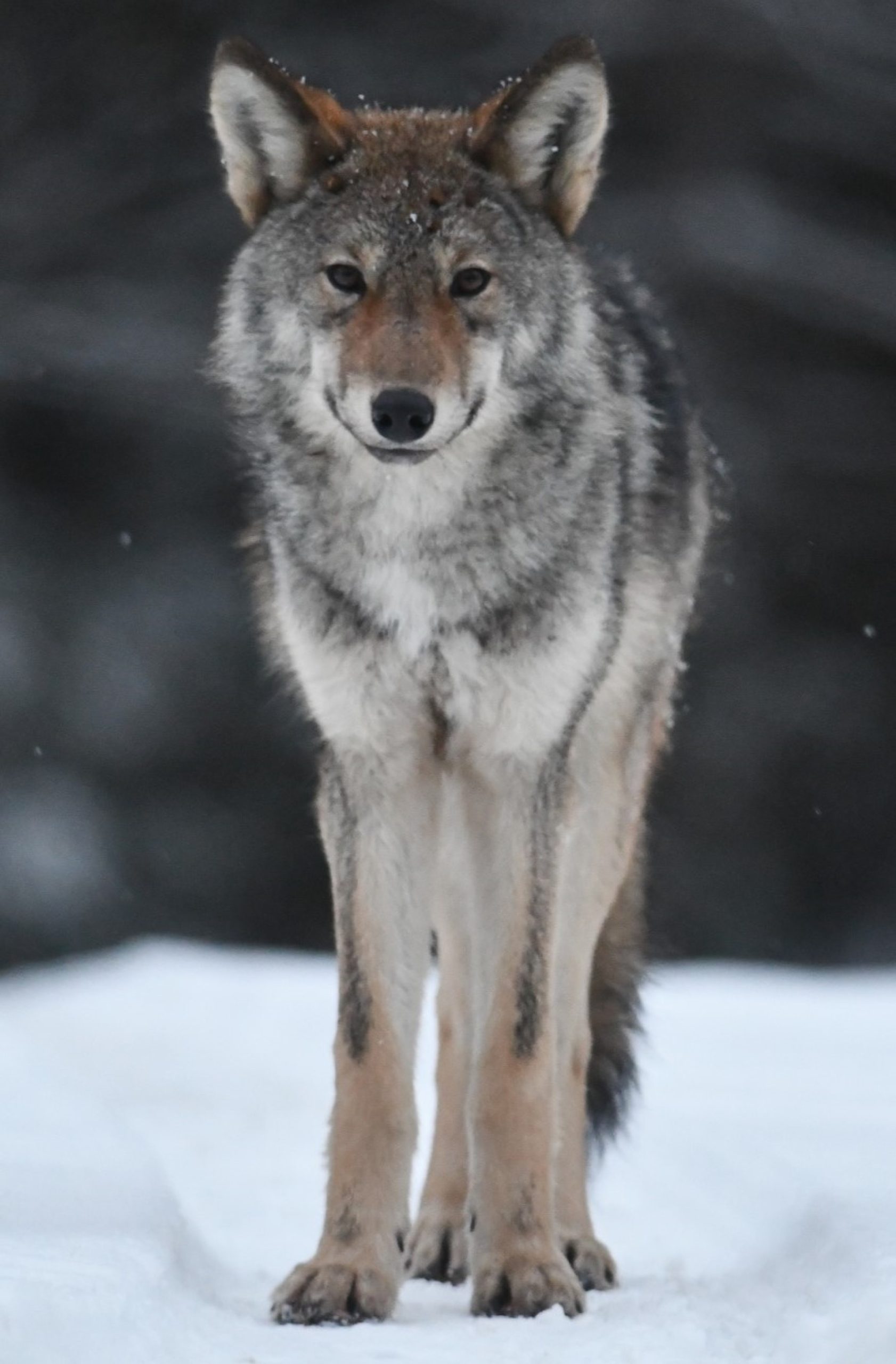
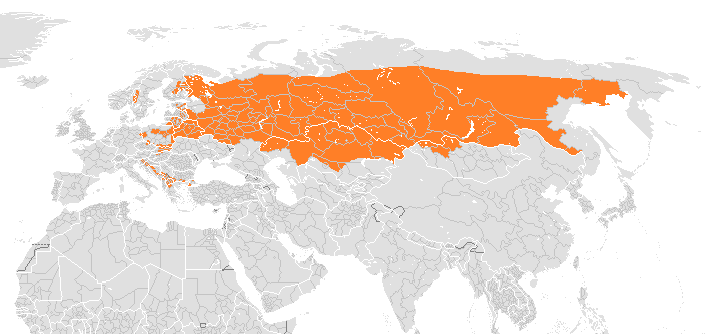 The Eurasian wolf (often referred to as the Russian wolf), is the subspecies which runs down the east coast of the Adriatic sea, as well as the majority of
The Eurasian wolf (often referred to as the Russian wolf), is the subspecies which runs down the east coast of the Adriatic sea, as well as the majority of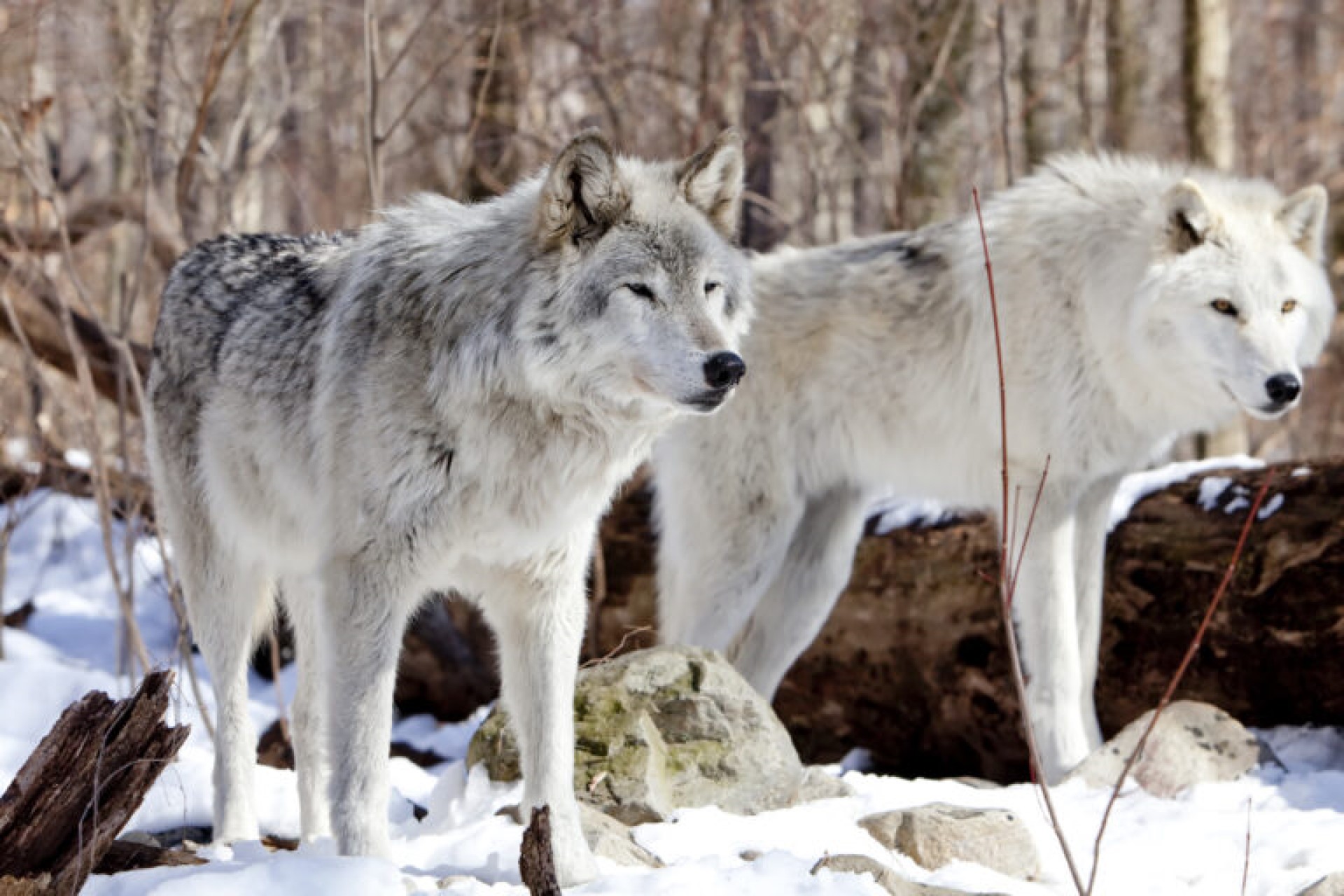 
 The Tundra wolf – Canis lupus Albus is the Eurasian equivalent of the Arctic wolf. Also known as the Turukhan wolf, it is native to Eurasia’s tundra and forest-tundra zones from Finland to the Kamchatka Peninsula. It was first described in 1792 by Robert Kerr.
The Tundra wolf – Canis lupus Albus is the Eurasian equivalent of the Arctic wolf. Also known as the Turukhan wolf, it is native to Eurasia’s tundra and forest-tundra zones from Finland to the Kamchatka Peninsula. It was first described in 1792 by Robert Kerr.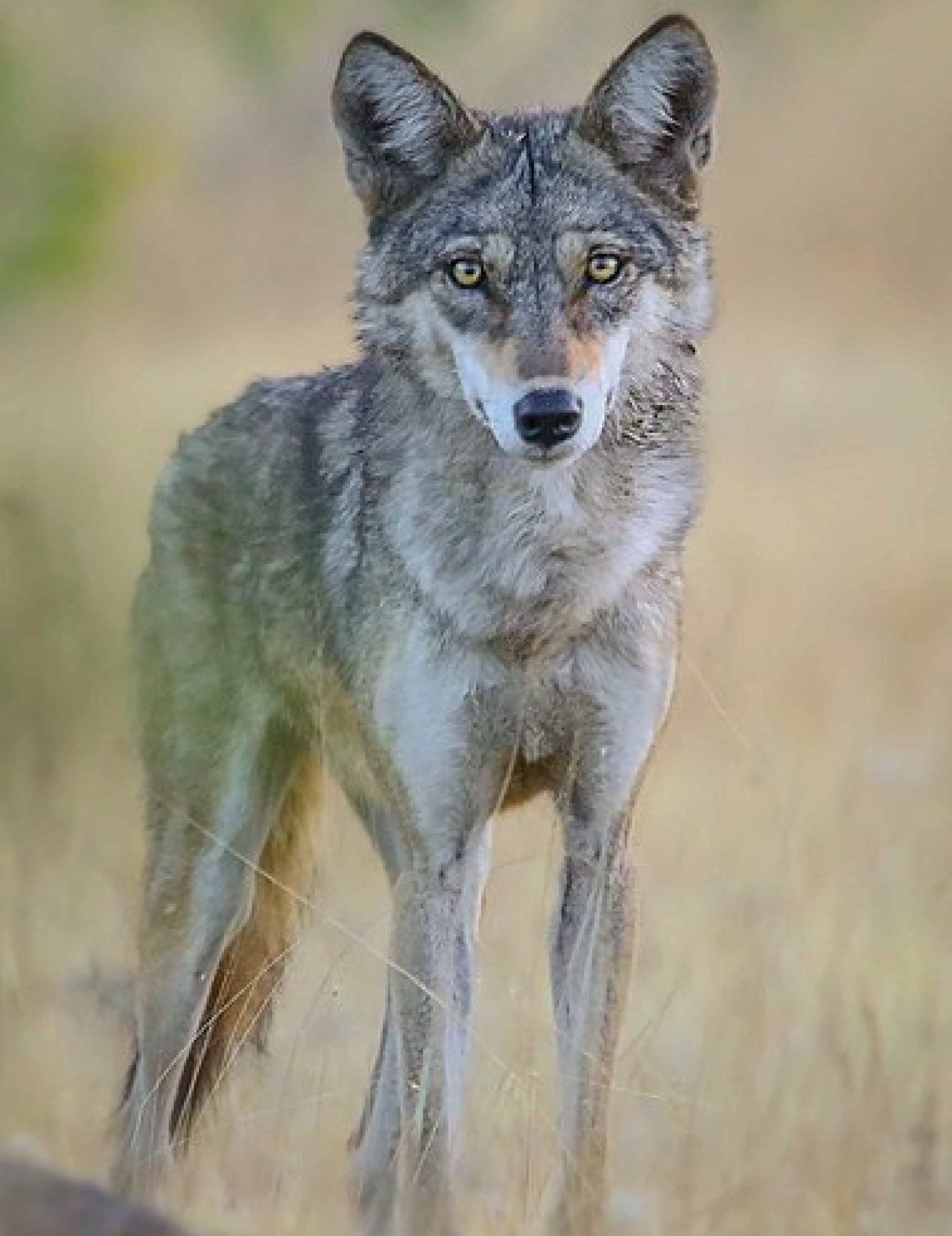
 The Indian wolf is one of the more well known, partly as their starring role in the Jungle book by Rudyard Kipling. I do remember my great grandmother talking about seeing 4 wolves running in the distance. It is thought to have 2000-3000 individuals left in the wild, though given its former large range, this does not appear very high. It should not be surprising, therefore, to hear that this is considered as one of the most endangered subspecies of the grey wolf – it officially has the conservation status of endangered – now it is considered endangered, and people talk about it at high risk, but it should be remembered that there are still 2000-3000, which is a pretty high number for a species considered more than just endangered.
The Indian wolf is one of the more well known, partly as their starring role in the Jungle book by Rudyard Kipling. I do remember my great grandmother talking about seeing 4 wolves running in the distance. It is thought to have 2000-3000 individuals left in the wild, though given its former large range, this does not appear very high. It should not be surprising, therefore, to hear that this is considered as one of the most endangered subspecies of the grey wolf – it officially has the conservation status of endangered – now it is considered endangered, and people talk about it at high risk, but it should be remembered that there are still 2000-3000, which is a pretty high number for a species considered more than just endangered.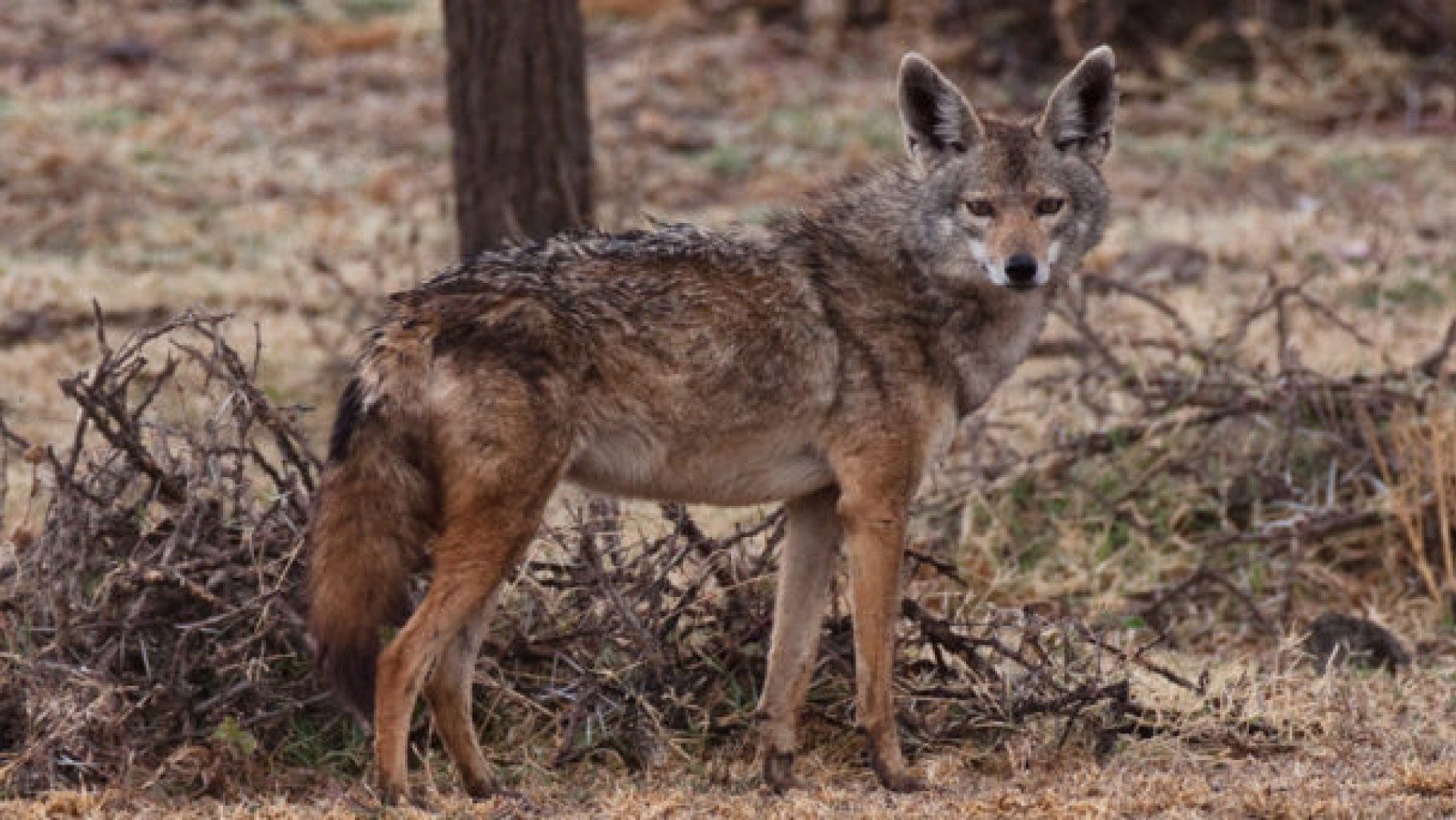
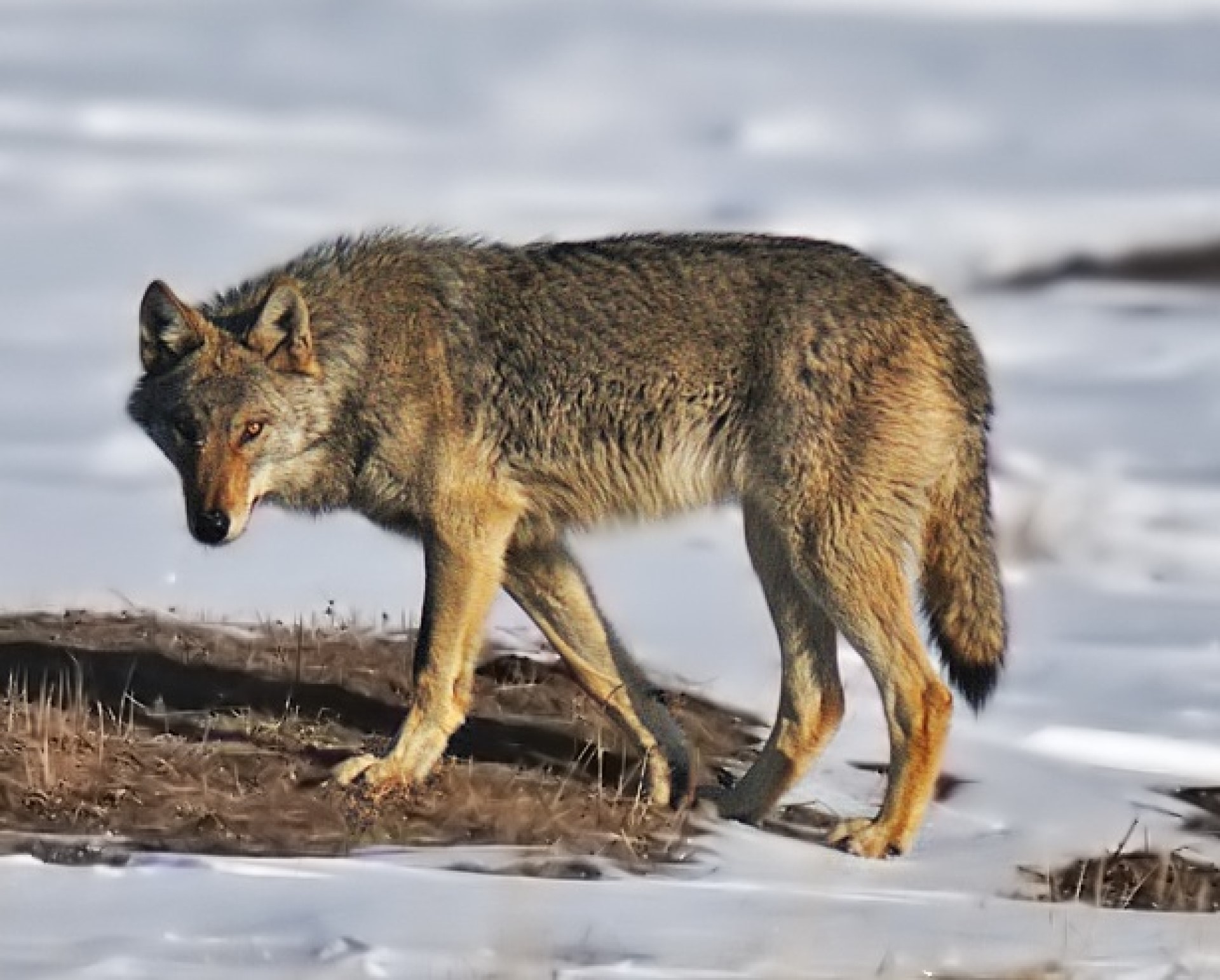

 The Steppe wolf also known as the Caspian sea wolf is a wolf subspecies that is found in the region around the Caspian sea, though the Steppe wolf is perhaps more useful a name as it extends far from the Caspian sea. Much of its range is in
The Steppe wolf also known as the Caspian sea wolf is a wolf subspecies that is found in the region around the Caspian sea, though the Steppe wolf is perhaps more useful a name as it extends far from the Caspian sea. Much of its range is in 
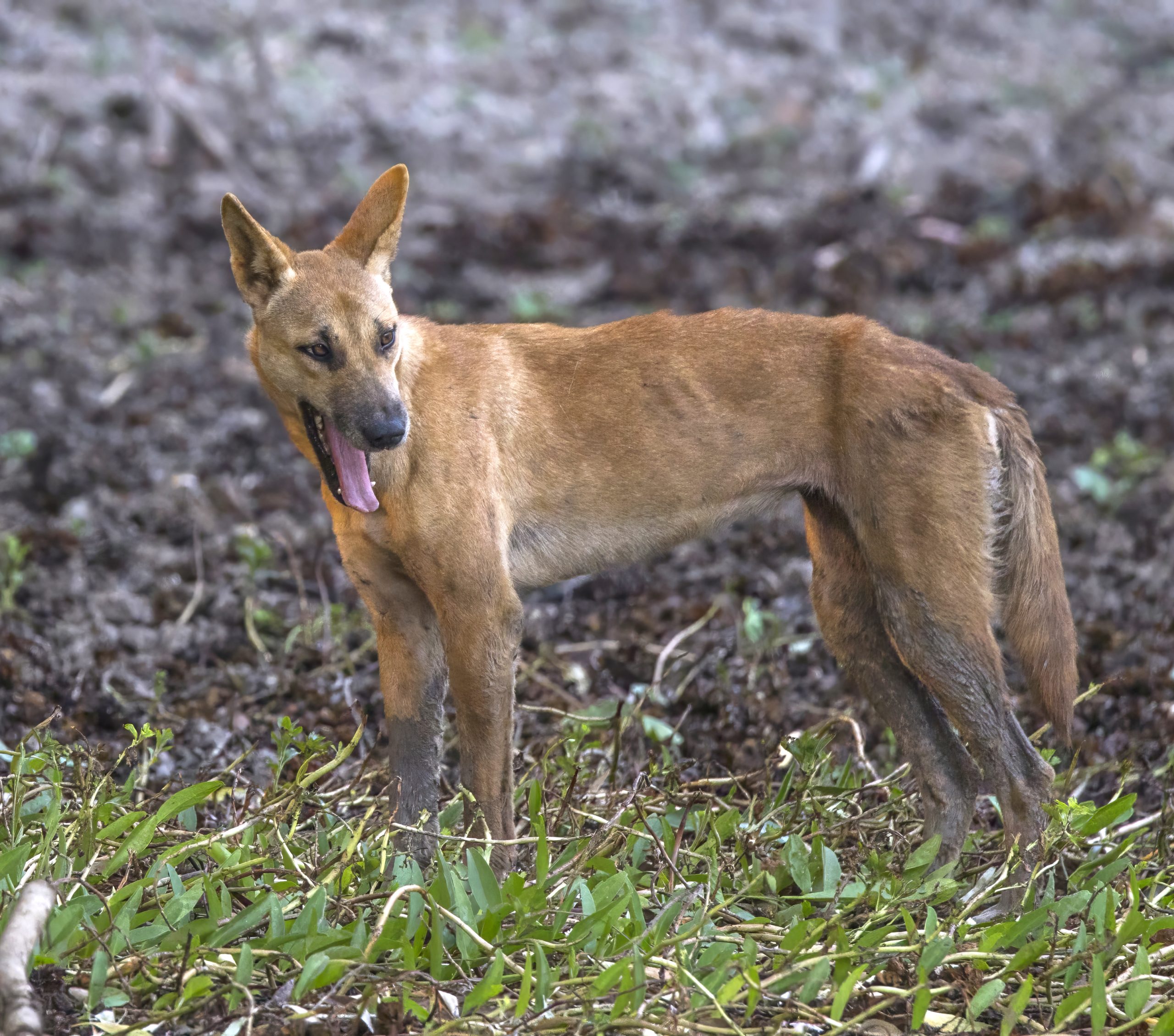





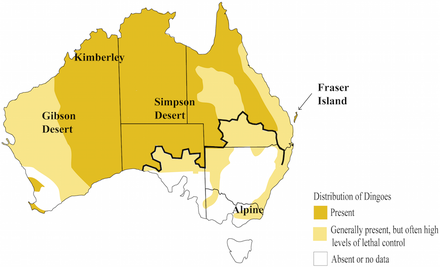 Closely related to the new Guinea singing dog, the Dingo is a dog species that has a relatively wide range. There is some debate about how it got to some of its homes, and whether it may have come alongside early humans.
Closely related to the new Guinea singing dog, the Dingo is a dog species that has a relatively wide range. There is some debate about how it got to some of its homes, and whether it may have come alongside early humans.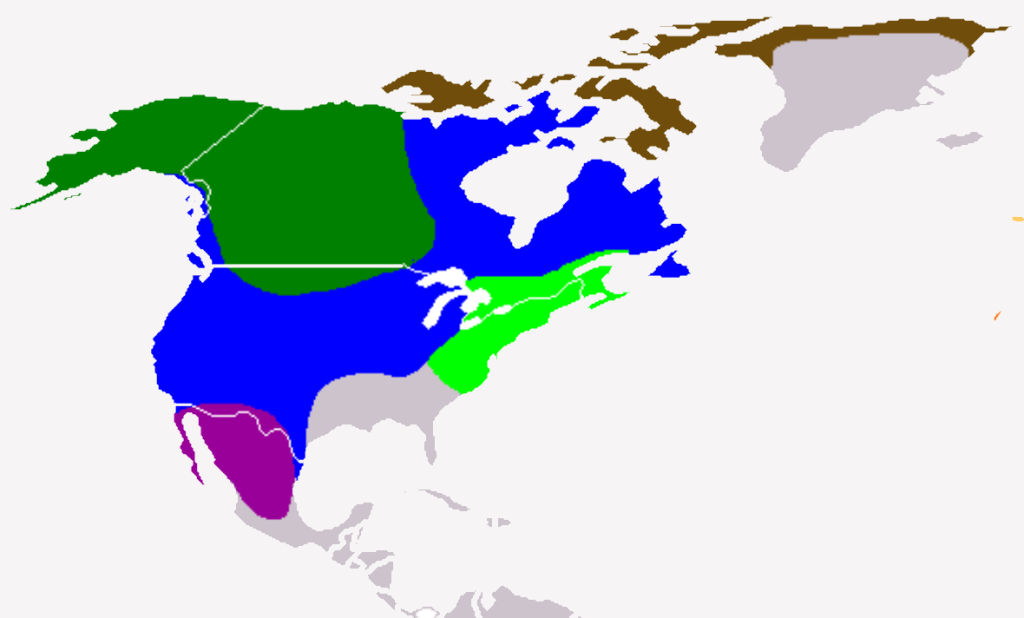
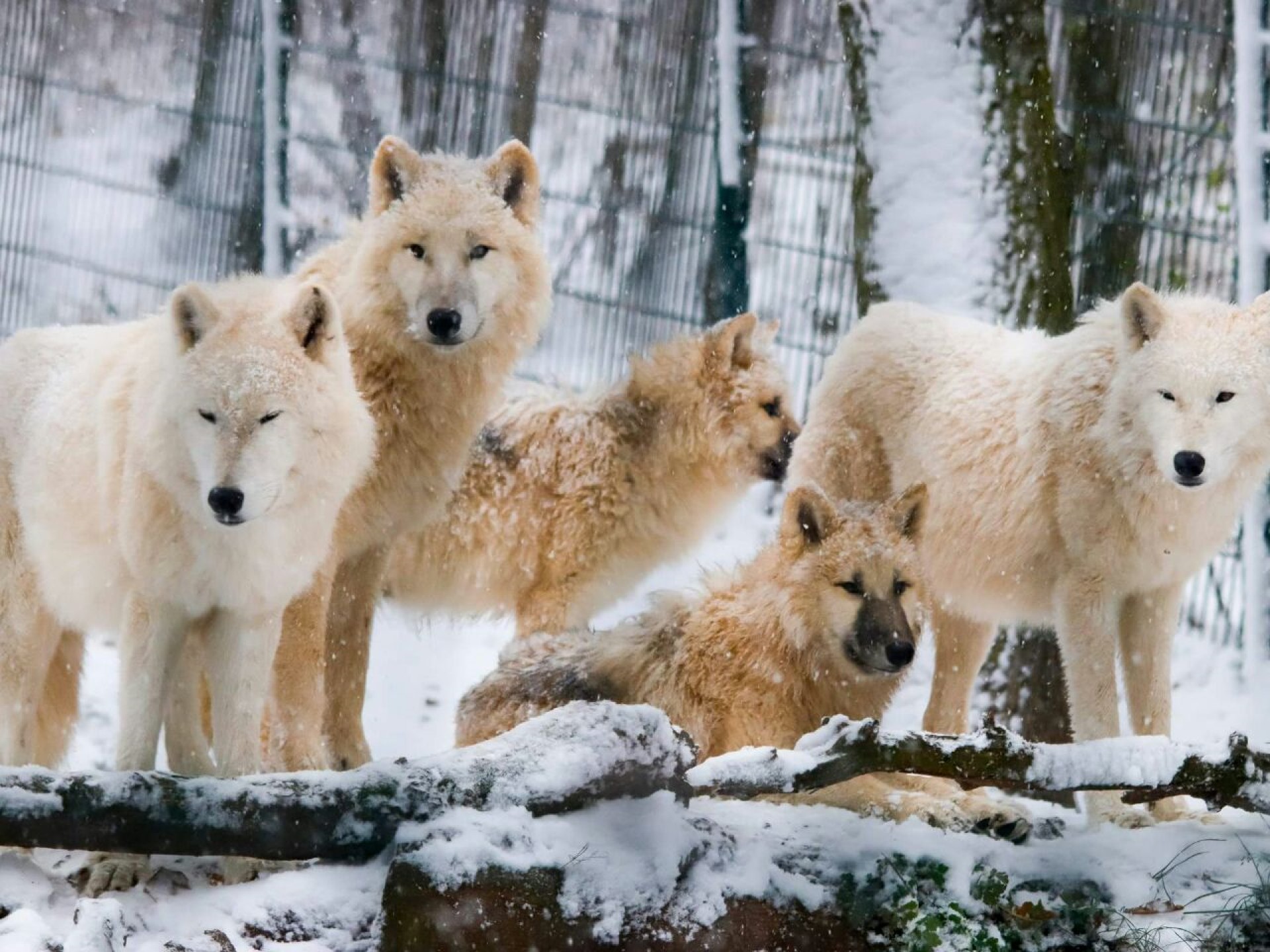
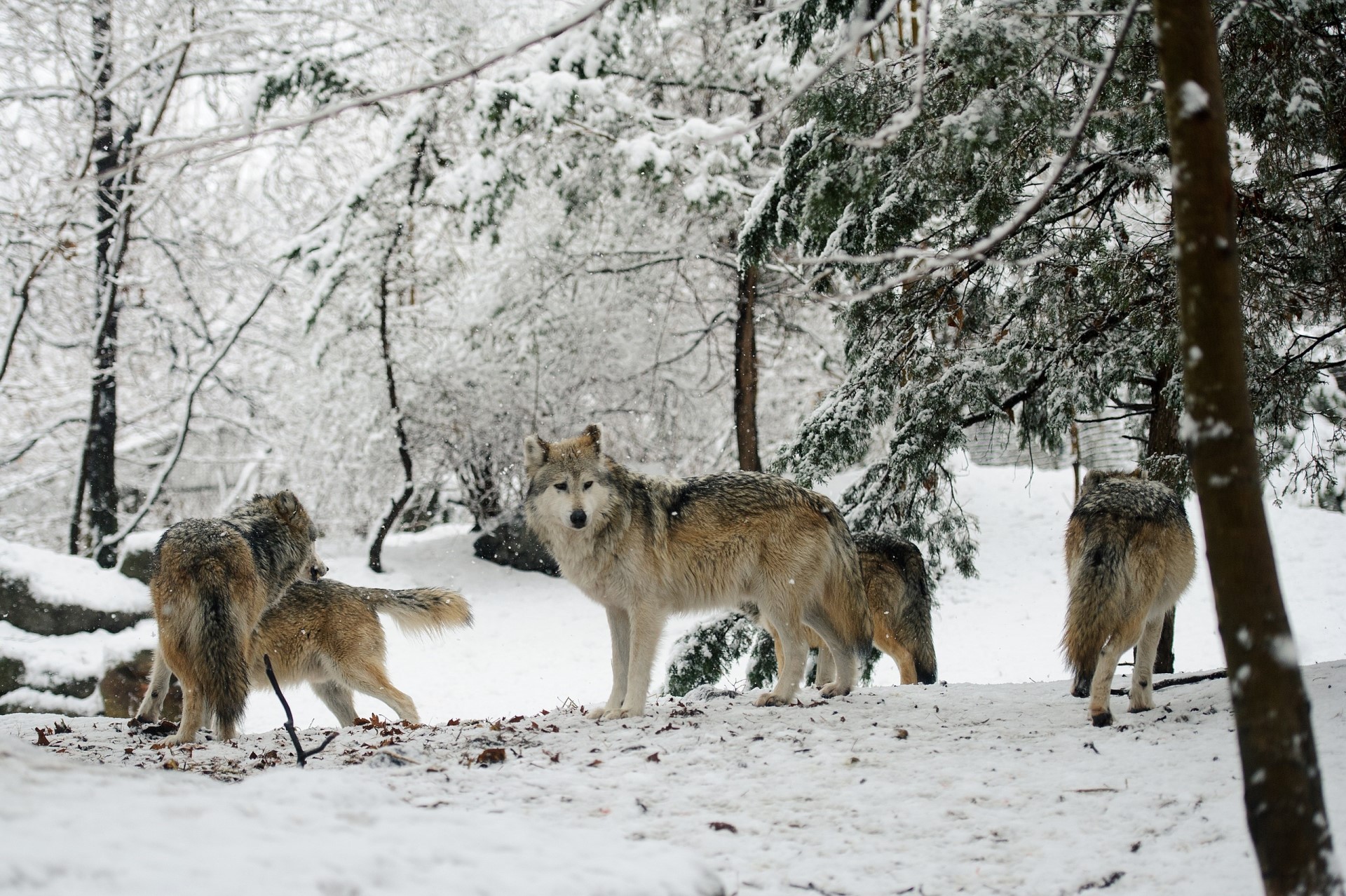


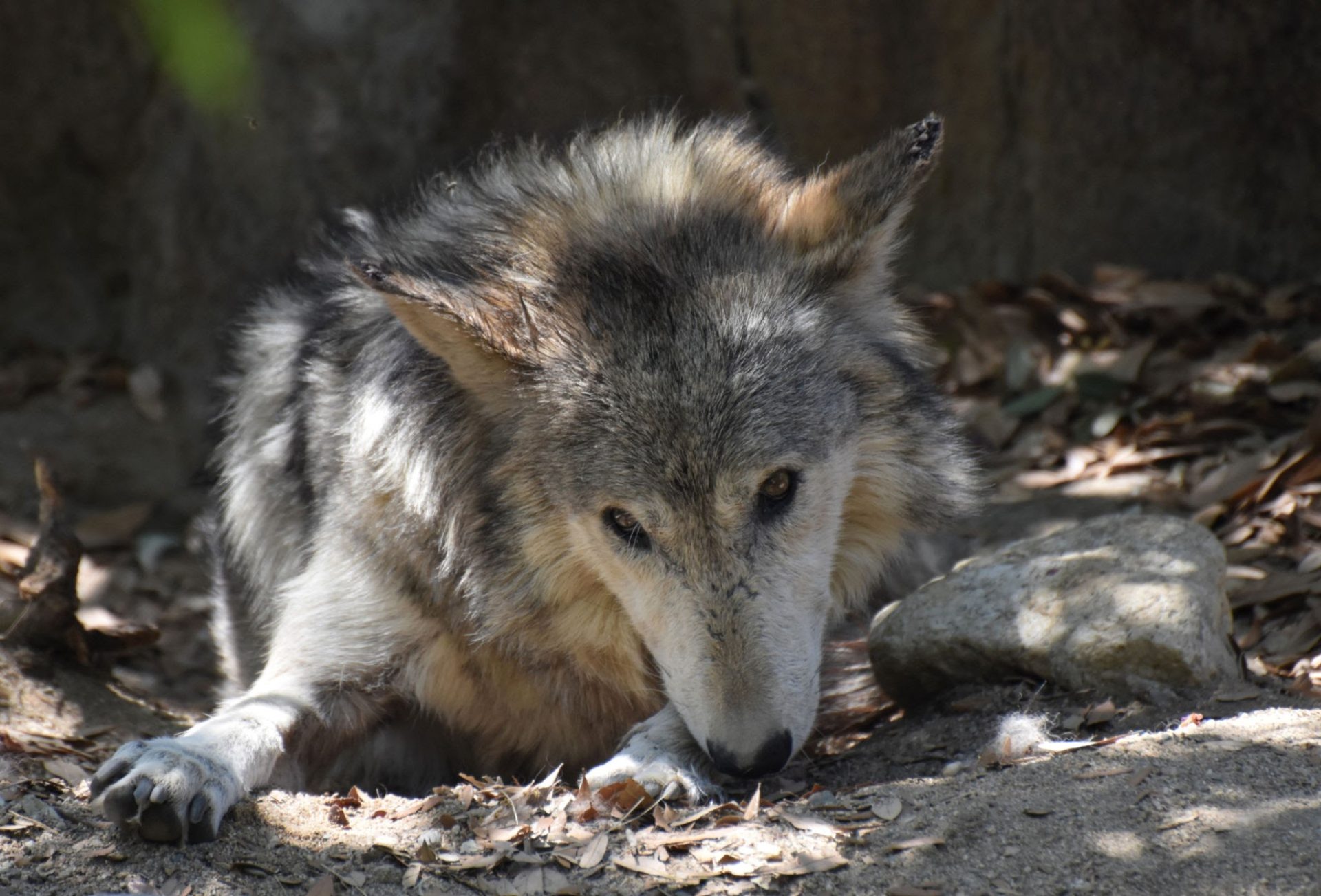
 Mexican wolves (scientific name is Canis lupus baileyi) are currently only found in a small area as seen on the map to the right. It is a fantastic improvement on the situation around 1970 when the species was extinct in the wild. The first reintroduction was carried out in 1998. Unfortunately, founded by just 7 individuals, the population is highly inbred. Never-the-less, currently, the
Mexican wolves (scientific name is Canis lupus baileyi) are currently only found in a small area as seen on the map to the right. It is a fantastic improvement on the situation around 1970 when the species was extinct in the wild. The first reintroduction was carried out in 1998. Unfortunately, founded by just 7 individuals, the population is highly inbred. Never-the-less, currently, the 
















