Unfortunately, this disagreement, is not restricted to within the royal family, quite to the contrary.
There are many species that it is hard to live alongside – I am not thinking of animals like elephants or rhino or buffalo, which will also be dangerous to life, but provided you behave in the right way, you can live in close proximity with and rarely have a problem. Indeed, there are populations who succeed to live in the close proximity with big cats such as lions and leopards. However, in many other places, lions and leopards can turn to man-eating, or indeed livestock eating. These reserves, seem best to be kept as so called fortress reserves, where people live outside (though bushmen still live in these areas, and having passed down information for thousands of generations, so can live with big cats). A large number of these huge reserves were set up while the land was held as parts of empires, and as such may not be the best way to do things, though in many of these places, it is the way things are set.
On the other hand, William believes that you should be community led schemes which focus on locals and allow them to benefit from the wildlife. I would argue that these are not incompatible. My experience of the Kruger, was that many locals did very well from their proximity to the Kruger national park – not to the extent that perhaps they should, but those willing to learn can become guides, while the rest can work in hospitality and the like. Even beyond this, there is the ability for artisans to sell their products on the way in and out of the park.
Personally, I believe that the path falls somewhere between the two. It is essential, that were possible, migration routes between reserves are created before these become built over.
Our website aims to allow both – we have a space on this website (called Wild places) for listing large reserves, and chances to see the wildlife they contain. Alongside this, we offer our area called “in the shadow of mankind” which is aimed at all of the other wildlife, often found alongside where people live, or where their livestock lives. To a large extent, to allow the natural world to truly thrive, we need both ends of this spectrum.
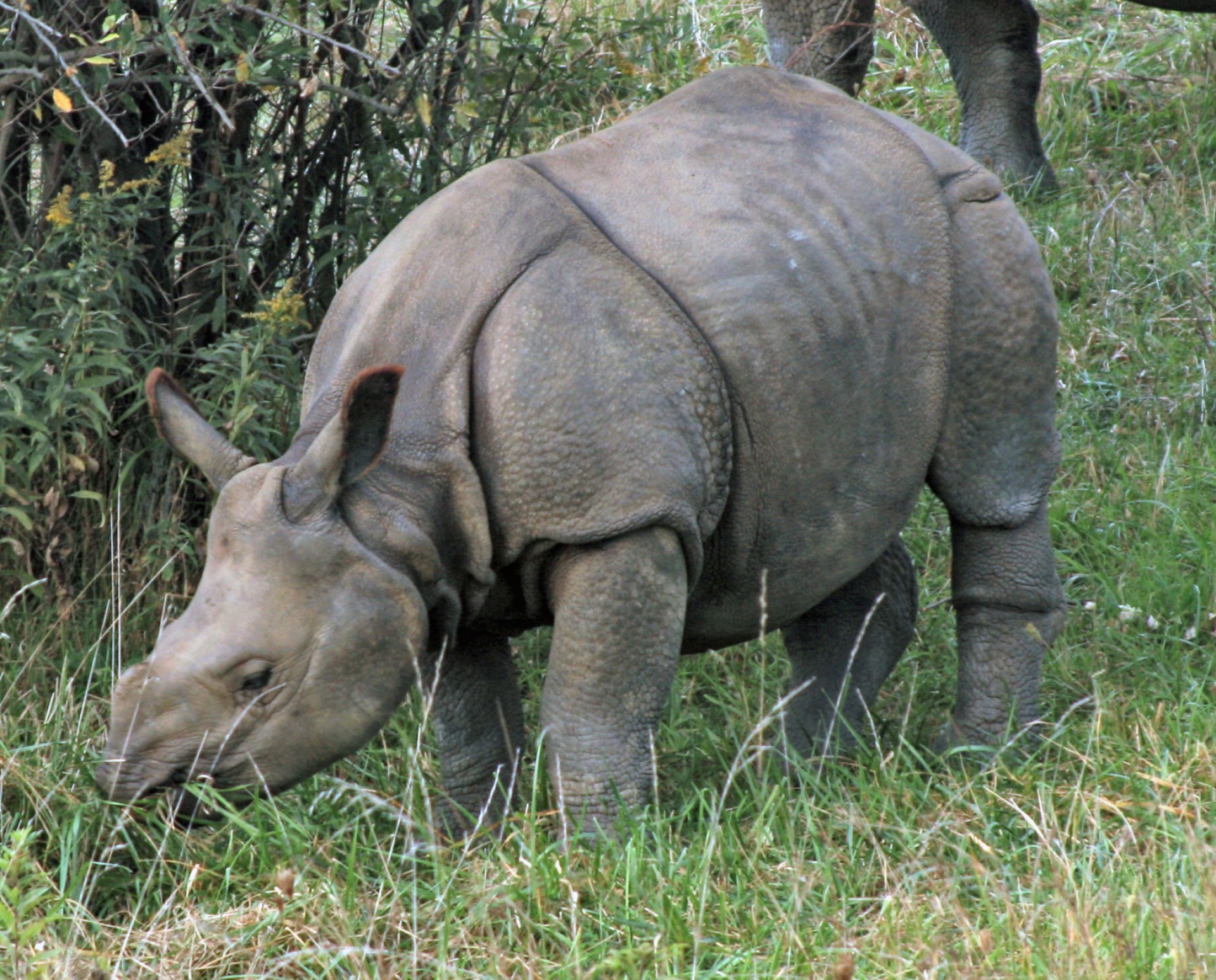




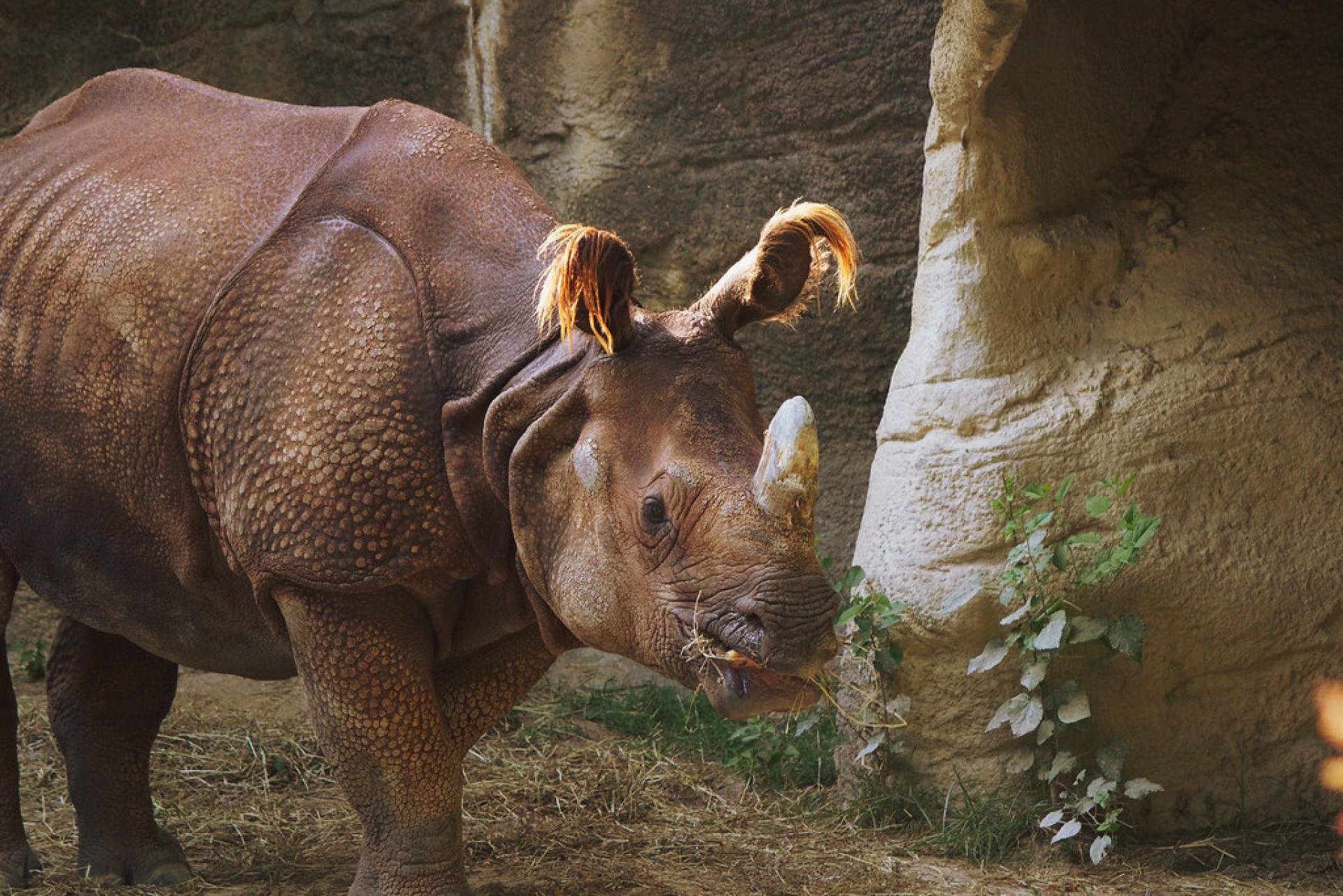
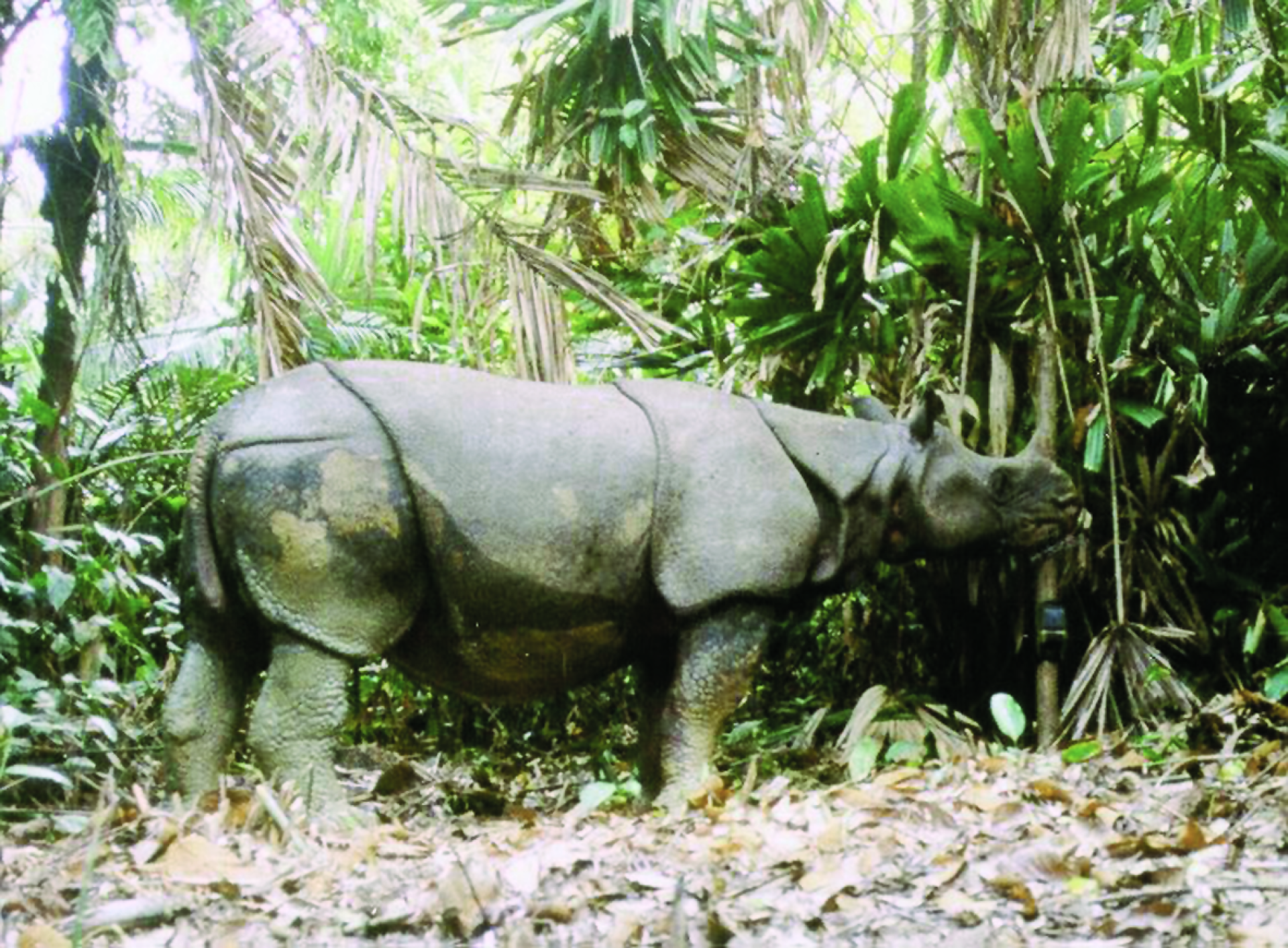
 Native to the Indian sub-continent, it is listed on the red list, and is only found across 20,000
Native to the Indian sub-continent, it is listed on the red list, and is only found across 20,000