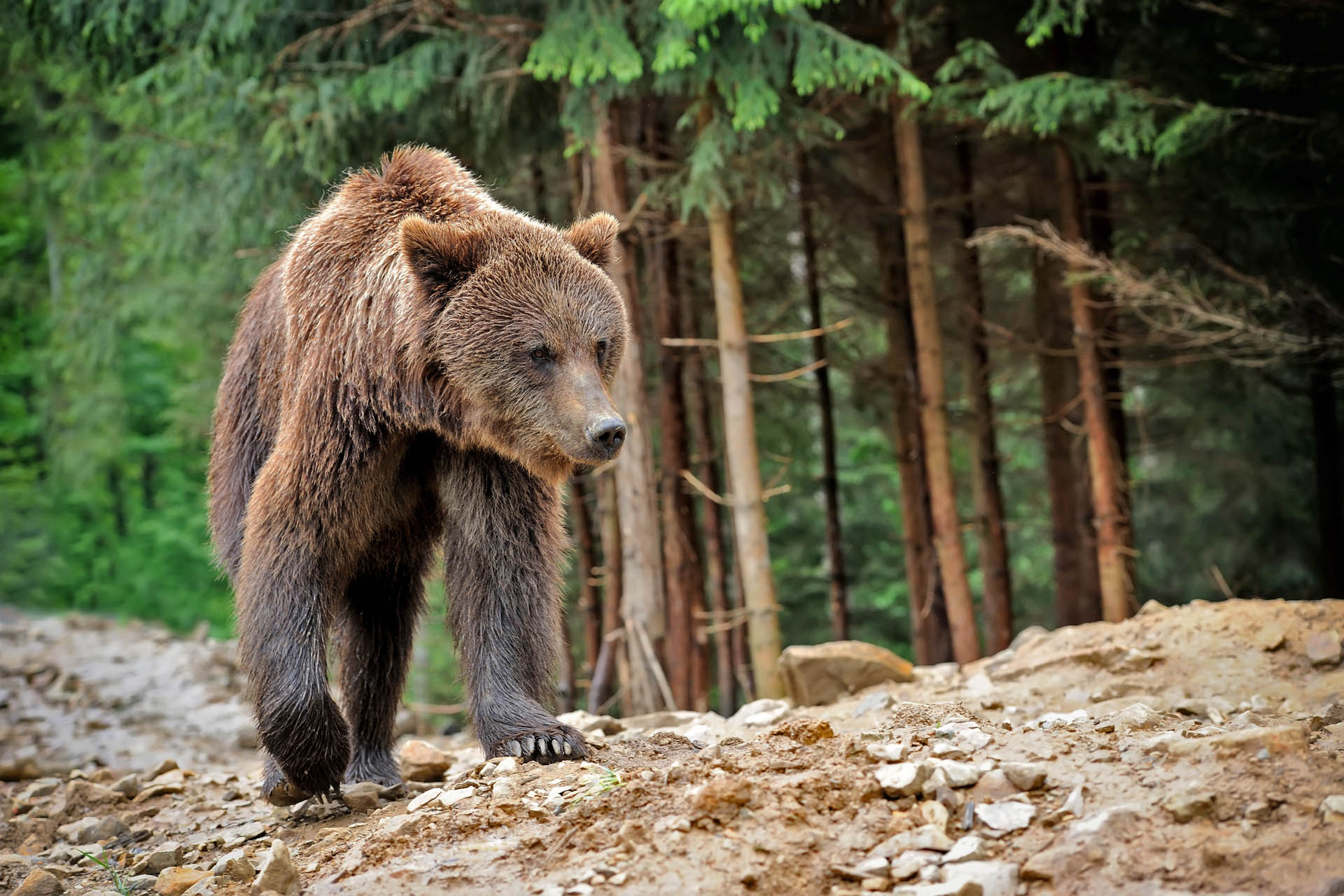
Brown bear
With it’s range originally encompassing the whole of Europe, much of Asia, most of North America and the atlas mountains of Africa (the only native African bear), it has unfortunately been in decline for some time. These days the bear habitat consists of Alaska and parts of Canada as well as northern regions of the USA, relict populations in Western Europe though they still have a stronghold in Eastern Europe and and Russia as well as sections of central Asia. Highly intelligent they have never lived at high densities, as members high on the the food chain, few places can support large populations for long. With their impressive intelligence, and inquisitive nature, the can be tough to live alongside. With all that in mind brown bear watching can be an enjoyable pastime in many different places. Around much of the world there are newer hides in places that bears still exist – these allow you to watch bears in their natural habitat. We currently only have one listed (it’s will with a visit, link below) but we are always keen to list many more.
There are many places where bears live happily live alongside humans and are rarely seen.
Over time we hope to list many places where you can visit bears and see them in their wild home. These will be done by country (visit the tabs below). Below this, is a list of any articles that have been written on this species, below that will be links that we have to see bears yourself.
Spanish bears have done incredibly well, over the last few decades. There are 2 areas of the country where the bears exist. One is in the Pyrenees, and the other was in the Cantabria mountains. In the 1990s
Cantabria
The Cantabria bears population fell to just 50 bears in 2 populations in the mid 1990s, though oddly hunting was banned in 1973, so it took around 20 years for the population to stop falling – put down to illegal hunting and poaching (I am not sure what the difference is between illegal hunting and poaching (the difference is that poaching often catches the animal alive). What was more concerning, was that there was only a handful of breeding females in the whole population. This population has grown very fast, the current population officially is around 370 strong (250 in the west, and 120 in the east with a gap of 40-50km however, it has been shown that bears have been moving from the large to the smaller population with relative regularity suggesting it cannot be too hard). Many people suggest that the population might be as high as 500 (It is good to under-estimate the population, as it allows the population to naturally grow to its previous size).
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees mountain chain run along the border between France and Spain, and in the early 20th century, there were around 150 bears in this population. This was reduced to 70 by 1954. By the 1990s, bears were missing from the central Pyrenees, which split the population, making both populations too small to retain significant genetic variability. In 1996, the French government introduced 3 bears from Slovenia (these are exactly the same subspecies, and the population was only split in modern times. Before this, there was just 7-8 living in the western part of the mountain range. Further reintroductions were made: five in 2006, and two in 2018. This new genetic material, allowed the population to recover, and at the current time, the Pyrenees population is estimated at 83 as of 2023. In recent times, the bear population has been growing at 11% per year. Being spread along the border, it is impossible to clearly differentiate a Spanish population and a French population.
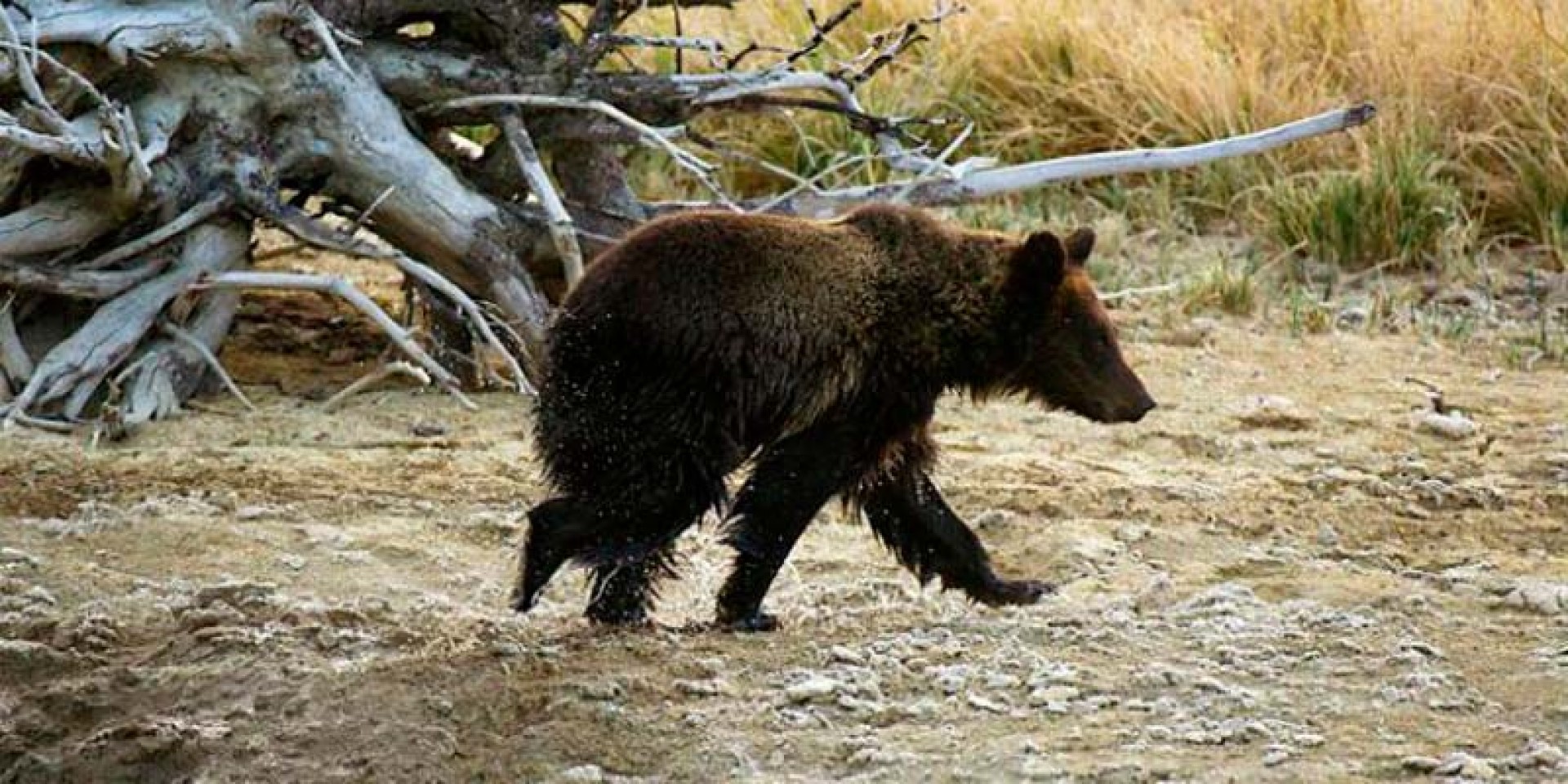

In May 2019, a brown bear was spotted in Portugal for the first time since 1843, confirming the return of the species to the country. The bear was spotted in Montesinho Natural Park, in the Bragança region of northeast Portugal, close to the Spanish border. The bear likely came from the western Cantabrian Mountains in Spain, where the brown bear population is slowly increasing. This is perfectly normal behaviour, as the male bears disperse some distance to avoid inbreeding.
Having said this, when I was there back 5 years earlier, 3 bears were being seen from time to time, around the Sierra de Culebra, right on the Portuguese border. As such, it is quite likely that bears have been crossing this border for some time, even if locals were unaware.
Given time, it is quite conceivable that this population will grow and become a permanent presence in the country – so long as it is allowed to be. It should be noted, that while bears can be a nuisance, it is an opportunistic omnivore. Eating mainly plants, roots, fruit, berries and nuts, its mostly vegetarian diet is supplemented by insects, eggs, honey, fungi and carrion. Given the presence of wolves in Portugal, the bear is capable of living alongside humans far easier than wolves. It is true that they have an annoying habit of breaking into bee hives, but that is little compared to the occasional livestock kill.
French bears have not done well, having come to the edge of extinction before a number of bears were translocated to the mountain range from Slovenia.
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees mountain chain run along the border between France and Spain, and in the early 20th century, there were around 150 bears in this population. This was reduced to 70 by 1954. By the 1990s, bears were missing from the central Pyrenees, which split the population, making both populations too small to retain significant genetic variability. In 1996, the French government introduced 3 bears from Slovenia (these are exactly the same subspecies, and the population was only split in modern times. Before this, there was just 7-8 living in the western part of the mountain range. Further reintroductions were made: five in 2006, and two in 2018. This new genetic material, allowed the population to recover, and at the current time, the Pyrenees population is estimated at 83 as of 2023. In recent times, the bear population has been growing at 11% per year. Being spread along the border, it is impossible to clearly differentiate a Spanish population and a French population.
There were once bears in the French alps as well, but the last one was shot in 1936. There are bears in the alps, but it appears that there is not a permanent
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees mountain chain run along the border between France and Spain, and in the early 20th century, there were around 150 bears in this population. This was reduced to 70 by 1954. By the 1990s, bears were missing from the central Pyrenees, which split the population, making both populations too small to retain significant genetic variability. In 1996, the French government introduced 3 bears from Slovenia (these are exactly the same subspecies, and the population was only split in modern times. Before this, there was just 7-8 living in the western part of the mountain range. Further reintroductions were made: five in 2006, and two in 2018. This new genetic material, allowed the population to recover, and at the current time, the Pyrenees population is estimated at 83 as of 2023. In recent times, the bear population has been growing at 11% per year. Being spread along the border, it is impossible to clearly differentiate a Spanish population and a French population on the French sideof the mountain range.
While Switzerland does not have a resident population of brown bears, there are occasional sightings of bears that immigrate from Italy. The last indigenous bear in Switzerland was shot in 1904.
Bear plan
In 2006, Switzerland implemented a “bear plan” to promote coexistence between humans and bears. This plan includes killing bears that pose a risk to humans, such as those that frequently enter human settlements. Having said this, in practice, in recent years, it has often meant that any bear which enters Switzerland and does not leave quick enough has been targeted. Thankfully being wild animals, they have often left on their own
Bear sightings
Bears have been spotted in the cantons of Bern, Grisons, Lucerne, Nidwald, Obwald, Schwyz, Ticino, Uri, and Valais.
The notorious brown bear known as M13 has been killed. He was shot in the early hours of Tuesday, after it proved impossible to keep him away from human settlements, the Federal Office for the Environment announced on Wednesday. M13 was the only bear known to have been living in Switzerland.
A male bear born in Italy in 2013, M29 is believed to have crossed into Switzerland in April 2016. He was spotted a few times before disappearing in September 2017. It is not clear what happened, but very often when a bear disappears, that means that it has been illegally killed (though we can hope he simple left of his own accord).
The Marsican brown bear is one of the surviving populations of bears in western Europe. At the current time, there are an estimated 50-60 bears living in the mountains, though only 10-12 of these are females of breeding age. In 1980s there were 100 bears in this region. However, if we could reduce the death rate, each breeding female, is capable of producing up to 3 bear cubs, every couple of years. This means that we can expect as high as 15 bear cub births a year, or an increase of 25% in the population.
The Marsican brown bear, also known as the Apennine brown bear, lives in a range of about 5,000 to 8,000 square kilometers in the Apennine Mountains of Italy. This range includes:
- The Abruzzo-Lazio-Molise National Park
- The Sibillini National Park
- The Gran Sasso-Laga National Park
- The Majella National Park
- The Velino-Sirente National Park
- The Simbruini Regional Park
Having gone extinct back in the 19th century, one might wonder why I have included it on this list. The closest population is in trentino in Italy, however, there have been many reported sightings, and given bears habits of dispersing hundreds of miles, this is not impossible to believe. While likely a shock to the people of Germany, and possible that the German government would choose to kill any bears that settled, Germany has plenty of wild space, after all, the country now hosts 1200 wolves.
Brown bears are roaming into the country, with increasing frequency, but none have as yet settled within the country.
However, while there is less wilderness in Hungary than many ccountries in Europe, meaning this population can only grow slowly.