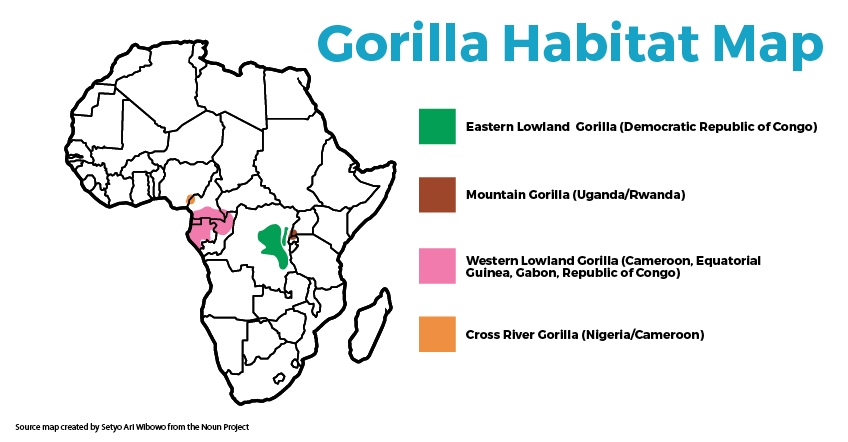
The Eastern gorilla (lowland)
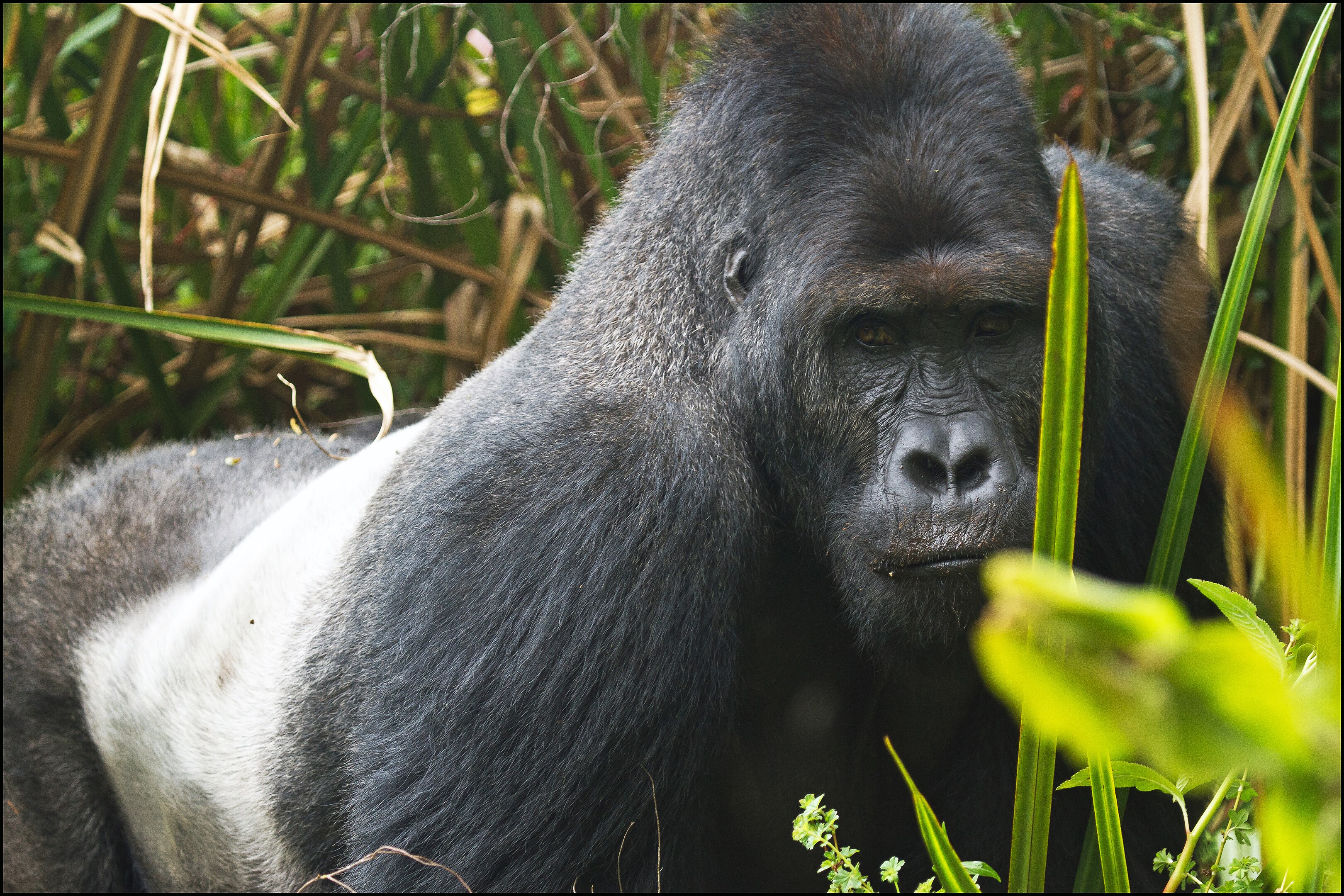

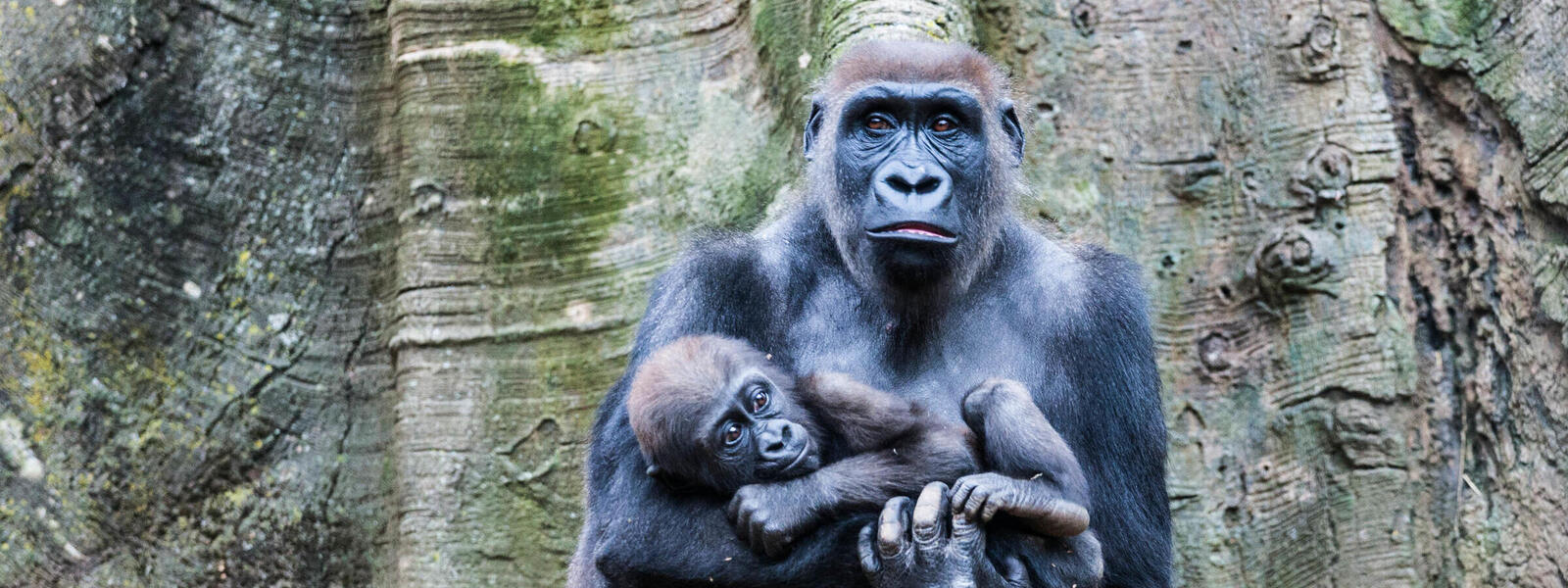
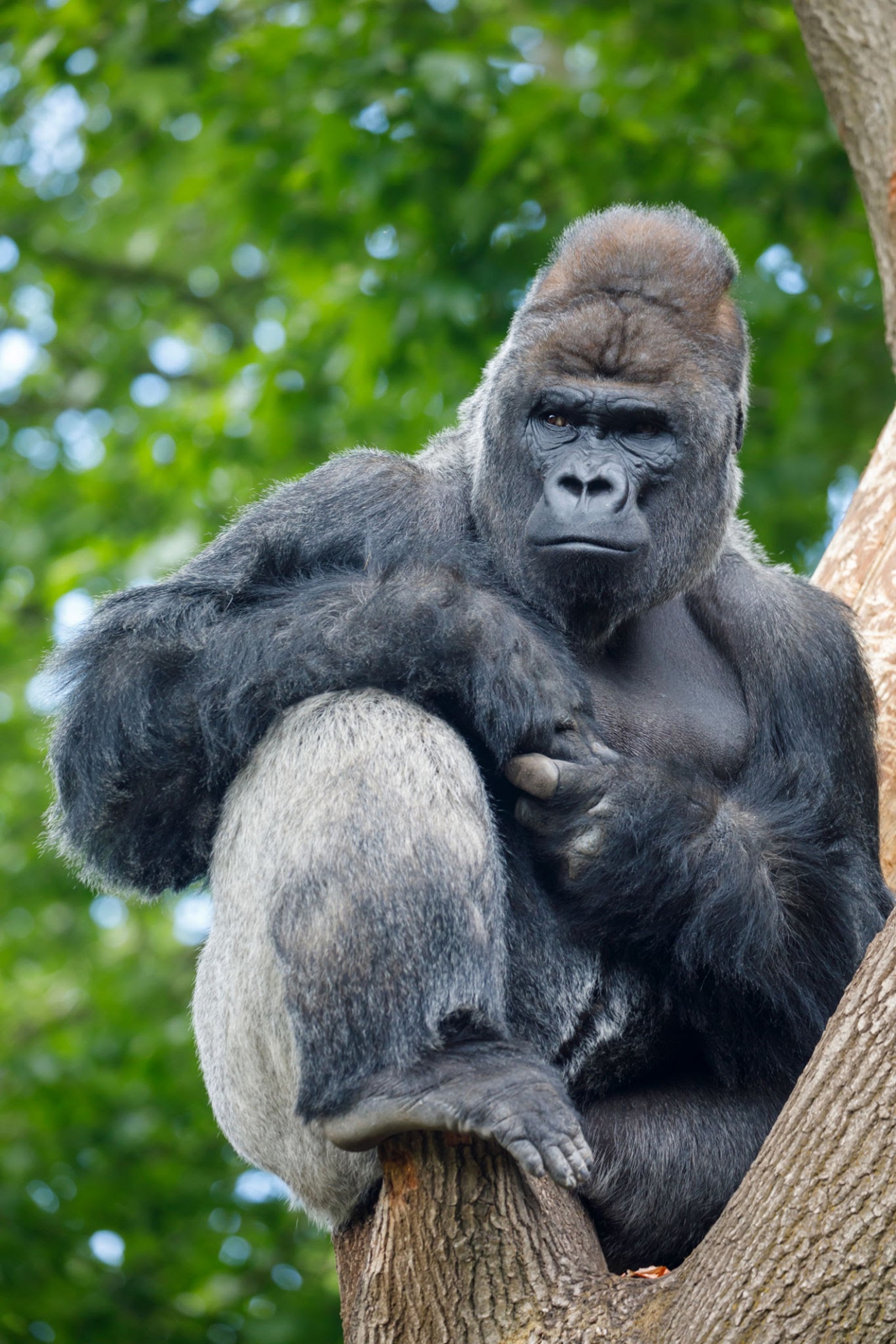
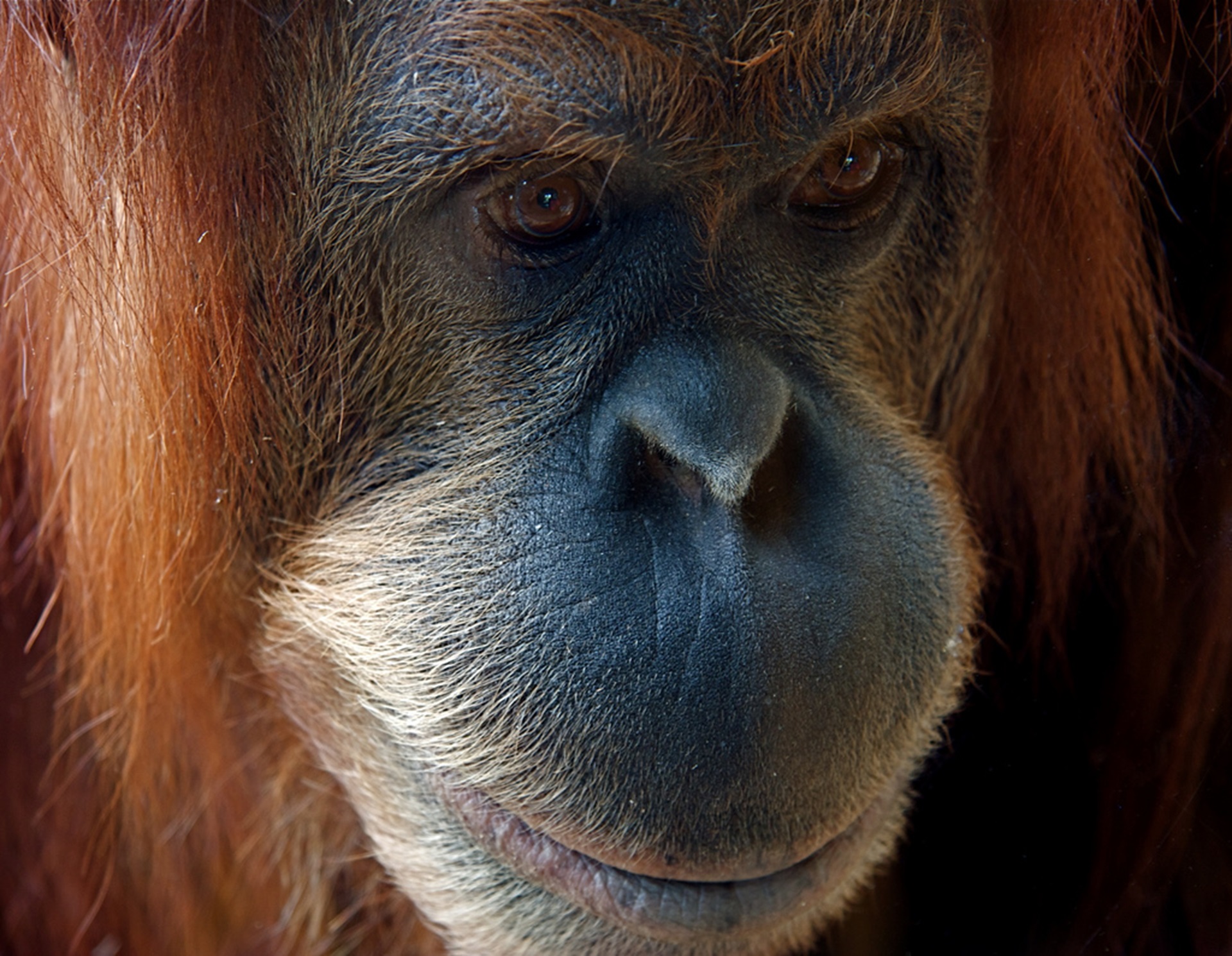
The Eastern Gorilla, or Eastern lowland gorilla (as the Eastern gorilla subspecies is the mountain gorilla) is a species which makes its home only in lowland tropical rainforests in the eastern DRC. In the last 50 years, its range has almost halved, from 8,100 square miles—about the size of the state of Massachusetts— to about 4,600 square miles today. This subspecies may now occupy only 13% of its historical range.
There are only about 5000 Eastern lowland gorillas left in the wild. While much of their numbers decrease over the last 50 years, has been as a result of a loss of habitat, their most immediate threat is currently, is that of the bushmeat trade. The area around their range is home to people with very little money. Tourism to this area, would likely greatly improve this issue and reduce the demand for Gorilla bush meat. Apart from the threat for the continued survival of this giant (alongside the mountain gorilla, this species is the largest great ape still living.
Any news articles will appear below, and links to allow travel to this region will be added below.
[smart_post_show id=”12533″]