Primate family tree
The primates are in some ways one of the most successful families. It is true that many are now endangered, however, unfortunately, that is as a result of the run-away success of the most successful member of the primate family us! Having left the rainforests behind, we have been reducing their coverage dramatically over the last few centuries.
The sad thing, is that while we have pushed many of our closest cousins towards extinction, the loss of forests may well cost us dearly in the future as well. As a species, we need to pull together to meet this challenge. in order to jump to the various families, click on the family of interest above – though all can also be reached by scrolling down.
Great Apes
Great ape Family split is thought to have split from its nearest relative – the gibbon family, around 17 million years ago.
4 million years later the Orangutan family split from the gorilla line and the human/chimp line.
3 million years after this (so around 10 million years ago) the gorilla family split from the Homo (humans) and Pan
Finally the human line (homo) split from the Pan line 5-6 million years ago.
It should be noted, that chimpanzees and Bonobos split from a common ancestor just 1.8 million years ago. This occurred as the two populations ceased to be able to have contact with each other – the Congo rive formed between 1.5 and 2 million years ago.
For more information on each species, click on their photo and this will take you to their page
It should be noted that while I have grouped eastern western and skywalker gibbon together, there is some contention that the skywalker gibbon should be in its own genus, having diverged around half a million years aog
Gibbons
Genus Nomascus
This family is the Genus: Nomascus or crested gibbon.
The last Genus of gibbons is Hylobates: dwarf gibbons.
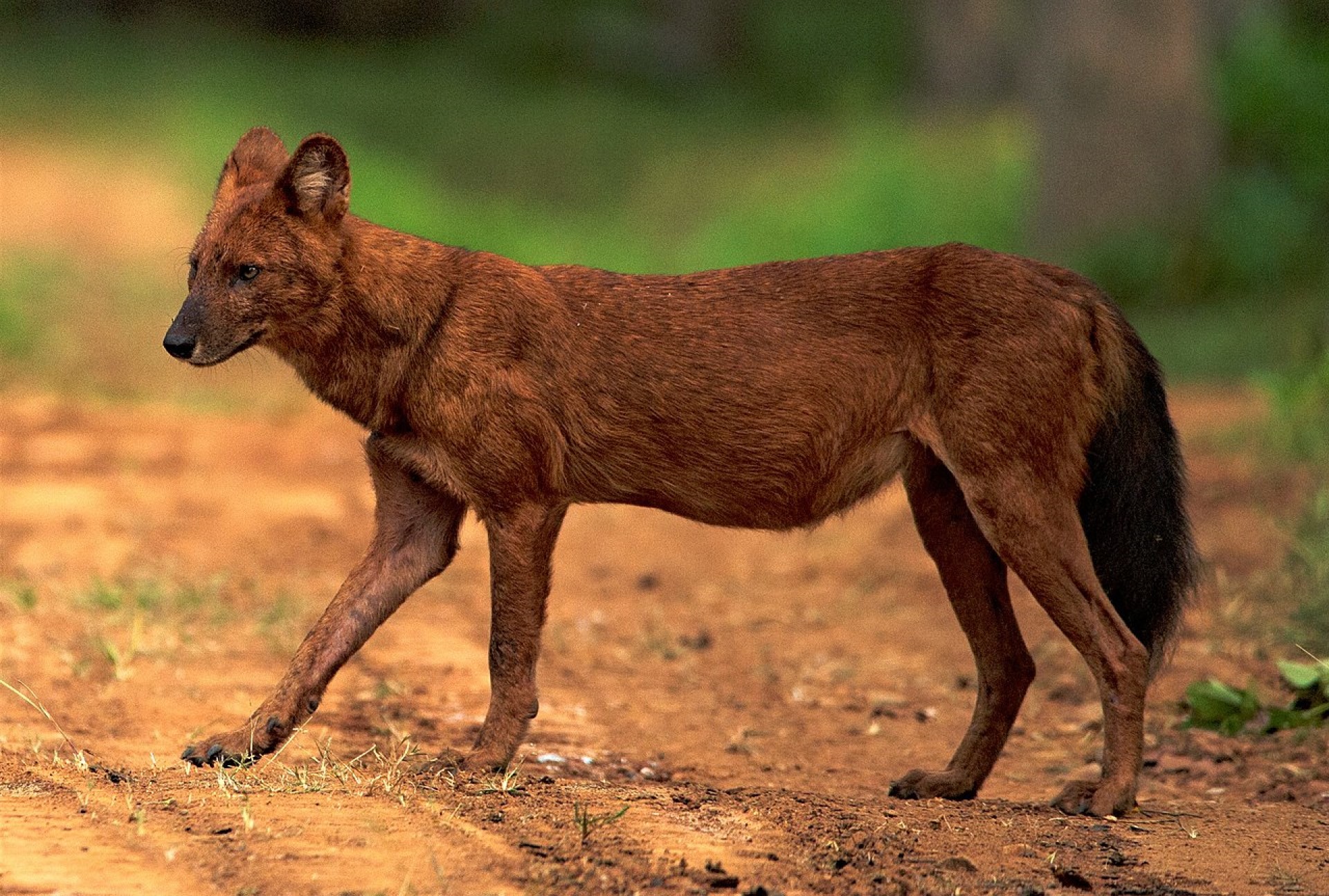




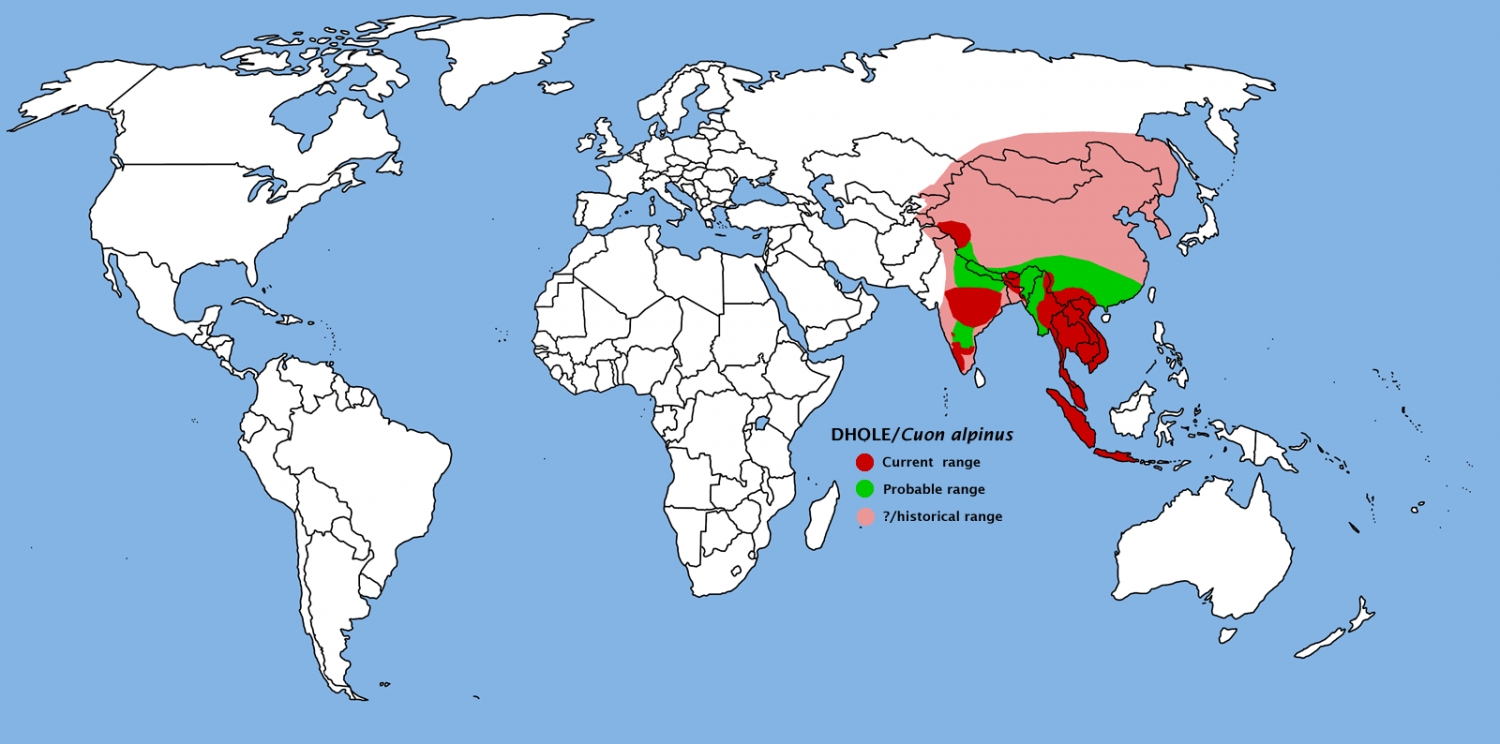 The Dhole is an ancient species of dog, It split from the rest of the dog family 5.2-7.6 million years ago.
The Dhole is an ancient species of dog, It split from the rest of the dog family 5.2-7.6 million years ago.















