The cheetah have arrived in India, and have been introduced into enclosures within the Kuno national park. At the current time, the enclosures are just 15x30m so a similar size to a large zoo enclosure. They will stay in this enclosure for a month in order for the team to be sure that their health is good.
After this, they will be shifted into a 1 kilometre square enclosure for up to another 4 months before being released fully into the Kuno national park.
A further 12 cheetah will be transferred next month with roughly 50 agreed to be transferred over the next few years.
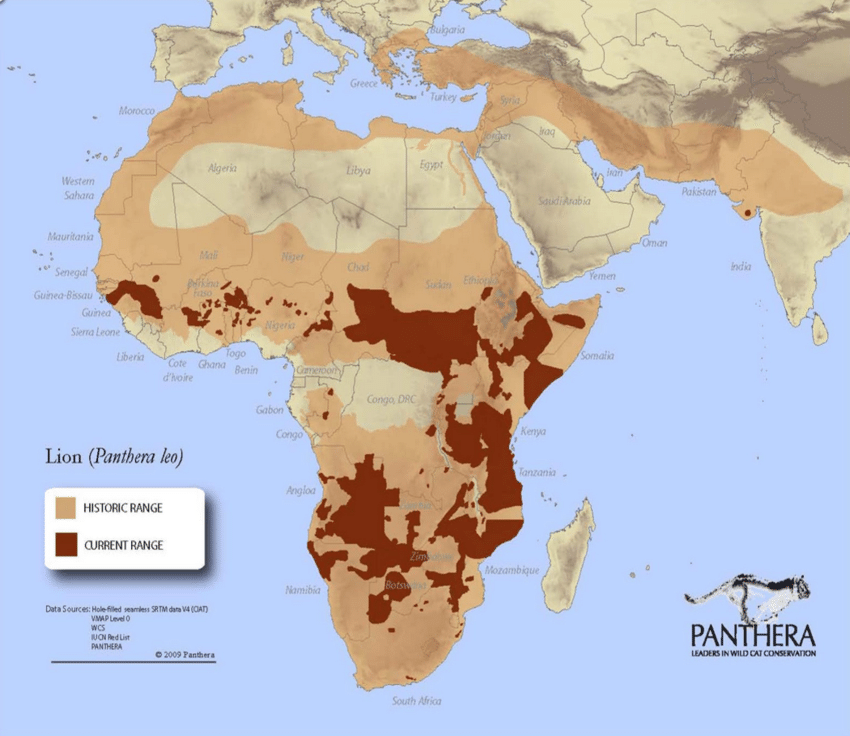
The simple question, though, is that cheetah do not do well in small reserves in Africa, as they cannot compete with large cats like lions or leopards (or in India, Tigers). With far less space, and a much greater density of people in India, is there going to be space for the returning cheetah? Furthermore, this situation is not likely to improve in the near future: predictions are that, without a significant break on fertility rates, India’s population could exceed 2 billion by the end of the century. In this senario, it is hard to see how there is space for much wildlife at all.