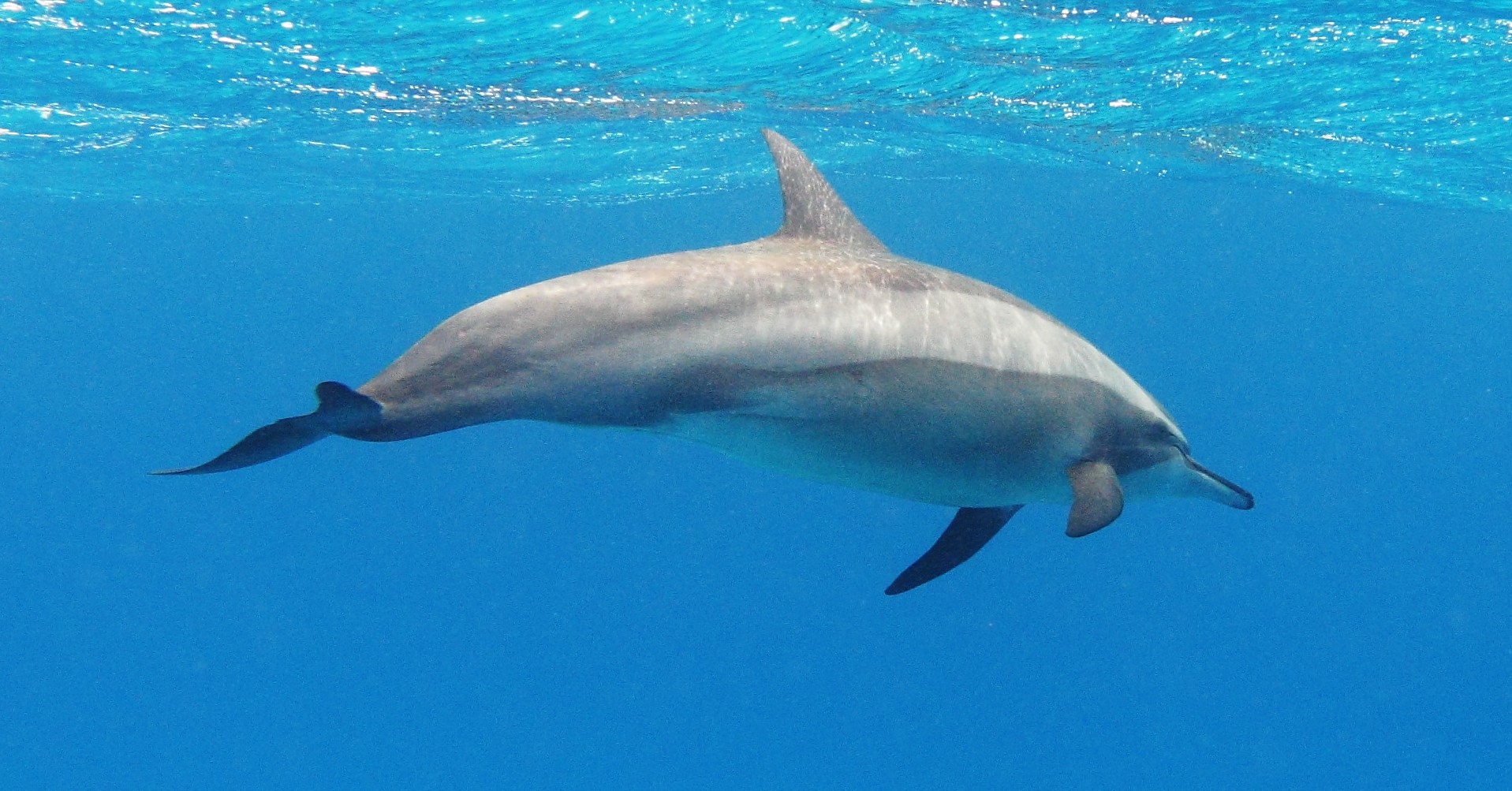
Due to the spinner dolphin foraging and feeding at night, in certain regions, such as Hawaii and northern Brazil, dolphins spend the daytime resting in shallow bays near deep water. Spinner dolphins rest as a single unit, moving back and forth slowly in a tight formation but just out of contact with one another. These resting behaviours are observed for about four to five hours daily. During rest periods, spinner dolphins rely on vision rather than echolocation. At dusk, they travel offshore to feed. They travel along the shore during foraging trips, and the individuals that occupy the same bay may change daily. Some individual dolphins do not always go to a bay to rest; however, in Hawaii, dolphins do seem to return to the same site each trip.
Spinner dolphins live in an open and loose social organization. The spinner dolphins of Hawaii live in family groups, but also have associations with others beyond their groups. Mothers and calves form strong social bonds. Spinner dolphins seem to have a promiscuous mating system, with individuals changing partners for up to some weeks. A dozen adult males may gather into coalitions. Vocalizations of spinner dolphins include whistles, which may be used to organize the school, burst-pulse signals, and echolocation clicks. The spinner dolphin has a 10-month gestation period, and mothers nurse their young for one to two years. Females are sexually mature at four to seven years, with three-year calving intervals, while males are sexually mature at seven to 10 years. Spinner dolphins live for about 20-25 years old. Breeding is seasonal, more so in certain regions than others.
Although most spinner dolphins are found in the deeper waters offshore of the islands, the rest of the Hawaiʻi population has a more coastal distribution. During daytime hours, the island-associated stocks of Hawaiian spinner dolphins seek sanctuary in nearshore waters, where they return to certain areas to socialize, rest, and nurture their young.
They get their name for their spinning jumps, a spinner dolphin comes out of the water front first and twists its body as it rises into the air. When it reaches its maximum height, the dolphin descends back into the water, landing on its side. A dolphin can make two to seven spins in one leap; the swimming and rotational speed of the dolphin as it spins underwater affects the number of spins it can do while airborne. These spins may serve several functions. Some of these functions are believed by experts to be acoustic signalling or communication. Another reason is to remove ectoparasites such as remoras. Dolphins may also make nose-outs, tail slaps, flips, head slaps, “salmon leaps”, and side and back slaps.
The protected status of spinner dolphins are CITES Appendix II and Marine Mammal Protection Act (MMPA) protected throughout its range as well as MMPA depleted in its eastern stock. Tens of thousands of spinner dolphins, mostly eastern and white-bellied varieties, were killed in the 30 years after purse seine fishing for tuna began in the 1950s; The process killed probably half of all eastern spinner dolphins. They have also been contaminated by pollutants such as DDT and PCBs. Spinner dolphins, as with other species affected by ETP tuna purse-seine fishing, are managed nationally by the coastal countries and internationally by the IATTC. The IATTC has imposed annual stock mortality limits on each purse seine and promulgated regulations regarding the safe release of dolphins. The eastern tropical Pacific and Southeast Asian populations of the spinner dolphin are listed on Appendix II of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS), since they have an unfavourable conservation status or would benefit significantly from international co-operation organized by tailored agreements. In addition, the spinner dolphin is covered by Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region (Pacific Cetaceans MoU) and the Memorandum of Understanding Concerning the Conservation of the Manatee and Small Cetaceans of Western Africa and Macaronesia (Western African Aquatic Mammals MoU). Spinner dolphins are susceptible to disease and two of the recorded diseases within them are toxoplasmosis and cetacean morbillivirus. The number of cases reported however is fairly low in the species.
Spinner dolphins in Hawaii receive multiple daily visits to their near-shore resting grounds, with boats taking people out daily to snorkel and interact with the local dolphin population. Such activities are increasingly coming under criticism on the grounds of possible harm to the dolphins, and efforts are being made both to educate the public in order to minimise human impact on the dolphins, and to bring in regulations to govern these activities. In 2023, 33 swimmers were arrested for reportedly harassing dolphins off the coast of the Big Island of Hawaii. The swimmers reportedly broke federal law by swimming within 45 meters (50 yards) of the dolphins. The ban went into effect in 2021 due to dolphins not getting enough rest during the day to forage for food at night. The swimmers were caught by drone footage pursuing the dolphins as they tried to escape.
We are eager to work with people who run boats to see these animals – provided they are run with due care for the animals. Do get in touch, or fill in a form you will find in ‘List your wild place’ at the top of the page (or click here).
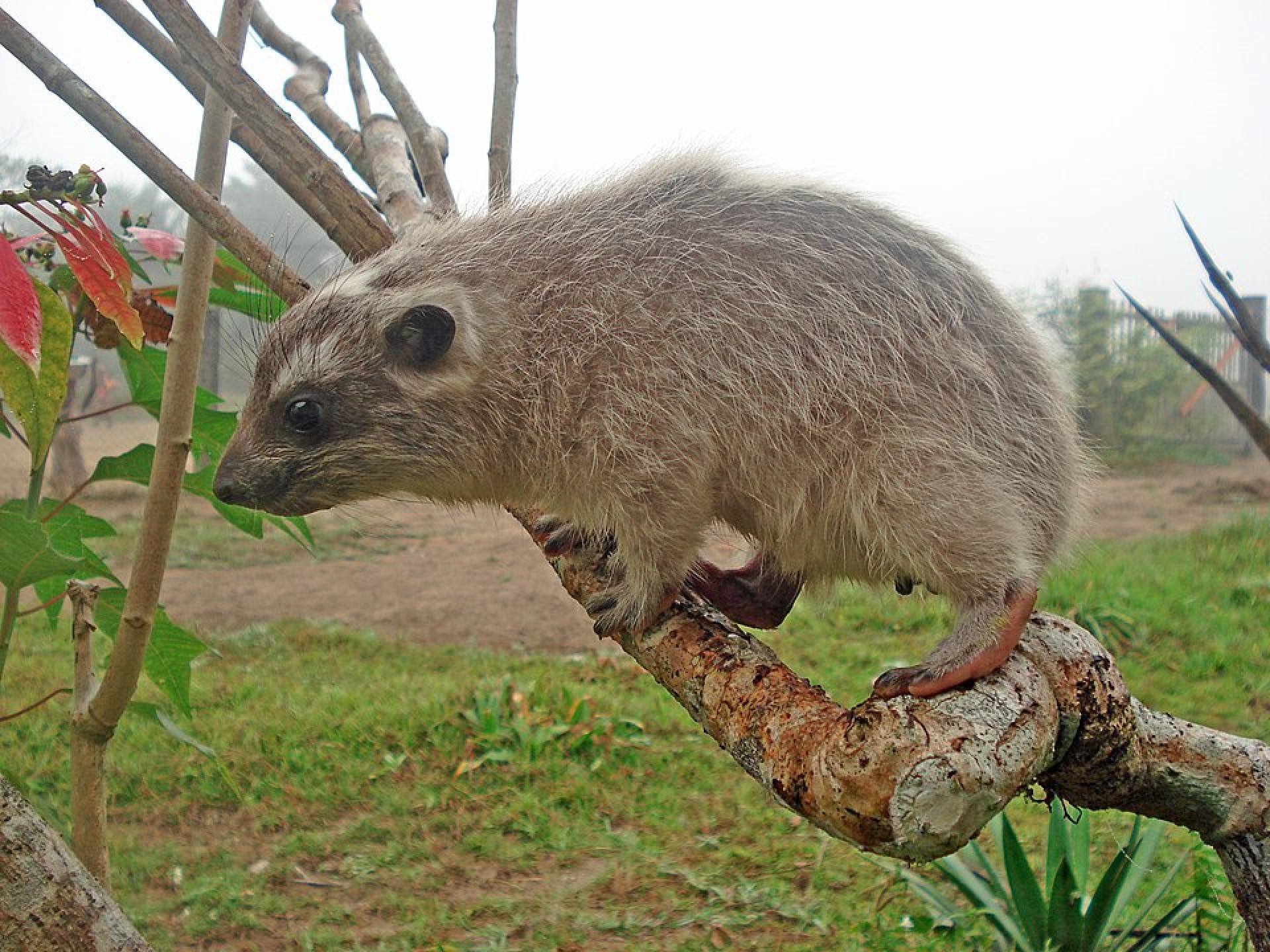


 Western tree hyrax, also known as the western tree dassie or Beecroft tree hyrax
Western tree hyrax, also known as the western tree dassie or Beecroft tree hyrax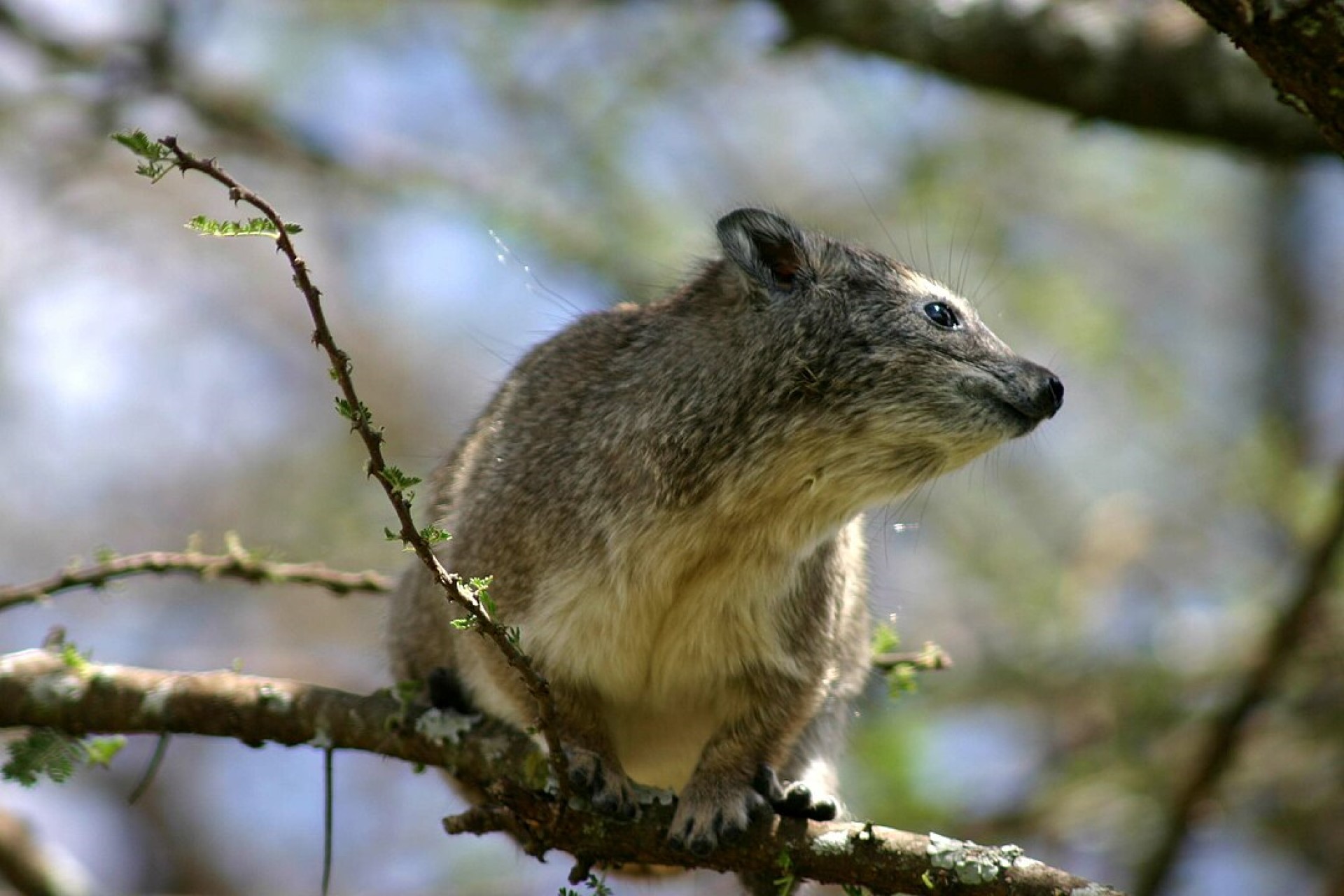
 Southern tree hyrax It is found in temperate forests, subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, moist savanna, and rocky areas.
Southern tree hyrax It is found in temperate forests, subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, moist savanna, and rocky areas.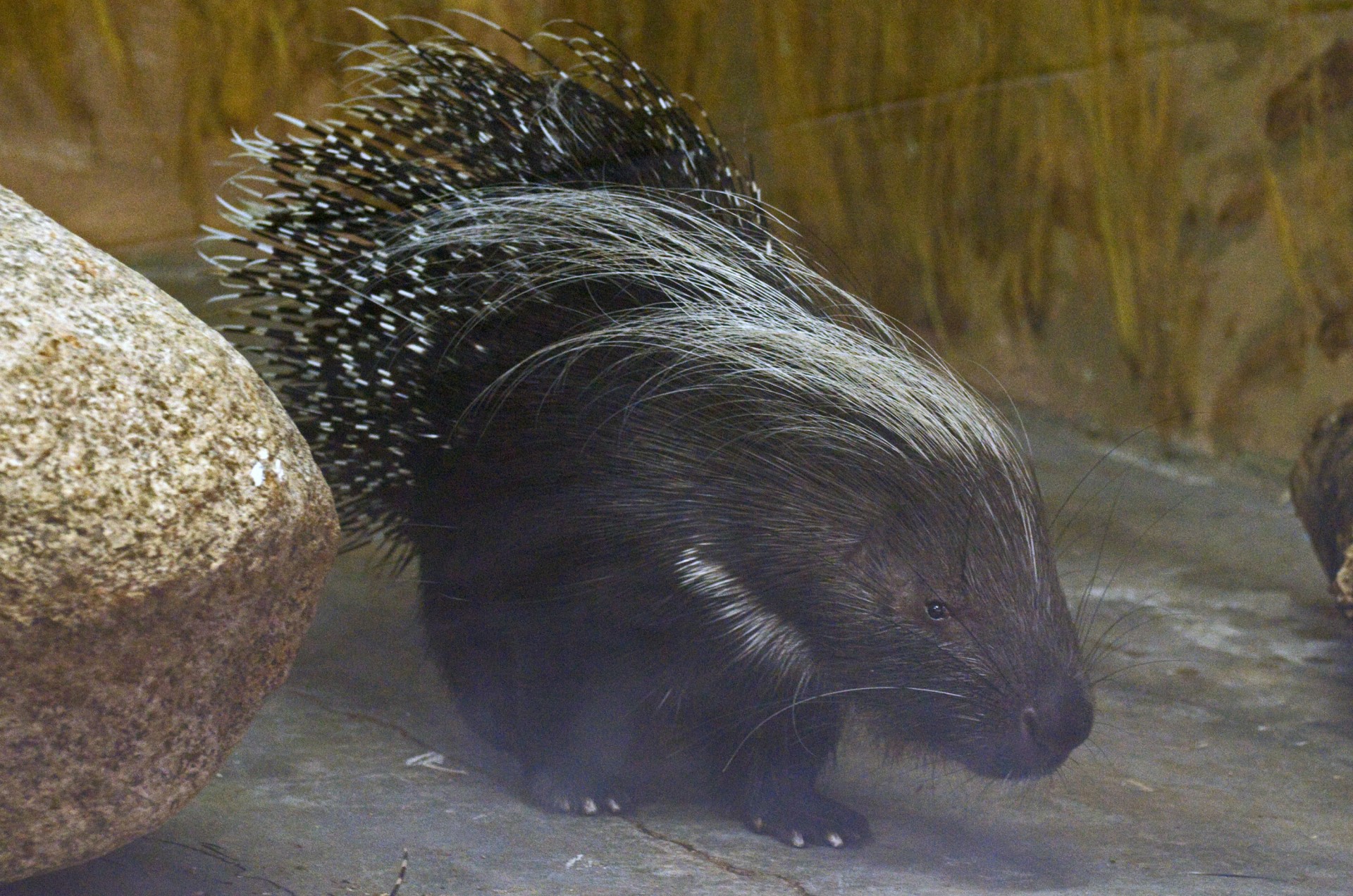
 This is a species of rat-like porcupine, found in a broad belt of Equatorial Africa, right across the continent from Guinea to Kenya.
This is a species of rat-like porcupine, found in a broad belt of Equatorial Africa, right across the continent from Guinea to Kenya. 

 porcupine, (also called the African crested porcupine) is native to North Africa (though it may be locally extinct in Egypt) and sub-Saharan Africa. It is also found in Italy, where the romans introduced it as an extra food source. While accurate estimates on the population size are not seemingly easy to find, Tuscany has a large enough population for it to be one of the more often sighted species when active (at night). Below, I have embedded some footage of an Italian Porcupine
porcupine, (also called the African crested porcupine) is native to North Africa (though it may be locally extinct in Egypt) and sub-Saharan Africa. It is also found in Italy, where the romans introduced it as an extra food source. While accurate estimates on the population size are not seemingly easy to find, Tuscany has a large enough population for it to be one of the more often sighted species when active (at night). Below, I have embedded some footage of an Italian Porcupine porcupine is a rodent species native to southern Asia and the Middle East. It weighs 11-18kg and is 70-90cm long. It has similar looking quills to the African Porcupine, and has a similar diet.
porcupine is a rodent species native to southern Asia and the Middle East. It weighs 11-18kg and is 70-90cm long. It has similar looking quills to the African Porcupine, and has a similar diet. porcupine or Himalayan porcupine is a species of rodent. The head and body measurement are around 56-74 cm and the tail is about 6–11 cm. They weigh around 10 kg-18 kg. They normally feed on roots, tubers, bark and fallen fruits. They also eat carrion, insects, and large tropical seeds. They forage at night and rests during the day. It may be found singly or in pairs. It can also swim and gnaw. The sow usually has one, but twins have also been recorded.
porcupine or Himalayan porcupine is a species of rodent. The head and body measurement are around 56-74 cm and the tail is about 6–11 cm. They weigh around 10 kg-18 kg. They normally feed on roots, tubers, bark and fallen fruits. They also eat carrion, insects, and large tropical seeds. They forage at night and rests during the day. It may be found singly or in pairs. It can also swim and gnaw. The sow usually has one, but twins have also been recorded.
 porcupine is a species of rodent. It is endemic to Indonesia. Due to the popularity of the hunting and consumption of the Sunda porcupine as an aphrodisiac, the Ministry of Environment and Forestry in Indonesia has listed this species as a protected animal as of June 2018.
porcupine is a species of rodent. It is endemic to Indonesia. Due to the popularity of the hunting and consumption of the Sunda porcupine as an aphrodisiac, the Ministry of Environment and Forestry in Indonesia has listed this species as a protected animal as of June 2018. porcupine
porcupine  (also called Palawan porcupine) is a species of rodent endemic to the island of Palawan in the Philippines. It is known locally as durian or landak.
(also called Palawan porcupine) is a species of rodent endemic to the island of Palawan in the Philippines. It is known locally as durian or landak. or Quichua porcupine is a species of rodent. It is found in the Andes of northern Ecuador and Colombia as well as in Panama. This porcupine is little known, but is probably arboreal, nocturnal and solitary like its relatives. The species is thought to be uncommon to rare and the population decreasing. It is threatened by deforestation, habitat fragmentation and agriculture. It is 60-80cm long (including tail), and weighs 2kg when fully grown. The ecology of this species is little known. Its behaviour is likely to resemble that of its close relatives in being nocturnal and arboreal, and feeding on fruit and leaves.
or Quichua porcupine is a species of rodent. It is found in the Andes of northern Ecuador and Colombia as well as in Panama. This porcupine is little known, but is probably arboreal, nocturnal and solitary like its relatives. The species is thought to be uncommon to rare and the population decreasing. It is threatened by deforestation, habitat fragmentation and agriculture. It is 60-80cm long (including tail), and weighs 2kg when fully grown. The ecology of this species is little known. Its behaviour is likely to resemble that of its close relatives in being nocturnal and arboreal, and feeding on fruit and leaves. porcupine (Coendou bicolor) is a species of nocturnal and arboreal rodent in the family Erethizontidae.
porcupine (Coendou bicolor) is a species of nocturnal and arboreal rodent in the family Erethizontidae. also called Koopman’s porcupine, is a porcupine species from the New World and is endemic to northern Brazil. It occurs in the Amazon rainforest east of the Madeira River and south of the Amazon River. It inhabits primary forest and possibly second growth. It was described as Coendou koopmani by Charles O. Handley Jr. and Ronald H. Pine in 1992, but was subsequently found to be identical to a species described in 1818. It is nocturnal and herbivorous.
also called Koopman’s porcupine, is a porcupine species from the New World and is endemic to northern Brazil. It occurs in the Amazon rainforest east of the Madeira River and south of the Amazon River. It inhabits primary forest and possibly second growth. It was described as Coendou koopmani by Charles O. Handley Jr. and Ronald H. Pine in 1992, but was subsequently found to be identical to a species described in 1818. It is nocturnal and herbivorous.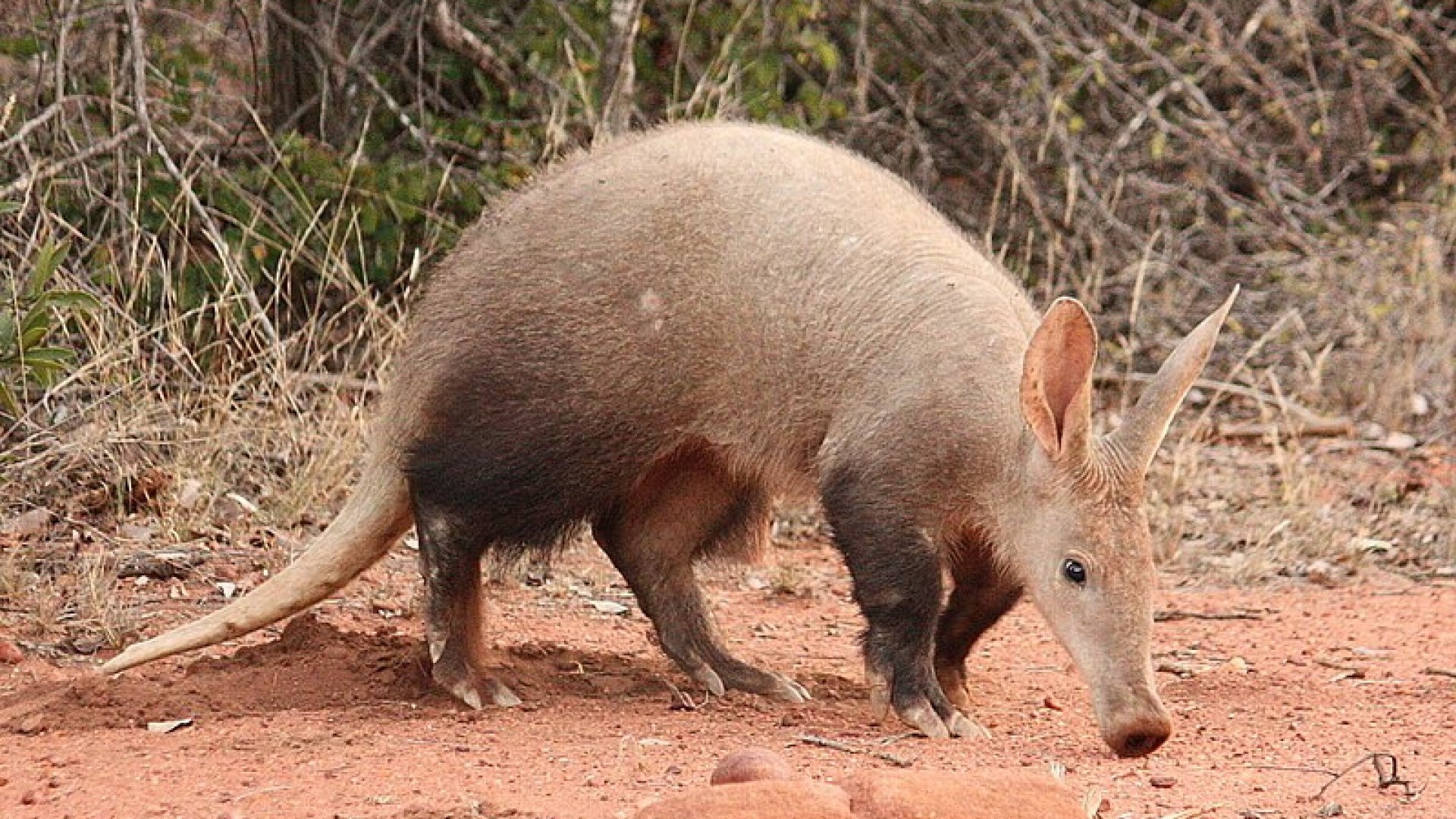
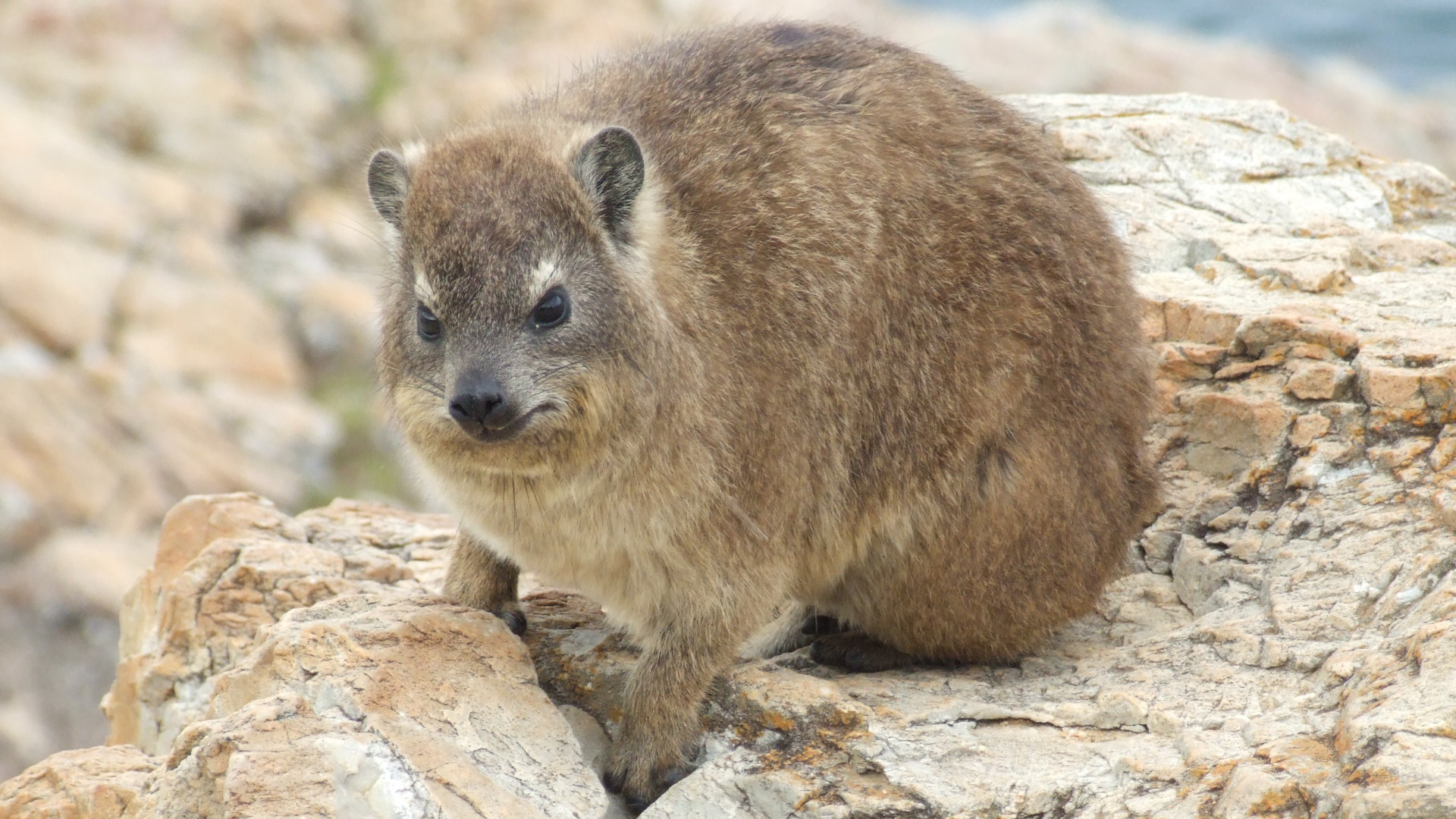


 Rock or cape hyrax has 5 recognized subspecies, again, unsurprising given its vast range. Generally having a hide within a natural rock cavity, Rock hyraxes are social animals that live in colonies of up to 50 individuals. They sleep in one group, and start the day, warming up in the sun
Rock or cape hyrax has 5 recognized subspecies, again, unsurprising given its vast range. Generally having a hide within a natural rock cavity, Rock hyraxes are social animals that live in colonies of up to 50 individuals. They sleep in one group, and start the day, warming up in the sun Eastern tree hyrax is the most localized of the tree hyrax species, only found in places within a narrow band of lowland and montane forests in Kenya and Tanzania and close-by islands. A solitary species, it lives in tree cavities, and communicates with others, through scent marking and high pitched calls.
Eastern tree hyrax is the most localized of the tree hyrax species, only found in places within a narrow band of lowland and montane forests in Kenya and Tanzania and close-by islands. A solitary species, it lives in tree cavities, and communicates with others, through scent marking and high pitched calls. 
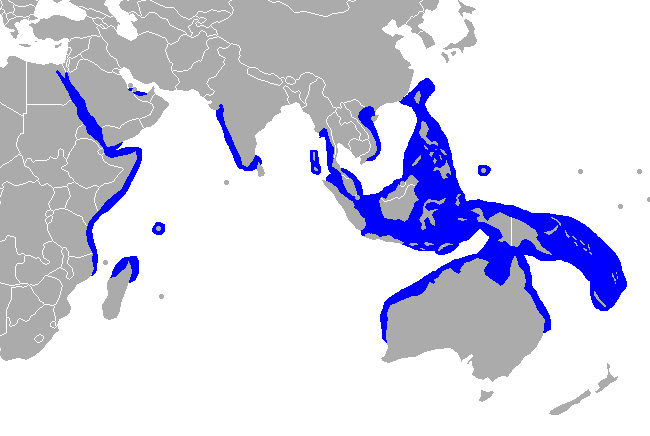 Dugong– The only surviving Dugongidae after the stellers sea cow (described in 1741 and hunted to extinction by 1768 for hide meat and fat) was lost.
Dugong– The only surviving Dugongidae after the stellers sea cow (described in 1741 and hunted to extinction by 1768 for hide meat and fat) was lost. ian Manatee
ian Manatee
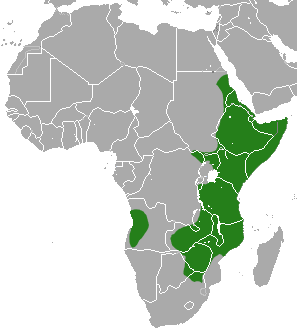
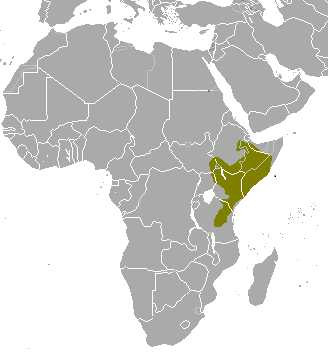
 Manatee) Although found both on the coast and inland, there is no significant genetic difference between these populations. African Manatees can be found in West African regions which include a wide range of countries – requiring cross nation action to save them. Manatees are found in brackish waters to freshwater: in oceans, rivers, lakes, coastal estuaries, reservoirs, lagoons, and bays on the coast.
Manatee) Although found both on the coast and inland, there is no significant genetic difference between these populations. African Manatees can be found in West African regions which include a wide range of countries – requiring cross nation action to save them. Manatees are found in brackish waters to freshwater: in oceans, rivers, lakes, coastal estuaries, reservoirs, lagoons, and bays on the coast.
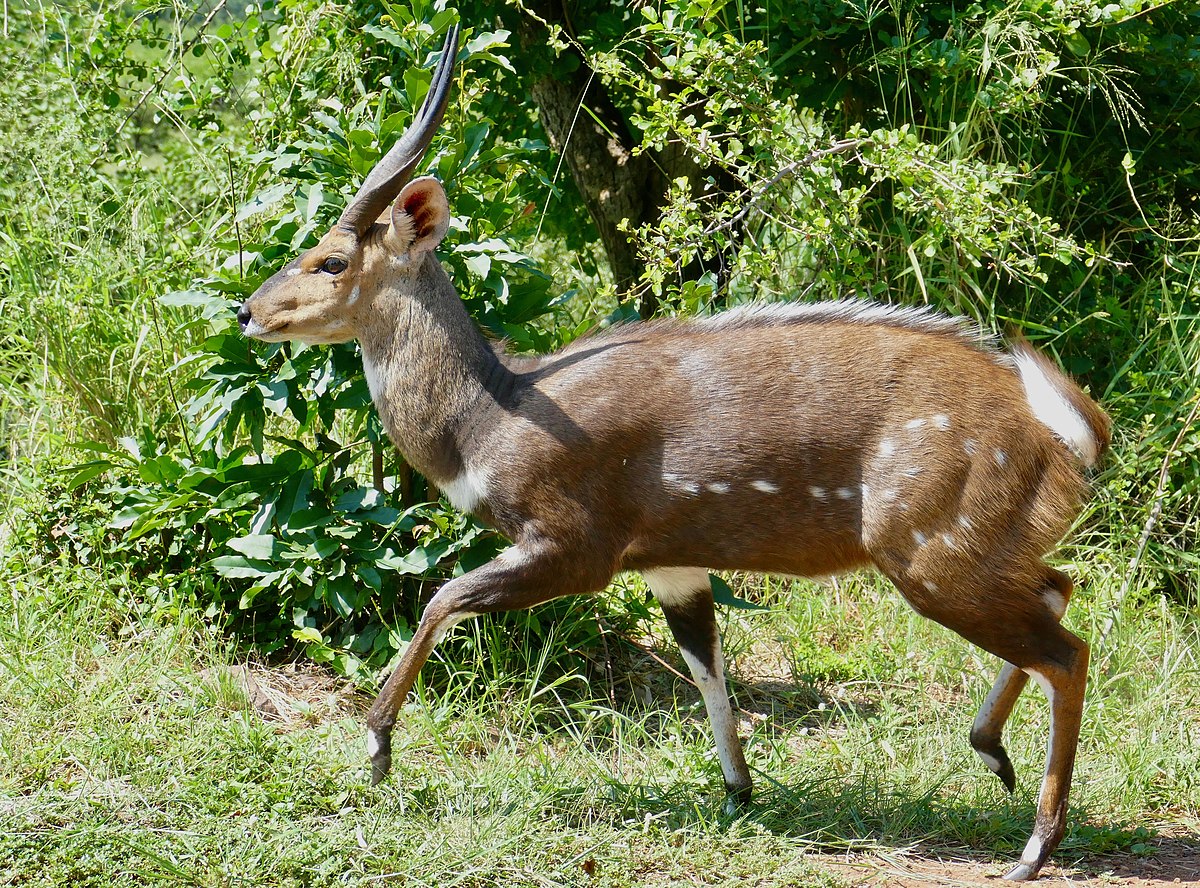


 known as imbabala is a
known as imbabala is a
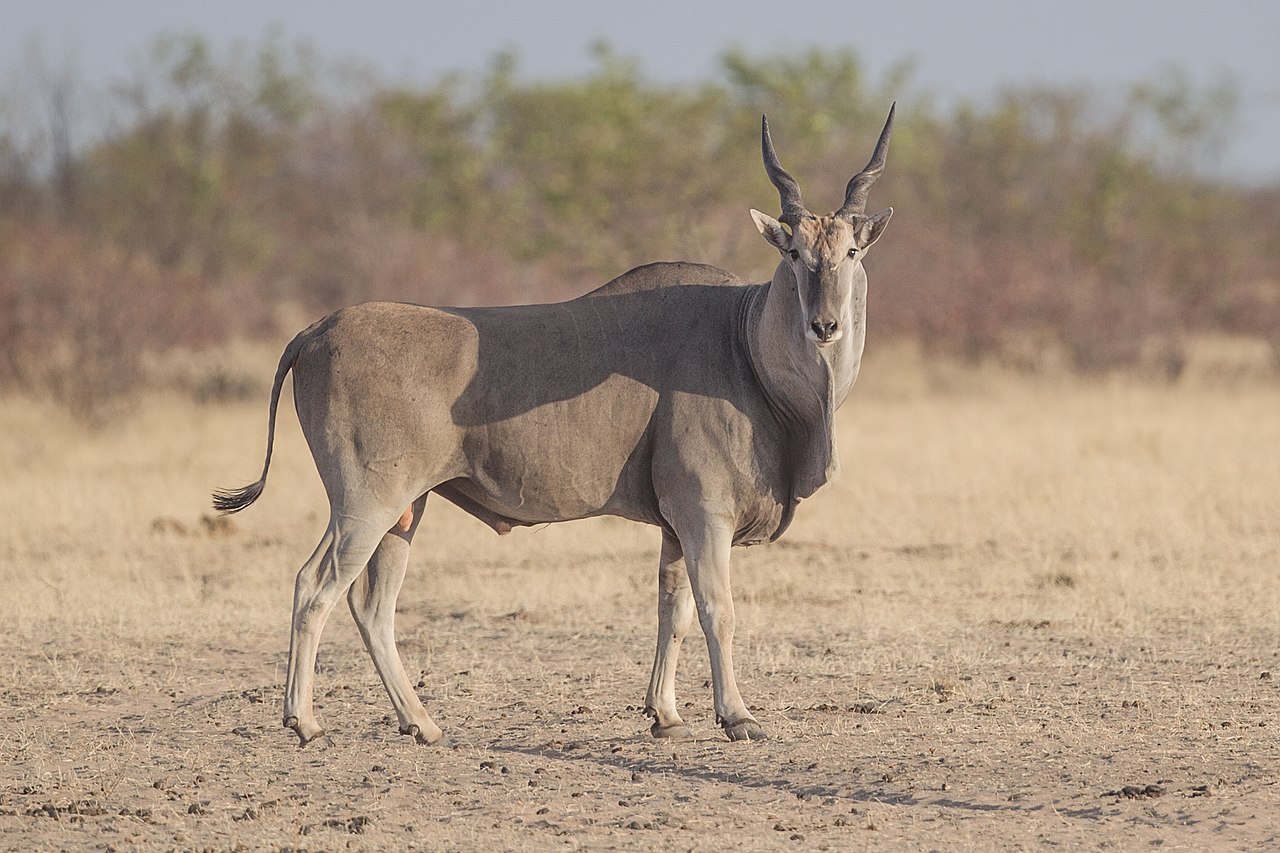
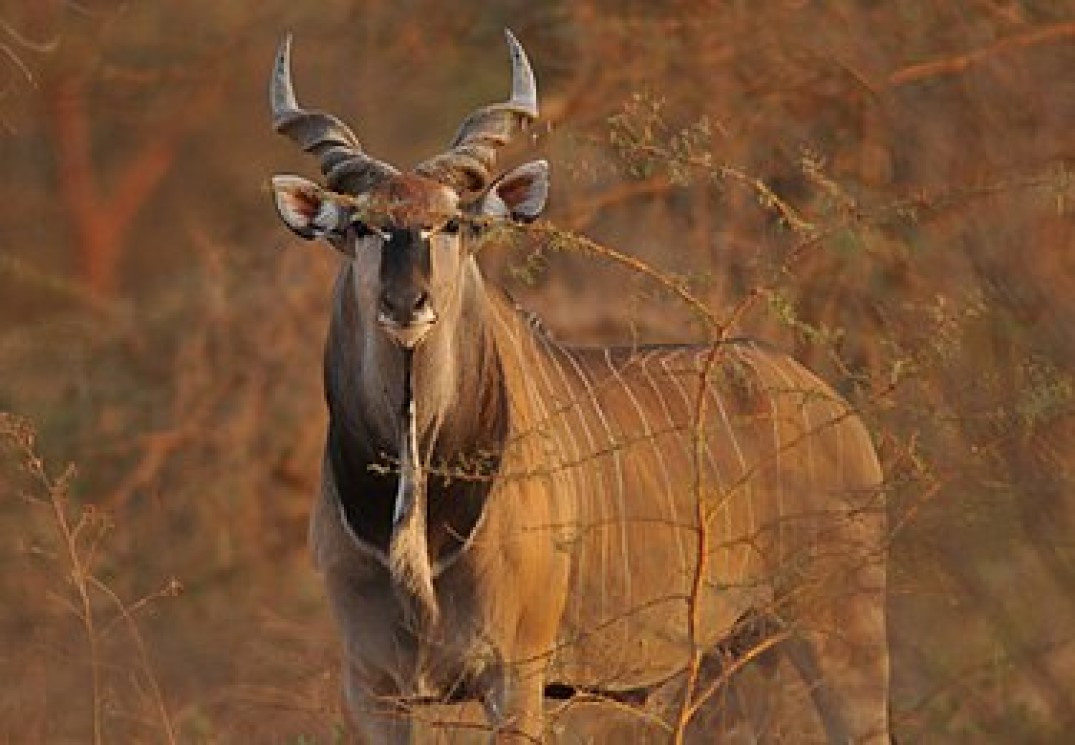
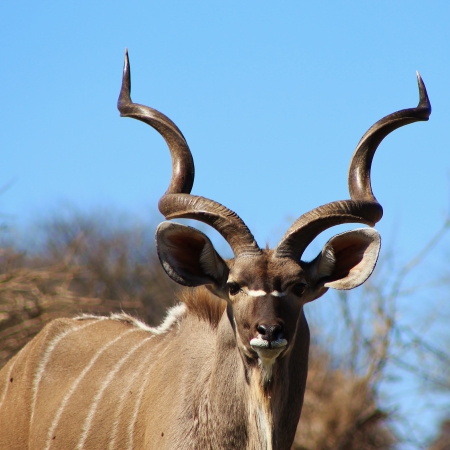





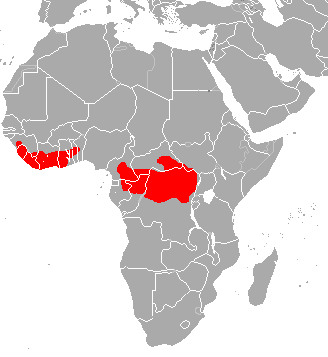 The bongo is a large, mostly nocturnal, forest-dwelling antelope, native to sub-Saharan Africa. Bongos are characterised by a striking reddish-brown coat, black and white markings, white-yellow stripes, and long slightly spiralled horns. It is the only member of its family in which both sexes have horns. Bongos have a complex social interaction and are found in African dense forest mosaics. They are the third-largest antelope in the world.
The bongo is a large, mostly nocturnal, forest-dwelling antelope, native to sub-Saharan Africa. Bongos are characterised by a striking reddish-brown coat, black and white markings, white-yellow stripes, and long slightly spiralled horns. It is the only member of its family in which both sexes have horns. Bongos have a complex social interaction and are found in African dense forest mosaics. They are the third-largest antelope in the world.
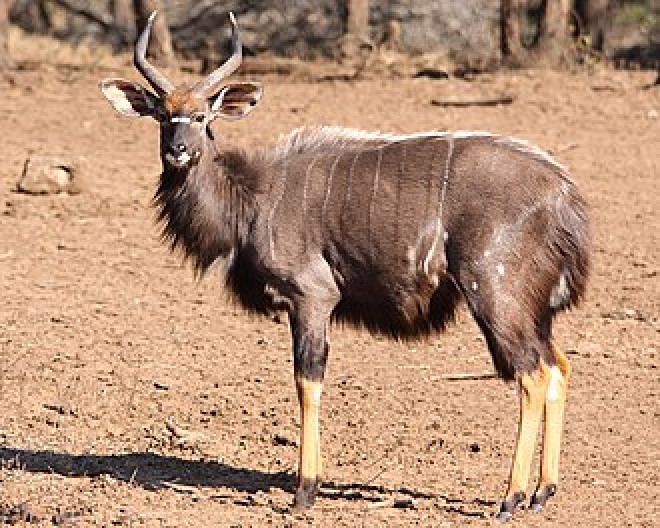
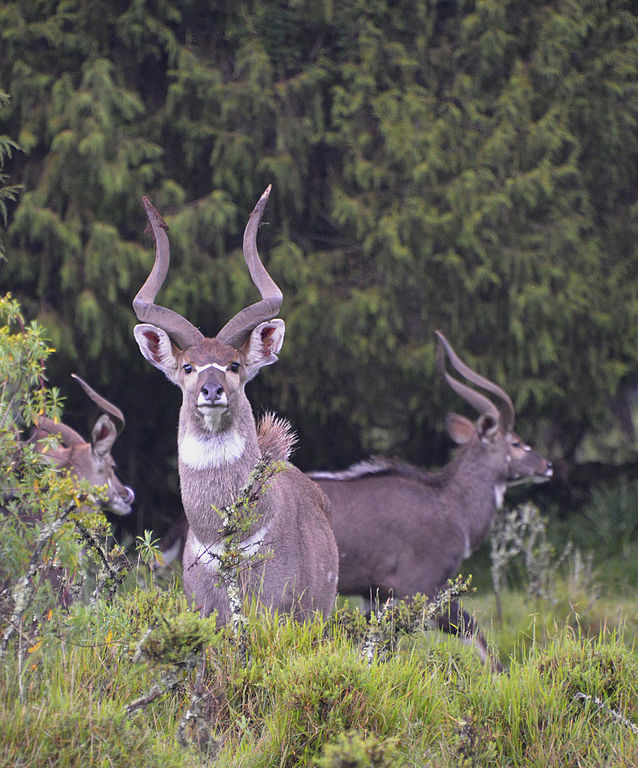





 swamp-dwelling medium-sized antelope found throughout central Africa (see the map to the right. The sitatunga is mostly confined to swampy and marshy habitats. Here they occur in tall and dense vegetation as well as seasonal swamps, marshy clearings in forests, riparian thickets and mangrove swamps.
swamp-dwelling medium-sized antelope found throughout central Africa (see the map to the right. The sitatunga is mostly confined to swampy and marshy habitats. Here they occur in tall and dense vegetation as well as seasonal swamps, marshy clearings in forests, riparian thickets and mangrove swamps.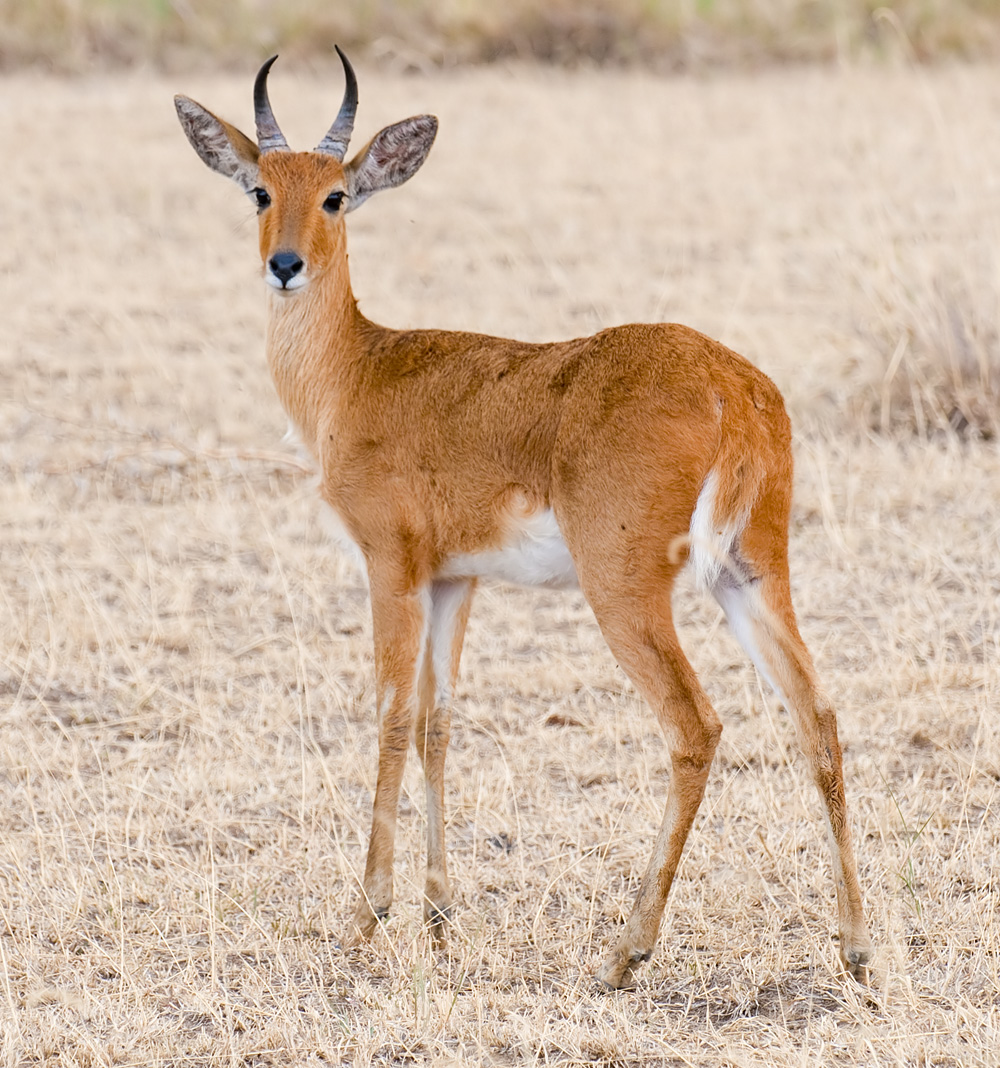



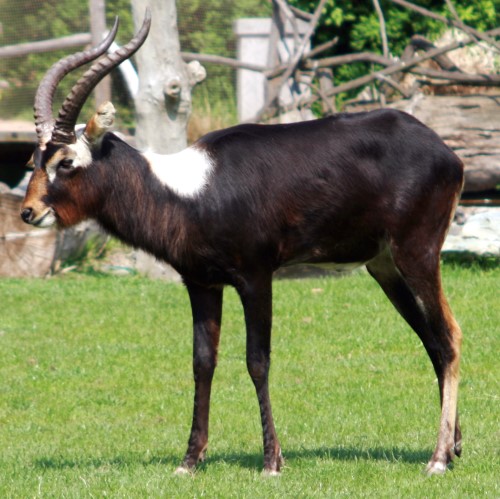
 Reedbuck is found in Southern Africa. It is a midsized
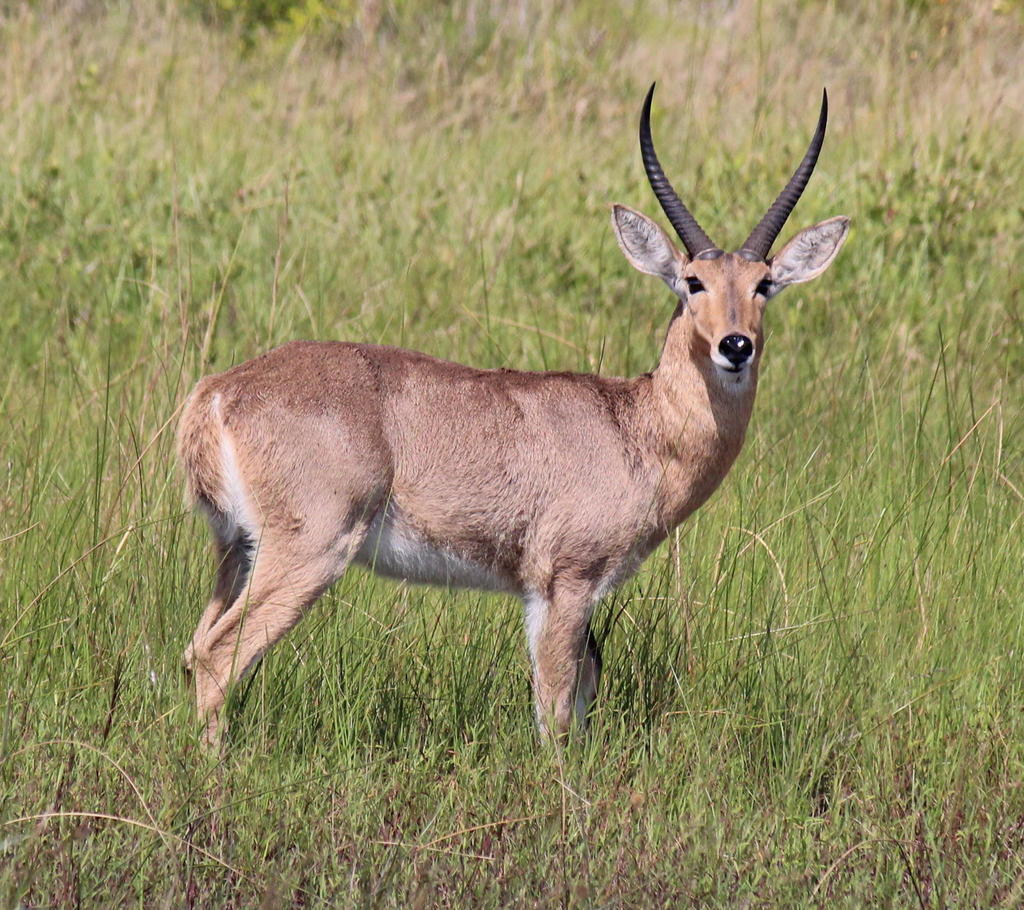
Reedbuck is found in Southern Africa. It is a midsized  are found in a band across Africa, including areas of Eastern, Central and Western Africa.
are found in a band across Africa, including areas of Eastern, Central and Western Africa.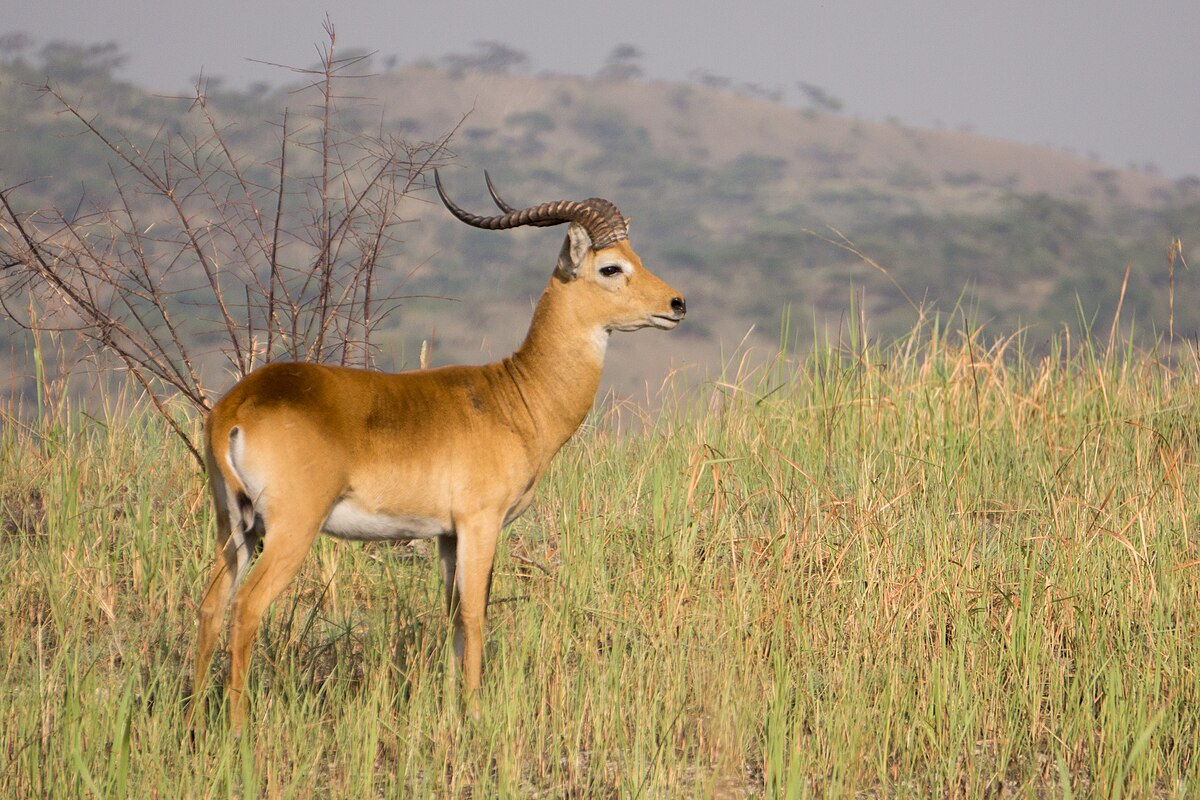
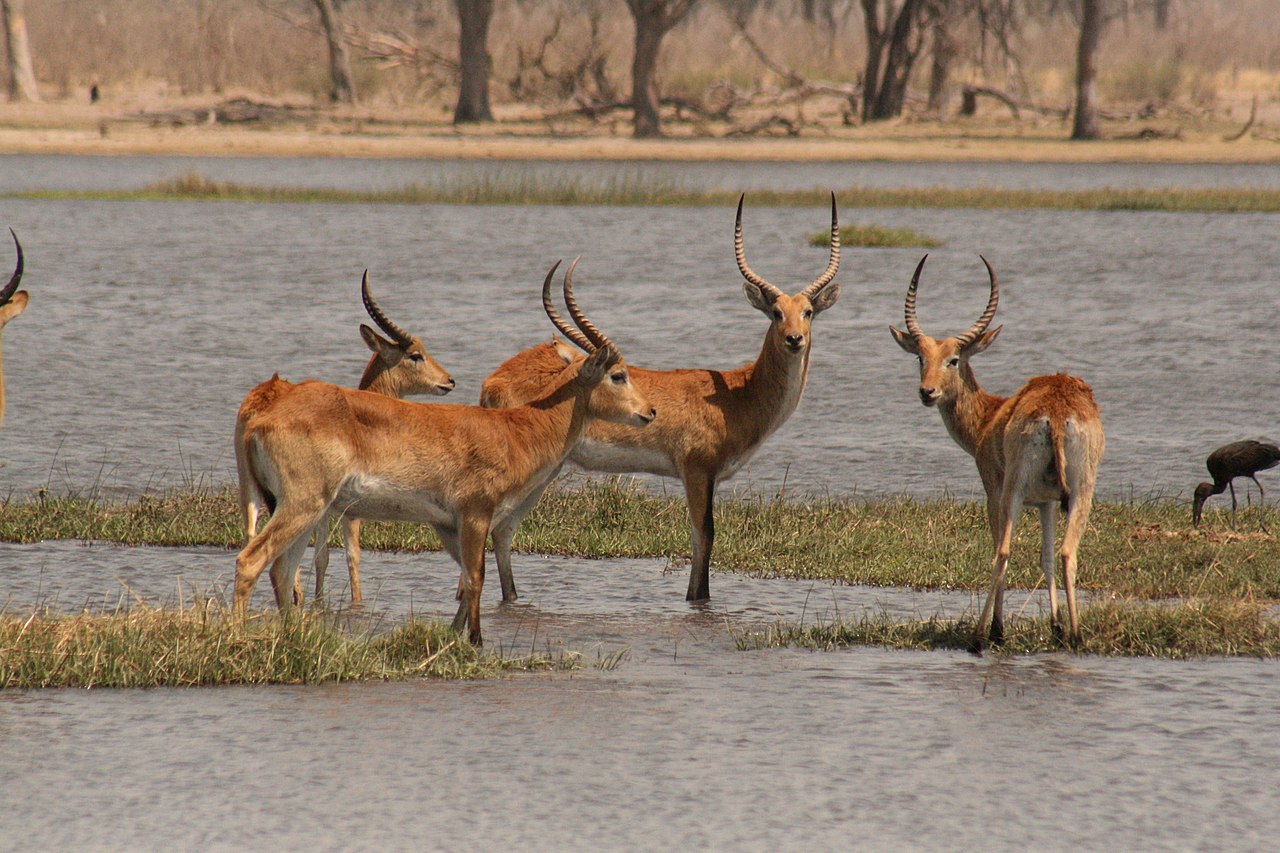

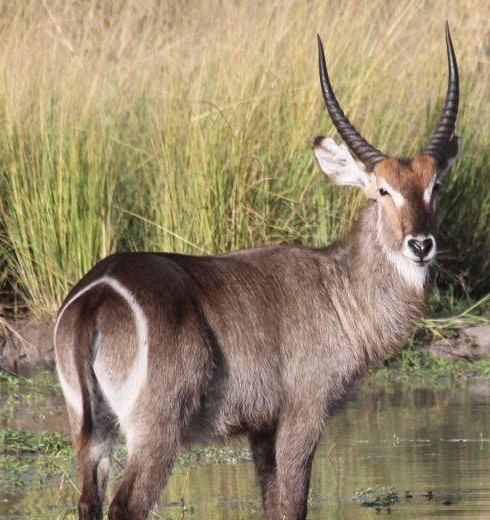
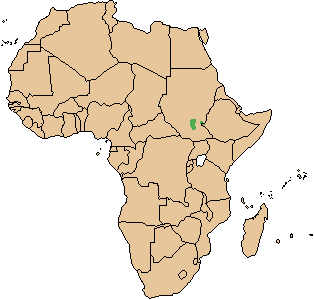 The Nile lechwe or Mrs Gray’s lechwe is an endangered species of antelope found in swamps and grasslands in South Sudan and Ethiopia.
The Nile lechwe or Mrs Gray’s lechwe is an endangered species of antelope found in swamps and grasslands in South Sudan and Ethiopia.


