
Declared extinct in the wild back in 2000, this species is now not only re-established in the wild, but has a big enough population to now only be listed as endangered (down from critically endangered).
Apart from supplying individuals for the reintroduction, Marwell zoo also helped with strategy.
The video below is just 2 minutes long. While it talks about Marwells other work as well, it shows a number of these animals living wild back in Africa.
This has got to become the reason for zoos. What ever else they do, there are many species at risk of extinction in the wild, these need to have enough captive individuals to re-establish wild populations, should the current conservation fail.
Of course, zoos have many other roles, from education, to fostering a love of wildlife in the next generation.
One thing that they should not be, is a curio house- many zoos are far to worried about displaying albino or melanistic individuals. Now while these individuals are fascinating and can be used as ambassadors for the species, their genetic health should be looked after (all white tigers are descended from one female, and closely related individuals are regularly bred togerther to ensure this trait is passed down. Indeed, as a result of this, white tigers are often not of good health.
The majority of zoos are now like Marwell – while like many, it started as the private zoo of wealthy owners it has turned into an important place of conservation and science. Another of their successes, is the cooperative breeding that occurs as standard in current times, across Europe. Regular loaning of animals is essential, so that we can treat all of the zoo animals in Europe as one single population, thereby making sure that all animals in the system are healthy.
There are many hundreds of zoos across Europe (some claim as many as 2000, though around 1500 is the estimated worldwide number suggesting that this is a rather large exaggeration. It is likely that around half of the worlds zoos are in Europe, and by cooperative breeding, we can make sure that healthy populations remain in captivity, so that should a population be lost from the wild, it can be returned, when the wild situation improves.
Almost all predictions about human population are expected to peak in the coming decades, and then decline after that. If this pattern is followed, it should be expected that we will need to re-establish wilderness in the future.
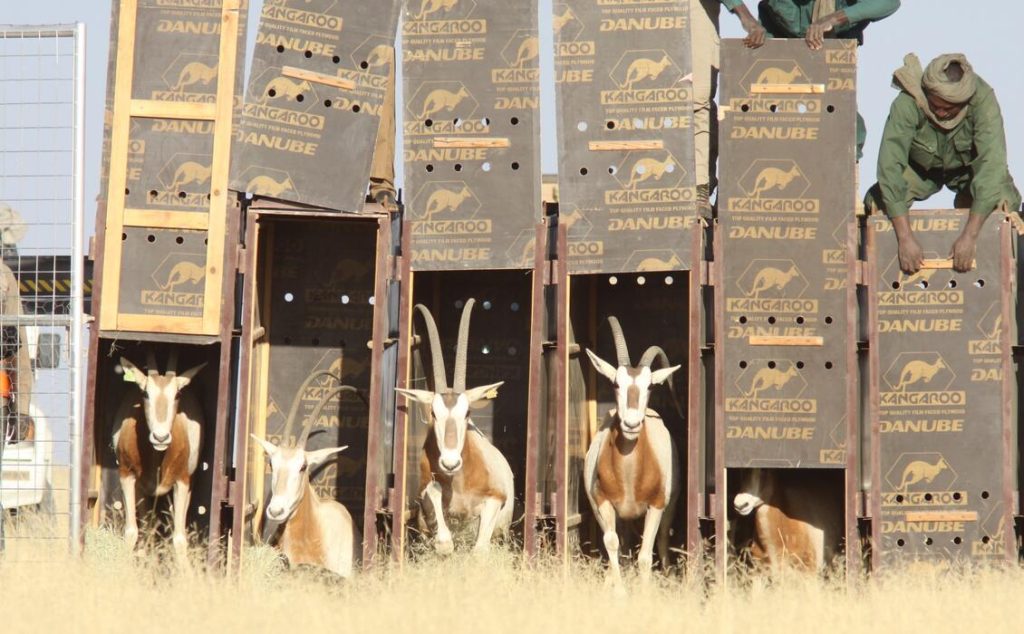
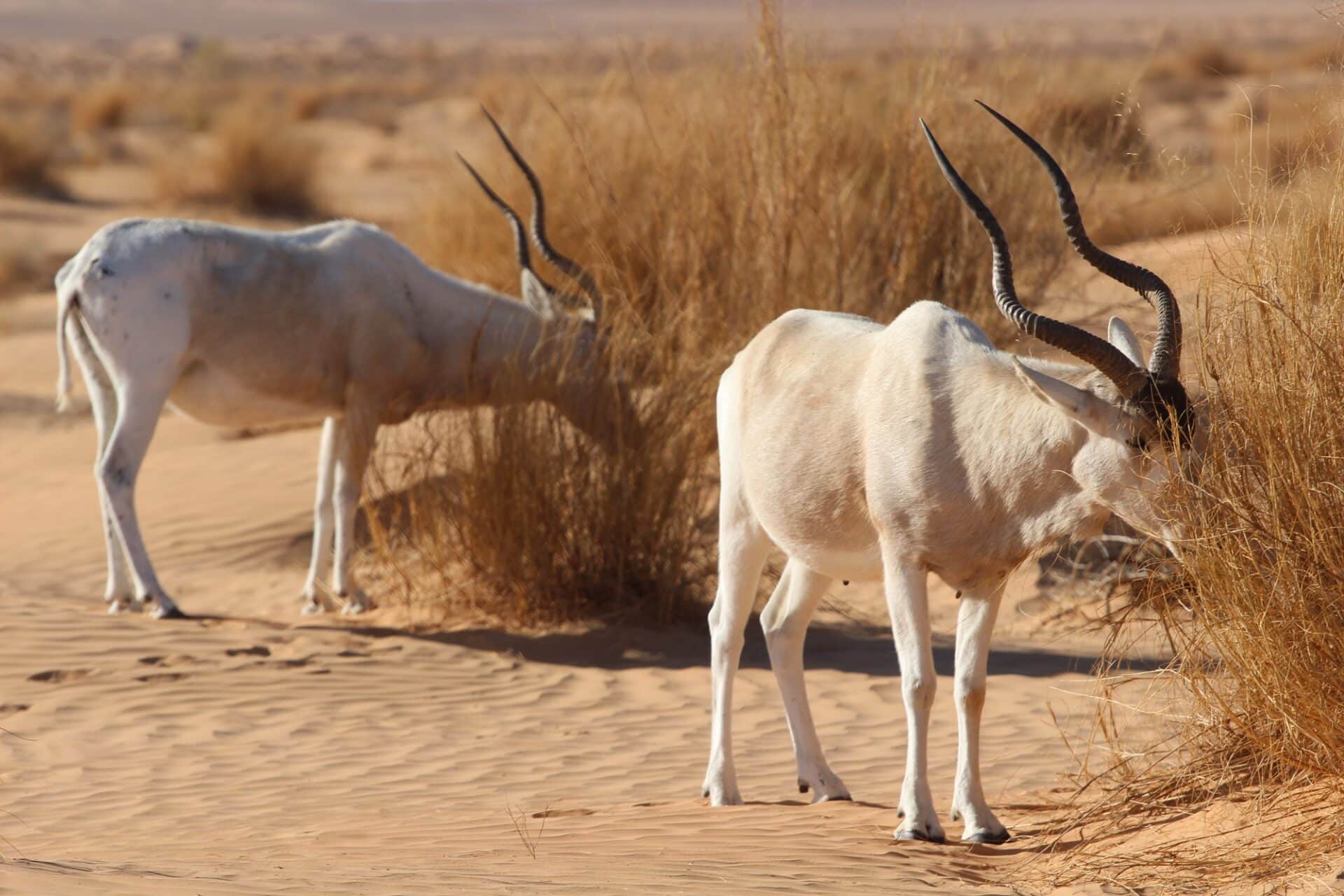
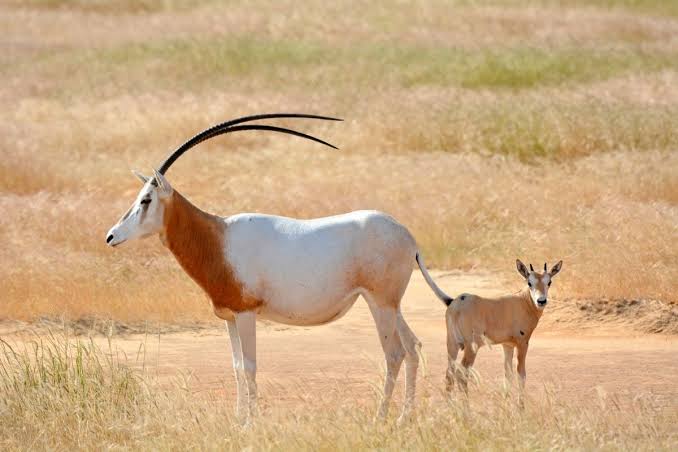
Scimitar-horned oryx have been returned to the wild in Tunisia, and Chad and there are plans to return them to the wild in Niger, in the near future.
Extinction was caused by a variety of features, but the primary one was over-hunting. This has virtually been eliminated, after a ban on hunting of this species was put into effect in 2013. Should this species be allowed to fully recover. In 1985, there was a population of at least 500 of this species living in the wild, so it took only 15 years for it to disappear, as such what is clearly essential is a regular assessment on how this species is faring, allowing earlier interventions.
Saving the natural world, may require this kind of success to be a regular feature.


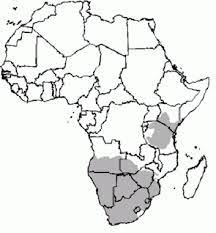
 The HIrola ( also known as the Hunters hartebeest or hunters antelope) is a critically endangered species. It was named by H.C.V Hunter (a big game hunter and zoologist) in 1888. It is the only member of the genus Beatragus, and it currently has 300-500 individuals living in the wild (there are none in captivity).
The HIrola ( also known as the Hunters hartebeest or hunters antelope) is a critically endangered species. It was named by H.C.V Hunter (a big game hunter and zoologist) in 1888. It is the only member of the genus Beatragus, and it currently has 300-500 individuals living in the wild (there are none in captivity).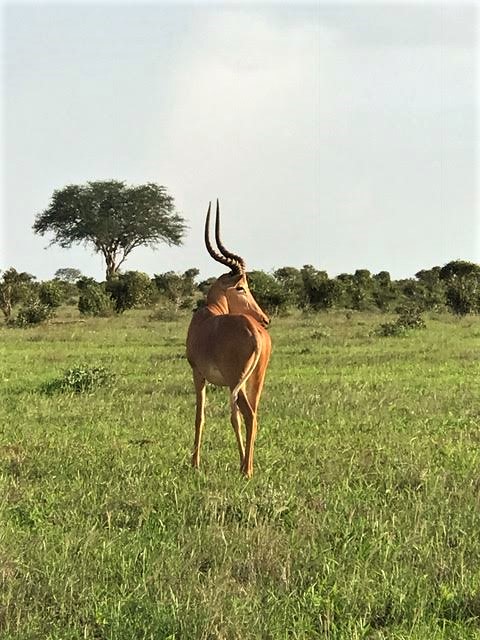
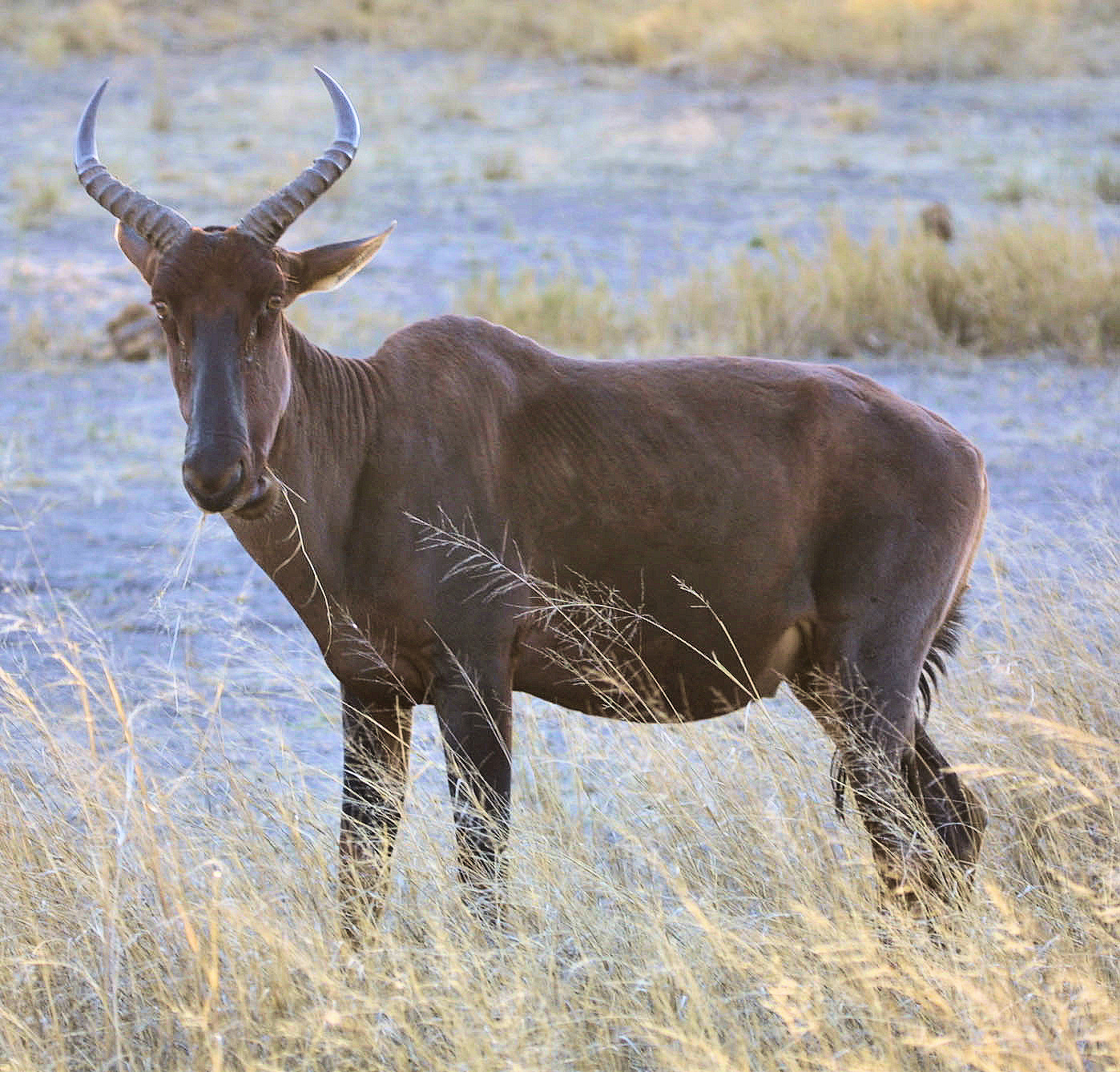




 many as 70 subspecies, local variants and similar have been suggested, however there is only one currently recognized species.
many as 70 subspecies, local variants and similar have been suggested, however there is only one currently recognized species. common wildebeest, white-bearded gnu or brindled gnu.
common wildebeest, white-bearded gnu or brindled gnu.
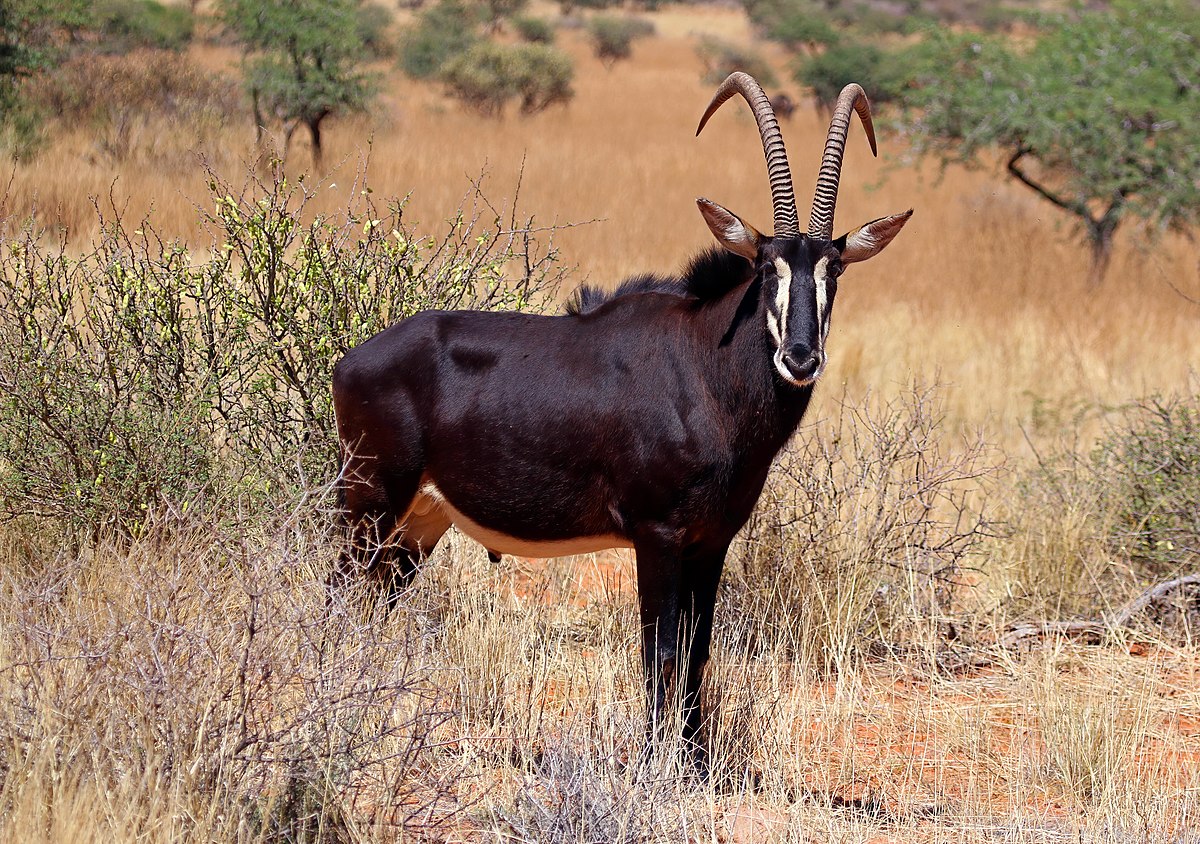






 are found in a band across Africa, including areas of Eastern, Central and Western Africa.
are found in a band across Africa, including areas of Eastern, Central and Western Africa.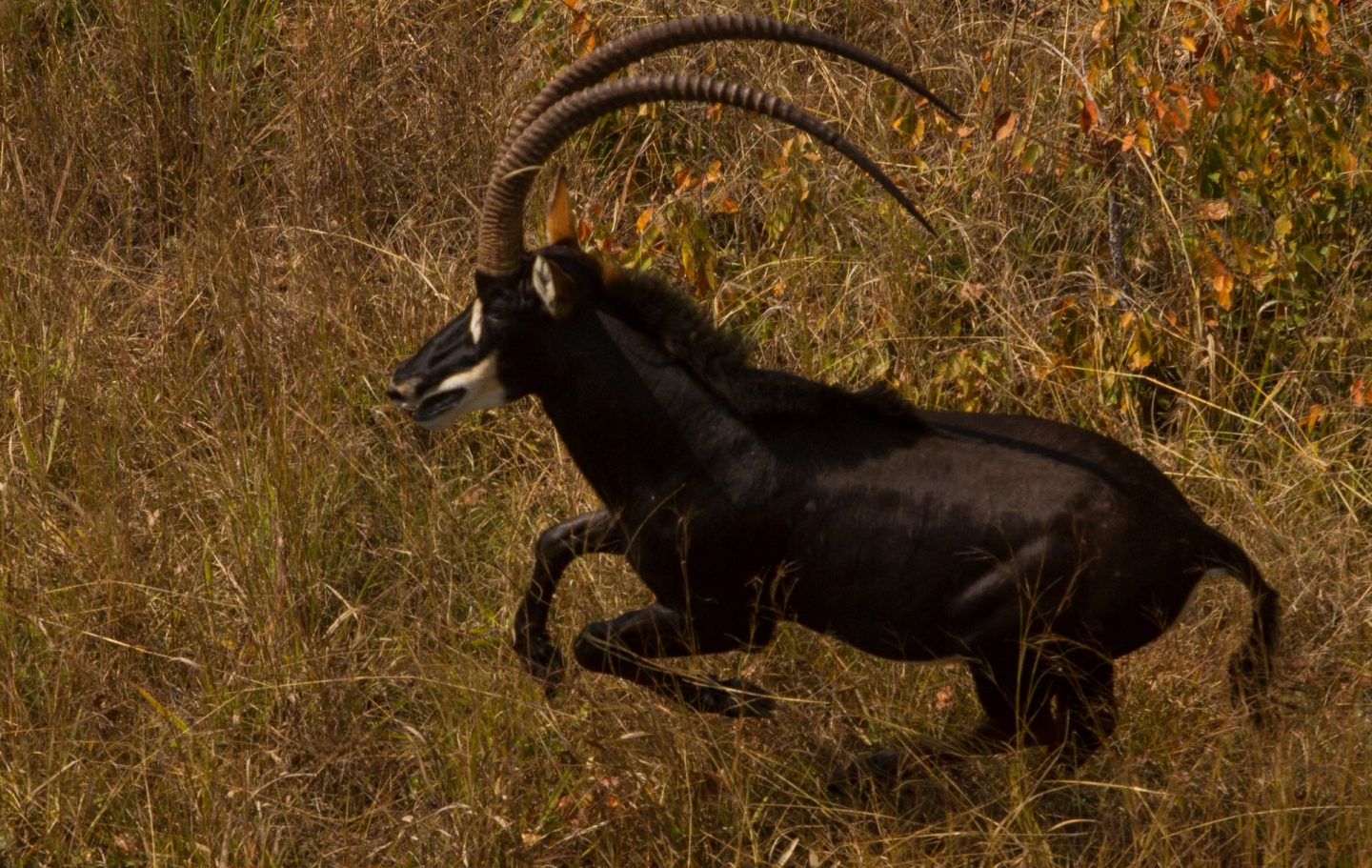
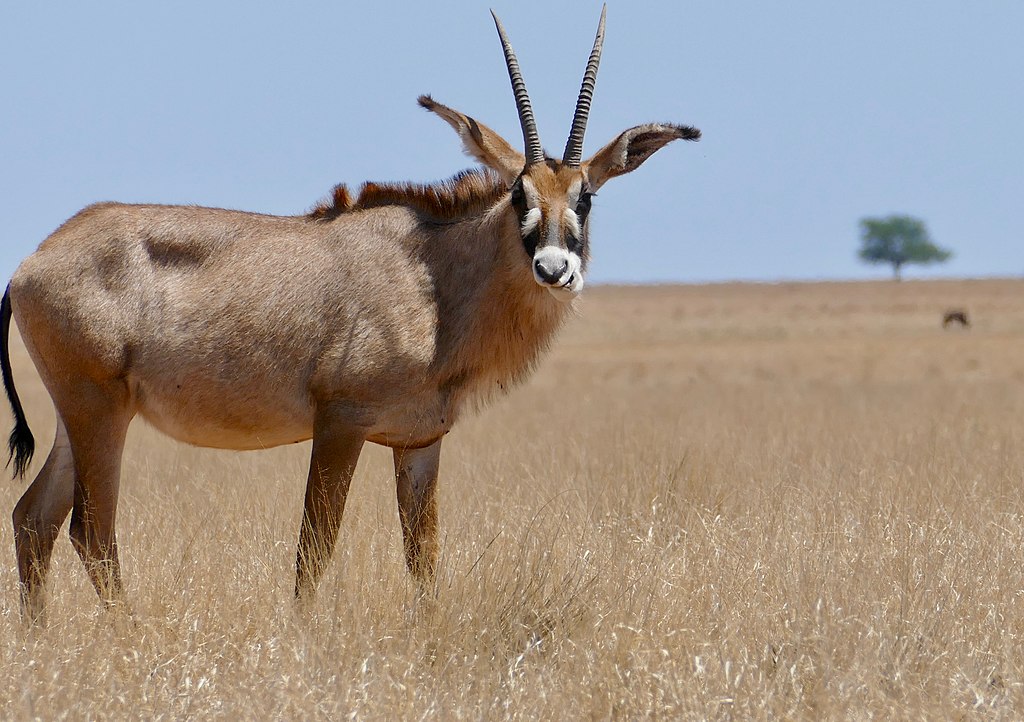
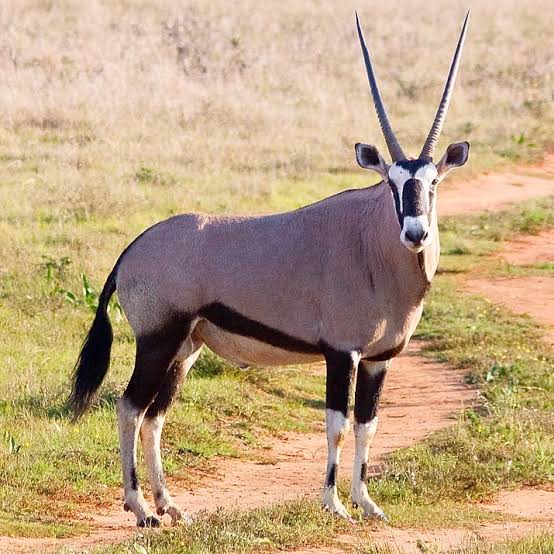





 Impala
Impala antelope, species with a handful of small populations acros central and western north Africa. It lives in the Sahara and the Sahel desert.
antelope, species with a handful of small populations acros central and western north Africa. It lives in the Sahara and the Sahel desert.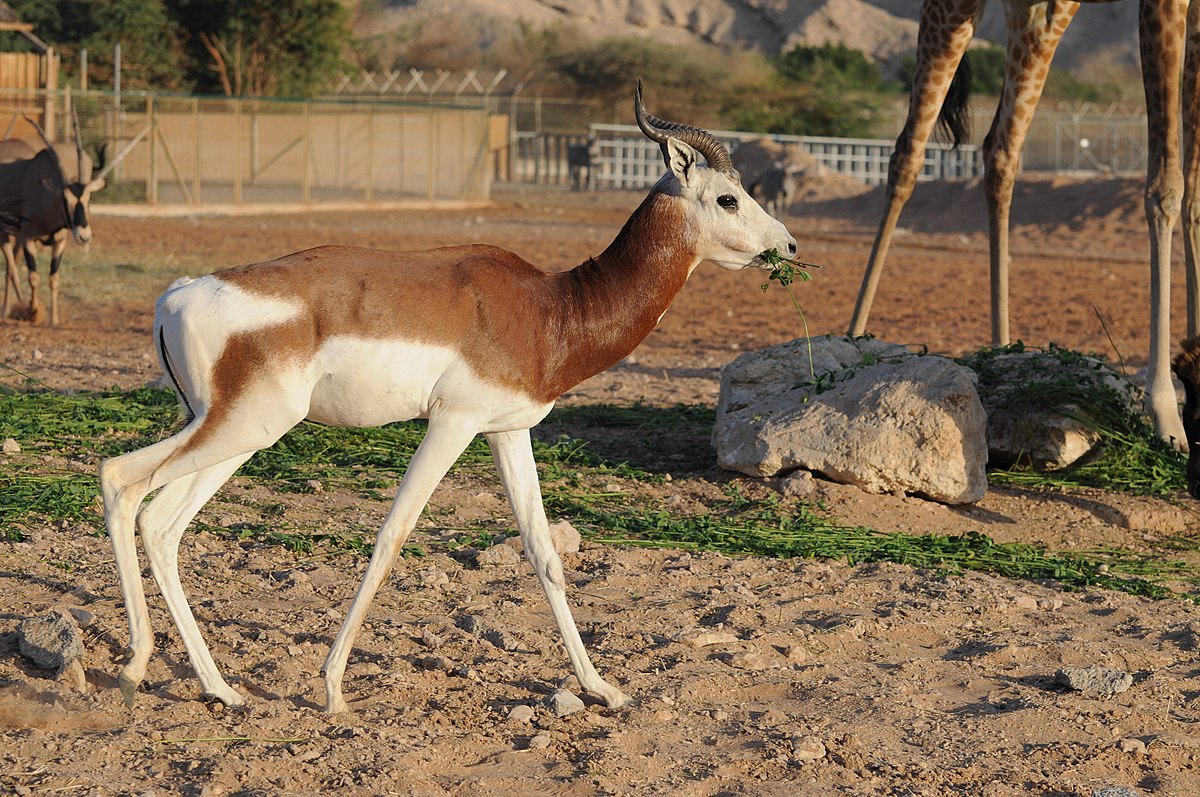 
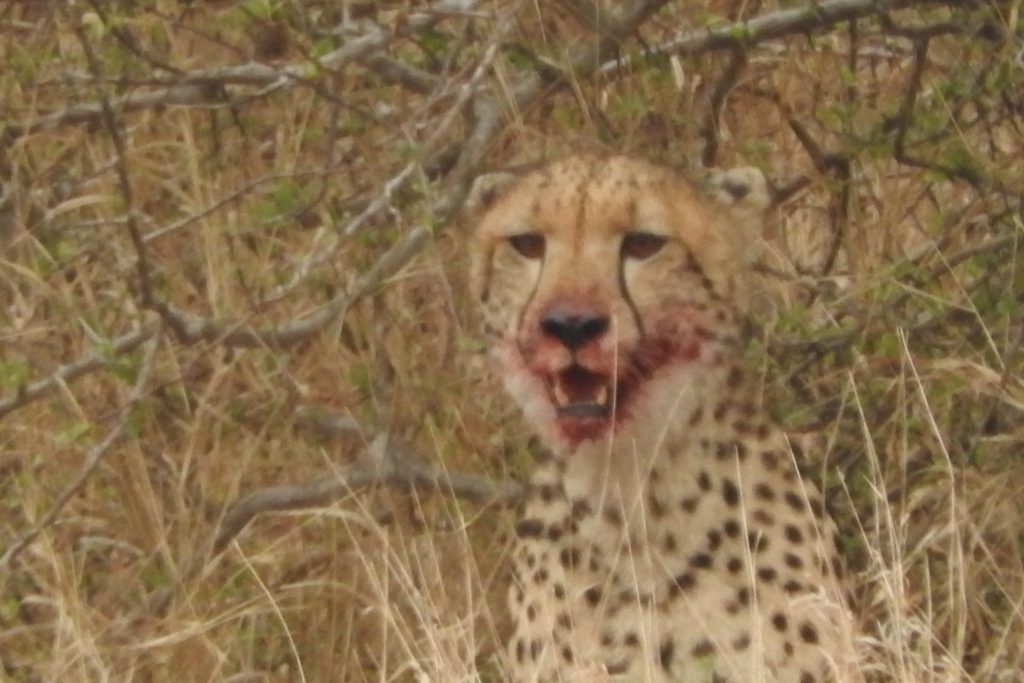
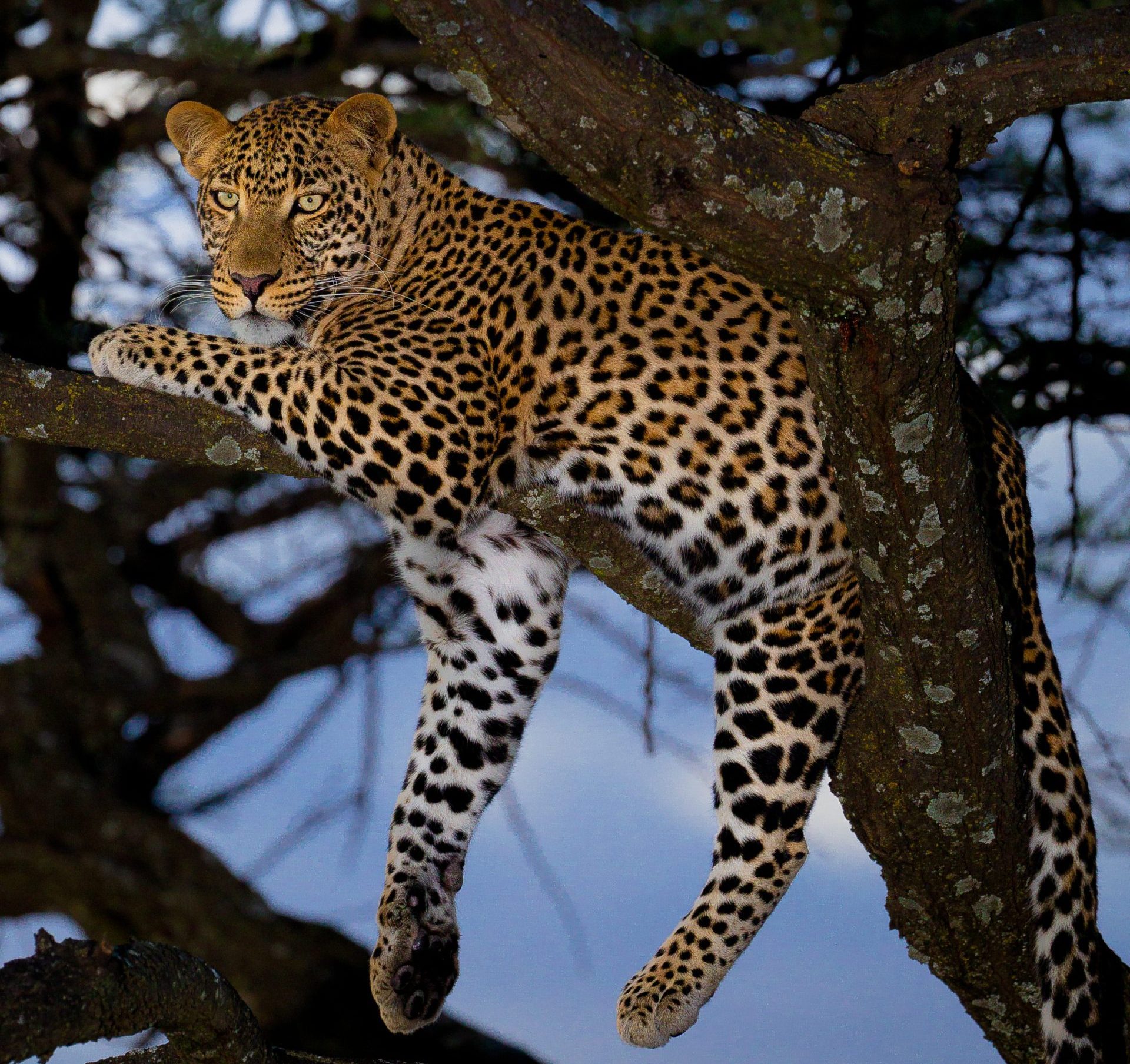







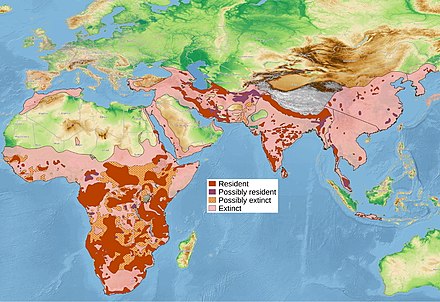 50 years ago, Africa was estimated to have 700,000 the current number is nearer to 50,000. This is not evenly spread, such that while 34 countries are thought to still host them. It should be noted, that the so called Barbary leopard is included in this subspecies. While there is still much debate (not least the suggestion that the Sahara might have stopped gene from from the Barbary region to the rest of Africa. In a similar way, there is discussion on a variety of different populations of leopards, but these will not get their own tab, until they are declared as recognized subspecies (there was, at one time as many as 37 claimed different subspecies of leopard spread across Africa and Asia, many were lost, when the genetic differences were found to be so small).
50 years ago, Africa was estimated to have 700,000 the current number is nearer to 50,000. This is not evenly spread, such that while 34 countries are thought to still host them. It should be noted, that the so called Barbary leopard is included in this subspecies. While there is still much debate (not least the suggestion that the Sahara might have stopped gene from from the Barbary region to the rest of Africa. In a similar way, there is discussion on a variety of different populations of leopards, but these will not get their own tab, until they are declared as recognized subspecies (there was, at one time as many as 37 claimed different subspecies of leopard spread across Africa and Asia, many were lost, when the genetic differences were found to be so small).




 Image source
Image source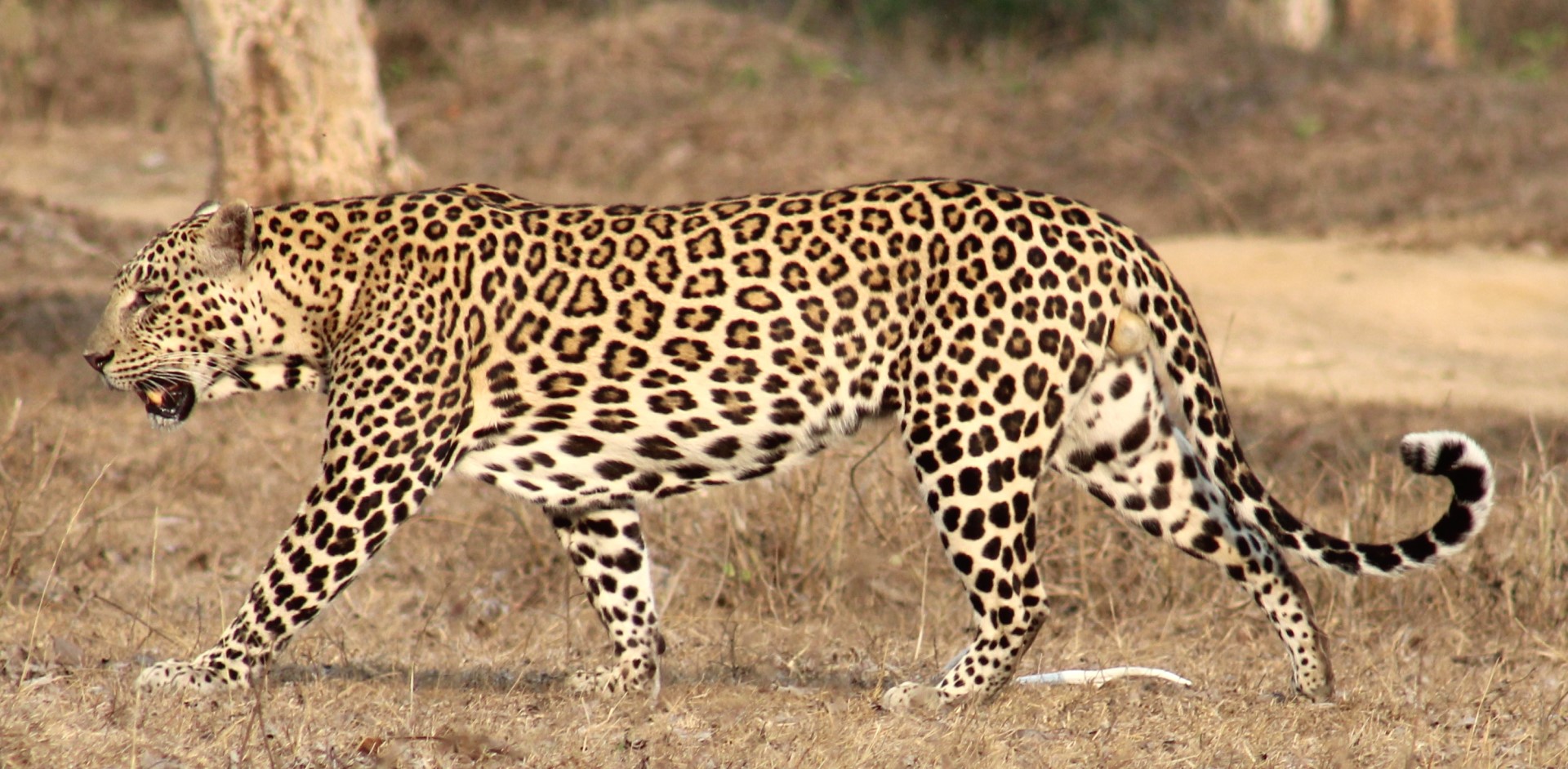 
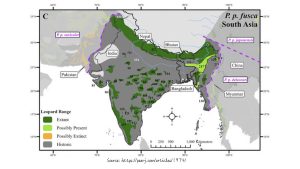 The number of Indian leopards in the wild is a worryingly low number. Some places suggest around 9500, while others suggest 12,000-14,000 (remember that the area of India is 10% of Africa, so this is far better by area.
The number of Indian leopards in the wild is a worryingly low number. Some places suggest around 9500, while others suggest 12,000-14,000 (remember that the area of India is 10% of Africa, so this is far better by area.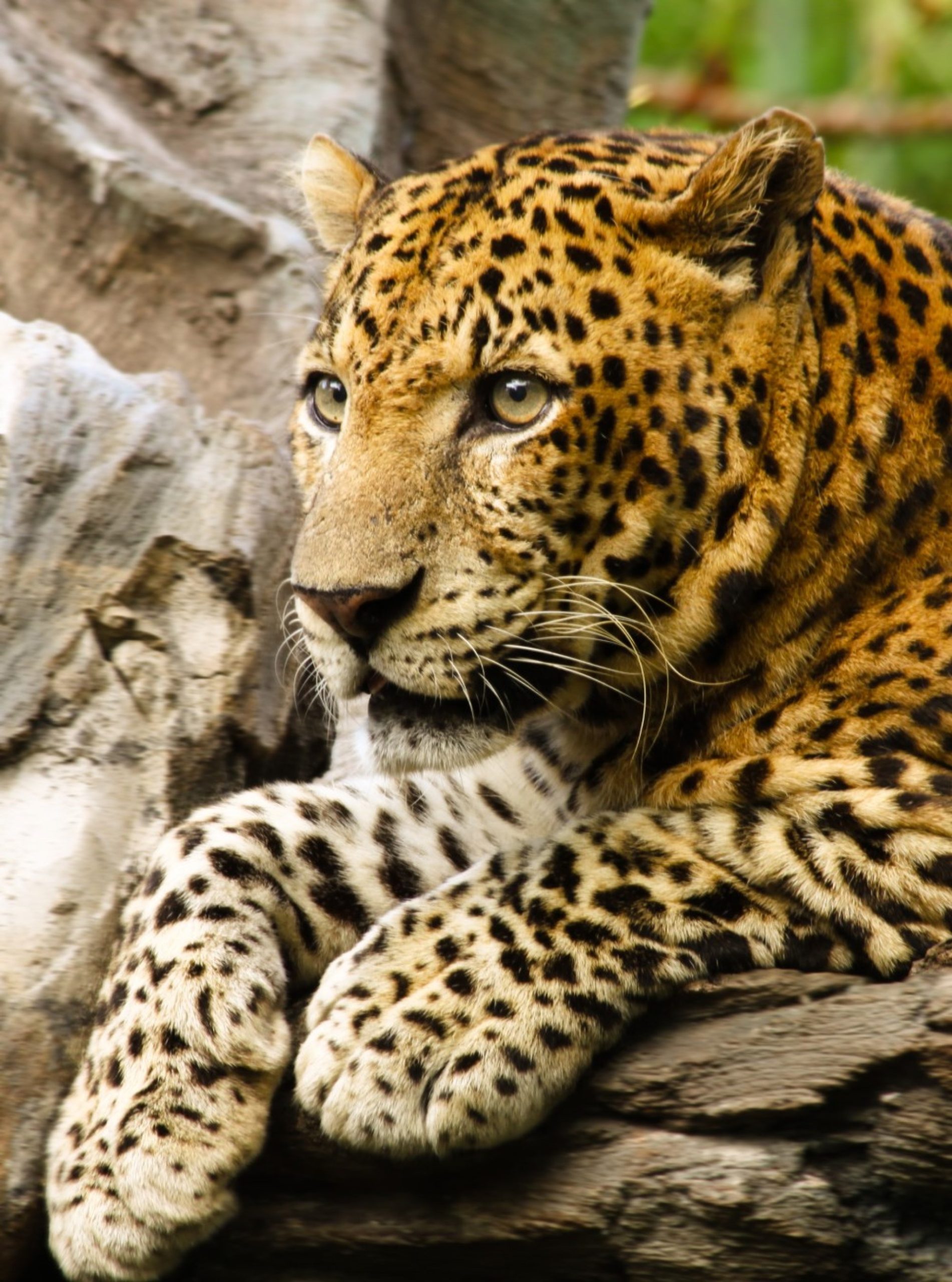
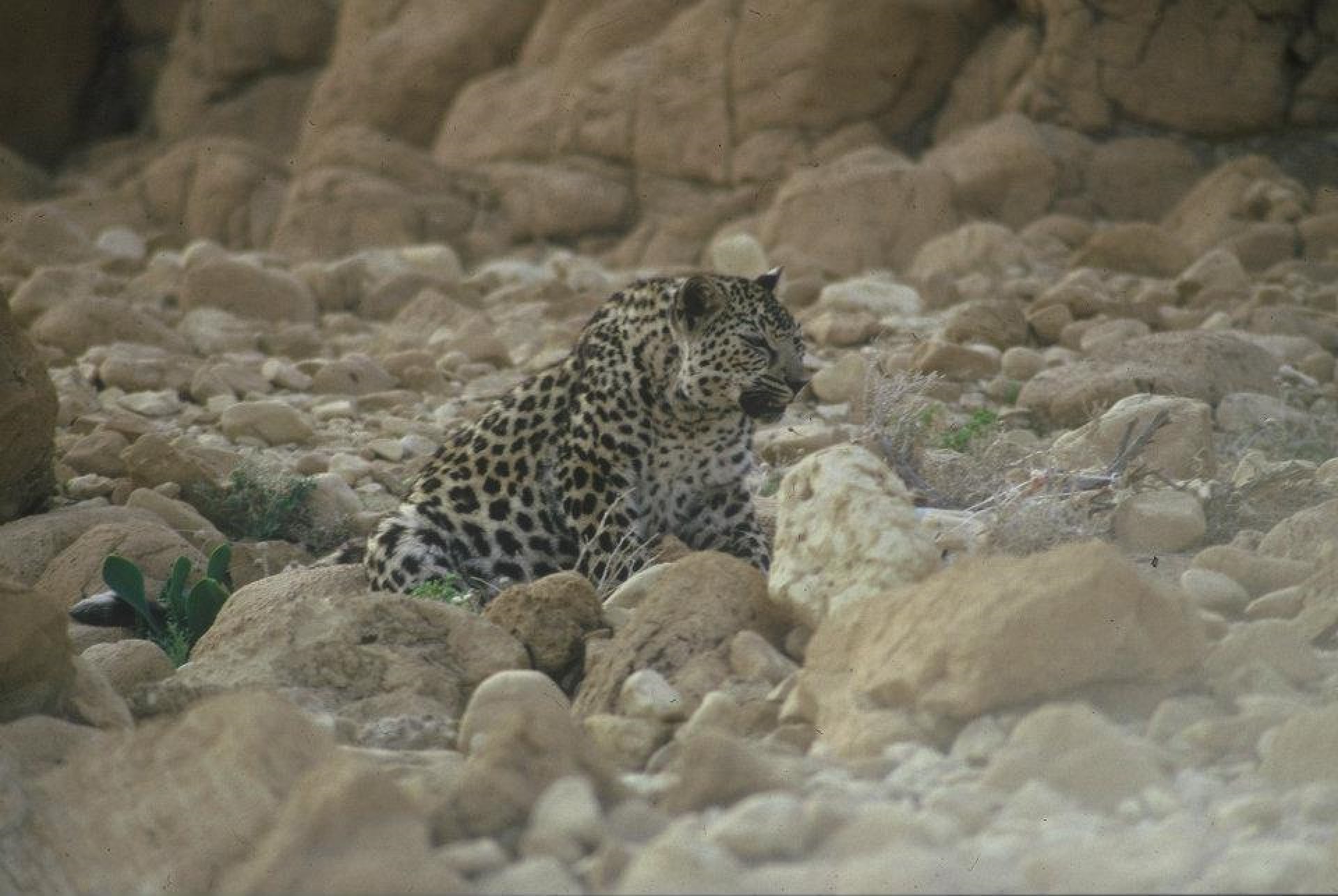


 In 2008, the size of this subspecies left in the wild was thought to be between 45 and 200. As such, it is perhaps not surprising that this subspecies has been critically endangered since 1996.
In 2008, the size of this subspecies left in the wild was thought to be between 45 and 200. As such, it is perhaps not surprising that this subspecies has been critically endangered since 1996.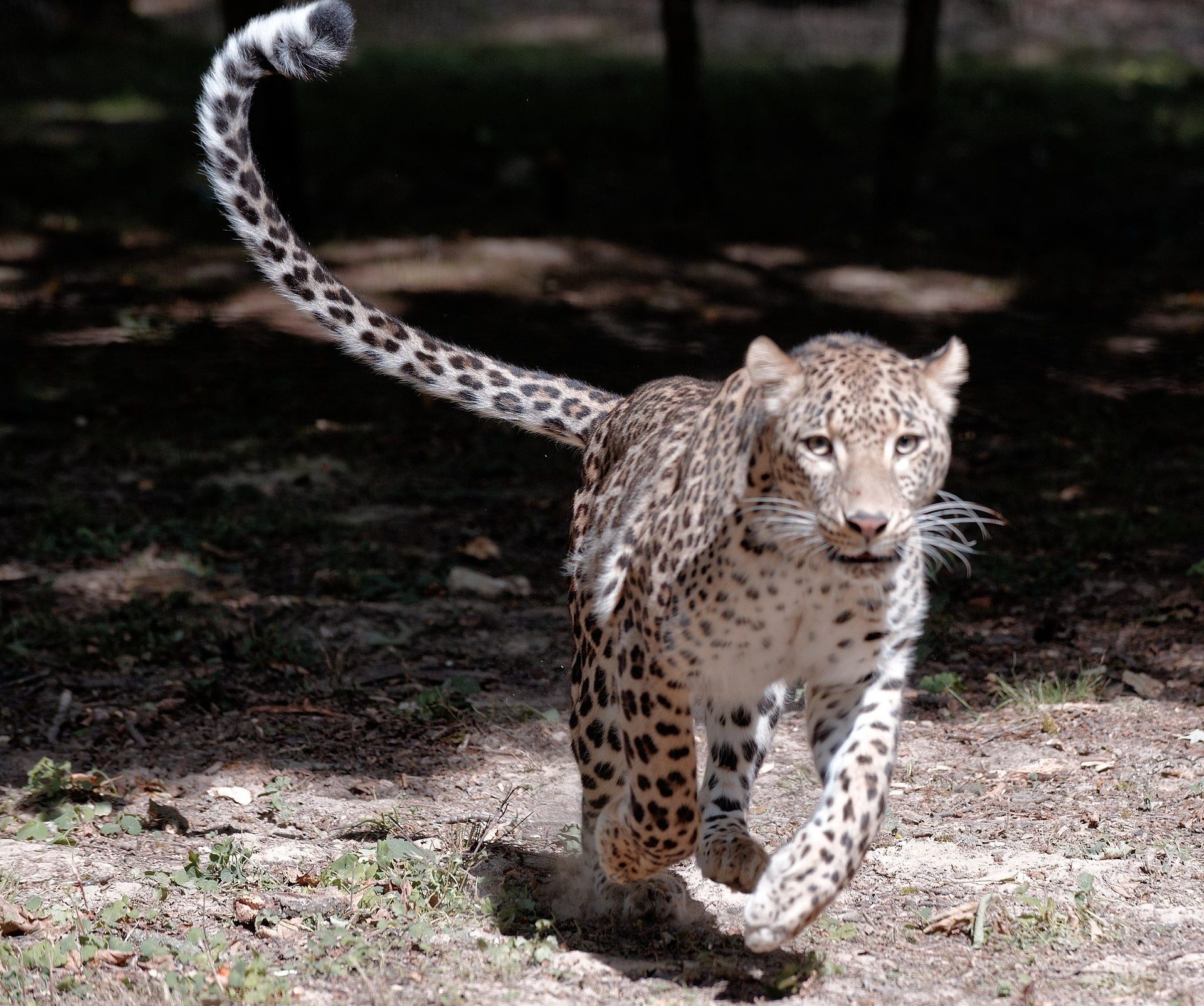
 Caucasian (also called Persian) Leopard)
Caucasian (also called Persian) Leopard) 
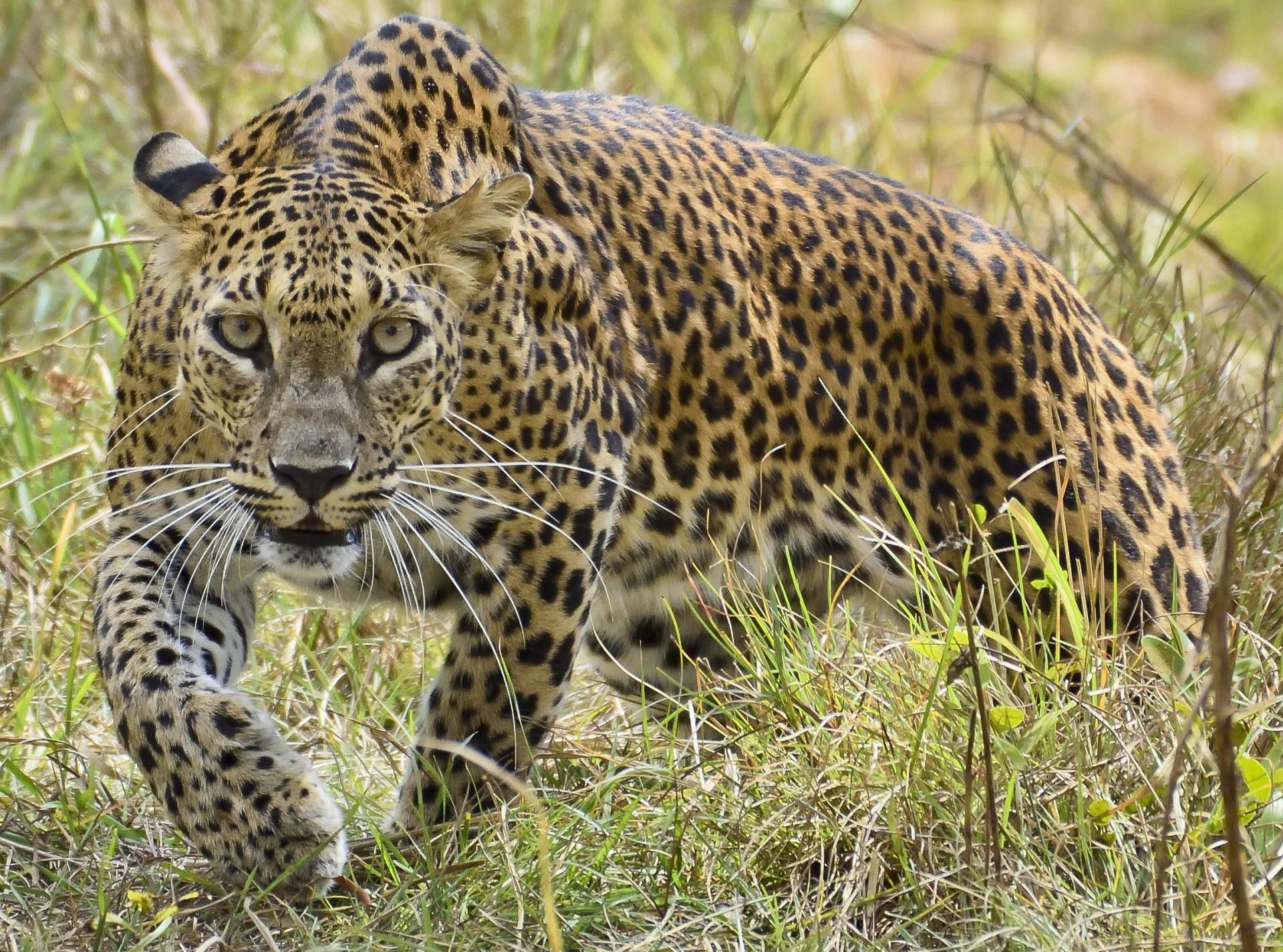

 Only described in 1956, they are relatively similar to the Indian Leopard, and were thought to be part of that subspecies until then. There are only 800 of this subspecies of leopard, and they were listed as vulnerable in 2020, and unfortunately it is thought to still be declining. It is thought, that as a result of being the apex predator on the island, they have got bigger.
Only described in 1956, they are relatively similar to the Indian Leopard, and were thought to be part of that subspecies until then. There are only 800 of this subspecies of leopard, and they were listed as vulnerable in 2020, and unfortunately it is thought to still be declining. It is thought, that as a result of being the apex predator on the island, they have got bigger.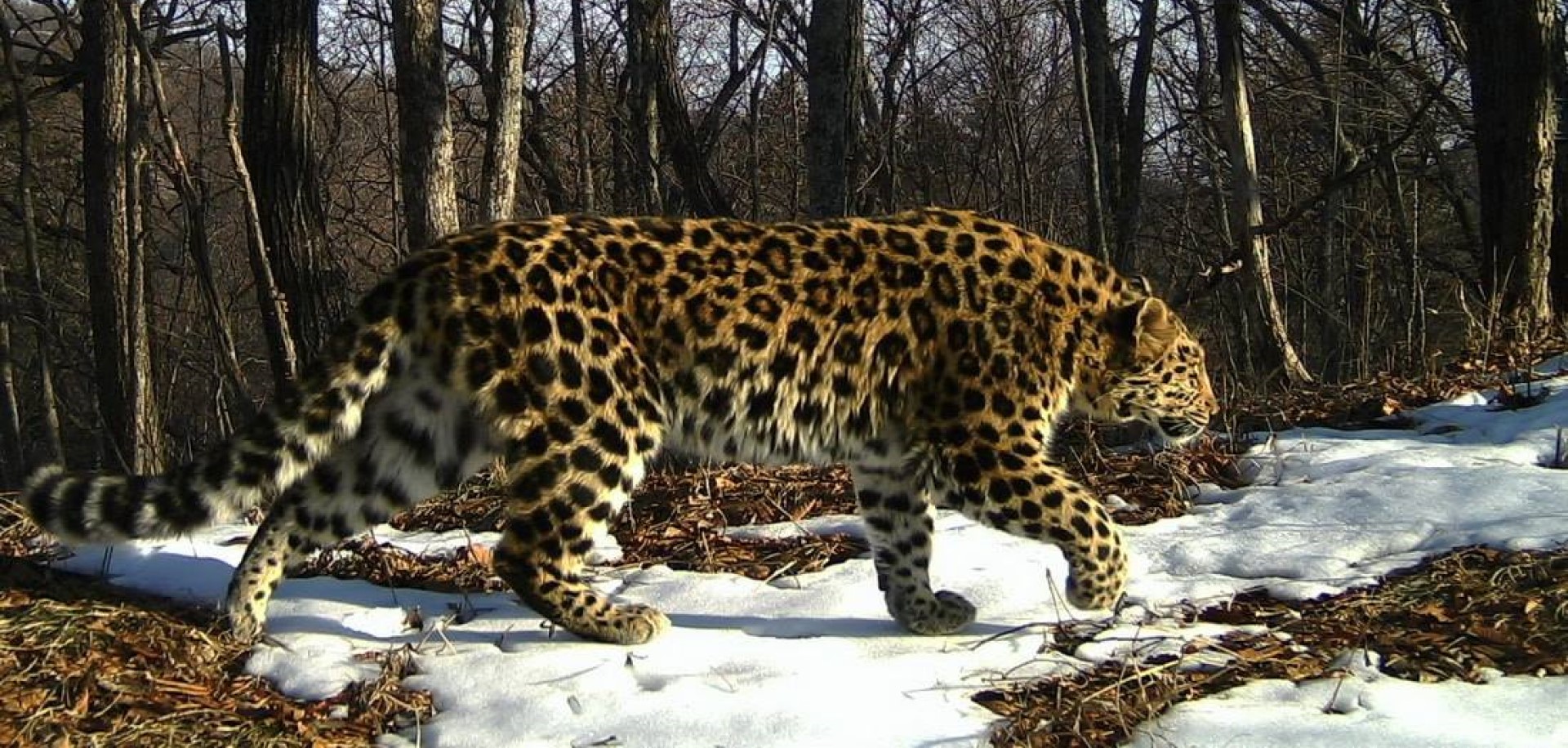


 Records from before 1930 suggest that this species of Leopard used to live near Beijing and in the mountains to the North-west. The wild population is estimated at around 110, so is one of the more endangered leopard species in the world. It is thought that this population and the Amur Leopard species were connected until just a few hundred years ago. As such, it may well be possible to boost genetic variability if that were to become necessary.
Records from before 1930 suggest that this species of Leopard used to live near Beijing and in the mountains to the North-west. The wild population is estimated at around 110, so is one of the more endangered leopard species in the world. It is thought that this population and the Amur Leopard species were connected until just a few hundred years ago. As such, it may well be possible to boost genetic variability if that were to become necessary.
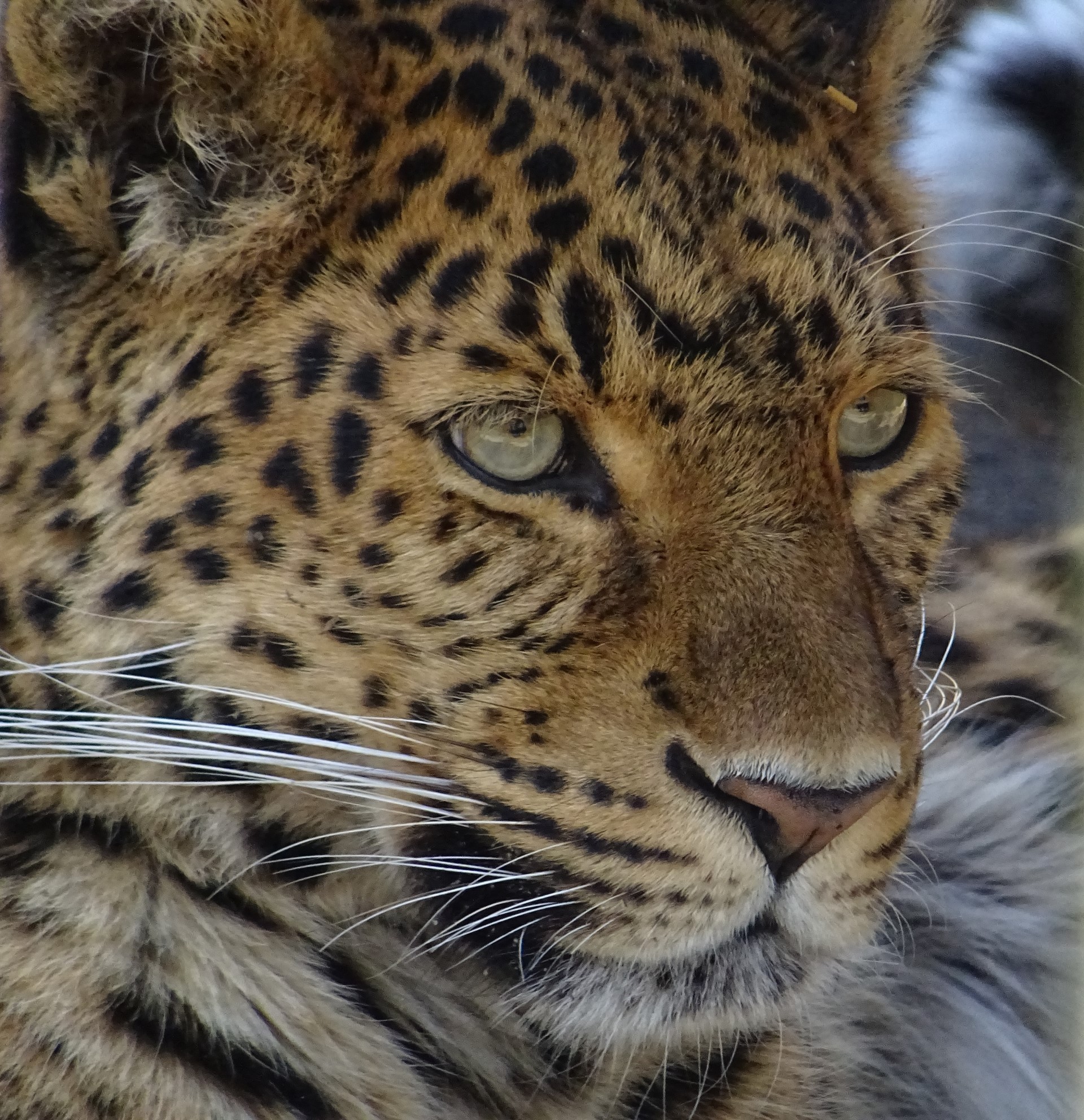
 Like many cats – both big and lesser cats, they have rare colourings. These are not separate species, instead they are either melanistic, or albino.
Like many cats – both big and lesser cats, they have rare colourings. These are not separate species, instead they are either melanistic, or albino.