Would you like to list your wildlife destination on this site?
Living alongside wildlife can be complicated. A farmer will struggle to enjoy the presence of predators, even if they have not attacked his livestock.
On this website, our aim is to allow people to benefit from wildlife that they share their land with, whether this is to bring in some extra money, or to pay for protection for livestock, or whether it is the primary use (any farmers care about the environment more than city dwellers, so our aim is to make sure that where possible protecting wildlife pays – by giving them the ability to list their land for people to see the wildlife that they farm beside). Whether you live or work in one of the worlds great wildernesses or national parks, or you own wilderness on the edge of one of these (Sabi sands, one of the oldest private reserves borders the Kruger) we want to help people find you, so that you can show them all the wonderful wildlife on your land.
There are examples of each type of page to look at. Do look at the ecosystem you are located in/by is already listed as we can add further options, but will not list ecosystems more than once.
We follow a relatively simplistic booking process, where a form on the website will generate an email booking. We can also include a calendar showing your availability.
There is a link to a form for each category, as well as a further form at the bottom of the page for any questions. This form includes the ability to submit photos of your offering and the wildlife in your vicinity (both are of importance, unless your wildlife destination is already listed) . We work on a simple pricing structure, where we charge you 10% of the cost of any booking that you recieve through us. (opens in a new tab)
Do you run a lodge or campsite within a protected area?
As you can see we have listed a number of lodges in parts of Africa, but the aim of this site was to simplify wild travel and so we are keen to work with any lodge that would like to.
In order to list your property, we will need:
- Pictures of your accommodation, with information on cost and amenities
- Information on the wilderness that surrounds your property, whether it is information on a national park or reserve. (While information on the area around where you operate is always good, should your reserve already be listed, we need less here)
- Information as to what wildlife can be seen in the area, with some good pictures.
Feel free to view our lodges and reserves currently public to see what your listing can look like. If you are particular about your branding look, we are happy to put up your listing as you would like. Fill in the form at the link below.
Fill in the form in this link to list your wild place -campsite lodge or similar
Or perhaps you share your vicinity with wildlife
Whatever the reason that you own land, it will be part of a natural ecosystem and as such you are likely to have some animals that live on it with you. This can cause complications with many land uses such as farming, where predators may eat some of your livestock.
Many people will happily pay to have a chance of seeing some of these animals that can be a complication, and by utilising these visits you can make some extra money to help offset any financial losses from predation or damage to property.
This could range from South African farmers who share their land with cheetahs, to European farmers who might share their land with bears or wolves, or perhaps simply an active badgers sett in the UK.
Alternatively, you could own a restaurant where bush babies could be seen in the evening.
The possibilities are endless.
To be listed we will need:
Photos of your land with the animal/bird in question (or information on the ecosystem in which your land sits. It is worth looking at what is already up, as we will list ecosystems only once- so if someone has already listed your ecosystem, we can simply add your wildlife opportunity below.
Details of what you are offering and where it is
- Accommodation (camping or hut etc). This is particularly important if the wildlife is nocturnal or is based in a particularly remote area
- A game drive to see the wildlife at a set time.
- A restaurant, from which wildlife can be watched. This could be anything from interesting birds, lizards or indeed perhaps a resident bush baby
- Anything else that you can think of that follows along similar lines
- Information on price
Or perhaps you run a wildlife hide of some kind
For many people the only way they can have a chance of seeing many animals, particularly nocturnal ones, is by sitting in a hide. Many of my most memorable wildlife moments have been had sitting in a wildlife hide watching something unfold in front of me. This need not be on protected land, so long as the hide is not ever used for hunting.
In order to list your hide, we will need:
- Pictures of your hide with information on cost and amenities.
- Pictures of the view people will get from the hide
- Pictures of some of the wildlife that has been photographed from the hide, as well as information on frequency and anything else of interest.
See our one example currently live
Finally, we are keen to support wildlife guides, boat trips, wildlife treks, wildlife drives & other similar ecotourism.
Even in some of the wildest places on earth, it is very easy to spend weeks there and see none of the local animals.
A wildlife guide can make a big difference. Be it a trip on a boat to sea the marine life, or a car journey into a reserve nearby.
I am aware though, how often, it is hard to connect with local guides when you are visiting an area.
As such I am keen to list local guides, and the ability to book.
To be listed, I will need:
- Some information about the wildlife you often see when you take people out, preferably with some pictures (and where)
- What services you offer (are you just a guide or can you offer a place to stay as well)
- Any other information that you would like to pass on
- Pricing
Fill in the form in this link if you are a wildlife guide and would like to list your services on our website, or you run trips to see marine wildlife, or in reserves around your home.
Below is a form, which will allow you to enter all the information that you need for your page to be built. in one of these categories please fill in the form below (we aim to be a place where the whole of the wildlife tourism industry (bar any form of hunting) can advertise). Iif we do not serve your field let us know, we can either create a new section or instead fit it into another area.
Have a look at the listings we currently have to get an idea of what your listing will look like, and what we need.




 Found in the West Indies, northern South America (including the Galápagos Islands) and the Yucatan Peninsula. It was considered cospecifc with the greater flamingo, but they are now recognized as separate species (it is also closely related to the Chilean flamingo).
Found in the West Indies, northern South America (including the Galápagos Islands) and the Yucatan Peninsula. It was considered cospecifc with the greater flamingo, but they are now recognized as separate species (it is also closely related to the Chilean flamingo).  of South America, it is in the same genus as the James Flamingo. Indeed, the Chilean Andea and James flamingo often share nesting sites and are relatively closely related.
of South America, it is in the same genus as the James Flamingo. Indeed, the Chilean Andea and James flamingo often share nesting sites and are relatively closely related. the American and greater flamingo, it is listed as near threatened in the wild with a wild population of about 200,000. Population declines are due to habitat loss and degradation, harvesting and
the American and greater flamingo, it is listed as near threatened in the wild with a wild population of about 200,000. Population declines are due to habitat loss and degradation, harvesting and 
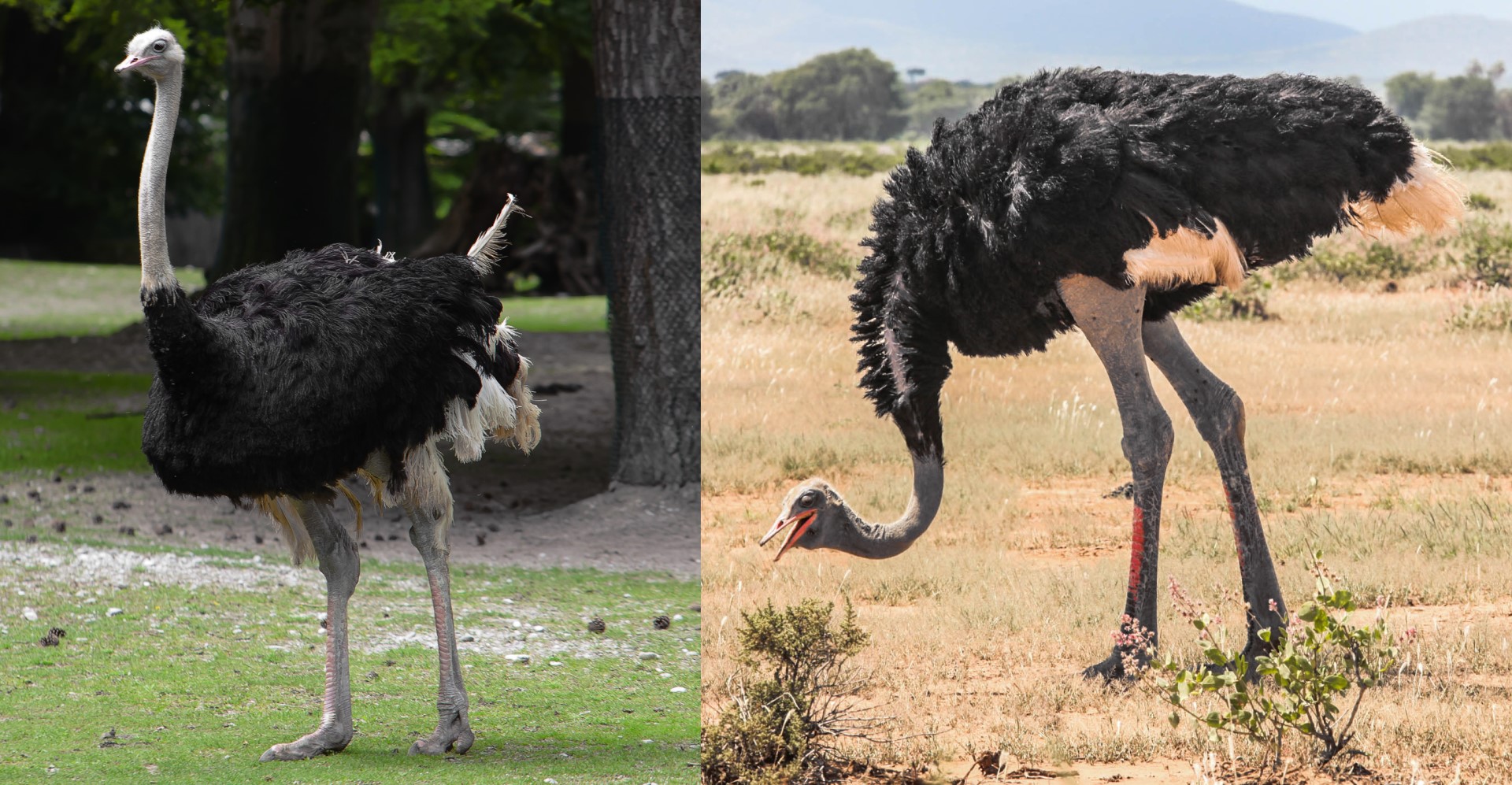


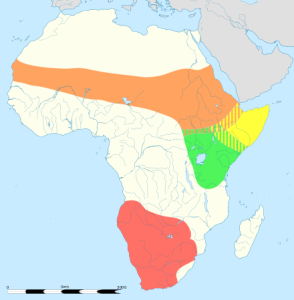 This is a map of the different Ostrich species and subspecies range
This is a map of the different Ostrich species and subspecies range