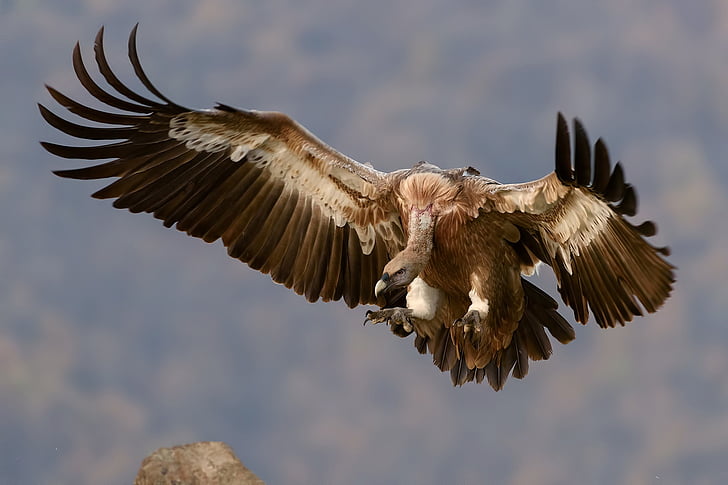
Have you heard of a pangolin? Would you recognize one? For many people, the pangolin is unfortunately known, only as a family of species, which have been poached for their scales (made of keratin, and with no medicinal basis) such that of the 8 species, half are endangered and the other half critically endangered. Click on any of the mentions of pangolin on this page to be taken to our pangolin family species page. This poaching is so extreme, that some estimate that this family of species are the most trafficked in the world.
Pangolin are very hard to take care of, which is why there are so few in zoos around the world. Indeed, the vast majority of even wildlife guides in somewhere like the Kruger have never seen a pangolin, even if they are known to exist in the park. A pangolin carers job, is to look after a pangolin, take it into the bush, and find places with many ants and termites, and generally get it ready to return to the wild.
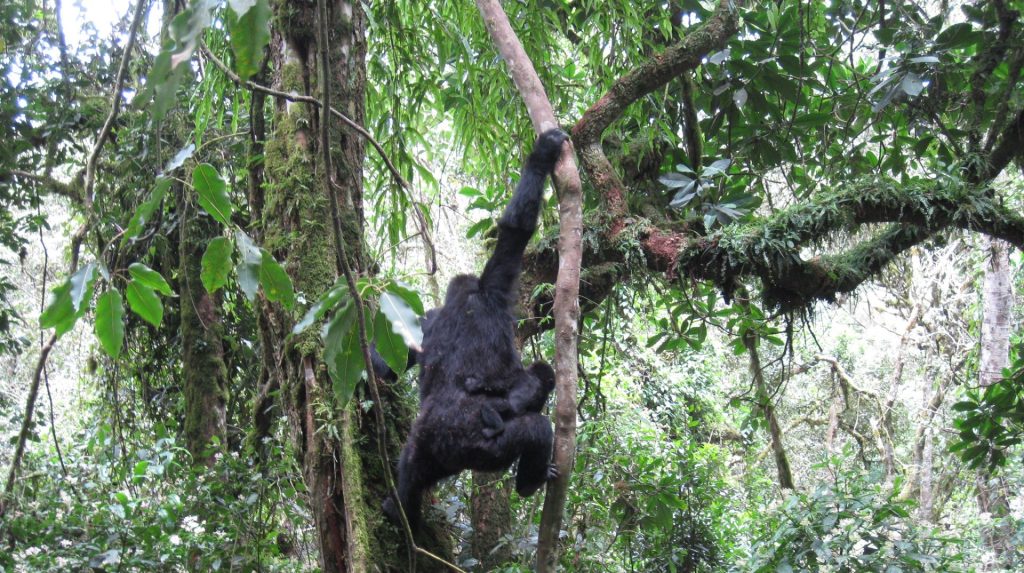
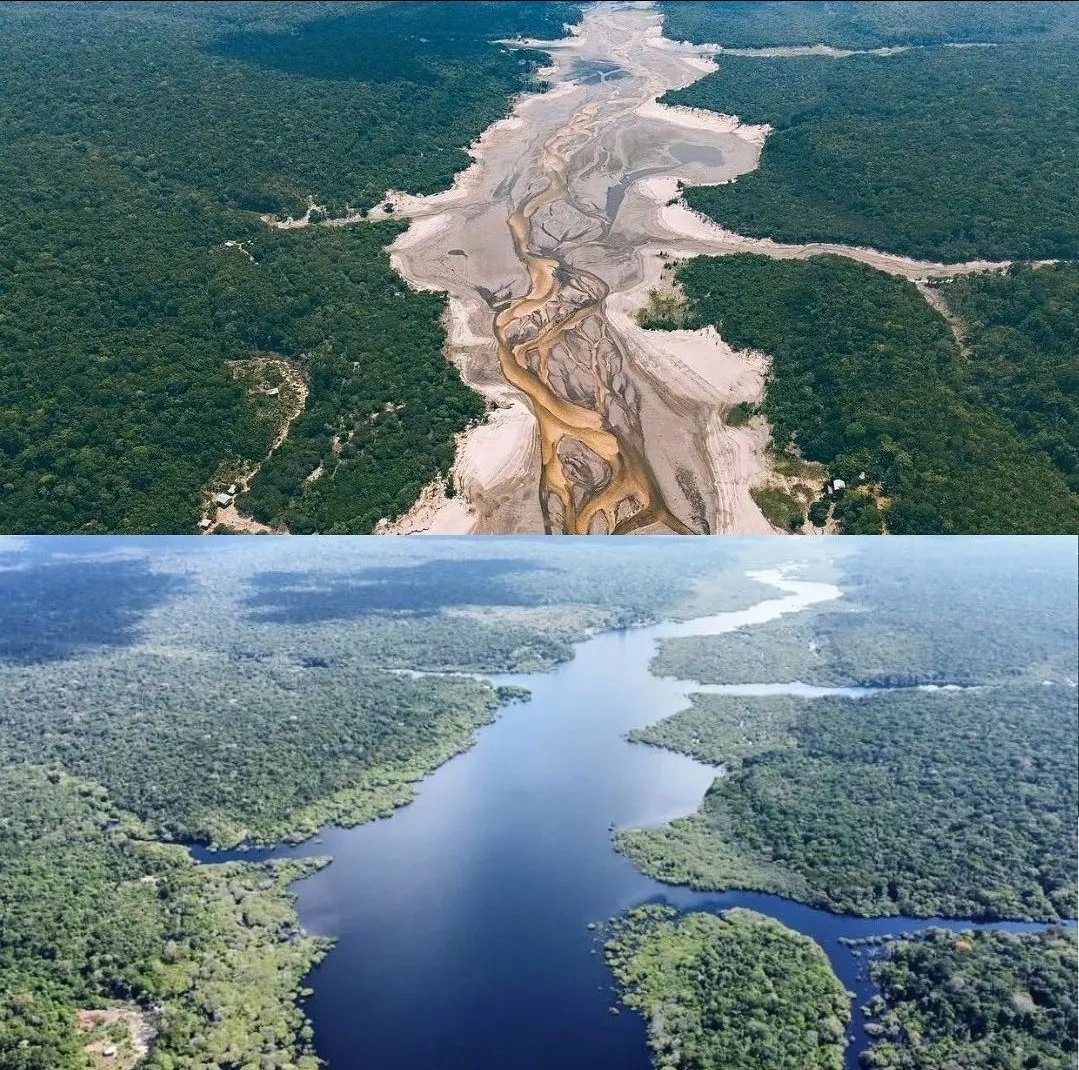
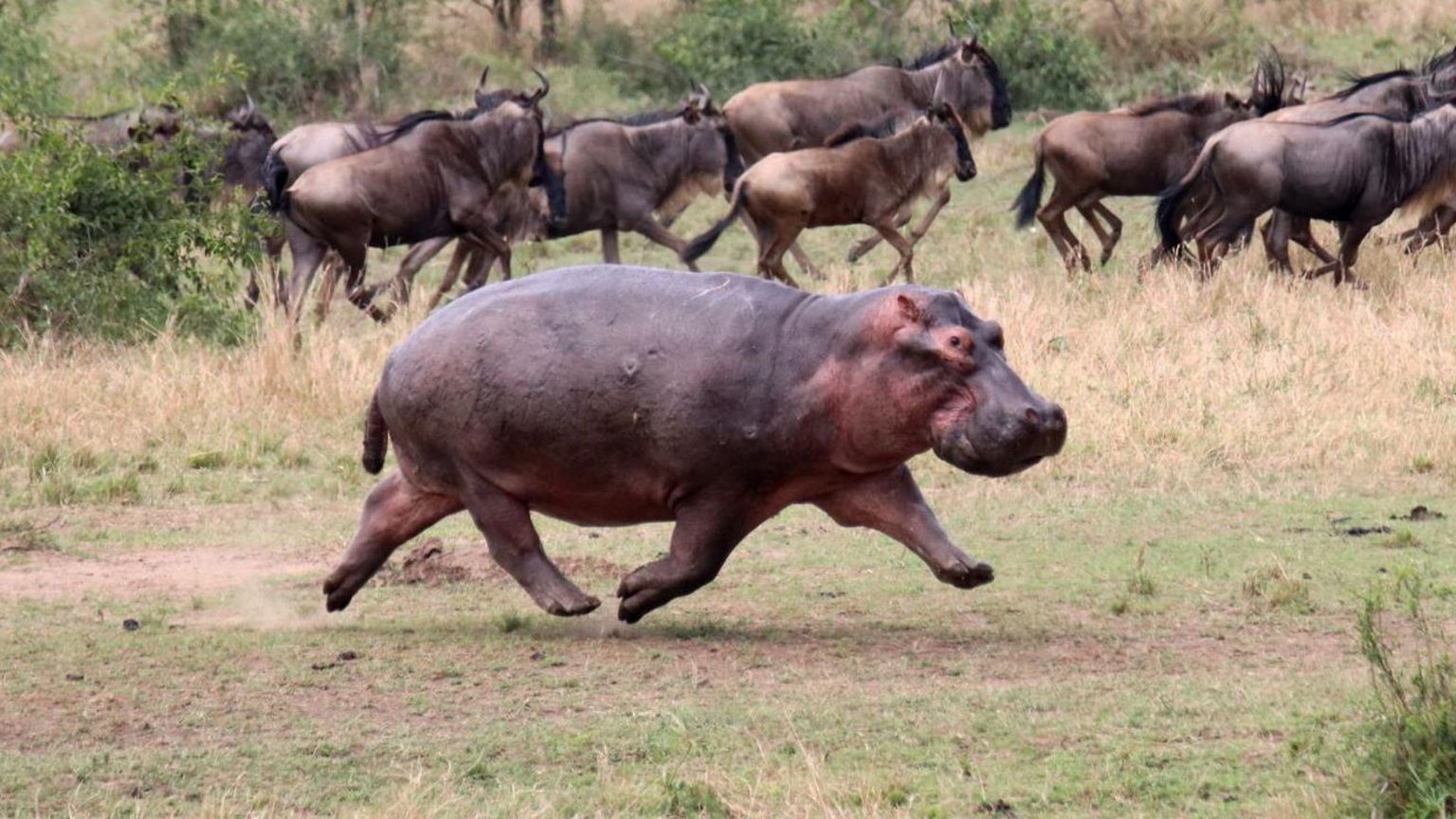






 known as
known as 
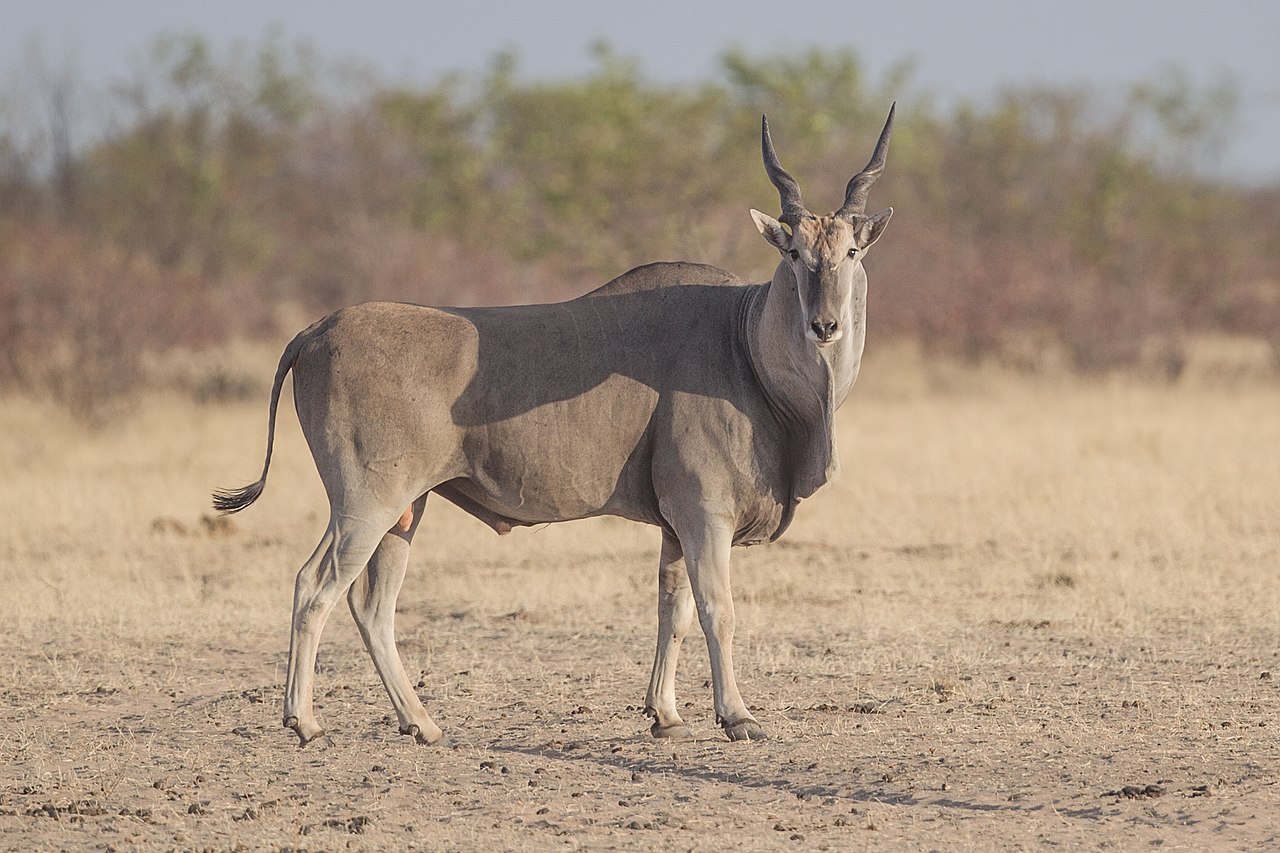
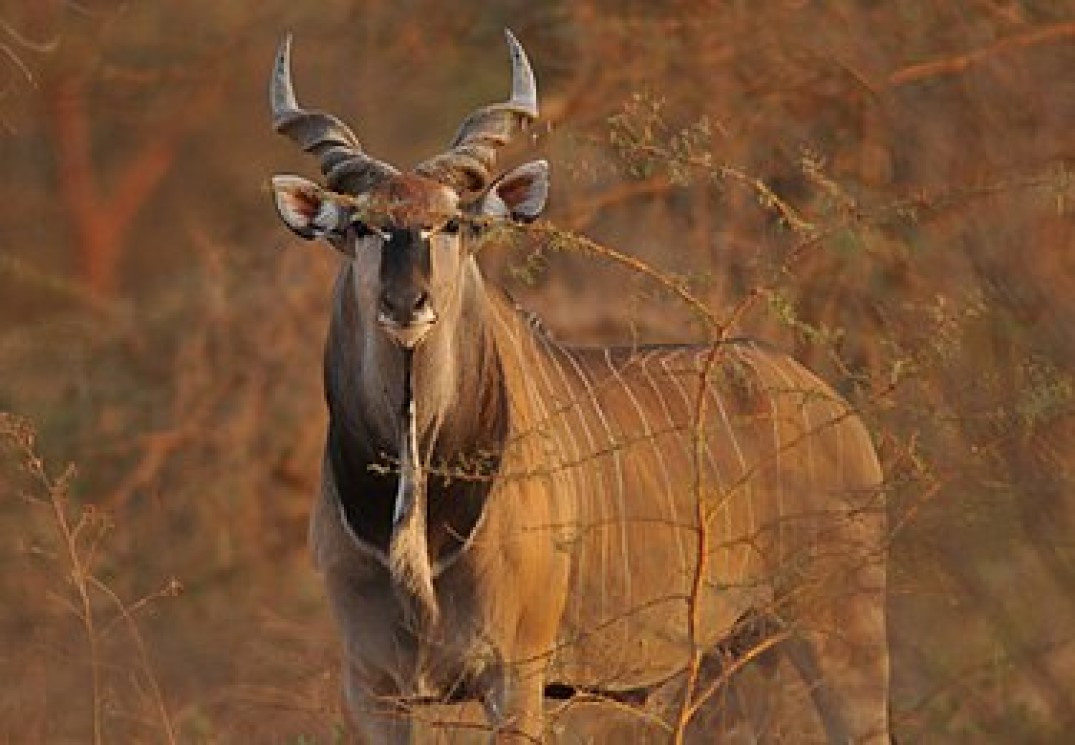





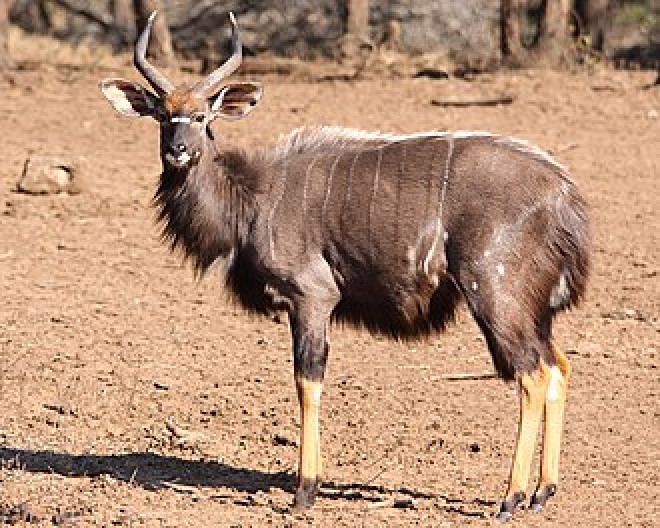
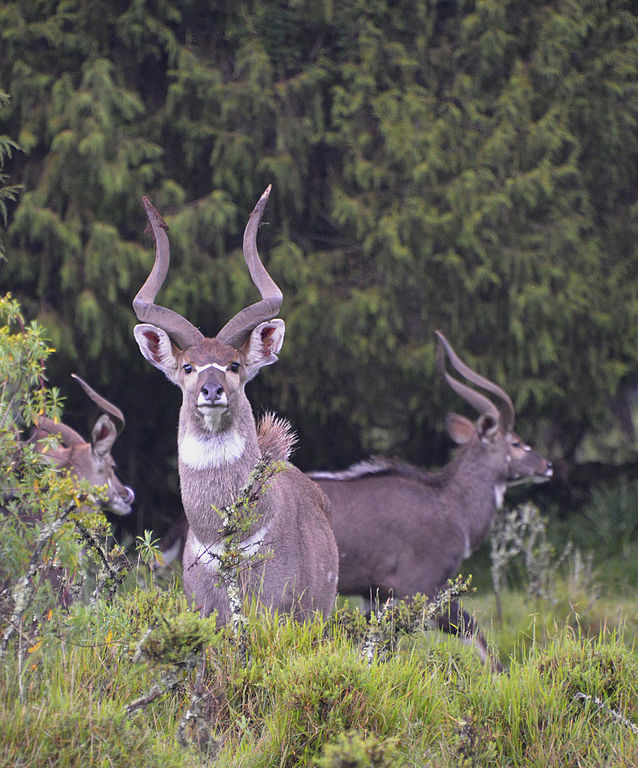
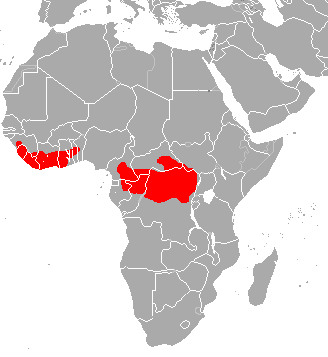 The bongo is a large, mostly nocturnal, forest-dwelling antelope, native to sub-Saharan Africa. Bongos are characterised by a striking reddish-brown coat, black and white markings, white-yellow stripes, and long slightly spiralled horns. It is the only member of its family in which both sexes have horns. Bongos have a complex social interaction and are found in African dense forest mosaics. They are the third-largest antelope in the world.
The bongo is a large, mostly nocturnal, forest-dwelling antelope, native to sub-Saharan Africa. Bongos are characterised by a striking reddish-brown coat, black and white markings, white-yellow stripes, and long slightly spiralled horns. It is the only member of its family in which both sexes have horns. Bongos have a complex social interaction and are found in African dense forest mosaics. They are the third-largest antelope in the world.





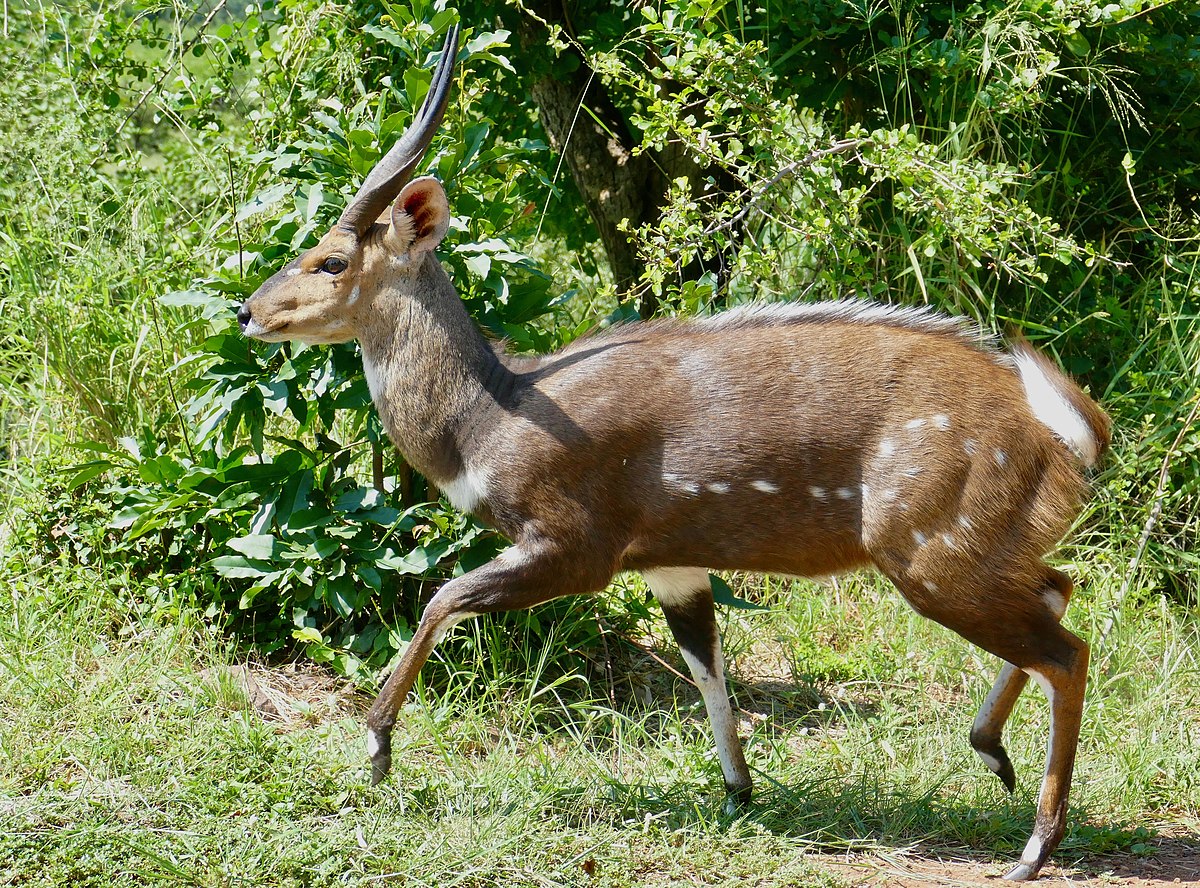
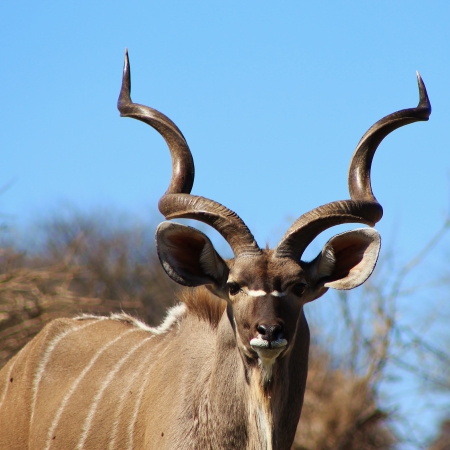
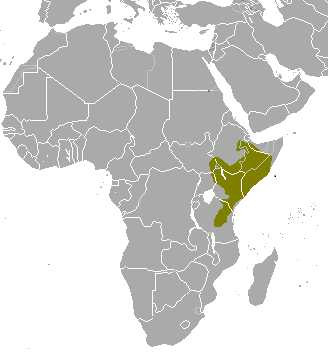
 swamp-dwelling medium-sized antelope found throughout central Africa (see the map to the right. The sitatunga is mostly confined to swampy and marshy habitats. Here they occur in tall and dense vegetation as well as seasonal swamps, marshy clearings in forests, riparian thickets and mangrove swamps.
swamp-dwelling medium-sized antelope found throughout central Africa (see the map to the right. The sitatunga is mostly confined to swampy and marshy habitats. Here they occur in tall and dense vegetation as well as seasonal swamps, marshy clearings in forests, riparian thickets and mangrove swamps.










