Swedish Lapland, far north of sweden
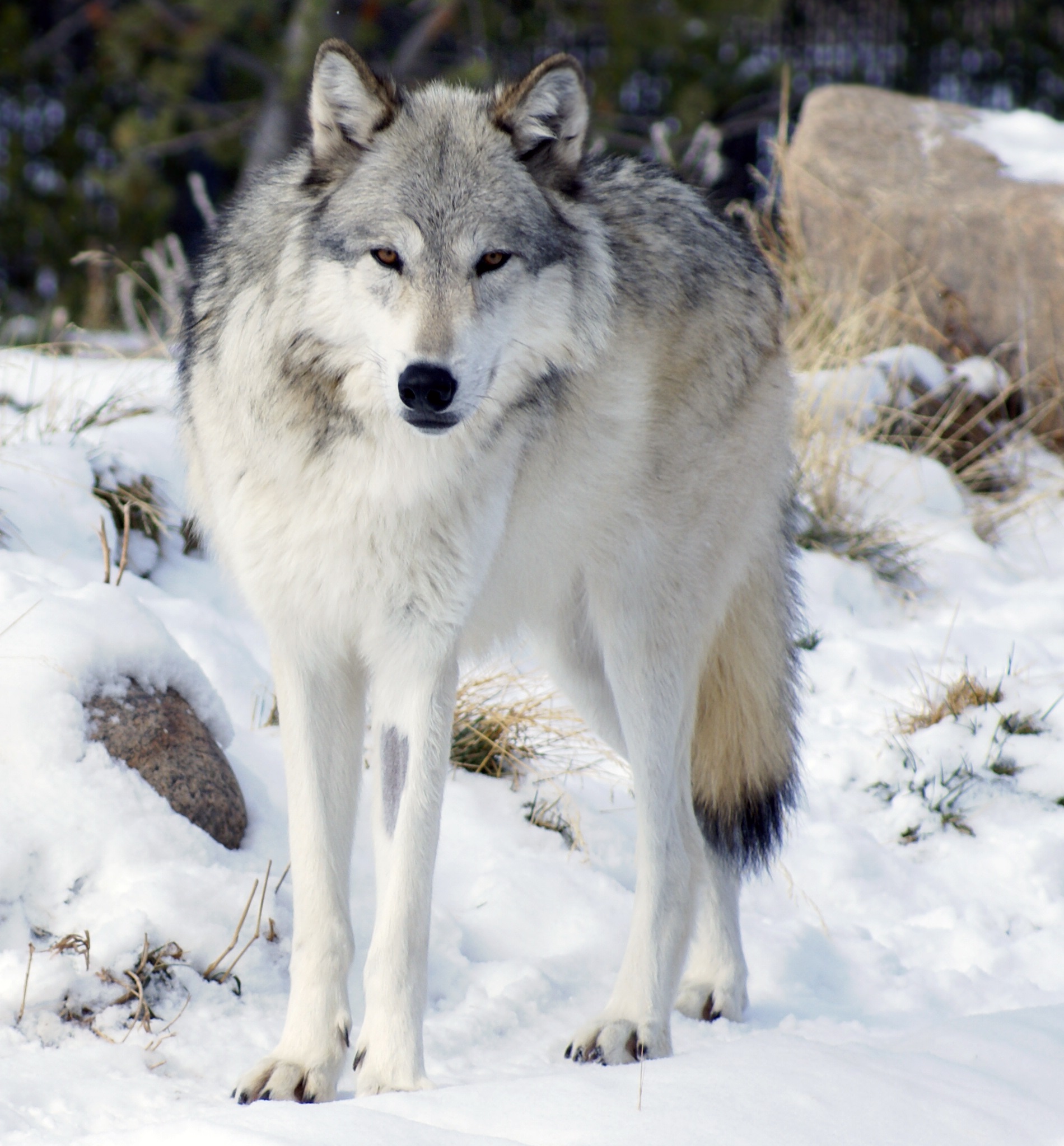
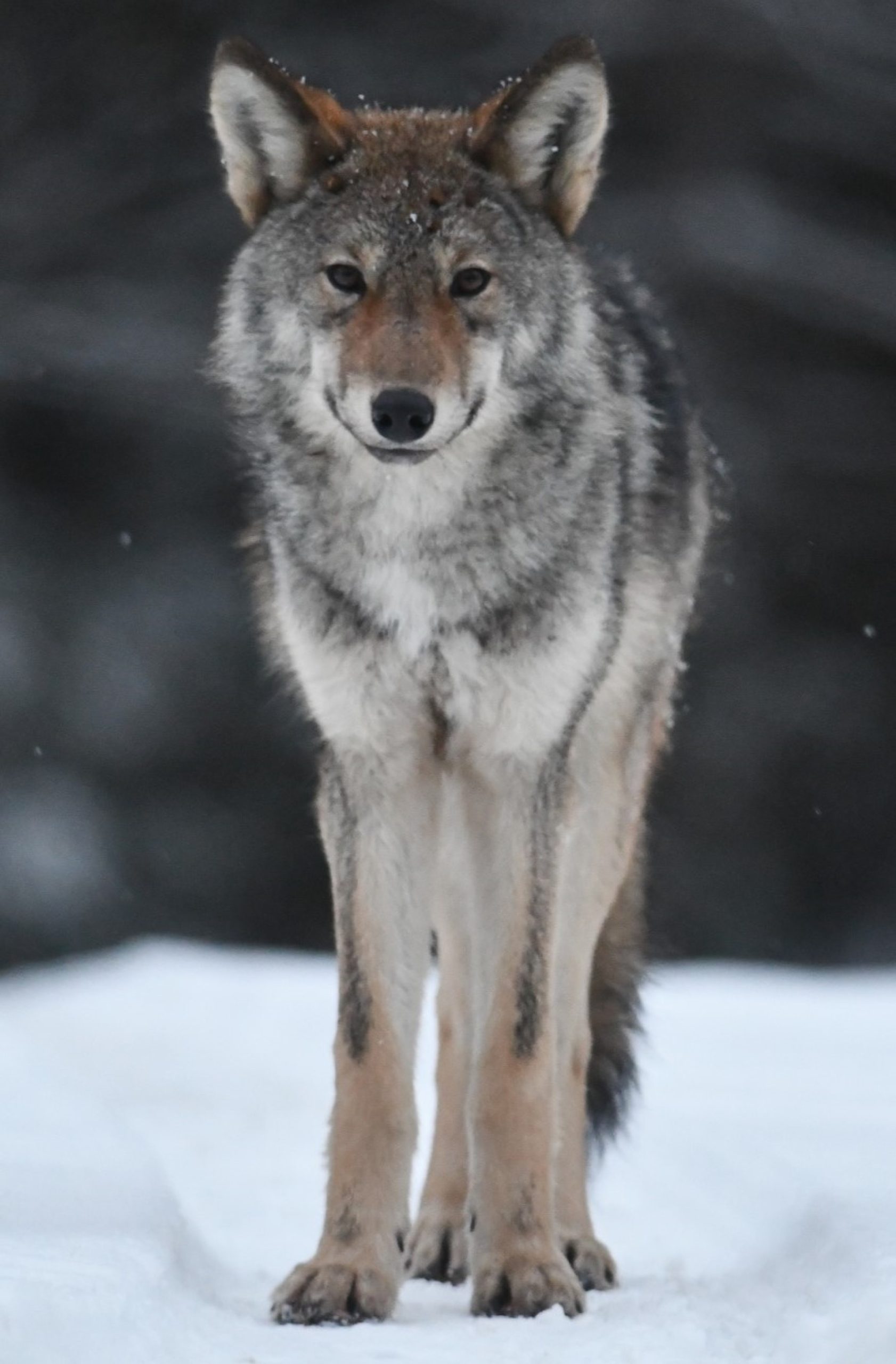
Sweden’s Lapland is a beautiful area. Lying in the far north of Sweden, like much of Sweden the land is heavily forested. Wolves are rare in Sweden, though this is as a result of over hunting – Europe has said that Sweden needs 170-270 wolves for a healthy population. Sweden is a huge country, which could support far more if they were allowed to naturally control their numbers. Being a country about the size of France, but with far fewer people, stating the country can only support 170 wolves is ridiculous. Bear numbers are higher, and there are thought to be around 2000 wolverines within its border (this was a population I was quoted if we visited).
It should be noted, that, the only difference between here and further south, is the number of wolverines – we did not get this far north, and where we were wolverines are just occasional visitors. The one difference is the reindeer presence. There are around 260,000 reindeer in Sweden, though it should be noted that these are only semi wild.
Sweden’s bear population is going up at the moment, and is currently thought to be around 2800. Generally, it takes some local knowledge to see wild bears, and your best chance is in a bear hide. We have one listed in the hides section of of this website. One of the big advantages of doing this in the northern parts of Sweden is the sunlight lasts more of the night. As bears are largely nocturnal, this allows more time to watch. When I visited the bear hide, it got to dark to see at about 2am but got light enough again at 5am.
Below is a video of the area. As you can see, while there is some wildlife, there is not a great deal. Generally you need a guide to take you out as finding the wildlife is a difficult job. We hope to be adding plenty of links below.
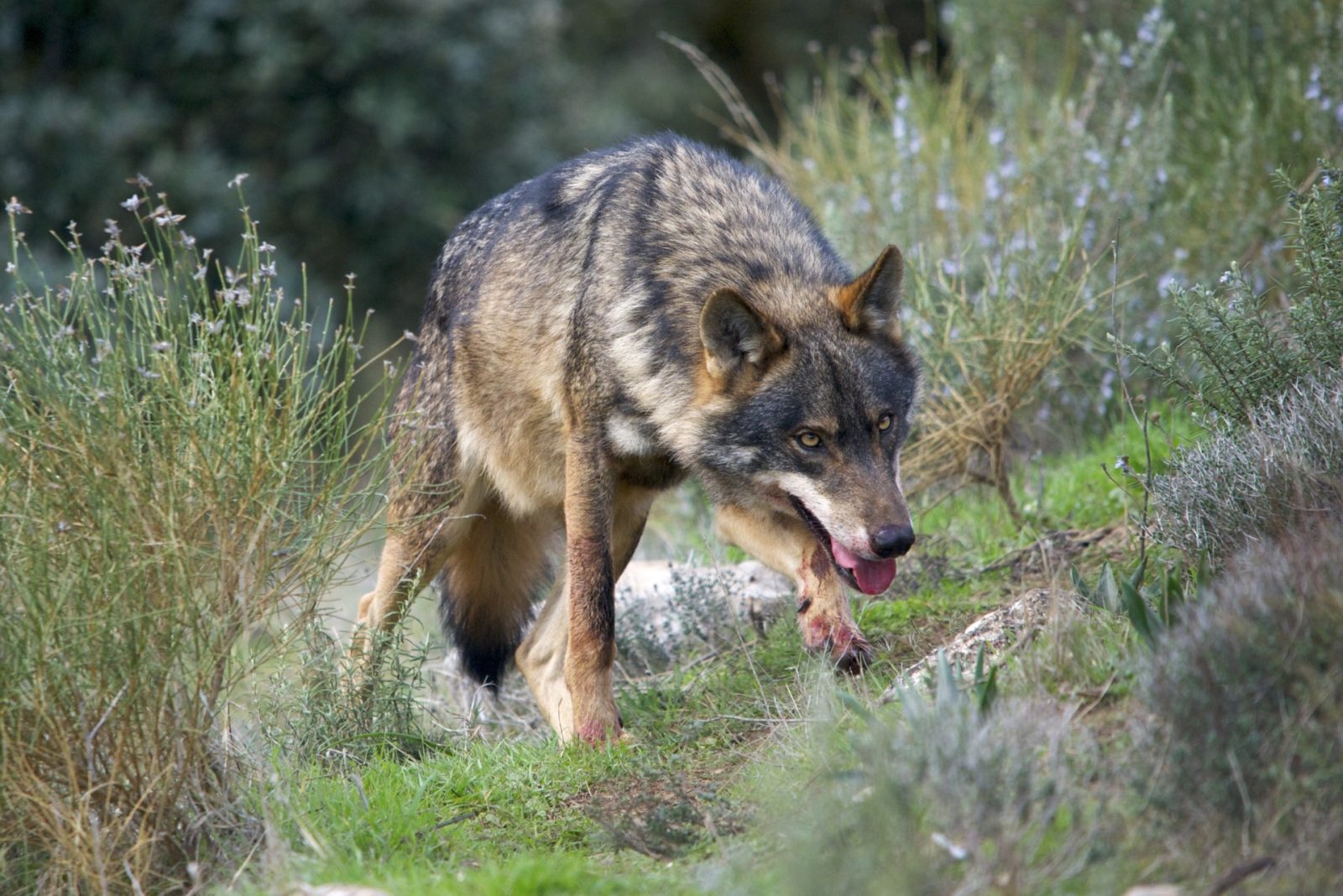





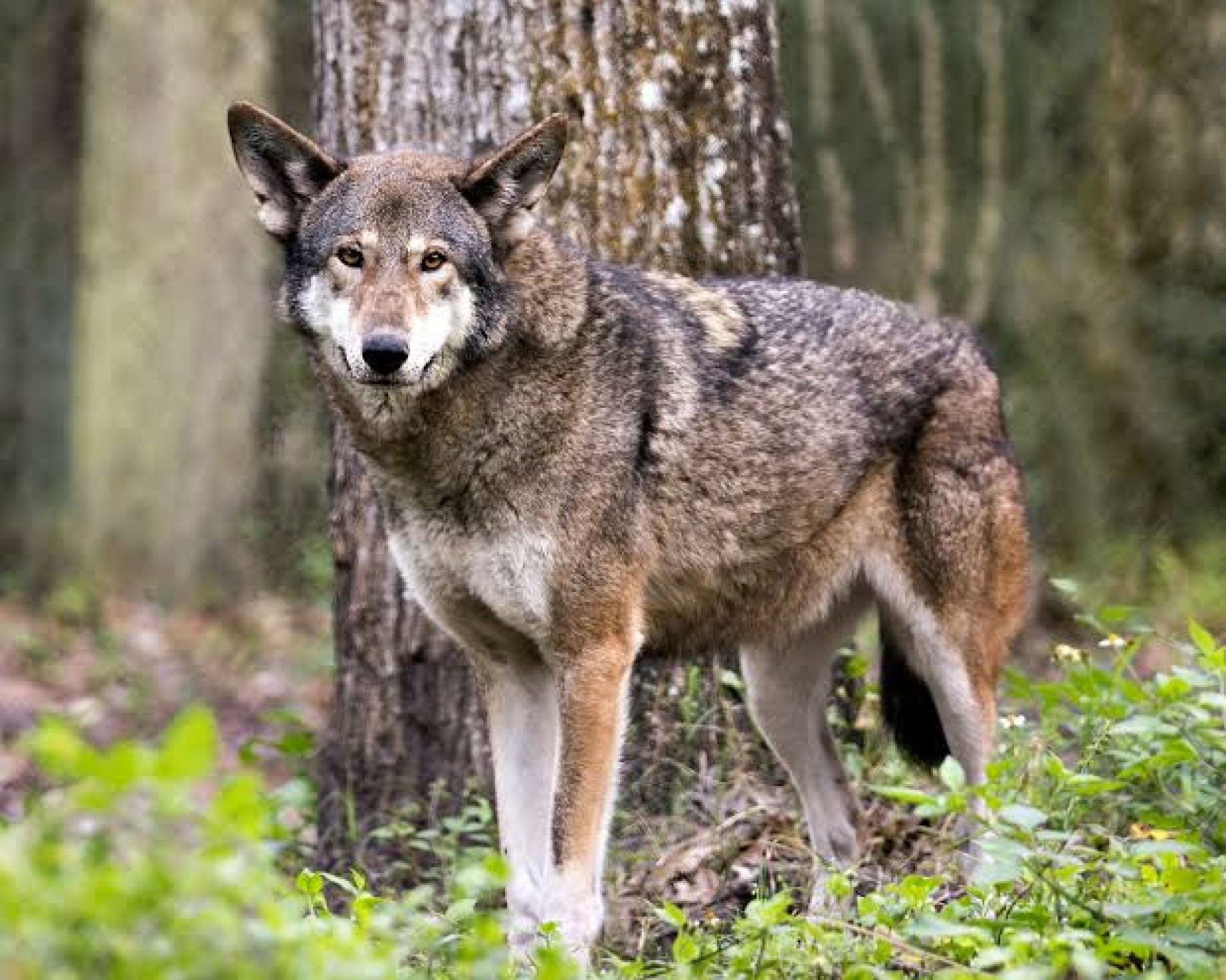
 The Iberian wolf is a subspecies of the grey wolf found on the Iberian peninsular. It reached its minimum in the 1970s with 500-700 iindividuals living in the wild. Until the middle of the 19th century, it was widespread, throughout the Iberian peninsular. It should be noted, that wolves have never had high densities, and the wolves of western Europe are not thought to have ever had a population much above 848–26 774 (depending on which end of the estimate you rely – but is the founding population of both the Iberian and Apennine population).
The Iberian wolf is a subspecies of the grey wolf found on the Iberian peninsular. It reached its minimum in the 1970s with 500-700 iindividuals living in the wild. Until the middle of the 19th century, it was widespread, throughout the Iberian peninsular. It should be noted, that wolves have never had high densities, and the wolves of western Europe are not thought to have ever had a population much above 848–26 774 (depending on which end of the estimate you rely – but is the founding population of both the Iberian and Apennine population).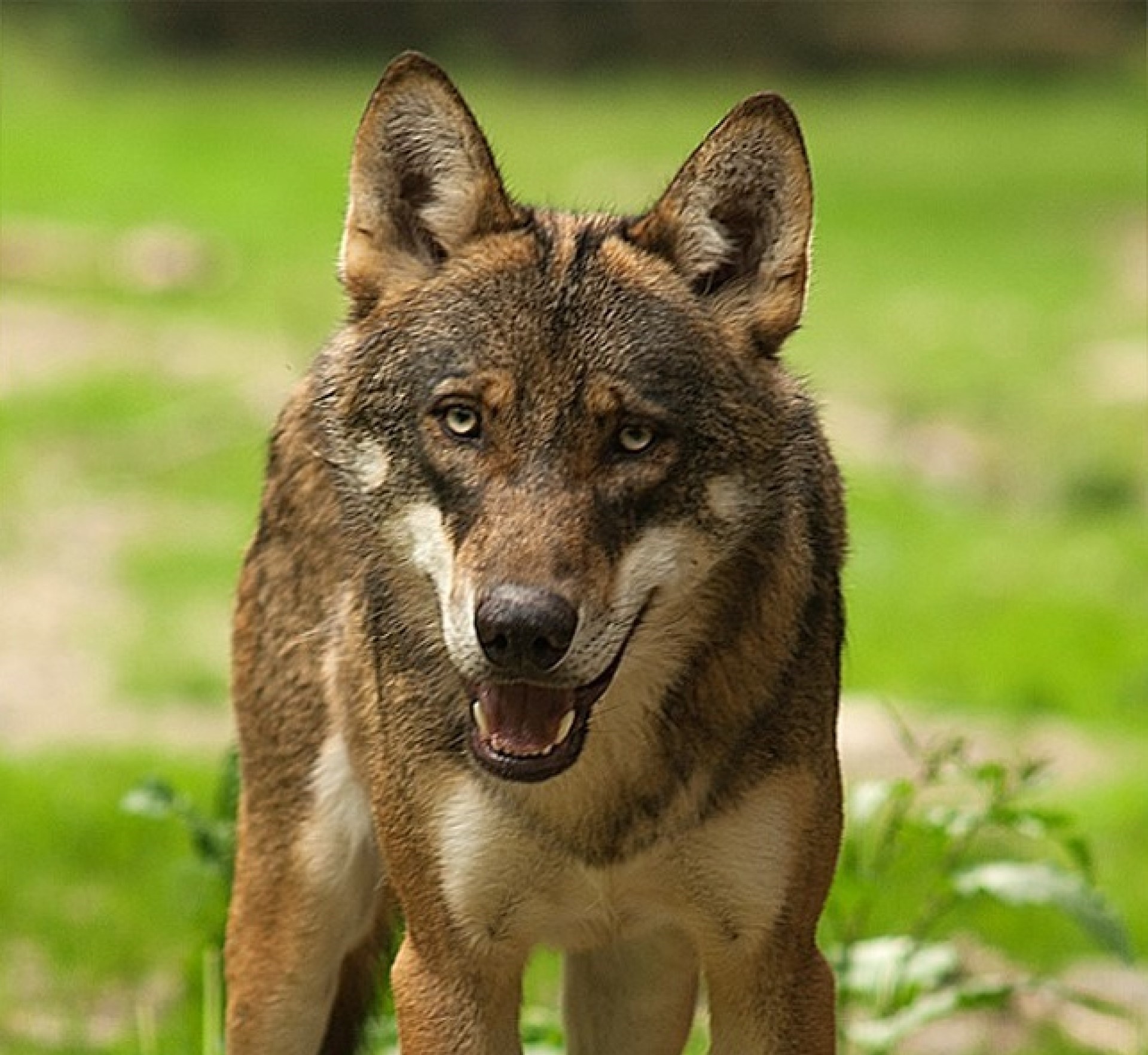
 The Apennine wolf is also known as the Italian wolf. Back in the 1970s the population reached its minimum, where the population reached 70-100 individuals. It has recovered well since then, with an Italian population of roughly 3300. However, since the early 1990s, this subspecies has been gradually moving into France. As such, at the end of 2022 the number was estimated at 1104 wolves in France.
The Apennine wolf is also known as the Italian wolf. Back in the 1970s the population reached its minimum, where the population reached 70-100 individuals. It has recovered well since then, with an Italian population of roughly 3300. However, since the early 1990s, this subspecies has been gradually moving into France. As such, at the end of 2022 the number was estimated at 1104 wolves in France.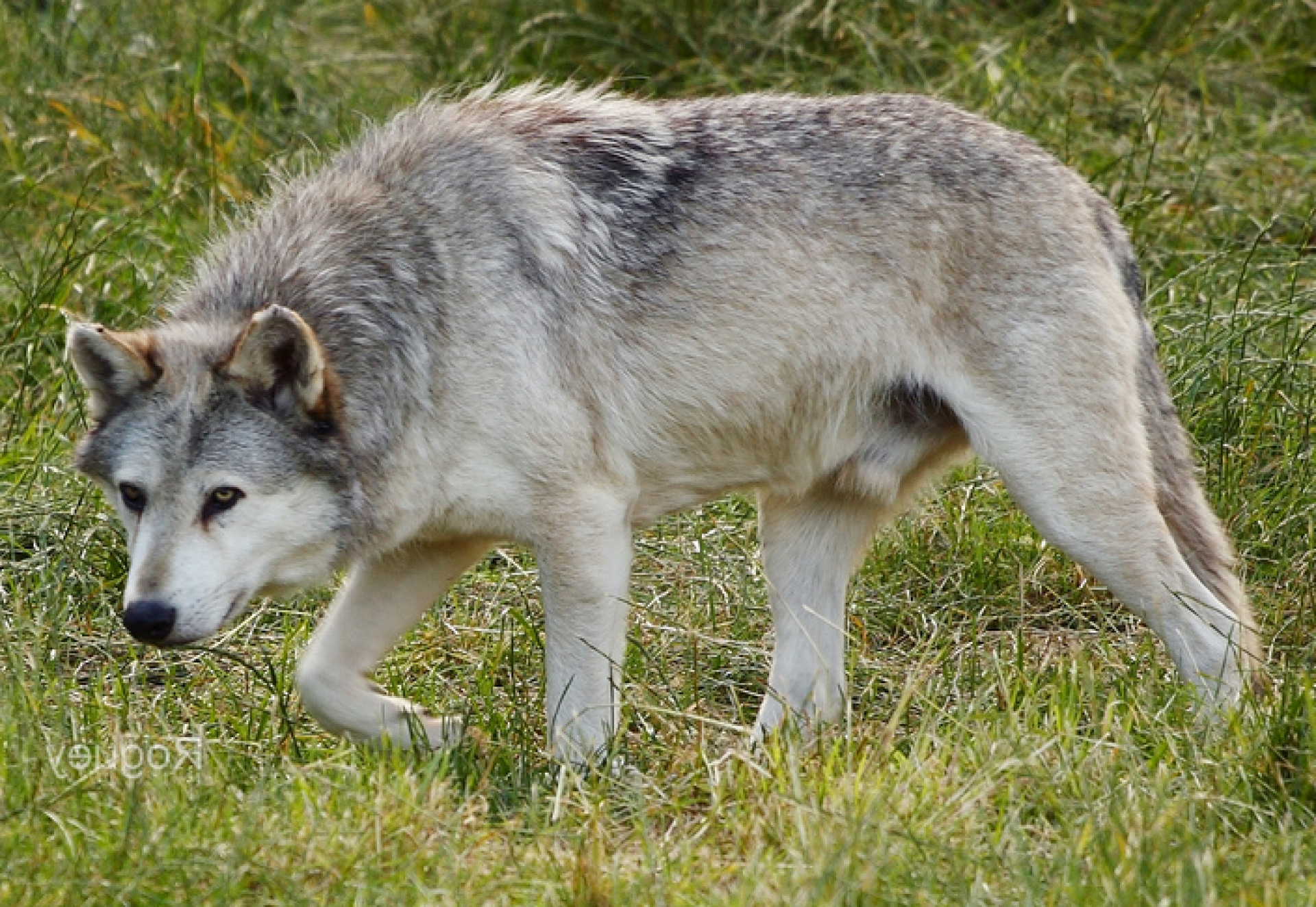
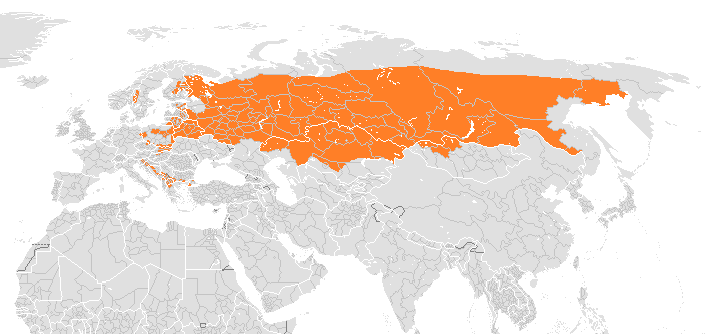 The Eurasian wolf (often referred to as the Russian wolf), is the subspecies which runs down the east coast of the Adriatic sea, as well as the majority of
The Eurasian wolf (often referred to as the Russian wolf), is the subspecies which runs down the east coast of the Adriatic sea, as well as the majority of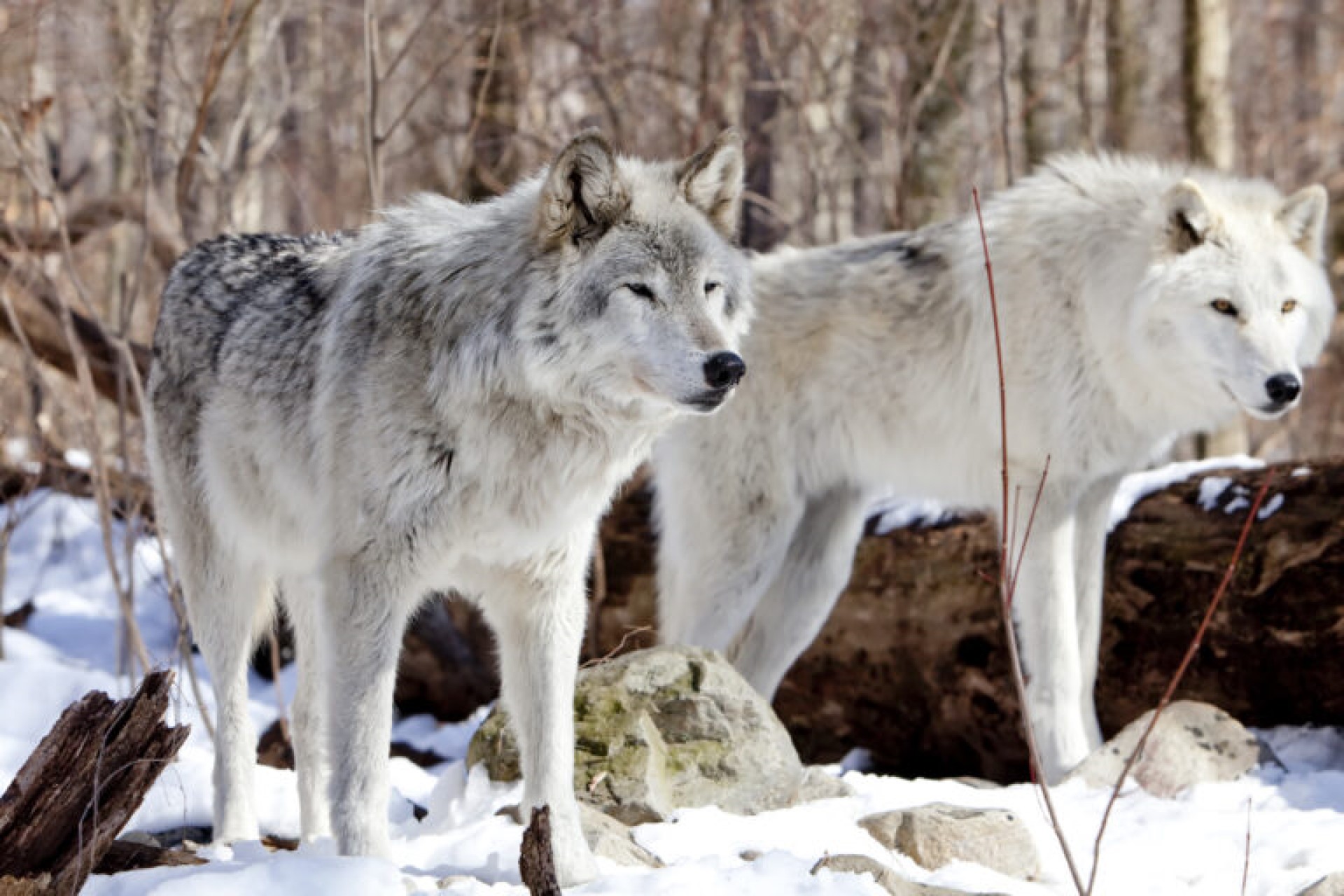 
 The Tundra wolf – Canis lupus Albus is the Eurasian equivalent of the Arctic wolf. Also known as the Turukhan wolf, it is native to Eurasia’s tundra and forest-tundra zones from Finland to the Kamchatka Peninsula. It was first described in 1792 by Robert Kerr.
The Tundra wolf – Canis lupus Albus is the Eurasian equivalent of the Arctic wolf. Also known as the Turukhan wolf, it is native to Eurasia’s tundra and forest-tundra zones from Finland to the Kamchatka Peninsula. It was first described in 1792 by Robert Kerr.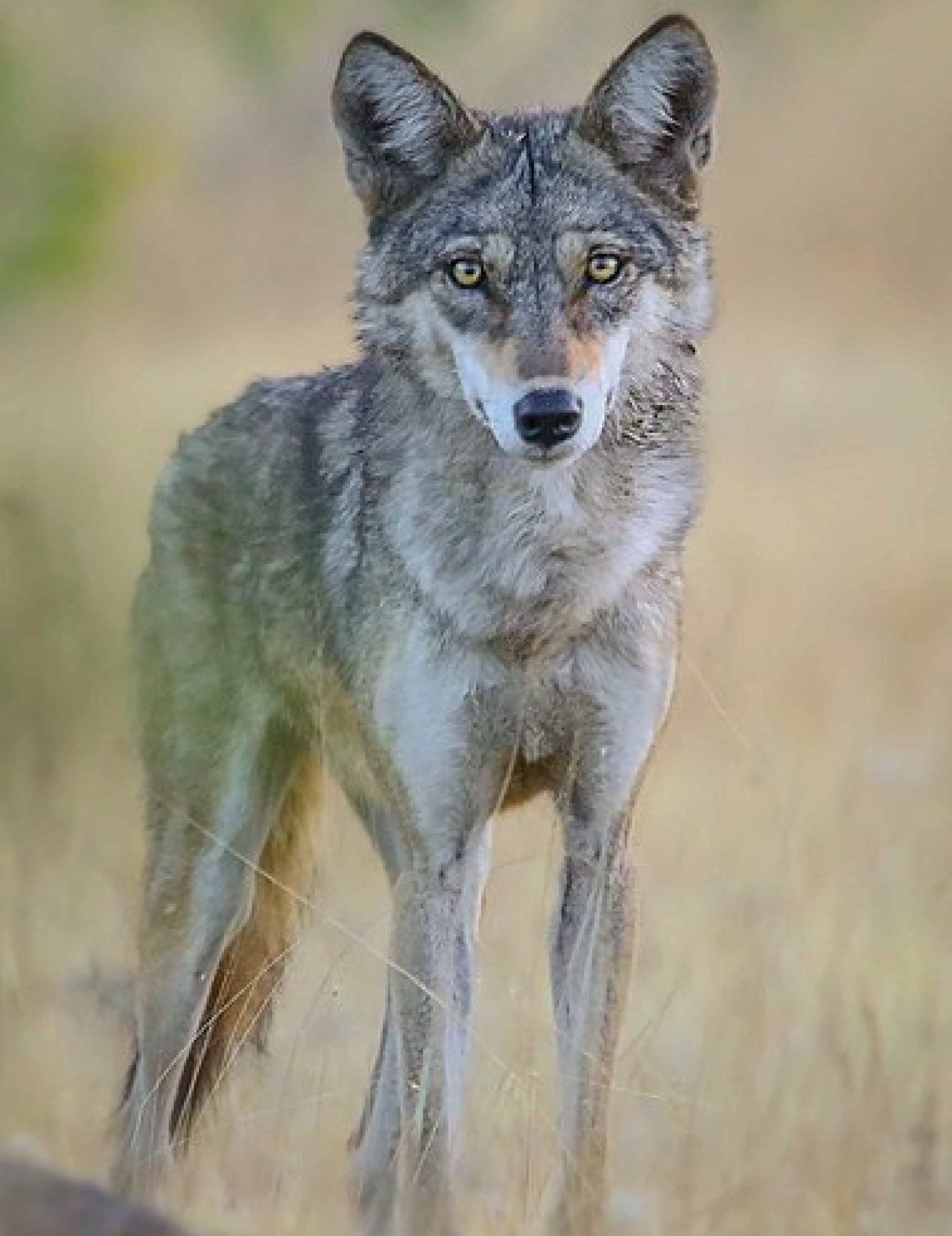
 The Indian wolf is one of the more well known, partly as their starring role in the Jungle book by Rudyard Kipling. I do remember my great grandmother talking about seeing 4 wolves running in the distance. It is thought to have 2000-3000 individuals left in the wild, though given its former large range, this does not appear very high. It should not be surprising, therefore, to hear that this is considered as one of the most endangered subspecies of the grey wolf – it officially has the conservation status of endangered – now it is considered endangered, and people talk about it at high risk, but it should be remembered that there are still 2000-3000, which is a pretty high number for a species considered more than just endangered.
The Indian wolf is one of the more well known, partly as their starring role in the Jungle book by Rudyard Kipling. I do remember my great grandmother talking about seeing 4 wolves running in the distance. It is thought to have 2000-3000 individuals left in the wild, though given its former large range, this does not appear very high. It should not be surprising, therefore, to hear that this is considered as one of the most endangered subspecies of the grey wolf – it officially has the conservation status of endangered – now it is considered endangered, and people talk about it at high risk, but it should be remembered that there are still 2000-3000, which is a pretty high number for a species considered more than just endangered.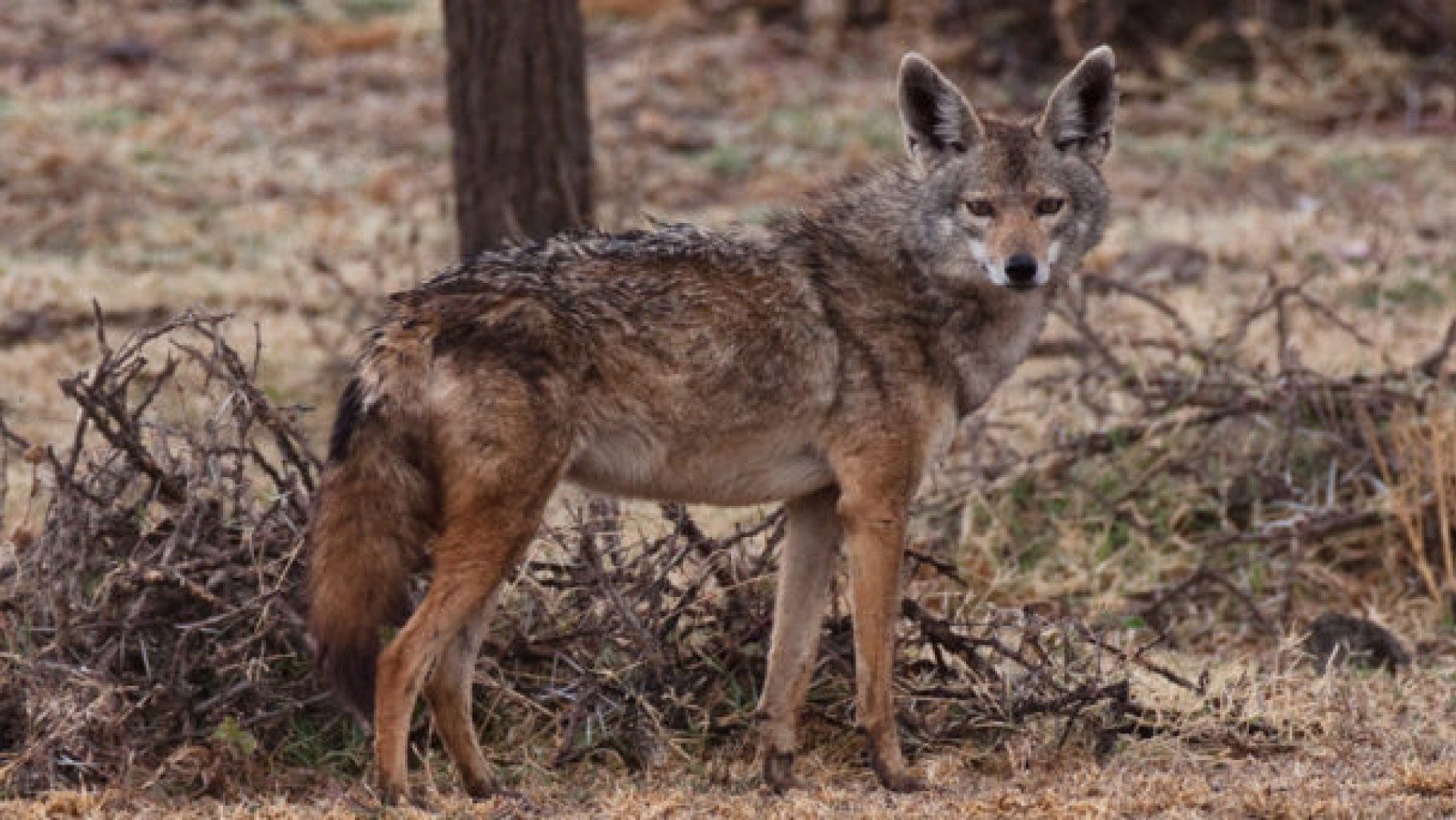
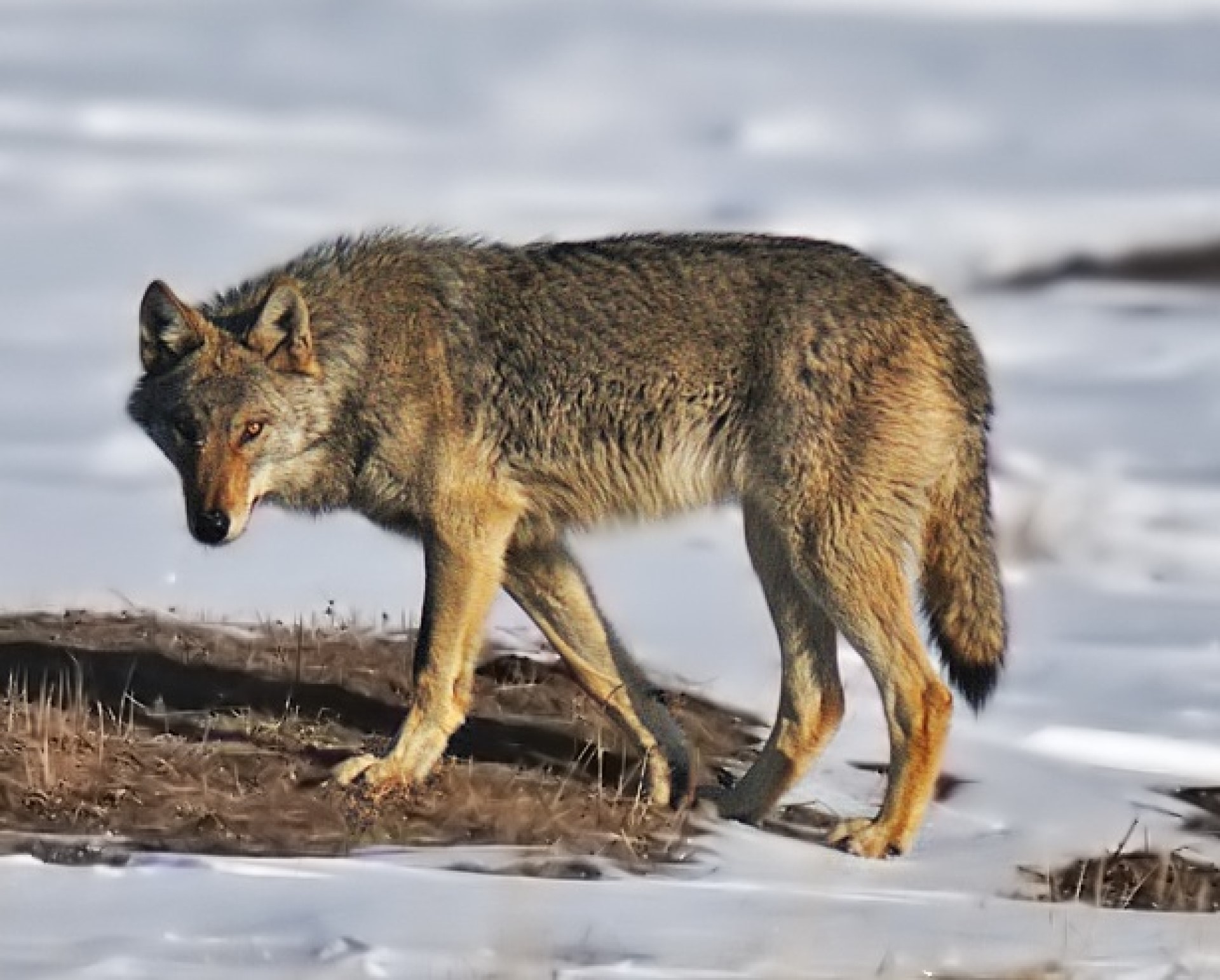

 The Steppe wolf also known as the Caspian sea wolf is a wolf subspecies that is found in the region around the Caspian sea, though the Steppe wolf is perhaps more useful a name as it extends far from the Caspian sea. Much of its range is in
The Steppe wolf also known as the Caspian sea wolf is a wolf subspecies that is found in the region around the Caspian sea, though the Steppe wolf is perhaps more useful a name as it extends far from the Caspian sea. Much of its range is in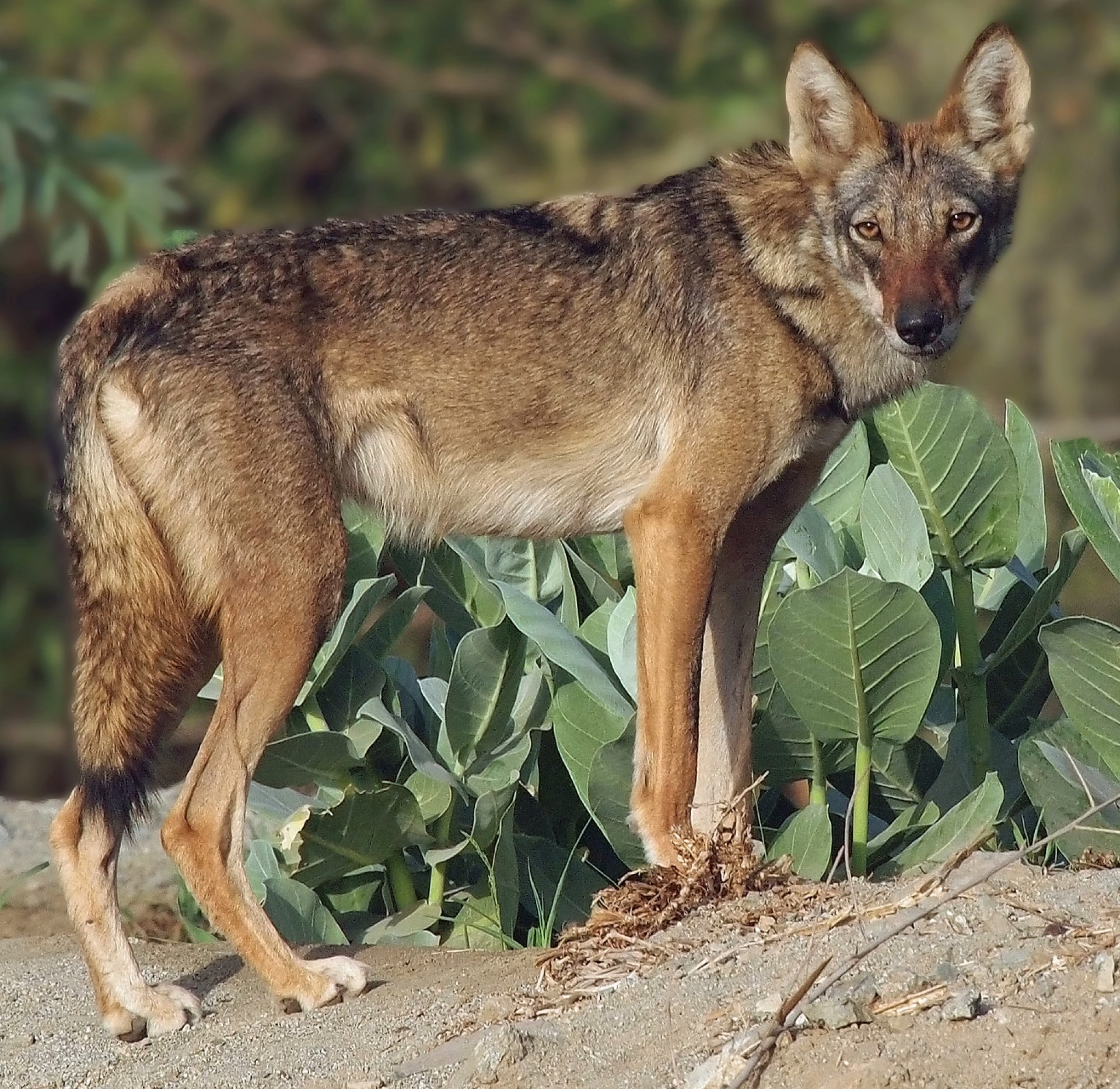 
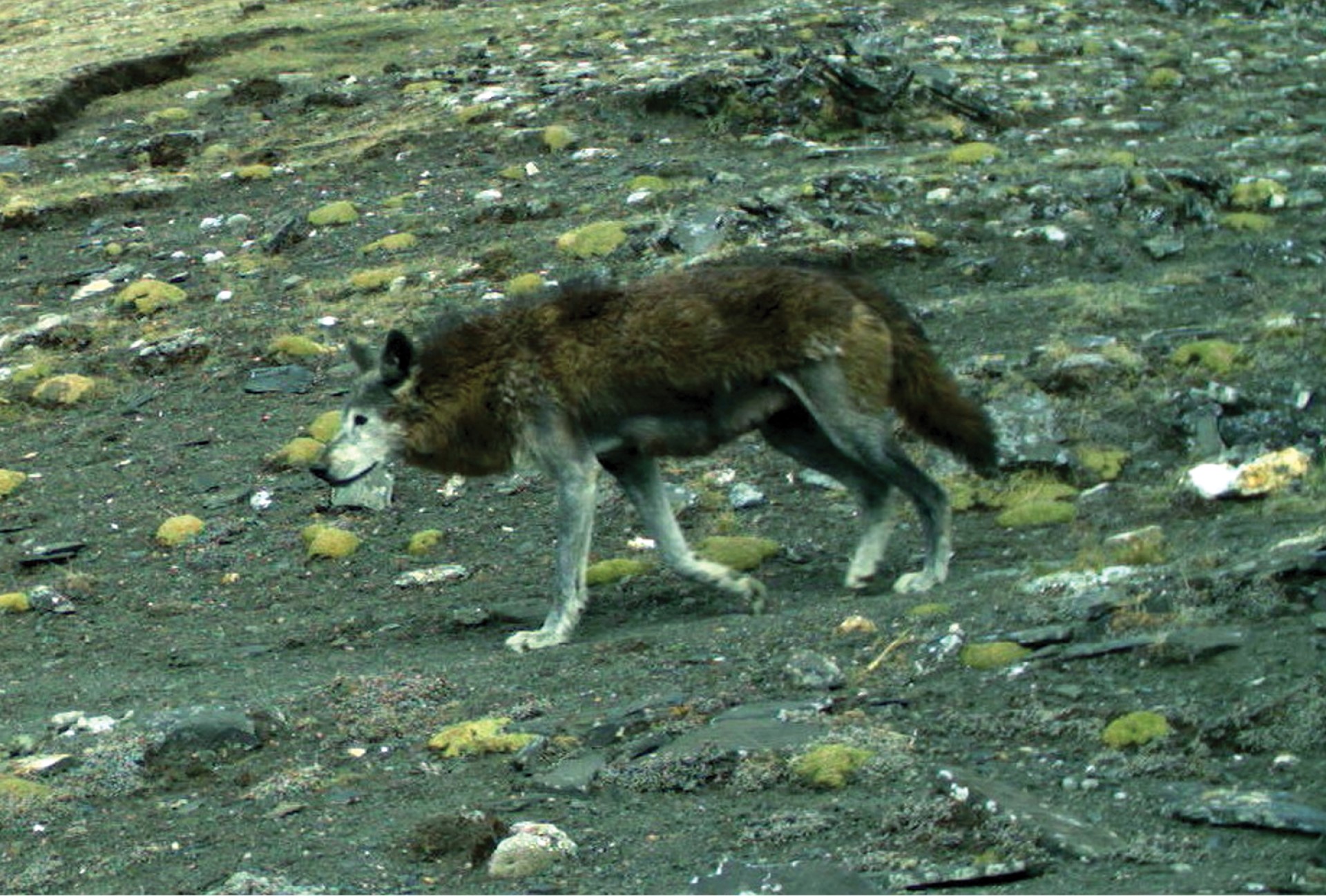
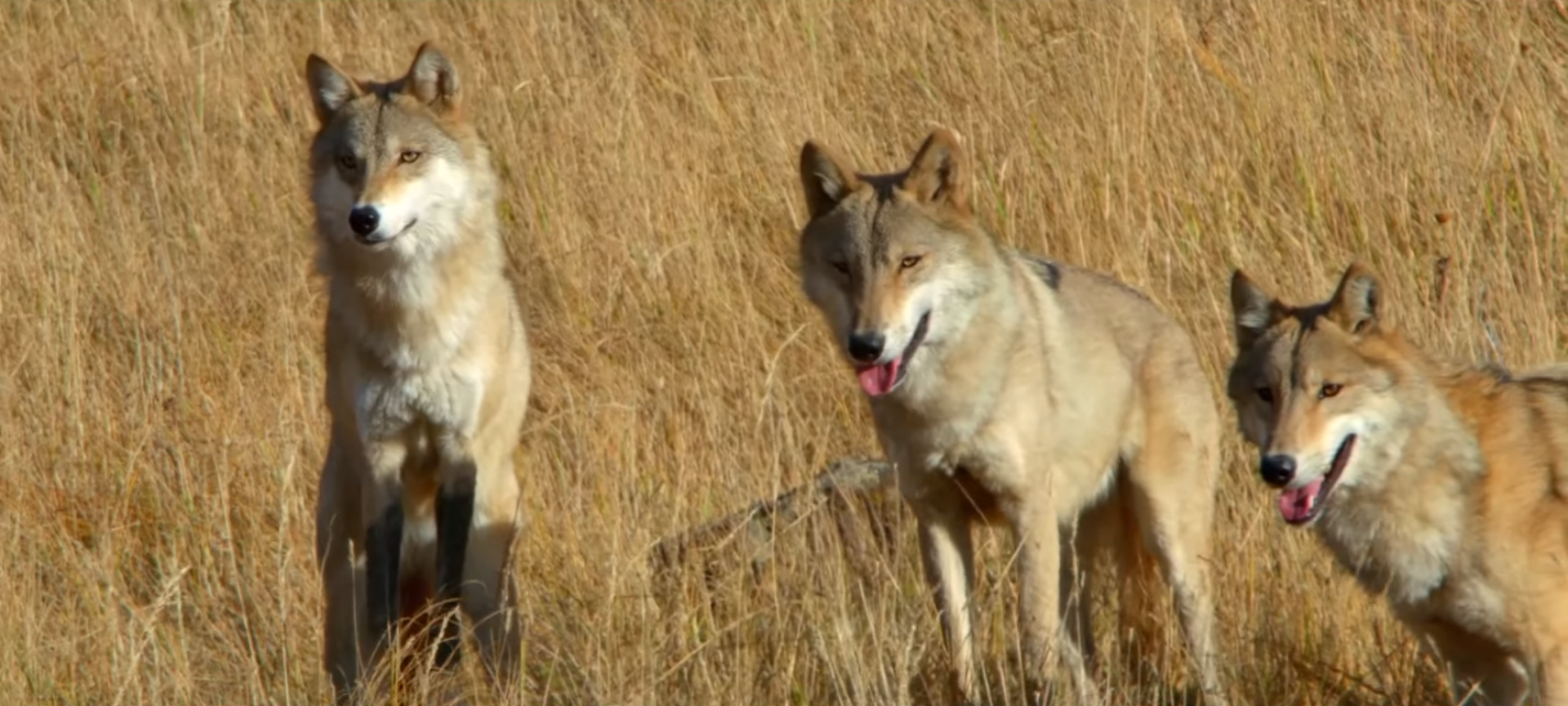
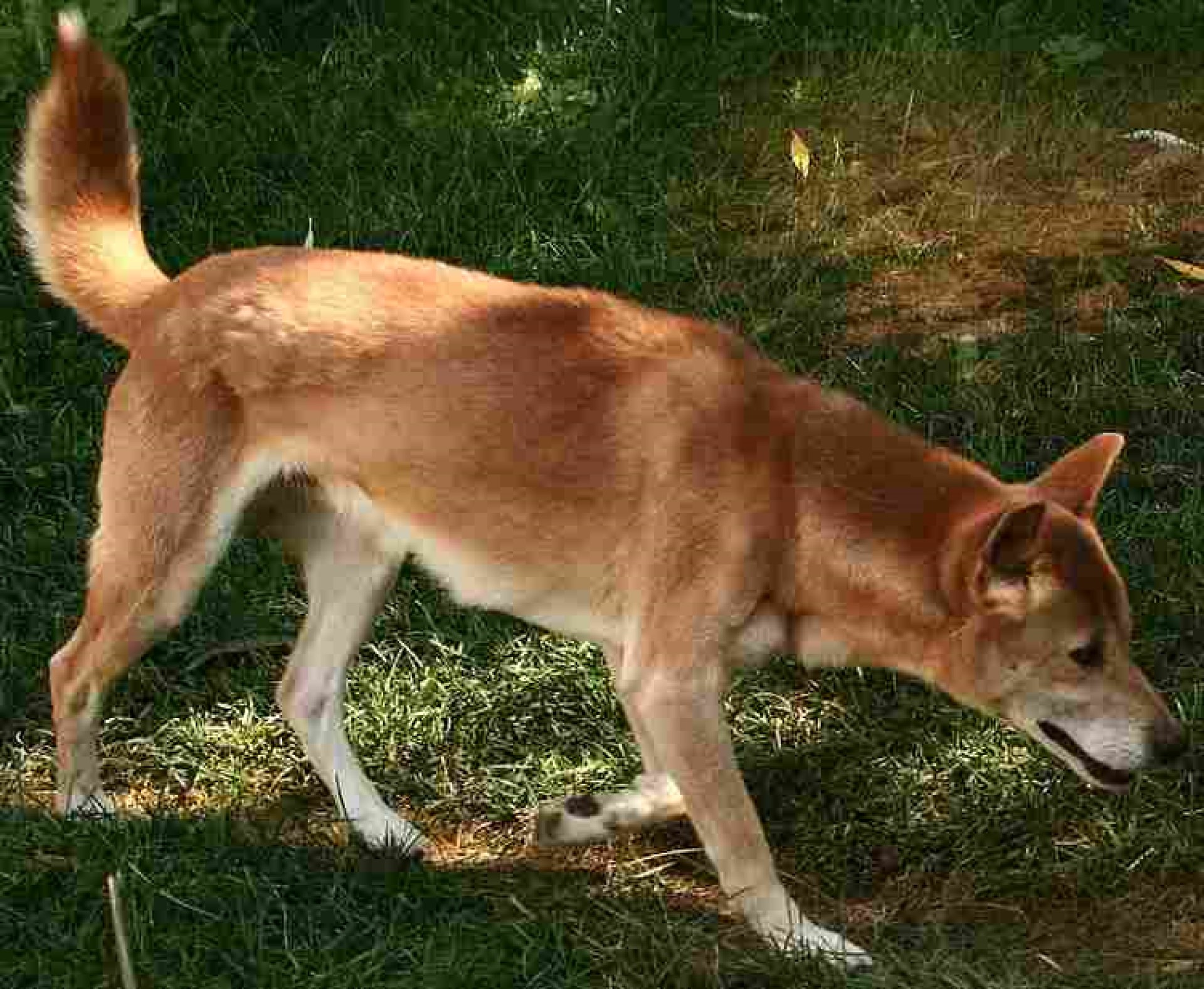
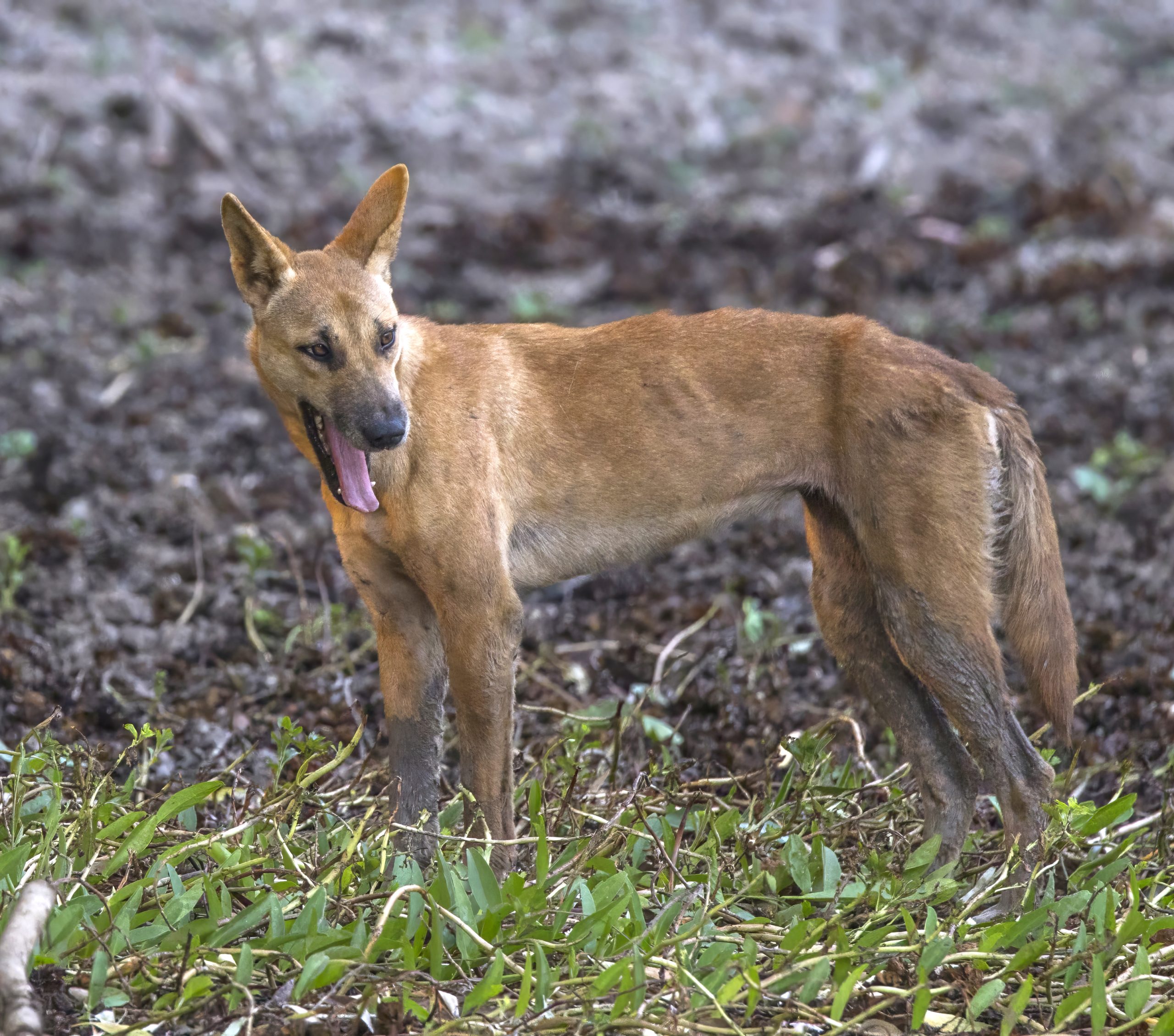





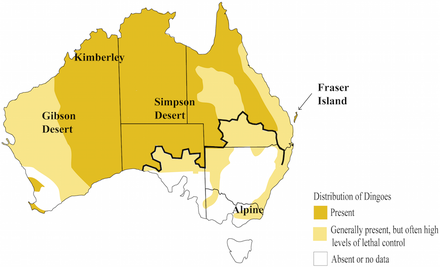 Closely related to the new Guinea singing dog, the Dingo is a dog species that has a relatively wide range. There is some debate about how it got to some of its homes, and whether it may have come alongside early humans.
Closely related to the new Guinea singing dog, the Dingo is a dog species that has a relatively wide range. There is some debate about how it got to some of its homes, and whether it may have come alongside early humans.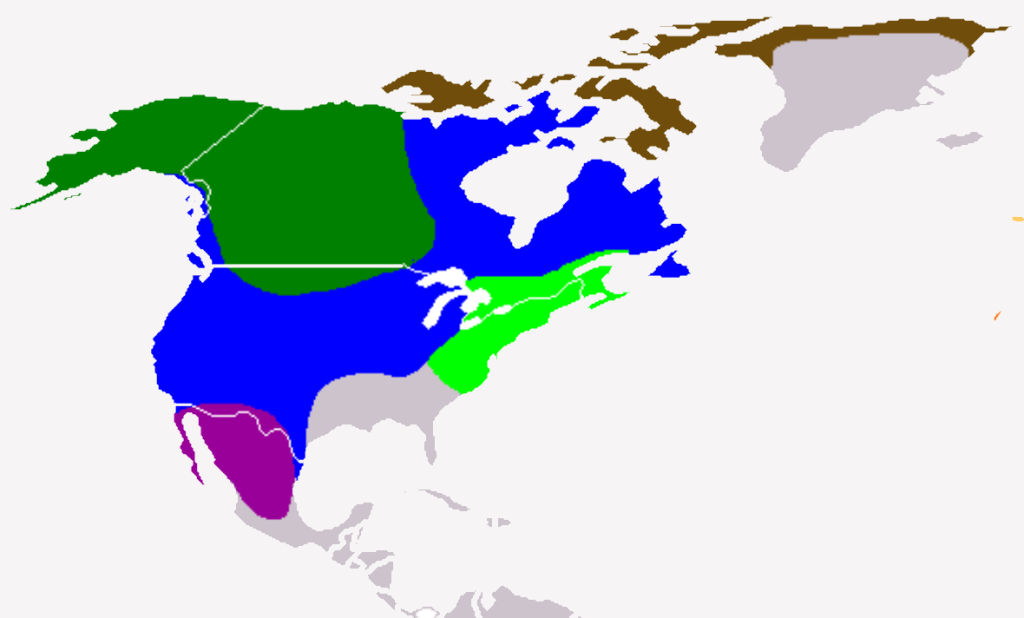
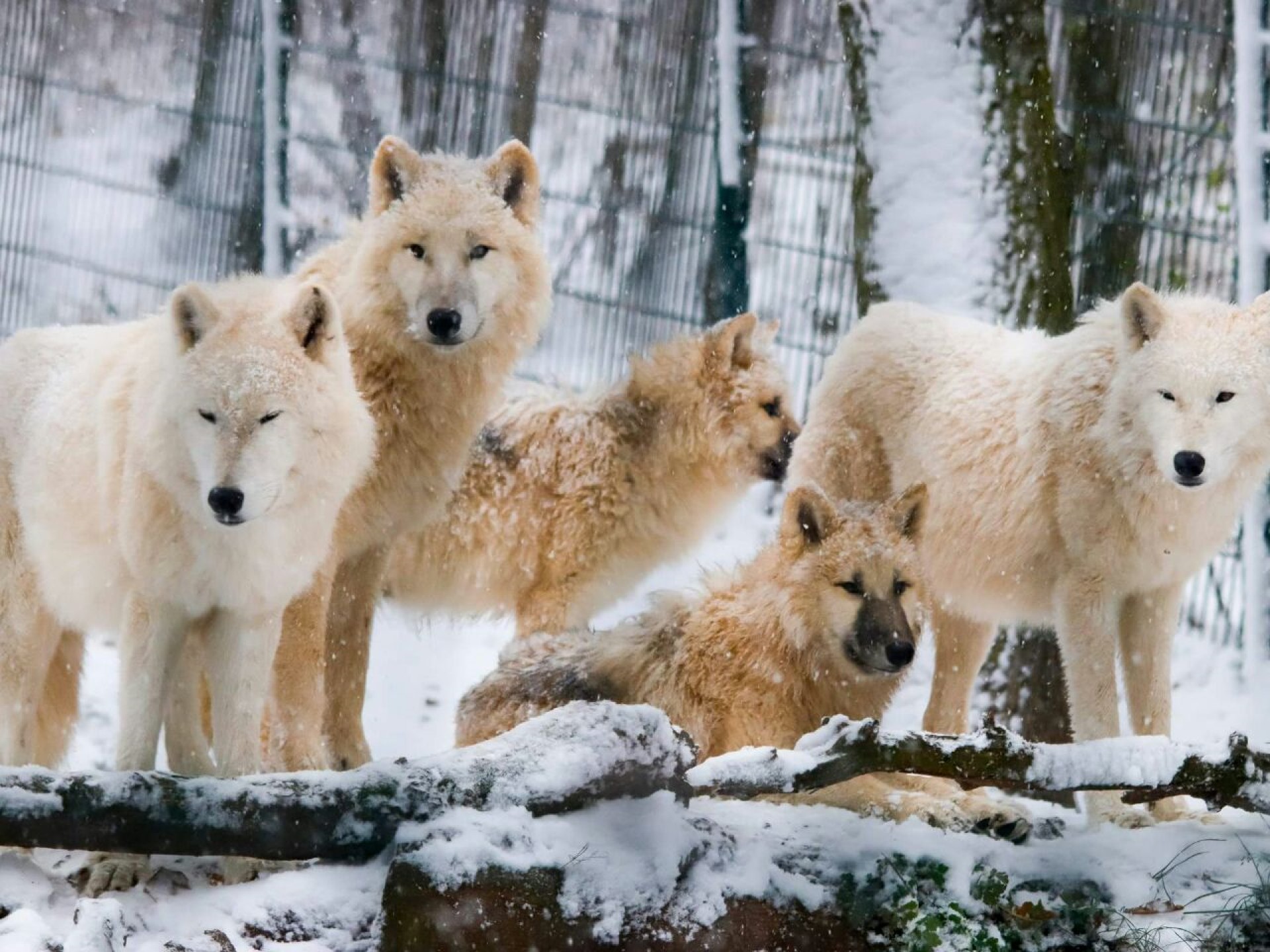
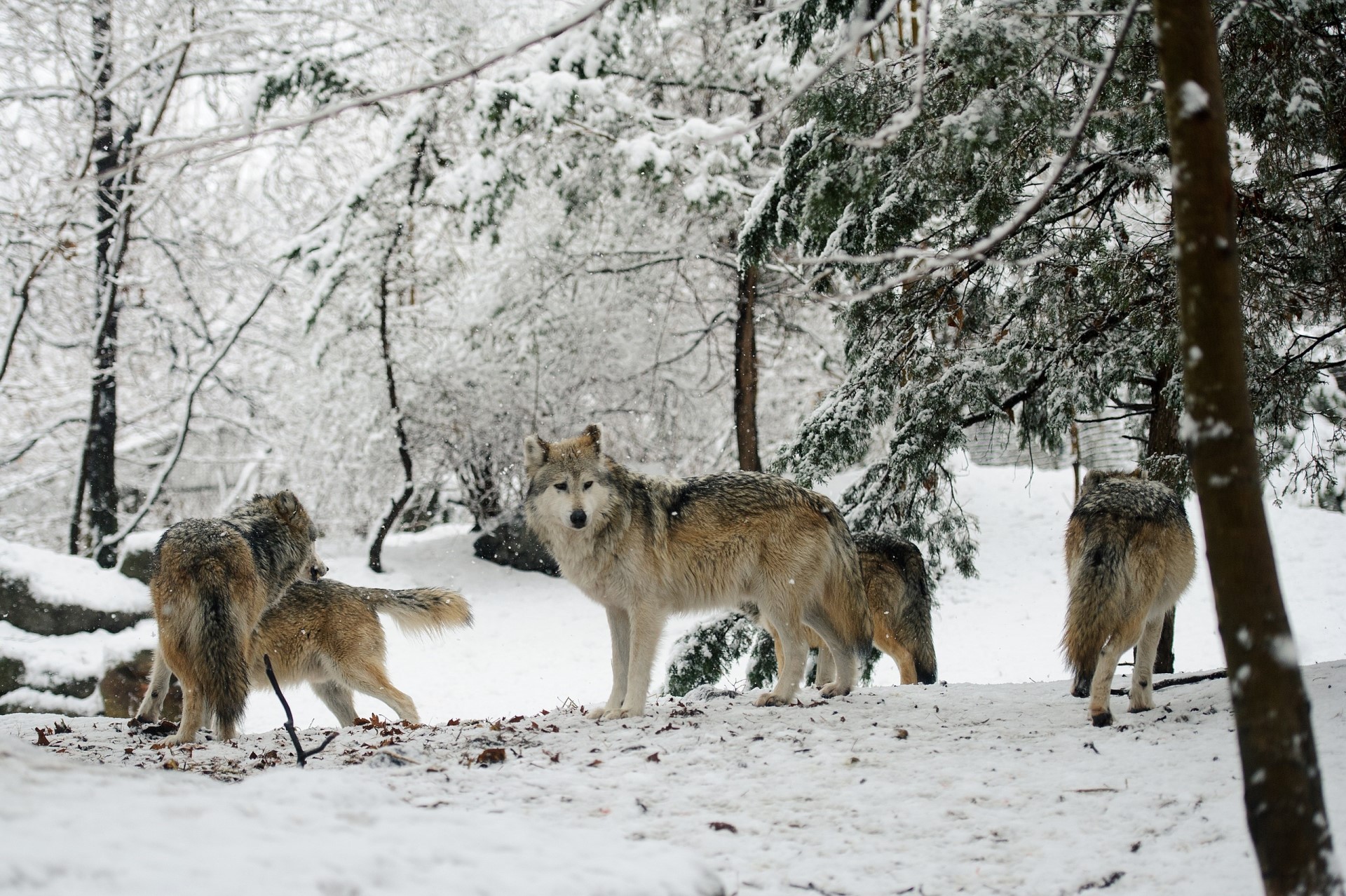


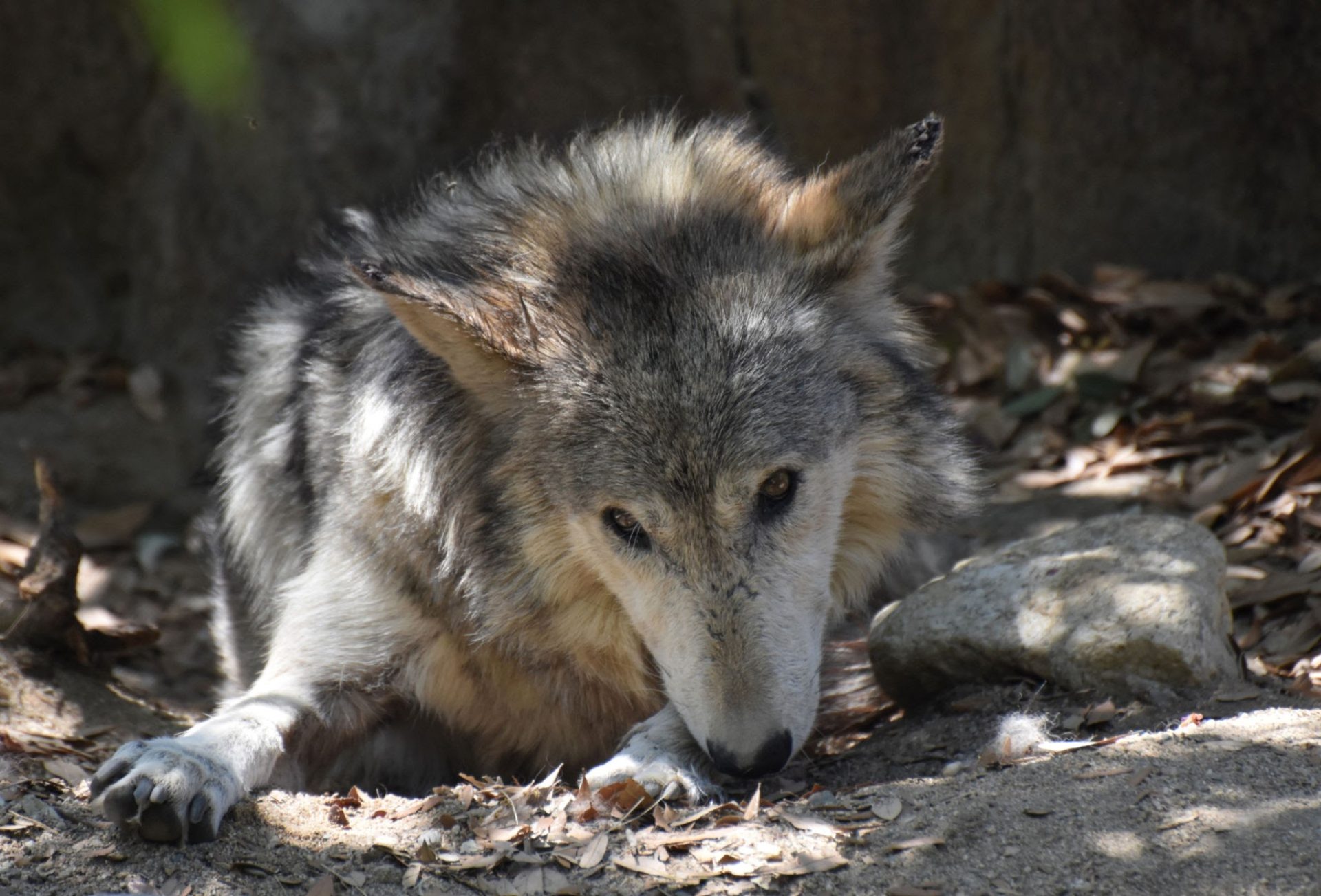
 Mexican wolves (scientific name is Canis lupus baileyi) are currently only found in a small area as seen on the map to the right. It is a fantastic improvement on the situation around 1970 when the species was extinct in the wild. The first reintroduction was carried out in 1998. Unfortunately, founded by just 7 individuals, the population is highly inbred. Never-the-less, currently, the
Mexican wolves (scientific name is Canis lupus baileyi) are currently only found in a small area as seen on the map to the right. It is a fantastic improvement on the situation around 1970 when the species was extinct in the wild. The first reintroduction was carried out in 1998. Unfortunately, founded by just 7 individuals, the population is highly inbred. Never-the-less, currently, the