Cetaceans -Whales, porpoise and dolphins
Few people can avoid stopping to watch, if they spot cetaceans from a cliff. While the family is wide and varied, they are all pretty interesting. From some of the largest and most intelligent hunters such as killer whales to the largest animal on earth the blue whale.
Whale and dolphin watching tourism is worth a lot of money – this can be essential, as in many places the extra money helps a community survive.
I hope, overtime, to make this section of the website as large a list of places to view cetaceans and people who will help you in that quest.
As might perhaps be suspected, all of the mammal species which have returned permanently to the sea, and developed breathing holes located on their back (and therefore perfectly placed for taking quick breaths) are related.
So what is the most closely related living land mammal? Perhaps obviously, it is a species which spends much time in the water – the hippopotamus.
As with all of these pages, as we create pages for each individual species, they will be linked to the photo below.
So the baleen whales are split into three families, these are not large as there are only 16 species of baleen whales in the world. At the current time, there are roughly 1.1 million baleen whales in the worlds oceans
Below is a family tree of the group
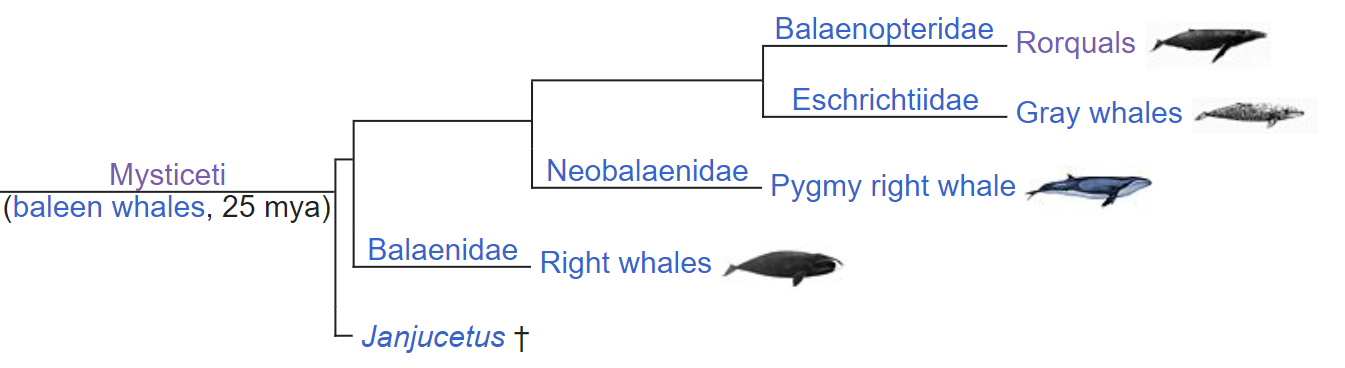
Baleen Whales
Baleenideae – the rhight whales
The first living split is Baleenidae, this family is not huge. The north atlantic and north pacific are closest related, these species are closely related to the Southern pacific right whales. Their name is unfortunate – it is called right whale for 3 reasons, it swims slowly, floats when dead and carries a large amount of oil. This lead to all these species being hunted close to extinction.
The other family is called Balaenopteroidea. Here species peel off slowly. I will list them in the order that they split.
The first split is the minke whale – of which there are 2 species, the common and southern minke whale, with the grey whale being the next most similar.
The next are the humpback whale and the fin whale followed by the Blue whale.
The last group of whales are from a group called the Brydes whales complex
This completes the list of baleen whales. The other branch of the Cetaceans is known as the toothed whales
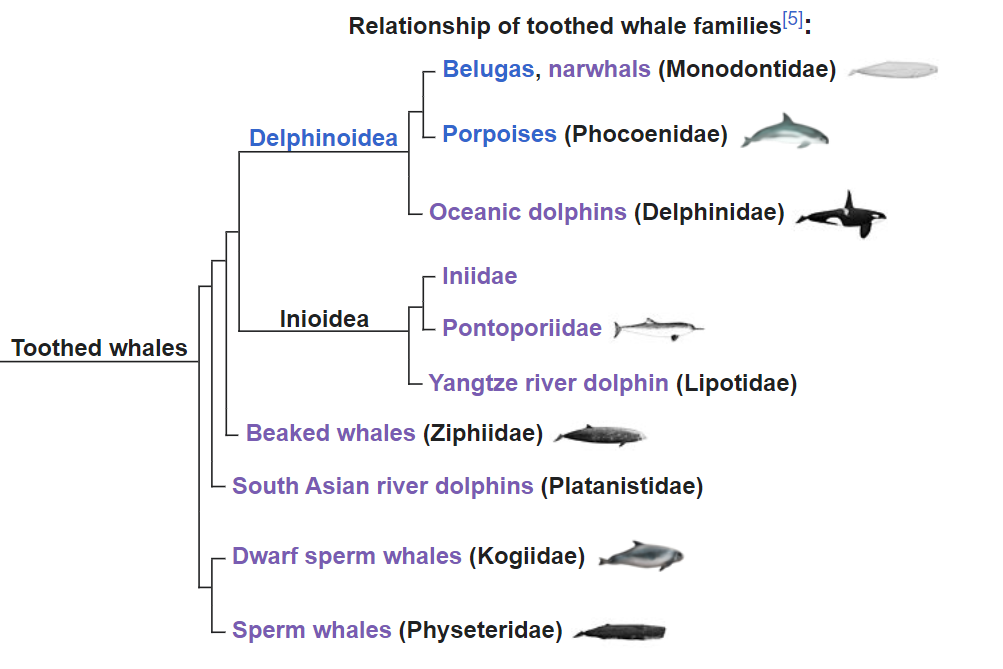
Toothed Whale
.I am going to look at them in 3 groups, though the third is not particularly closely related to each other
- Delphinoidea: This includes
- Monodontidaes – Belugas and narwhals
- Phocoenidae – The family of Porpoises (7 species) such as harbour porpoises and Vanquita
- Delphininidae – these are the oceanic dolphins – 37 species split into several subfamilies which we will deal with one by one.
Subfamily Globcephalinae 11 species
Subfamily incerta sedis (latin for “of uncertain placement” )6 species
Subfamily Lissodelphininae 6 sppecies
Subfamily Orcininae
- Inioidea : This includes 3 groups
- Iniidae (only 1 of 5 genus remains -Inea (4 species: Araguaian river dolphin, Bolivian river dolphin and Orinoco dolphin)
- Lipotidae: which contains only one species: the Baiji or Chinese river dolphin
- Pontoporiidae: which contains one species
The next family is the beaked whales. There are 24 species, of which only 3-4 have been well studied. This is because they spend much of their time deep in the sea, it appears that each species does not have many members and they are incredibly reclusive in their habits.
One might ask how an air breathing animal can spend so much of its time deep in the ocean? Well the Curved beaked whale has had a dive timed at 138 minutes. More incredible, they only need around 2 minutes to catch their breathe before sinking back into the depths. This means that if required, they can spend just 20 minutes out of 24 hours at the surface – an incredible stunt.
There appear to be a great number of species that are extinct – these we will not list, but will mention each subfamily in passing.
Incertae sedis contains 5 extinct genus, Basal forms include 13 extinct genus
Subfamily Berardiinae contains 3 genus, 2 of which are extinct, but the third contains 3 living species (and one dead) .
Genus Beradius
Next we cover the Bottlenose whales
Northern Southern and Tropical
Subfamily Ziphiinae contains 5 genus, 3 are extinct, but two have just one species in each
Genus Tasmacetus: Shepherds beaked whale Genus Ziphius: Cuviers beaked whale
Click on the image to see it in full
The most populous genus Mesoplodon – mesoplodont whales
As you can see, many of the pictures are of dead whales, or skulls or diagrams, or even just text. This is because sightings of many species are so rare that they have never had a photo taken
As you can see from the whale family tree, the sperm whales are separate from the rest. However, they are toothed whales so belong in this section of the page.