1. Tragelaphini - spiral-horned antelope
Bushbuck
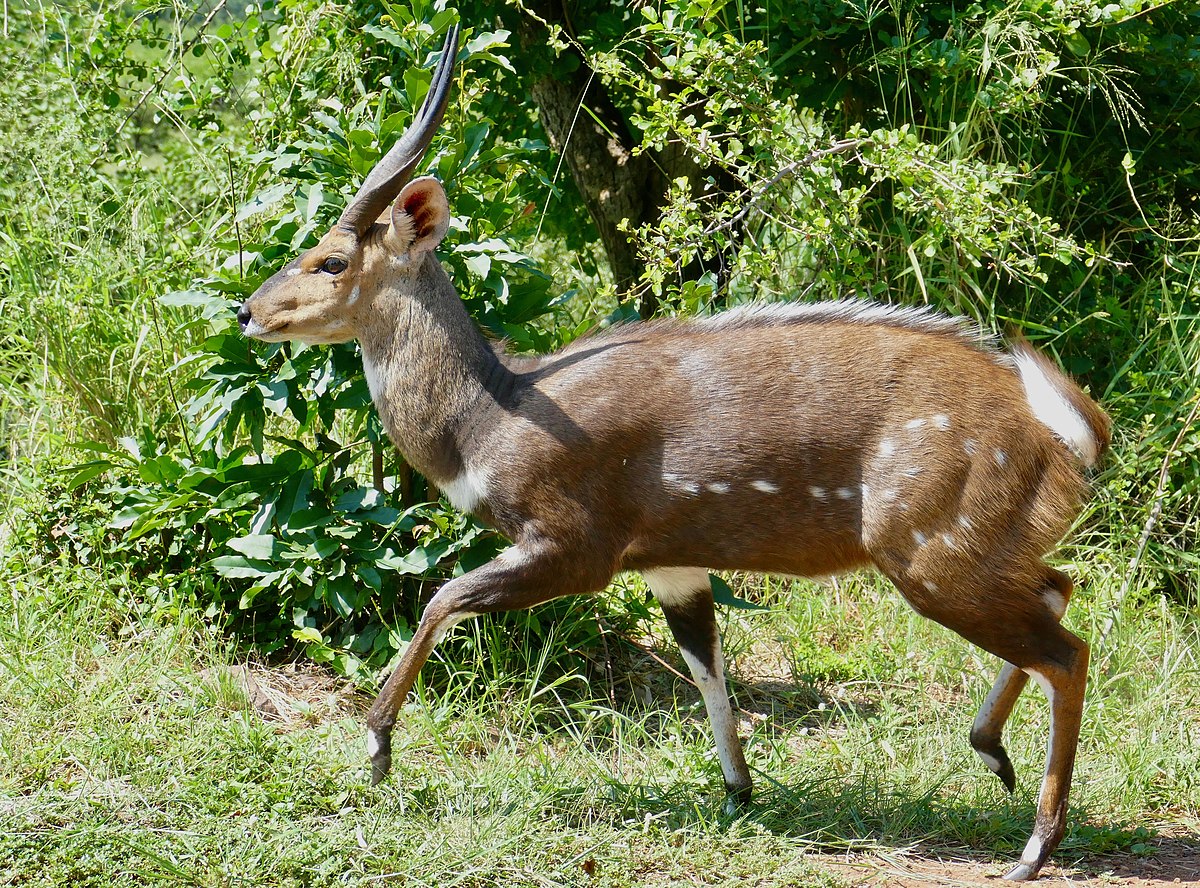
The Cape bushbuck , also known as imbabala is a common, medium-sized and a widespread species of antelope in sub-Saharan Africa. It is found in a wide range of habitats, such as rain forests, montane forests, forest-savanna mosaic, savanna, bushveld, and woodland. Its stands around 90 cm at the shoulder and weigh from 45 to 80 kg. They are generally solitary, territorial browsers.
known as imbabala is a common, medium-sized and a widespread species of antelope in sub-Saharan Africa. It is found in a wide range of habitats, such as rain forests, montane forests, forest-savanna mosaic, savanna, bushveld, and woodland. Its stands around 90 cm at the shoulder and weigh from 45 to 80 kg. They are generally solitary, territorial browsers.
Although rarely seen, as it spends most of its time deep in the thick bush, there are around 1 million in Africa
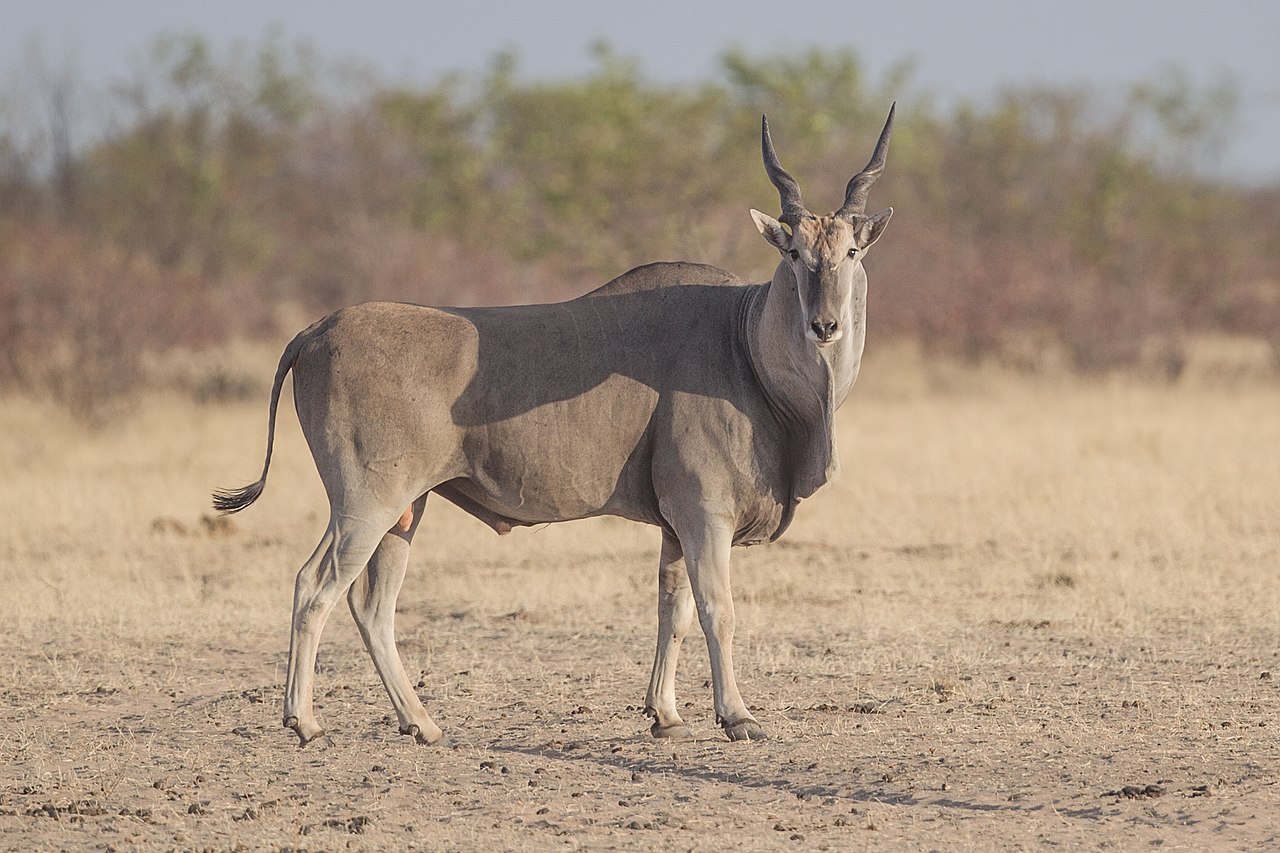
Common Eland
 The common eland (southern eland or eland antelope) is a large-sized savannah and plains antelope from East and Southern Africa. An adult male is around 1.6 m tall at the shoulder (females are 20 cm shorter) and can weigh up to 942 kg with a typical range of 500–600 kg. Only the giant eland is (on average bigger). It was described by Peter Simon Pallas in 1766. Population of 136,000, can form herds of 500
The common eland (southern eland or eland antelope) is a large-sized savannah and plains antelope from East and Southern Africa. An adult male is around 1.6 m tall at the shoulder (females are 20 cm shorter) and can weigh up to 942 kg with a typical range of 500–600 kg. Only the giant eland is (on average bigger). It was described by Peter Simon Pallas in 1766. Population of 136,000, can form herds of 500

Giant Eland
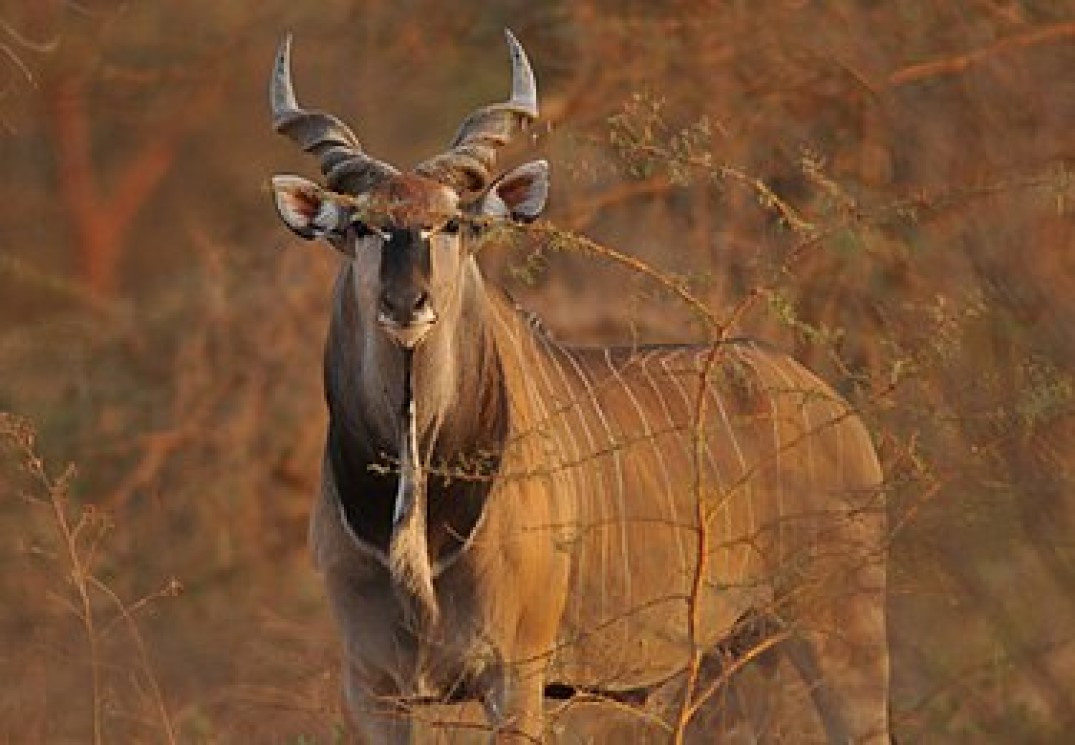

The giant eland, (also known as Lord Derby’s eland and greater eland) is an open-forest and savanna antelope.

It was described in 1847 by John Edward Gray. The giant eland is the largest species of antelope, with a body length ranging from 220–290 cm (87–114 in). There are two subspecies: T. d. derbianus and T. d. gigas.
The giant eland is a herbivore, living in small mixed gender herds consisting of 15–25 members. Giant elands have large home ranges. They can run at up to 70 km/h. They mostly inhabit broad-leafed savannas and woodlands and are listed as vulnerable and have a wild population of 12,000-14,000
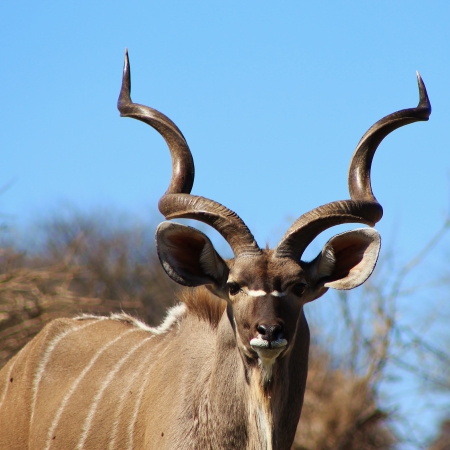
Greater Kudu
 The greater kudu is a large woodland antelope, you can see its distribution on the map. Despite occupying such widespread territory, they are sparsely populated in most areas due to declining habitat, deforestation, and poaching.
The greater kudu is a large woodland antelope, you can see its distribution on the map. Despite occupying such widespread territory, they are sparsely populated in most areas due to declining habitat, deforestation, and poaching.
The spiral horns are impressive, and grow at one curl every 3 years – they are fully grown at 7 and a half years with 2 and a half turns. Three subspecies have been agreed (one described has been rejected) :
- T. s. strepsiceros – southern parts of the range from southern Kenya to Namibia, Botswana, and South Africa
- T. s. chora – northeastern Africa from northern Kenya through Ethiopia to eastern Sudan, Somalia, and Eritrea
- T. s. cottoni – Chad and western Sudan

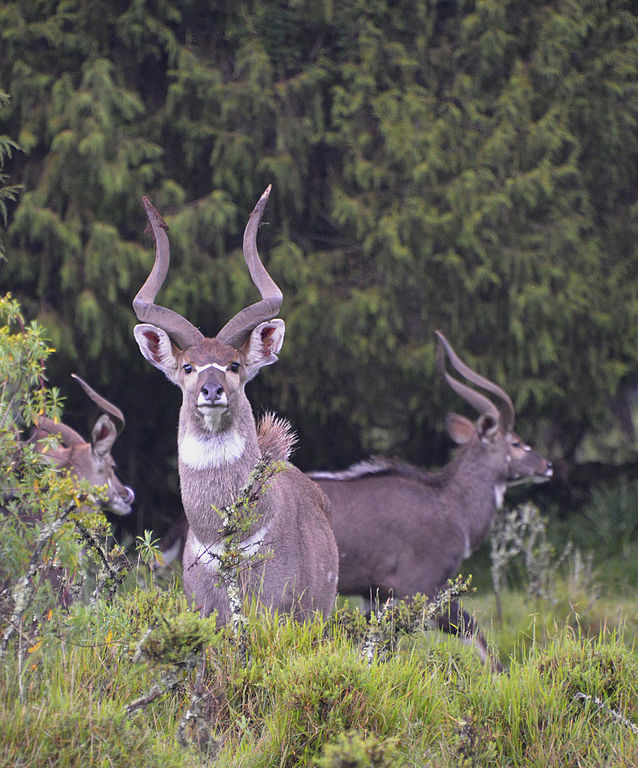
Lesser Kudu
The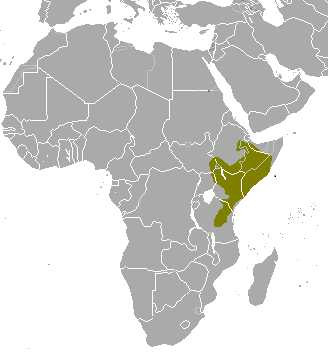 lesser kudu is a medium-sized bushland antelope found in East Africa. It was first scientifically described by English zoologist Edward Blyth (1869).It stands around 90 cm at the shoulder and weigh from 45 to 80 kg. They are generally solitary, territorial browsers.
lesser kudu is a medium-sized bushland antelope found in East Africa. It was first scientifically described by English zoologist Edward Blyth (1869).It stands around 90 cm at the shoulder and weigh from 45 to 80 kg. They are generally solitary, territorial browsers.
While currently rated not threatened, its population is decreasing. It currently stands at 100,000, but it is loosing territory to humans
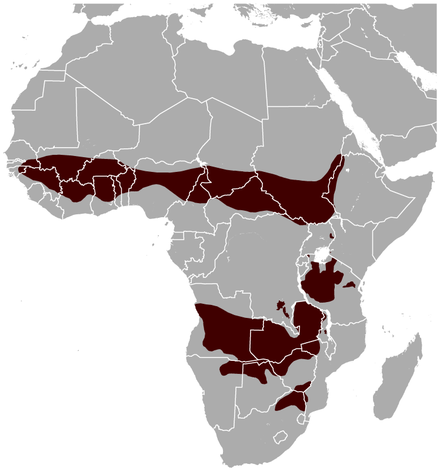
Common Bongo (and mountain Bongo)
 The bongo is a large, mostly nocturnal, forest-dwelling antelope, native to sub-Saharan Africa. Bongos are characterised by a striking reddish-brown coat, black and white markings, white-yellow stripes, and long slightly spiralled horns. It is the only member of its family in which both sexes have horns. Bongos have a complex social interaction and are found in African dense forest mosaics. They are the third-largest antelope in the world.
The bongo is a large, mostly nocturnal, forest-dwelling antelope, native to sub-Saharan Africa. Bongos are characterised by a striking reddish-brown coat, black and white markings, white-yellow stripes, and long slightly spiralled horns. It is the only member of its family in which both sexes have horns. Bongos have a complex social interaction and are found in African dense forest mosaics. They are the third-largest antelope in the world.
The Common (western or lowland bongo), faces an ongoing population decline, and the IUCN considers it to be Near Threatened.
The mountain bongo (or eastern) of Kenya, has a coat even more vibrant than the common version. The mountain bongo is only found in the wild in a few mountain regions of central Kenya. This bongo is classified by the IUCN as Critically Endangered (where it breeds readily). (this is not on the map above). Only 100 live wild, split between 4 areas of Kenya

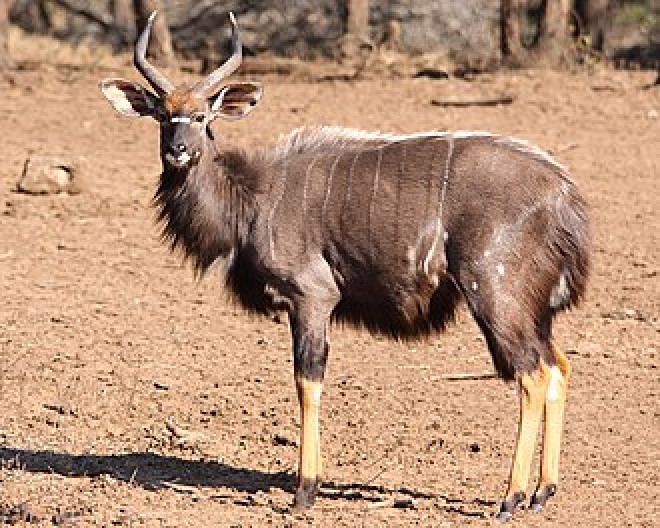
Nyala
The Nyala is a spiral horned species
found in Southern Africa. The nyala is mainly active in the early morning and the late afternoon. It generally browses during the day if temperatures are 20–30 °C and during the night in the rainy season. The nyala feeds upon foliage, fruits and grasses, and requires sufficient fresh water. It is a very shy animal, and prefers water holes to the river bank. Not territorial, they are very cautious creatures. They live in single-sex or mixed family groups of up to 10 individuals, but old males live alone. They inhabit thickets within dense and dry savanna woodlands. The main predators of the nyala are lion, leopard and African wild dog, while baboons and raptorial birds prey on juveniles. Males and females are sexually mature at 18 and 11–12 months of age respectively, though they are socially immature until five years old. They have one calf after 7 months of gestation. Its population is stable, with the greatest threat coming from habitat loss as humans expand. There are thought to be 36500 and the population is stable.
Mountain Nyala
The mountain Nyala ( also known as the Balbok) is a large antelope found in high altitude woodlands in just a small part of central Ethiopia. The coat is grey to brown, marked with two to five poorly defined white strips extending from the back to the underside, and a row of six to ten white spots. White markings are present on the face, throat and legs as well. Males have a short dark erect crest, about 10 cm (3.9 in) high, running along the middle of the back. Only males possess horns.
also known as the Balbok) is a large antelope found in high altitude woodlands in just a small part of central Ethiopia. The coat is grey to brown, marked with two to five poorly defined white strips extending from the back to the underside, and a row of six to ten white spots. White markings are present on the face, throat and legs as well. Males have a short dark erect crest, about 10 cm (3.9 in) high, running along the middle of the back. Only males possess horns.
The mountain nyala are shy and elusive towards human beings. They form small temporary herds. Males are not territorial. Primarily a browser. They will grazing occasionally. Males and females are sexually mature at 2 years old.. Gestation lasts for eight to nine months, after which a single calf is born. The lifespan of a mountain nyala is around 15 to 20 years.
Found in mountain woodland -between 3000m and 4000m. Human settlement and large livestock population have forced the animal to occupy heath forests at an altitude of above 3,400 m (11,200 ft). Mountain nyala are endemic to the Ethiopian highlands east of the Rift Valley. As much as half of the population live within 200 square km (77 sq mi) area of Gaysay, in the northern part of the Bale Mountains National Park. The mountain nyala has been classified under the Endangered category of the (IUCN). Their influence on Ethiopian culture is notable, with the mountain nyala being featured on the obverse of Ethiopian ten cents coins.

Situnga Antelope

The sitatunga (or marshbuck)is a  swamp-dwelling medium-sized antelope found throughout central Africa (see the map to the right. The sitatunga is mostly confined to swampy and marshy habitats. Here they occur in tall and dense vegetation as well as seasonal swamps, marshy clearings in forests, riparian thickets and mangrove swamps.
swamp-dwelling medium-sized antelope found throughout central Africa (see the map to the right. The sitatunga is mostly confined to swampy and marshy habitats. Here they occur in tall and dense vegetation as well as seasonal swamps, marshy clearings in forests, riparian thickets and mangrove swamps.
The scientific name of the sitatunga is Tragelaphus spekii. The species was first described by the English explorer John Hanning Speke in 1863.
It is listed as least concern with 170,000-200,000, and are found in 25 countries. However 40% live outside reserves, so the situation could get worse fast.
Note: these animals have been dealt with in less detail than others. Should you be interested in finding out if I have written on these animals or what exactly I said, you can find a list of articles about each below its information.








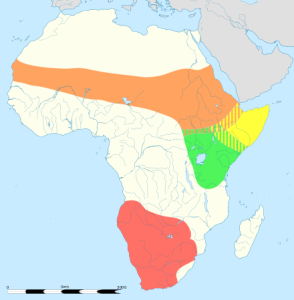 This is a map of the different Ostrich species and subspecies range
This is a map of the different Ostrich species and subspecies range









 The
The 
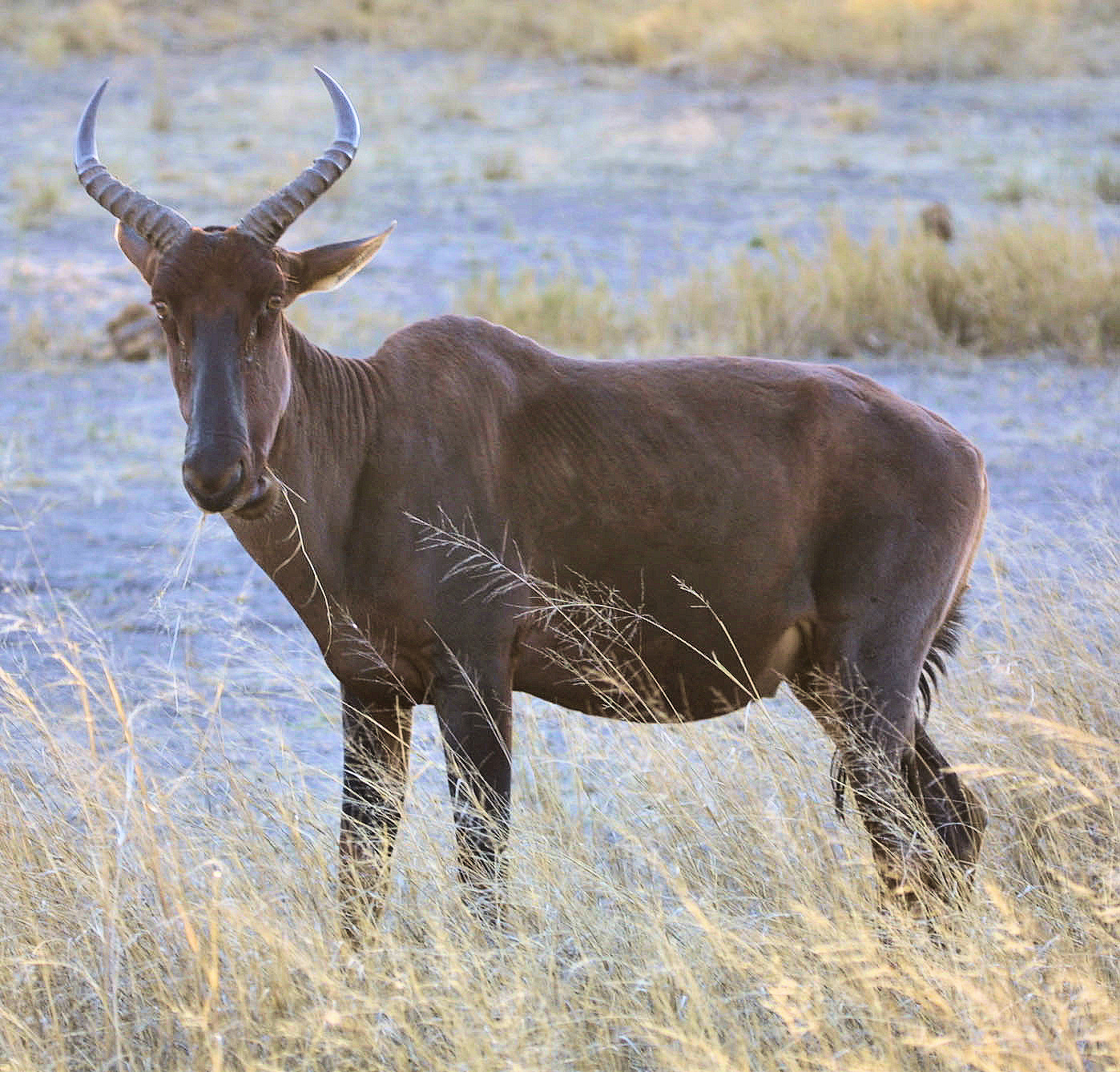
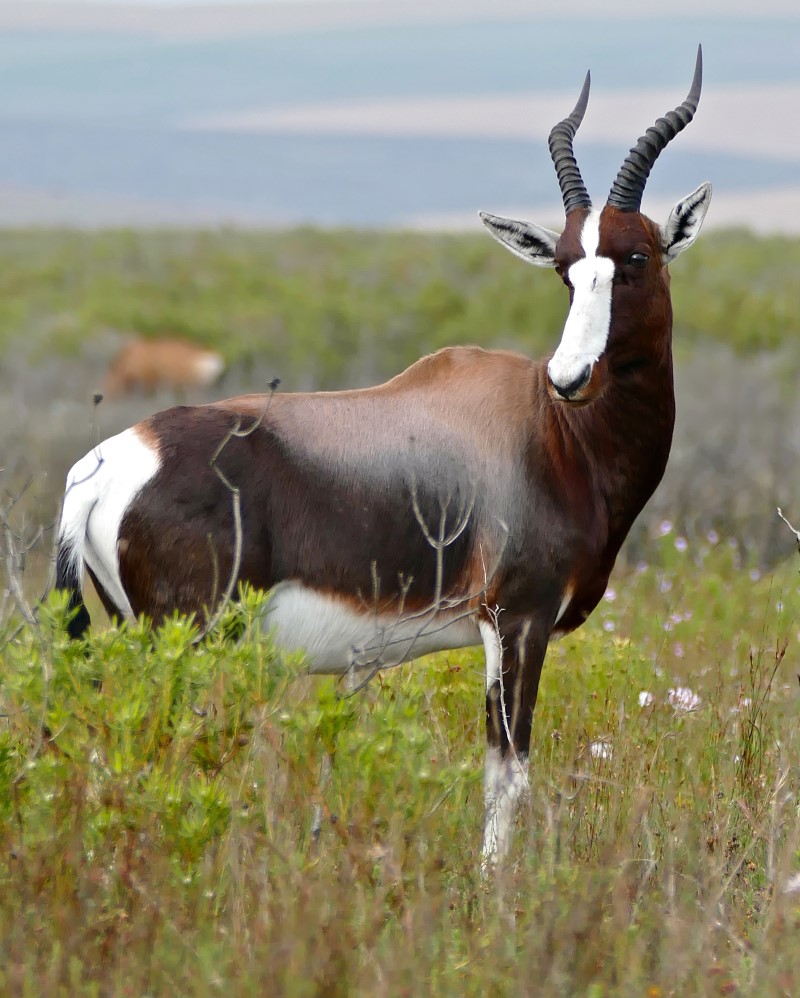




 many as 70 subspecies, local variants and similar have been suggested, however there is only one currently recognized species.
many as 70 subspecies, local variants and similar have been suggested, however there is only one currently recognized species. common wildebeest, white-bearded gnu or brindled gnu.
common wildebeest, white-bearded gnu or brindled gnu.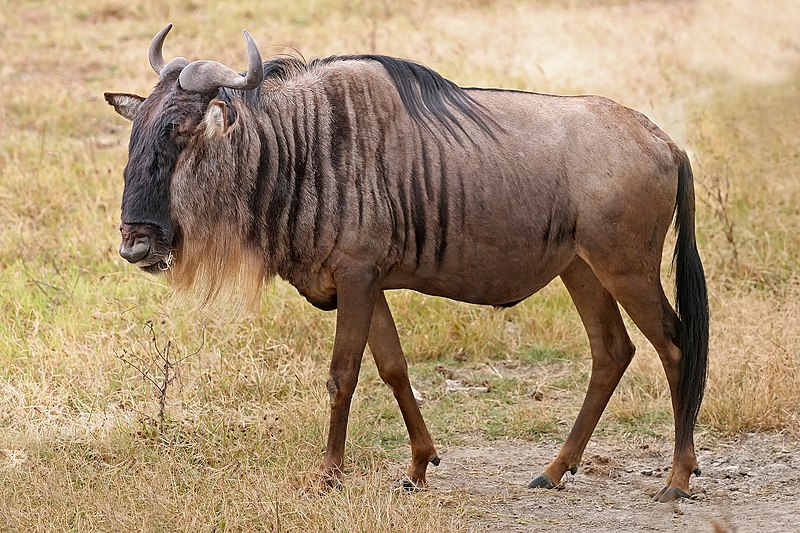
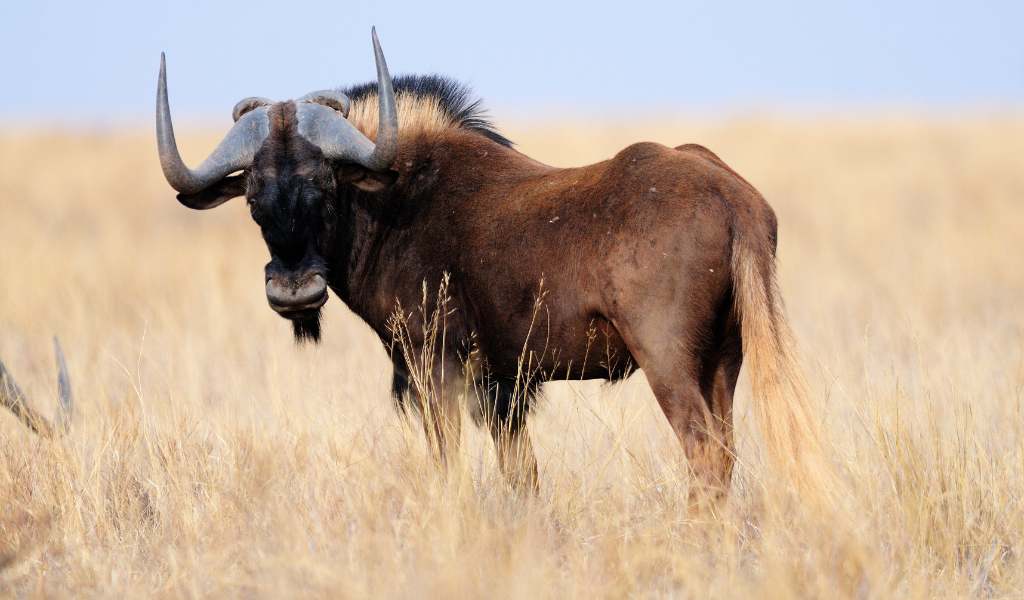
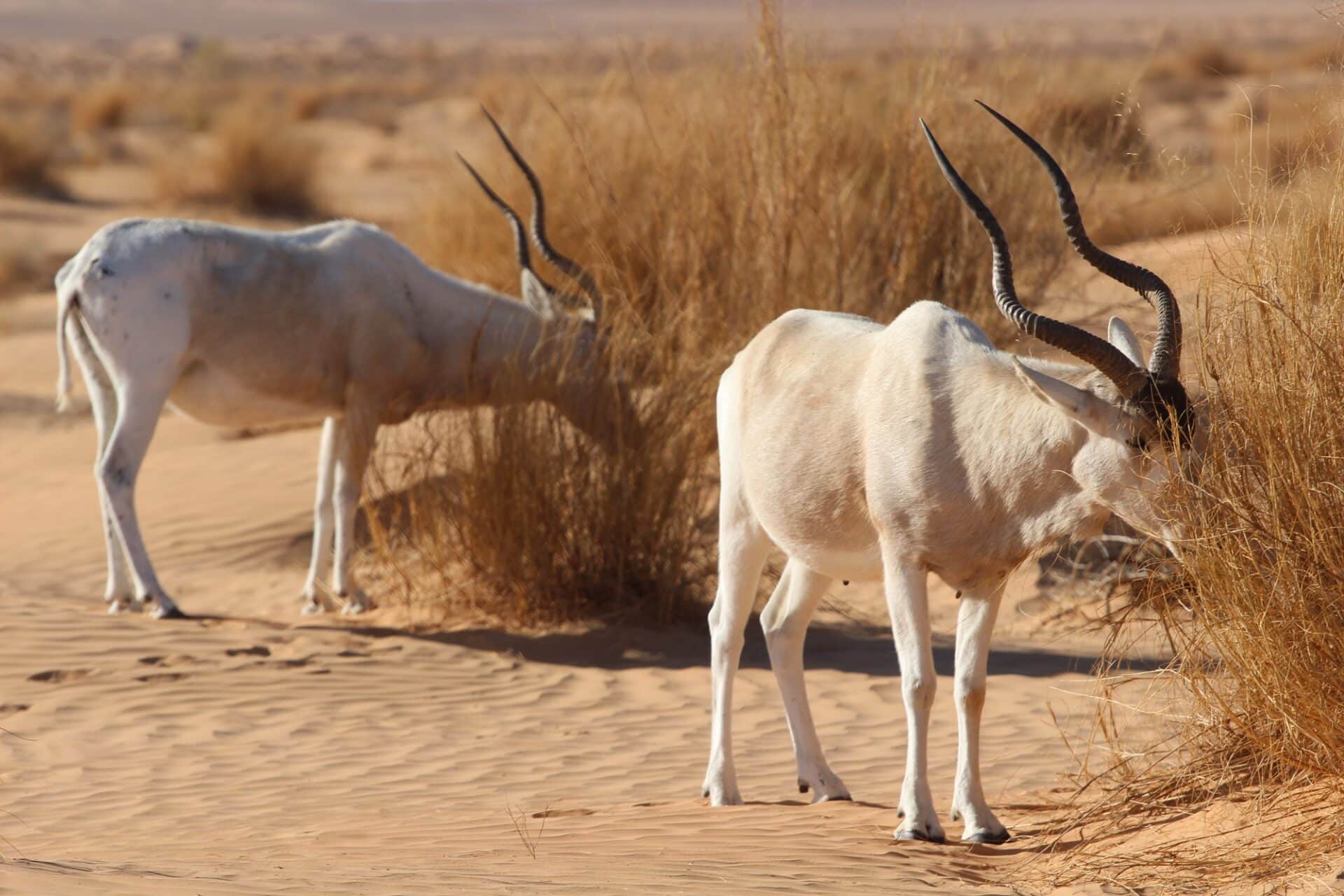






 The gemsbok or South African oryx, is a large antelope in the genus Oryx. It is endemic to the dry and barren regions of Botswana, Namibia, South Africa and (parts of) Zimbabwe, mainly inhabiting the Kalahari and Namib Deserts, areas in which it is supremely adapted for survival. Previously, some sources classified the related East African oryx, or beisa oryx, as a subspecies.
The gemsbok or South African oryx, is a large antelope in the genus Oryx. It is endemic to the dry and barren regions of Botswana, Namibia, South Africa and (parts of) Zimbabwe, mainly inhabiting the Kalahari and Namib Deserts, areas in which it is supremely adapted for survival. Previously, some sources classified the related East African oryx, or beisa oryx, as a subspecies.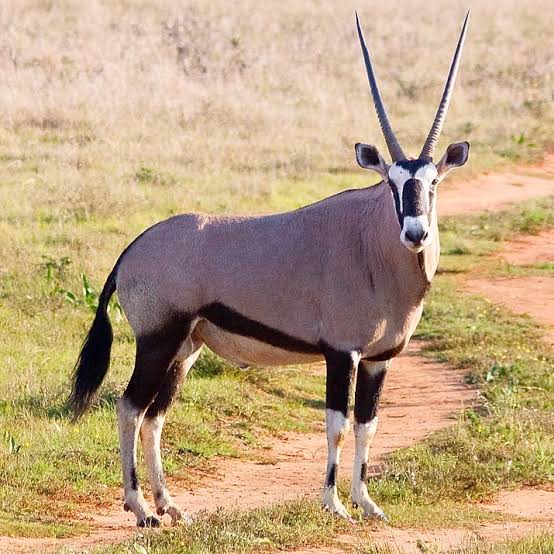
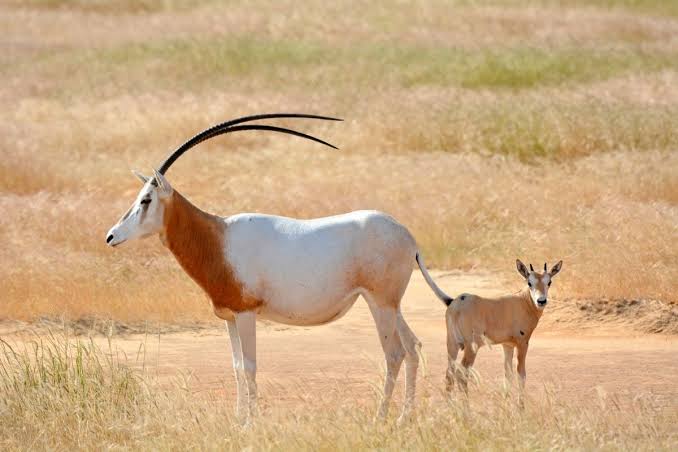



 Impala
Impala antelope, species with a handful of small populations acros central and western north Africa. It lives in the Sahara and the Sahel desert.
antelope, species with a handful of small populations acros central and western north Africa. It lives in the Sahara and the Sahel desert.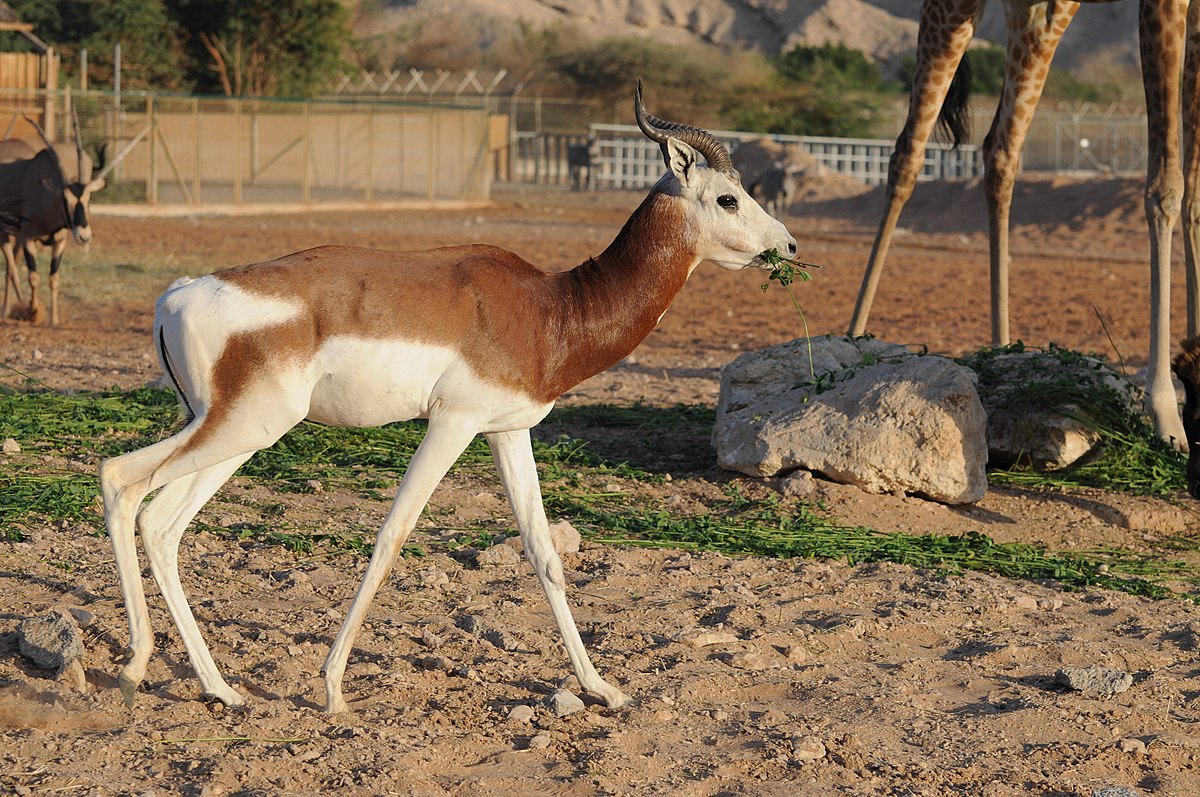 

 The gerenuk is an odd species, which in appearance looks like a cross between an impala and a giraffe. They increase this effect, by standing on their hind legs while they eat. A herd, eating in this way is quite a weird sight.
The gerenuk is an odd species, which in appearance looks like a cross between an impala and a giraffe. They increase this effect, by standing on their hind legs while they eat. A herd, eating in this way is quite a weird sight.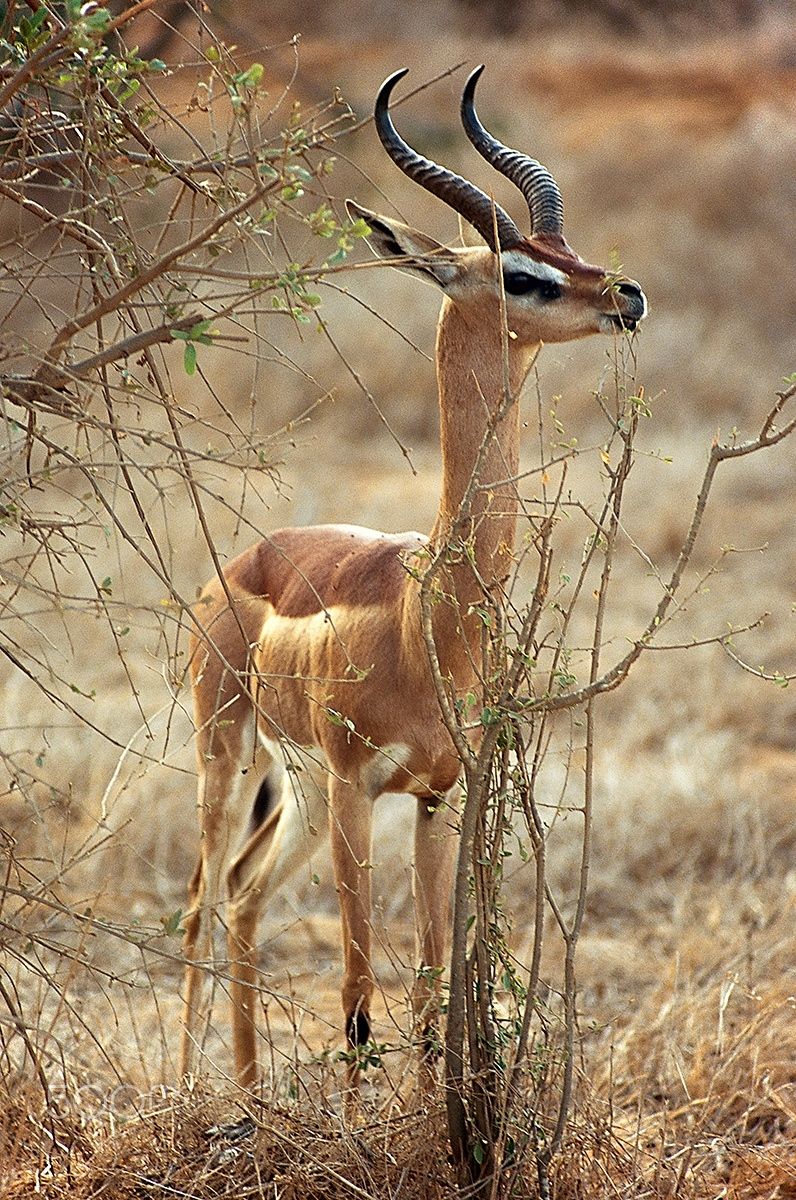




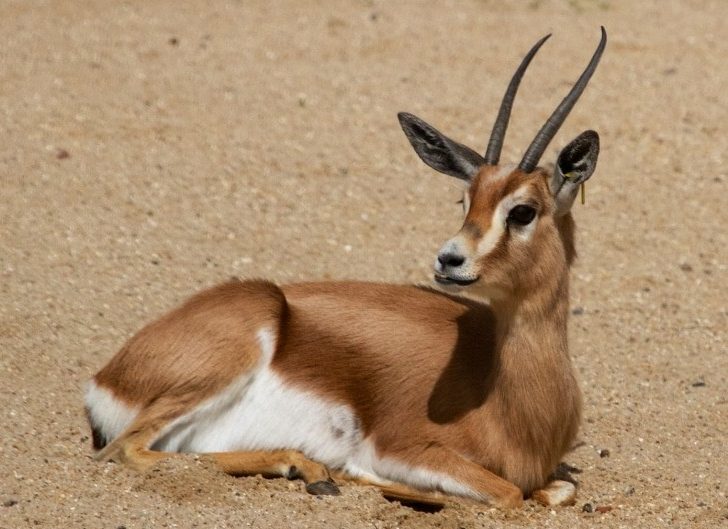
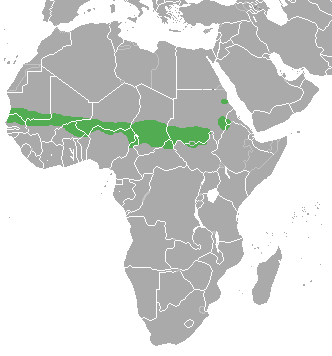 The red-fronted Gazelle is found in a wide but uneven band across the middle of Africa from Senegal to north-eastern Ethiopia. It mainly lives in the Sahel zone, a narrow cross-Africa band south of the Sahara, where it prefers arid grasslands, wooded savannas and shrubby steppes. There are some people who consider the more famous Thompson gazelle of east Africa a subspecies of the red-fronted Gazelle.
The red-fronted Gazelle is found in a wide but uneven band across the middle of Africa from Senegal to north-eastern Ethiopia. It mainly lives in the Sahel zone, a narrow cross-Africa band south of the Sahara, where it prefers arid grasslands, wooded savannas and shrubby steppes. There are some people who consider the more famous Thompson gazelle of east Africa a subspecies of the red-fronted Gazelle.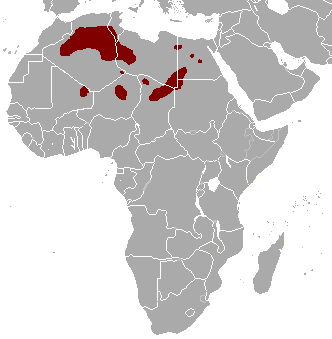 Also known as the Rhim gazelle, African sand gazelle or Loder’s gazelle while its name in Tunisia and Egypt means white gazelle, it is pale and well suited to the desert, however there are only 2500 of them left in the wild. Widely found, they have populations across They are found in Algeria, Egypt, Tunisia and Libya, and possibly Chad, Mali, Niger, and Sudan (this can be seen on the map opposite).
Also known as the Rhim gazelle, African sand gazelle or Loder’s gazelle while its name in Tunisia and Egypt means white gazelle, it is pale and well suited to the desert, however there are only 2500 of them left in the wild. Widely found, they have populations across They are found in Algeria, Egypt, Tunisia and Libya, and possibly Chad, Mali, Niger, and Sudan (this can be seen on the map opposite).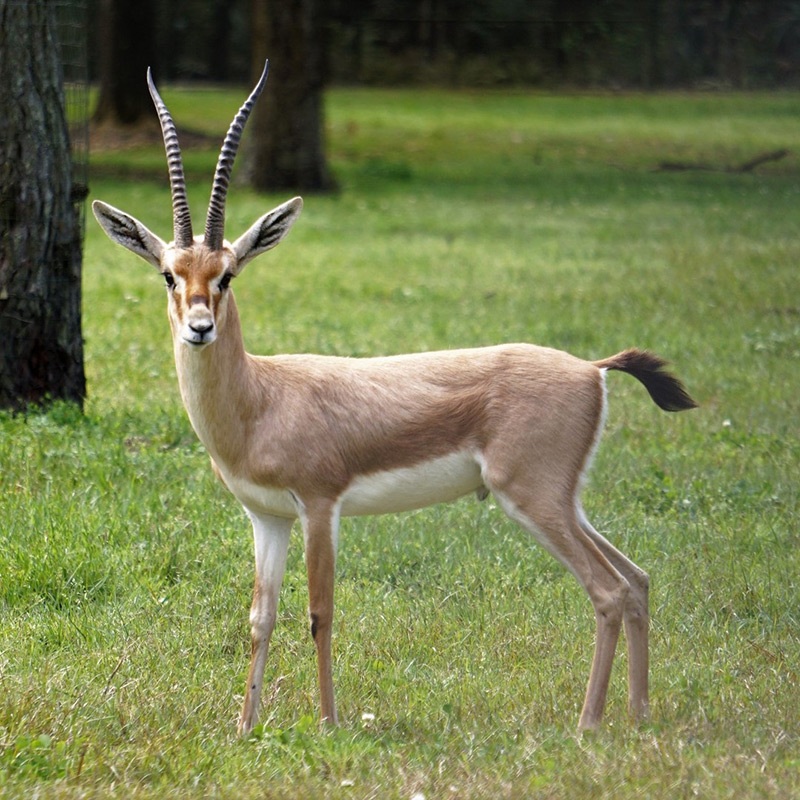
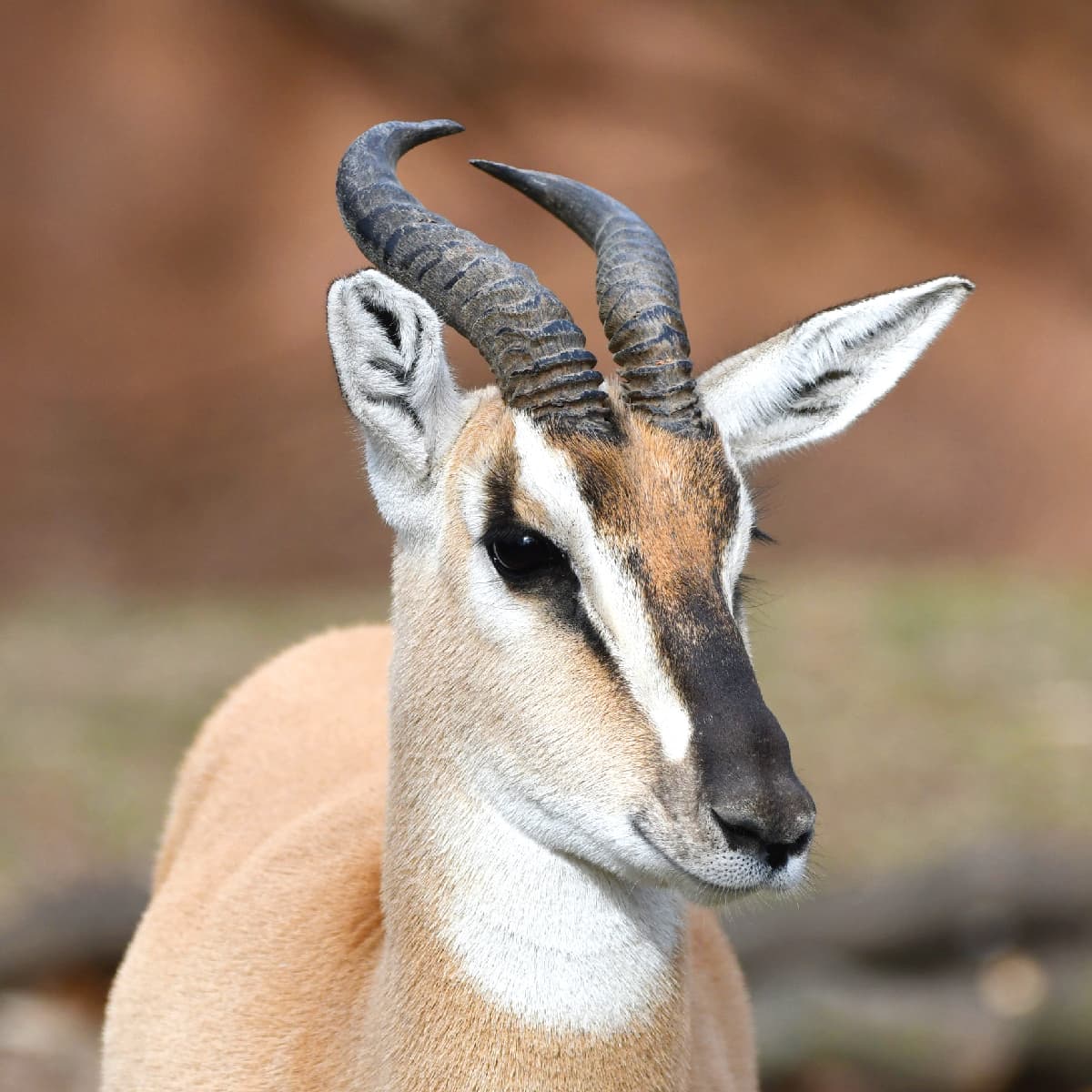

 The Speke’s gazelle is the smallest gazelle and is found in the horn of Africa (Somalia and Ethiopia – though hunted to extinction in Ethiopia). They number roughly in the low 10,000s. Unfortunately having been hunted to extinction in Ethiopia, its one remaining home is a war zone, which does not give us reassurance that it will survive into the future. While the population has increased in recent times, the animal has recently been upgraded from vulnerable to endangered. It takes its name from John Hanning Speke, who was an English explorer in central Africa. It is similar to the Dorcas gazelle, and it has been considered a subspecies at times.
The Speke’s gazelle is the smallest gazelle and is found in the horn of Africa (Somalia and Ethiopia – though hunted to extinction in Ethiopia). They number roughly in the low 10,000s. Unfortunately having been hunted to extinction in Ethiopia, its one remaining home is a war zone, which does not give us reassurance that it will survive into the future. While the population has increased in recent times, the animal has recently been upgraded from vulnerable to endangered. It takes its name from John Hanning Speke, who was an English explorer in central Africa. It is similar to the Dorcas gazelle, and it has been considered a subspecies at times.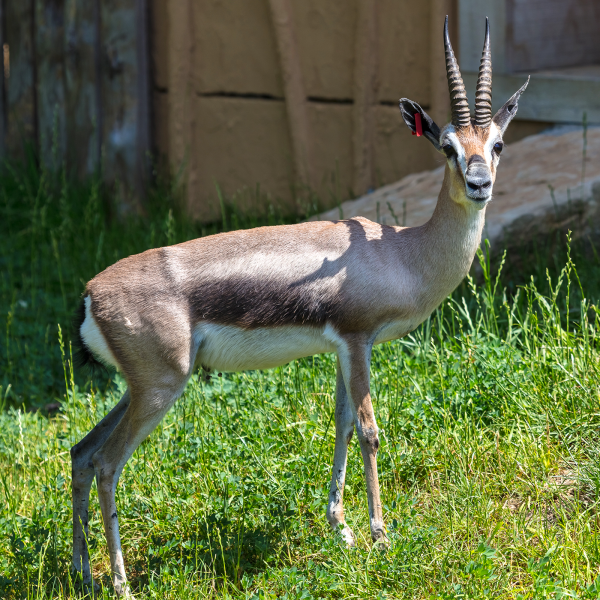

 The common name “springbok”, first recorded in 1775, comes from the Afrikaans words spring (“jump”) and bok (“antelope” or “goat”). It is only found in South Africa and the south west (including Namibia and southern Botswana and parts of Angola)
The common name “springbok”, first recorded in 1775, comes from the Afrikaans words spring (“jump”) and bok (“antelope” or “goat”). It is only found in South Africa and the south west (including Namibia and southern Botswana and parts of Angola)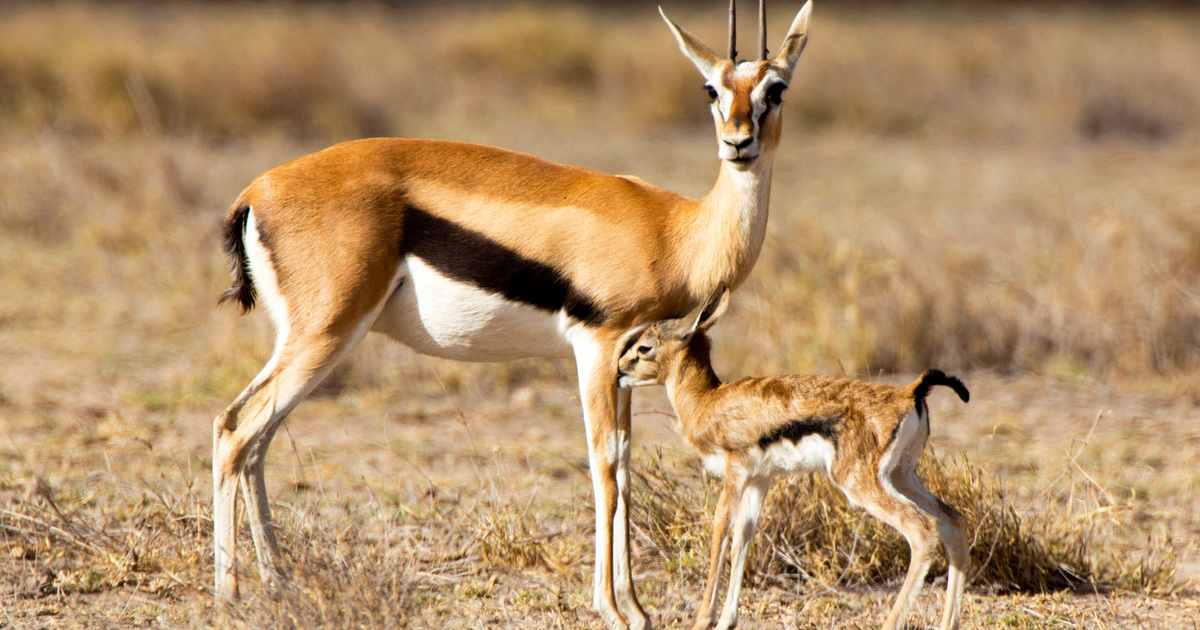

 Also known as the Clarkes gazelle, it is another species restricted to Ethiopia and Somalia. It is not a true gazelle, though it does still have markings on its legs similar to the gazelles. They are classed as vulnerable, with their biggest threat being poaching.
Also known as the Clarkes gazelle, it is another species restricted to Ethiopia and Somalia. It is not a true gazelle, though it does still have markings on its legs similar to the gazelles. They are classed as vulnerable, with their biggest threat being poaching.







 The Kirks dik-dik has two areas of habitat, oddly split, suggesting that at one point their range may have been far larger.
The Kirks dik-dik has two areas of habitat, oddly split, suggesting that at one point their range may have been far larger.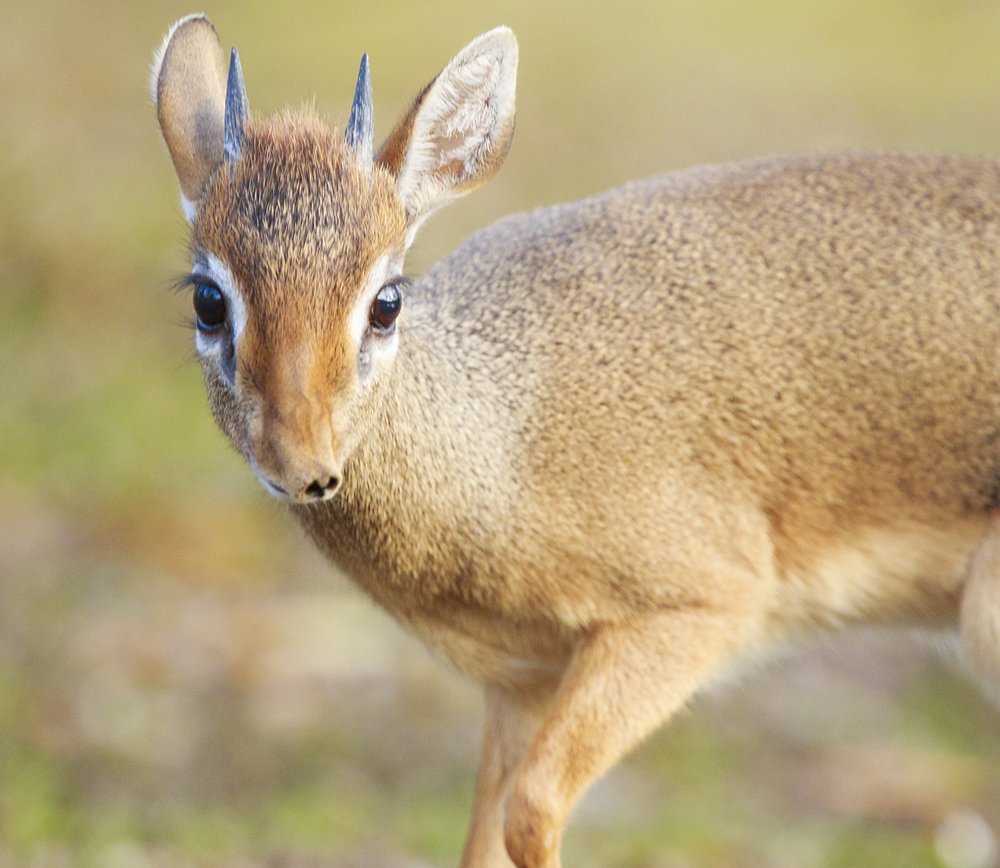

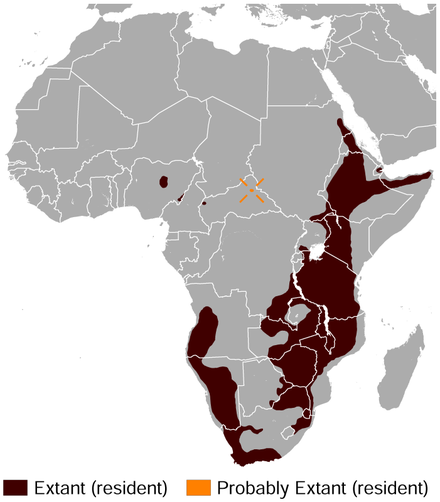 The klipspringer has a large range, being found across a large range of Africa. In places like the Kruger, virtually ever outcrop of rock has a pair of klipspringers. They are able to stand on particularly steep rocks, which allows them to get away from predators. This is important, as when there are not large enough trees available, leopards will often live in similar places.
The klipspringer has a large range, being found across a large range of Africa. In places like the Kruger, virtually ever outcrop of rock has a pair of klipspringers. They are able to stand on particularly steep rocks, which allows them to get away from predators. This is important, as when there are not large enough trees available, leopards will often live in similar places. A small antelope, though found across a wide range of habitats. They are secretive, and as such are generally seen far less often than their population would suggest. They are rarely seen in the Kruger, but overall are not doing badly.
A small antelope, though found across a wide range of habitats. They are secretive, and as such are generally seen far less often than their population would suggest. They are rarely seen in the Kruger, but overall are not doing badly.




 The Sharpe’s Grysbok, is another small antelope that is found in the east of southern Africa (its most southerly point is the northern Kruger. As a small species, however, it is another antelope that can regularly pass without notice.
The Sharpe’s Grysbok, is another small antelope that is found in the east of southern Africa (its most southerly point is the northern Kruger. As a small species, however, it is another antelope that can regularly pass without notice. The steenbok (also known as steinbuck or steinbok) is a small species of antelope found in the southern and eastern Africa. Its closest relatives are the dik-diks and gazelles.
The steenbok (also known as steinbuck or steinbok) is a small species of antelope found in the southern and eastern Africa. Its closest relatives are the dik-diks and gazelles.





 Also known as Nunga, and is found in Kenya and on the island of Zanzibar. It may be a subspecies of the red, Harvey’s, or Peters’s duiker or a hybrid of a combination of these – but is named after W Mansfield Aders – a zoologist with the Zanzibar government service. It is small, only standing 30cm at the shoulder, and weigh between 75.-12kg (the heaviest is in Zanzibar).
Also known as Nunga, and is found in Kenya and on the island of Zanzibar. It may be a subspecies of the red, Harvey’s, or Peters’s duiker or a hybrid of a combination of these – but is named after W Mansfield Aders – a zoologist with the Zanzibar government service. It is small, only standing 30cm at the shoulder, and weigh between 75.-12kg (the heaviest is in Zanzibar).
 The black duiker is another species found in the rainforests of west Africa. It is estimated that there are 100,000 of this species in the wild, though how much faith can be placed in this number, is I think an important question. Standing roughly 50cm tall, and weighing 15-20kg.
The black duiker is another species found in the rainforests of west Africa. It is estimated that there are 100,000 of this species in the wild, though how much faith can be placed in this number, is I think an important question. Standing roughly 50cm tall, and weighing 15-20kg.
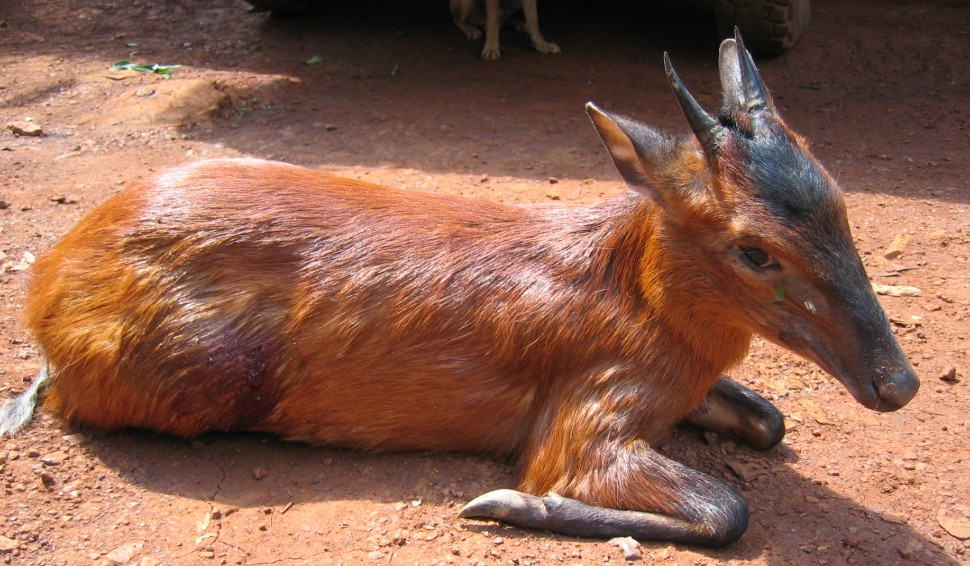

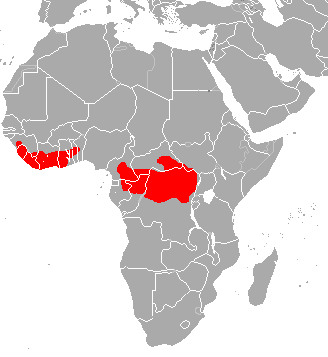
 The black-fronted duiker is found in central and west-central Africa, with an isolated population in the Niger Delta in eastern Nigeria and then from southern Cameroon east to western Kenya and south to northern Angola, and occurs in montane, lowland, and swamp forests, from near sea level up to an altitude of 3,500m. It is frequently recorded in wetter areas such as marshes or on the margins of rivers or streams.
The black-fronted duiker is found in central and west-central Africa, with an isolated population in the Niger Delta in eastern Nigeria and then from southern Cameroon east to western Kenya and south to northern Angola, and occurs in montane, lowland, and swamp forests, from near sea level up to an altitude of 3,500m. It is frequently recorded in wetter areas such as marshes or on the margins of rivers or streams.  The blue duiker is found in a wide range of habitats. While much of its range falls in countries like the Democratic republic of the Congo (and thereby makes the blue duiker a rainforest species) they also live in large parts of eastern Tanzania, and places like South Africa where there is no rainforest. The habitat consists of a variety of forests, including old-growth, secondary, and gallery forests.
The blue duiker is found in a wide range of habitats. While much of its range falls in countries like the Democratic republic of the Congo (and thereby makes the blue duiker a rainforest species) they also live in large parts of eastern Tanzania, and places like South Africa where there is no rainforest. The habitat consists of a variety of forests, including old-growth, secondary, and gallery forests.



 Jentink’s duiker also known as gidi-gidi in Krio and kaikulowulei in Mende, is a forest-dwelling duiker found in the southern parts of Liberia, southwestern Côte d’Ivoire, and scattered enclaves in Sierra Leone. It is named in honor of Fredericus Anna Jentink.
Jentink’s duiker also known as gidi-gidi in Krio and kaikulowulei in Mende, is a forest-dwelling duiker found in the southern parts of Liberia, southwestern Côte d’Ivoire, and scattered enclaves in Sierra Leone. It is named in honor of Fredericus Anna Jentink. A small antelope found in west Africa, first described in 1827 by Charles Hamilton-Smith, it shares a genus with the blue duiker and the Walters duiker
A small antelope found in west Africa, first described in 1827 by Charles Hamilton-Smith, it shares a genus with the blue duiker and the Walters duiker
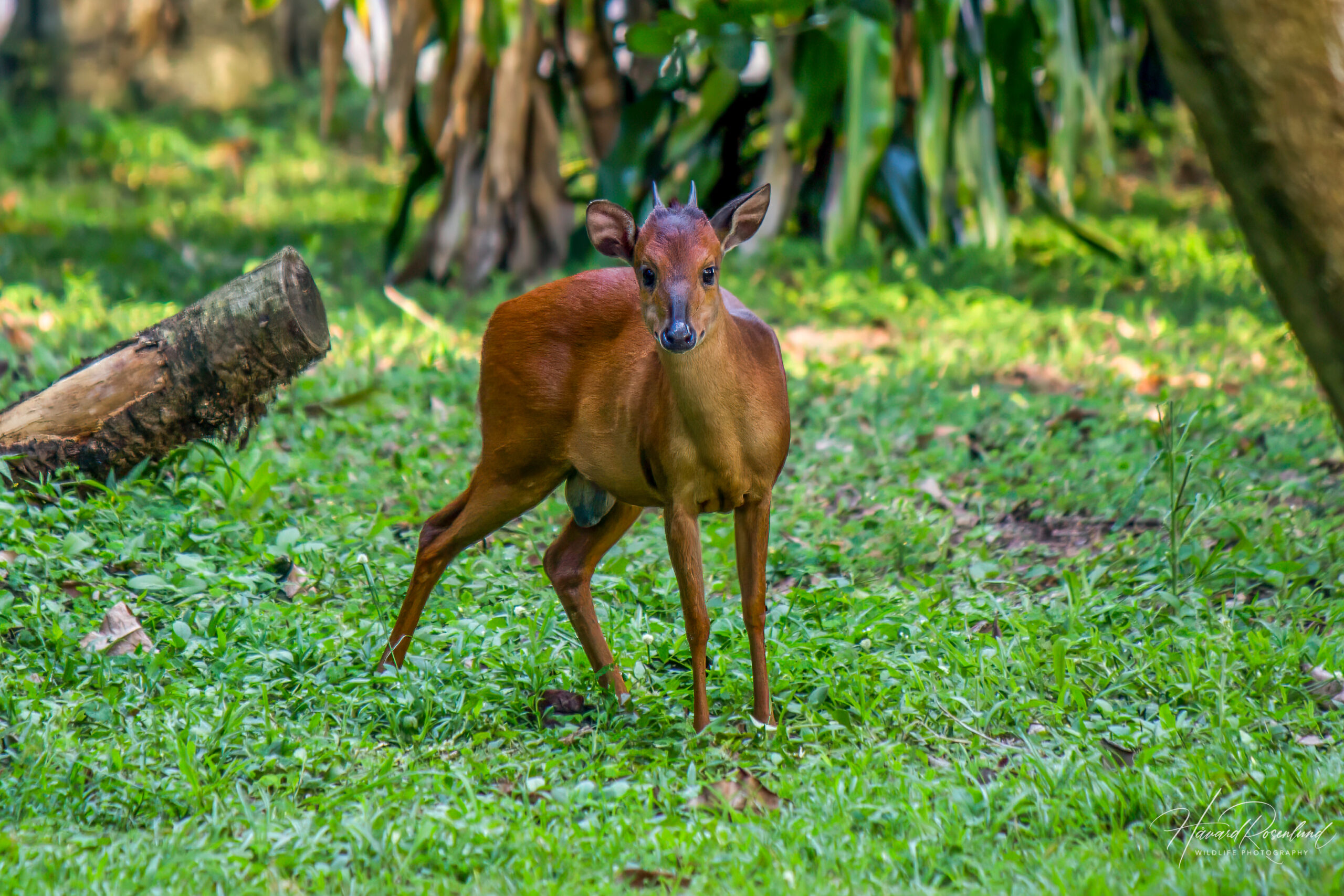

 Also known as Red forest duiker (as well as other mixes of these words), is very similar to the common duiker. It is very similar to the common duiker with though with a redder coat.
Also known as Red forest duiker (as well as other mixes of these words), is very similar to the common duiker. It is very similar to the common duiker with though with a redder coat.


 Measuring 34-37cm tall and 12-14kg, this small species of antelope. They are classed as least concern and have a large range with around 170,000 living in the wild. It has often done well out of deforestation, as it has often expanded its range during these times.
Measuring 34-37cm tall and 12-14kg, this small species of antelope. They are classed as least concern and have a large range with around 170,000 living in the wild. It has often done well out of deforestation, as it has often expanded its range during these times.
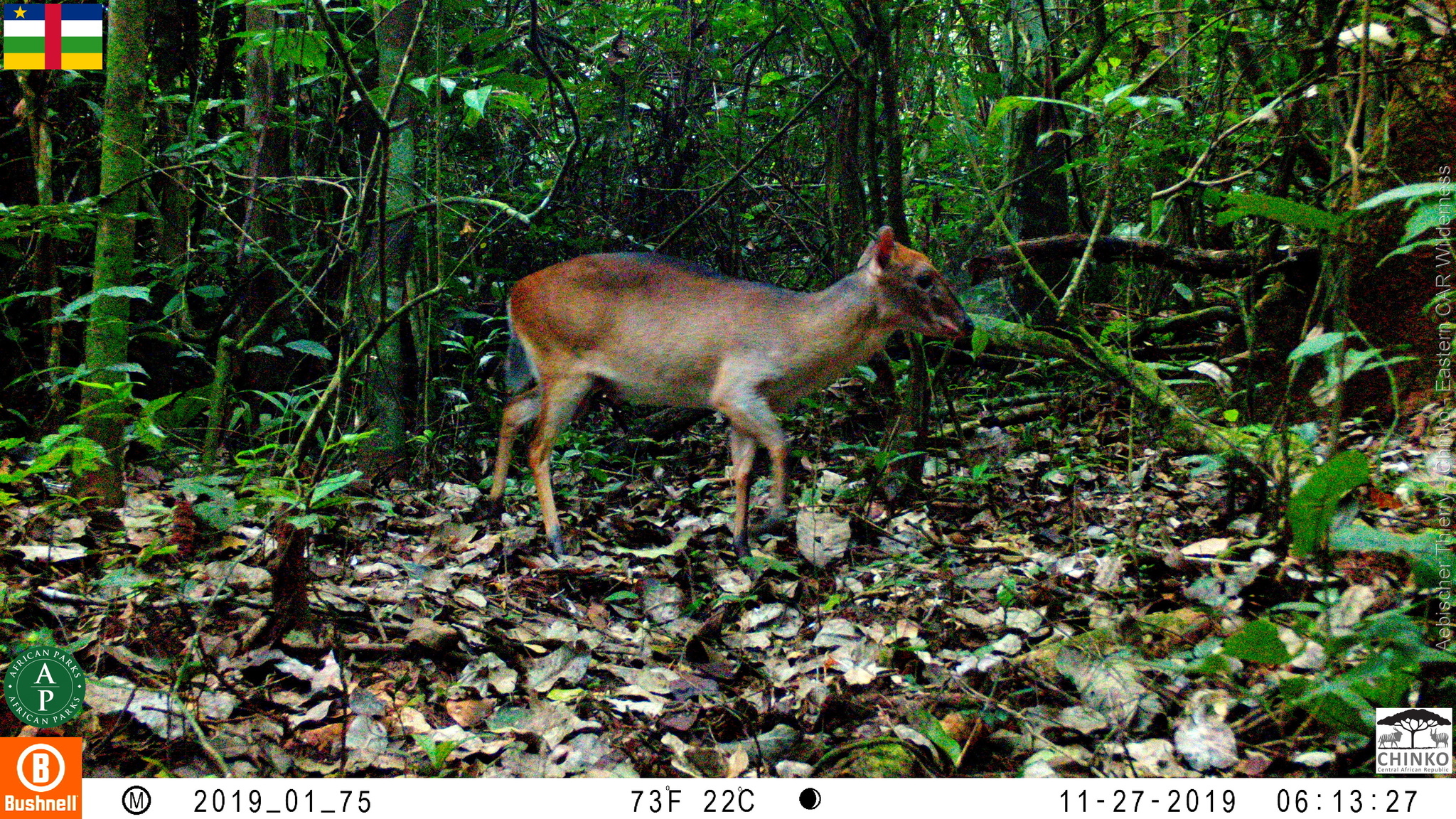

 This species range is shown on the map , and is found in Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, and Gabon, while it is likely to have been extirpated in Uganda.
This species range is shown on the map , and is found in Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, and Gabon, while it is likely to have been extirpated in Uganda. The yellow-backed duiker has a wide range of places it is found (ranging from Senegal and Gambia on the western coast, through to the Democratic Republic of the Congo to western Uganda; their distribution continues southward into Rwanda, Burundi, and most of Zambia).
The yellow-backed duiker has a wide range of places it is found (ranging from Senegal and Gambia on the western coast, through to the Democratic Republic of the Congo to western Uganda; their distribution continues southward into Rwanda, Burundi, and most of Zambia).

