
There are many species around the world which are so important to their habitat, that even a reduction in the population can cause problems – this is one of them. After tadpoles have lost their tails, many will climb onto the hairy back of the water buffalo, getting a ride to other rich feeding areas (and the buffalo gets any irritating flies eaten). There can be as many as 20 frogs on each water buffalo.
Water buffalo were first domesticated 3000 years ago, in Asia, but have proved to be so useful, there are now 200 million spread across 77 countries, on 5 continents. Initially considered as useful animals for plough and similar farm work, in recent times, it has been recognized for its ecosystem engineer duties.
Thriving in wetlands, they can force their way through places that other herbivores fail. While they are not native to many of their current homes, they are capable of filling ecological niches that have long been empty after the initial large cattle like animals were killed off, or all taken into captivity. It should be noted, that in some places, like Australia, there are few to no predators, to control such a large animal, which has lead to a population of 200,000. There is a native water buffalo (Anatolian).
A variety of characteristics help this species to easily fill the ecological niche of the European water buffalo (lost around 10,000 years ago). From transporting seeds in their fur, they fill in many of the roles that the extinct European water buffalo did in the long past. Even in places like the UK, which is one of the most nature depleted countries, the water buffalo are replacing long extinct species, and recovering ecosystems as a result.
This sort of behaviour has to be carefully managed, as in many places, introducing a closely related species can be very costly. In the UK, the grey squirrel has decimated the population of the native red squirrel, and this is not an isolated example, with many others from around the world. However, so long as their effect is closely managed, and there is not a closer relation to the missing species, the impact is likely to be a net positive. Over the last 50 years, 1/3 of the worlds wetlands have been lost, these species, when carefully managed, are likely to be able to bring some of this back.
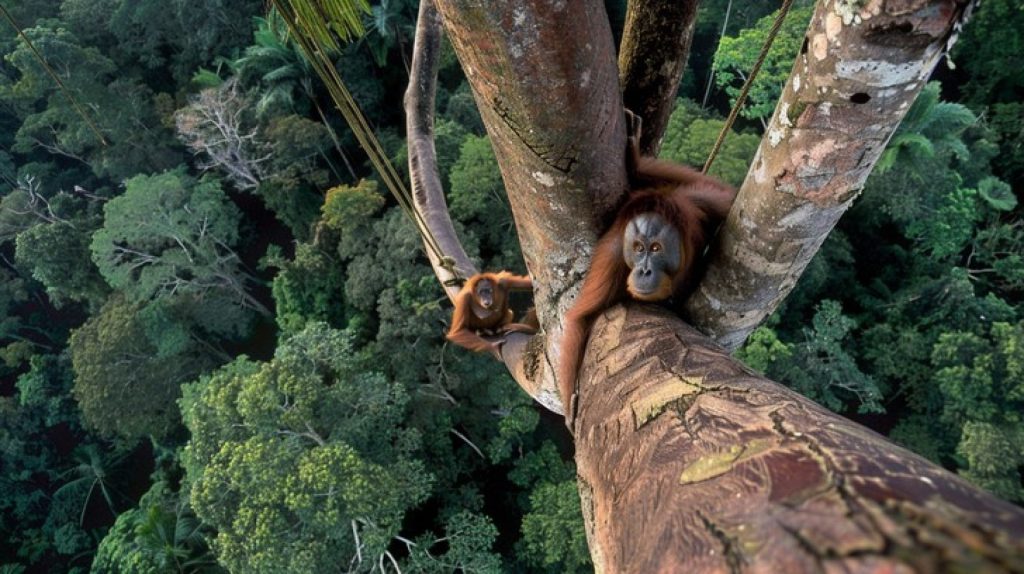
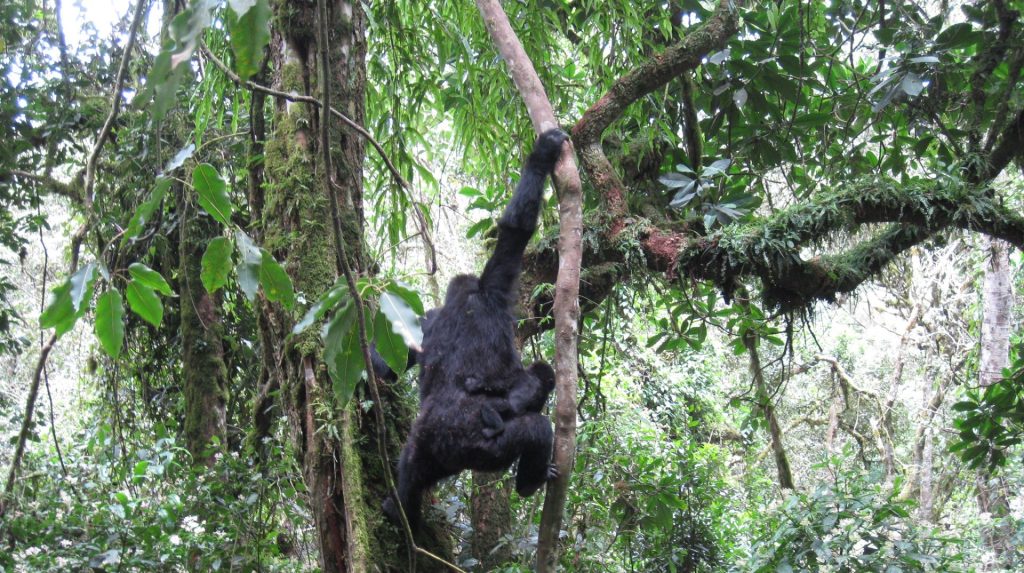
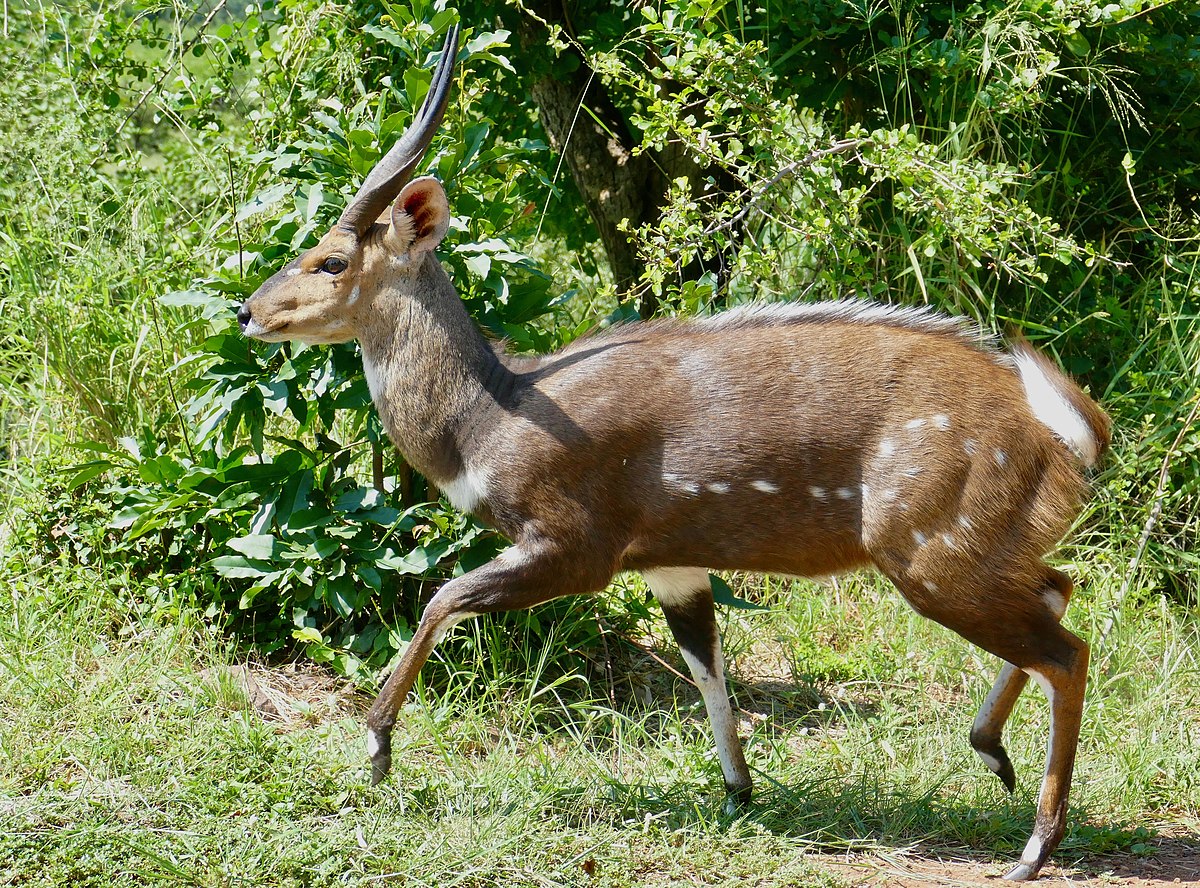







 known as
known as 
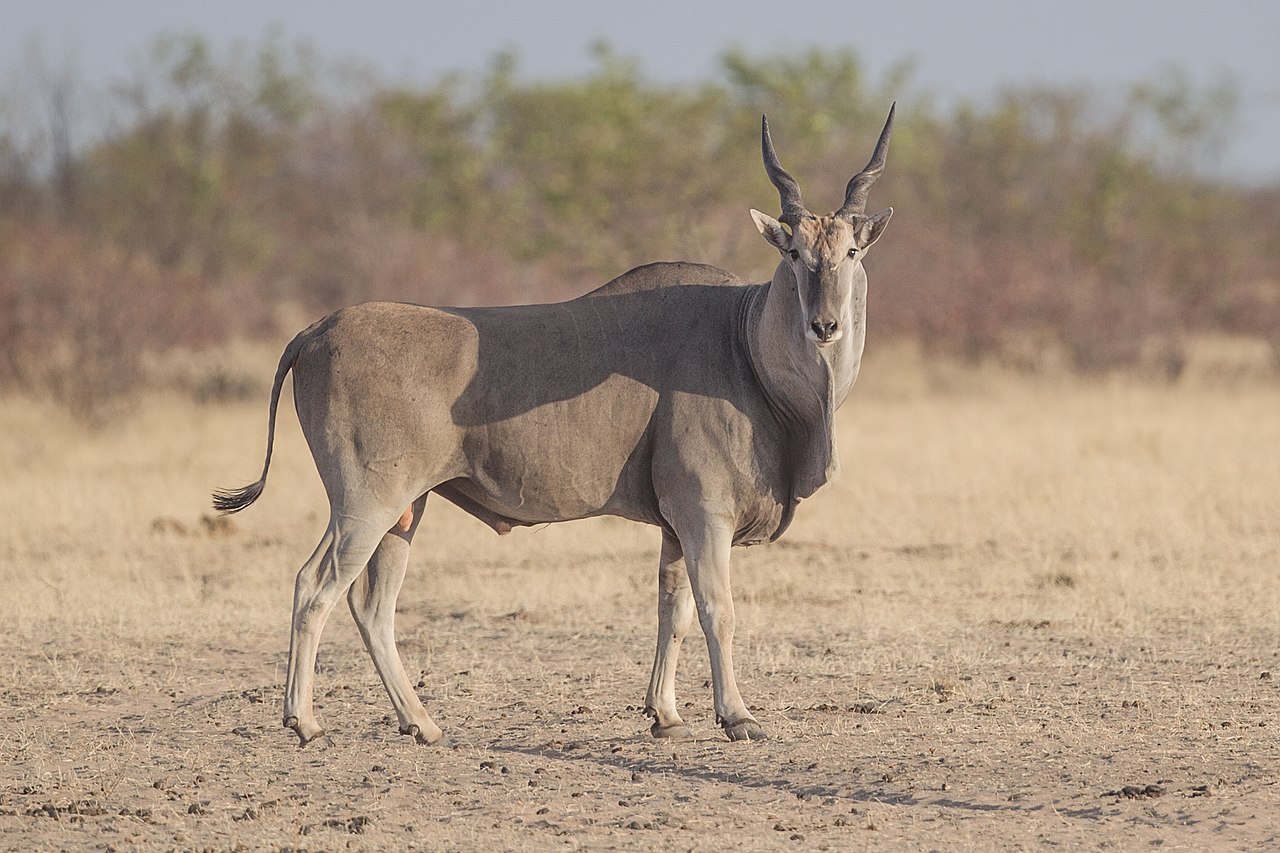
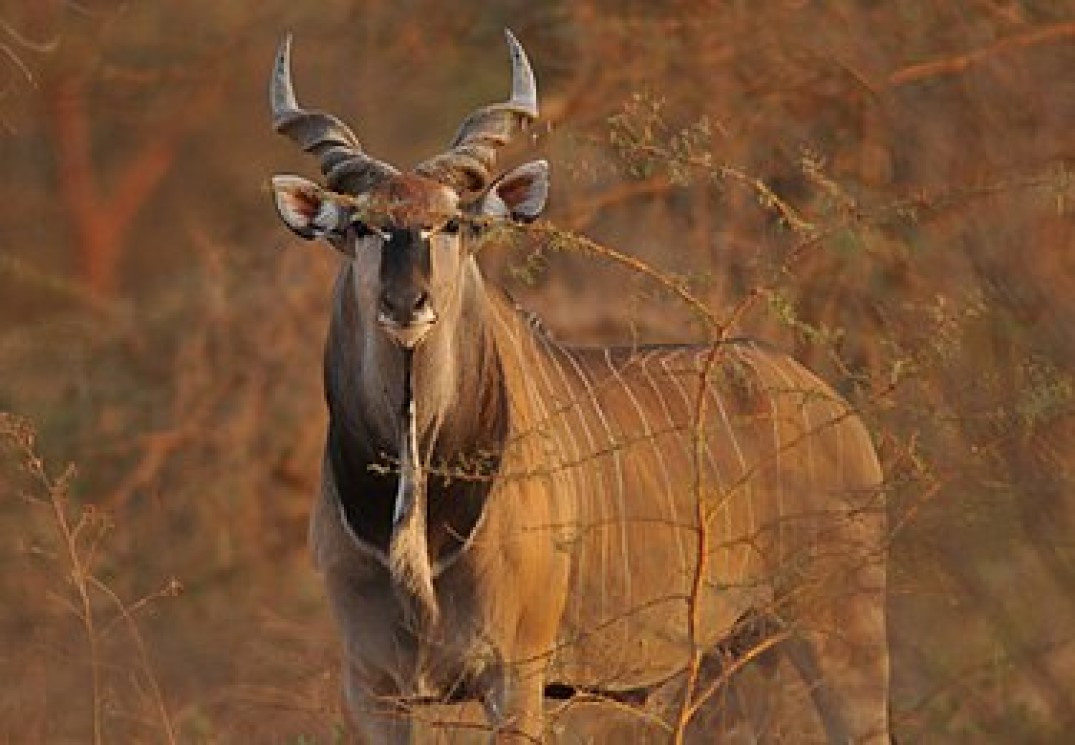
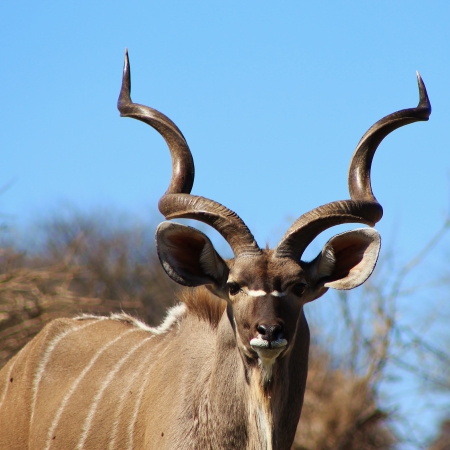





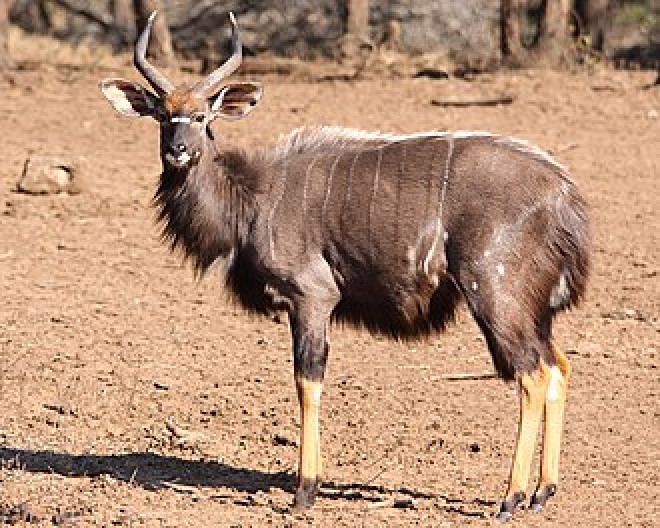
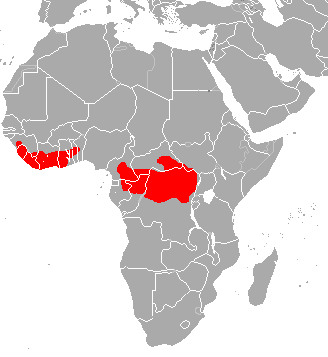 The bongo is a large, mostly nocturnal, forest-dwelling antelope, native to sub-Saharan Africa. Bongos are characterised by a striking reddish-brown coat, black and white markings, white-yellow stripes, and long slightly spiralled horns. It is the only member of its family in which both sexes have horns. Bongos have a complex social interaction and are found in African dense forest mosaics. They are the third-largest antelope in the world.
The bongo is a large, mostly nocturnal, forest-dwelling antelope, native to sub-Saharan Africa. Bongos are characterised by a striking reddish-brown coat, black and white markings, white-yellow stripes, and long slightly spiralled horns. It is the only member of its family in which both sexes have horns. Bongos have a complex social interaction and are found in African dense forest mosaics. They are the third-largest antelope in the world.
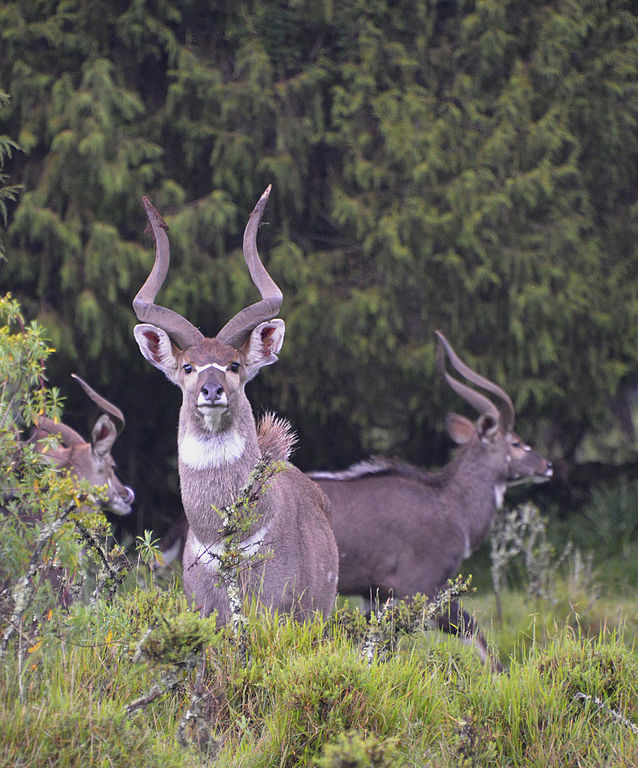





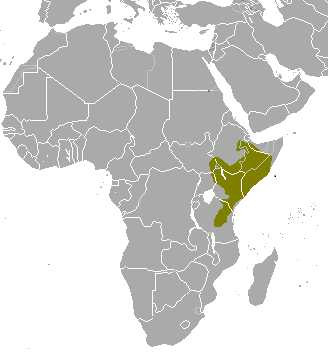
 swamp-dwelling medium-sized antelope found throughout central Africa (see the map to the right. The sitatunga is mostly confined to swampy and marshy habitats. Here they occur in tall and dense vegetation as well as seasonal swamps, marshy clearings in forests, riparian thickets and mangrove swamps.
swamp-dwelling medium-sized antelope found throughout central Africa (see the map to the right. The sitatunga is mostly confined to swampy and marshy habitats. Here they occur in tall and dense vegetation as well as seasonal swamps, marshy clearings in forests, riparian thickets and mangrove swamps. Found in the West Indies, northern South America (including the Galápagos Islands) and the Yucatan Peninsula. It was considered cospecifc with the greater flamingo, but they are now recognized as separate species (it is also closely related to the Chilean flamingo).
Found in the West Indies, northern South America (including the Galápagos Islands) and the Yucatan Peninsula. It was considered cospecifc with the greater flamingo, but they are now recognized as separate species (it is also closely related to the Chilean flamingo).  of South America, it is in the same genus as the James Flamingo. Indeed, the Chilean Andea and James flamingo often share nesting sites and are relatively closely related.
of South America, it is in the same genus as the James Flamingo. Indeed, the Chilean Andea and James flamingo often share nesting sites and are relatively closely related. the American and greater flamingo, it is listed as near threatened in the wild with a wild population of about 200,000. Population declines are due to habitat loss and degradation, harvesting and
the American and greater flamingo, it is listed as near threatened in the wild with a wild population of about 200,000. Population declines are due to habitat loss and degradation, harvesting and 










