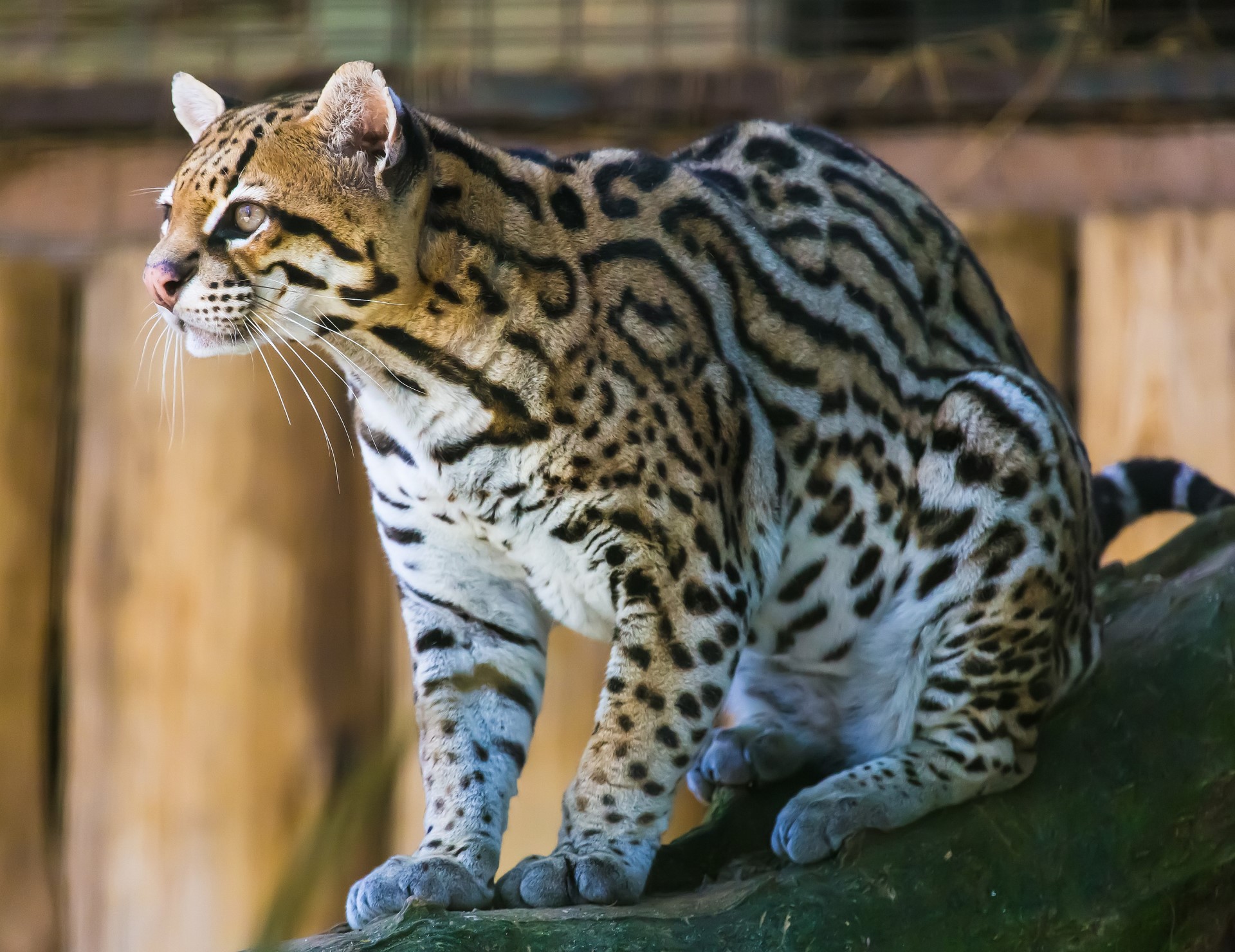
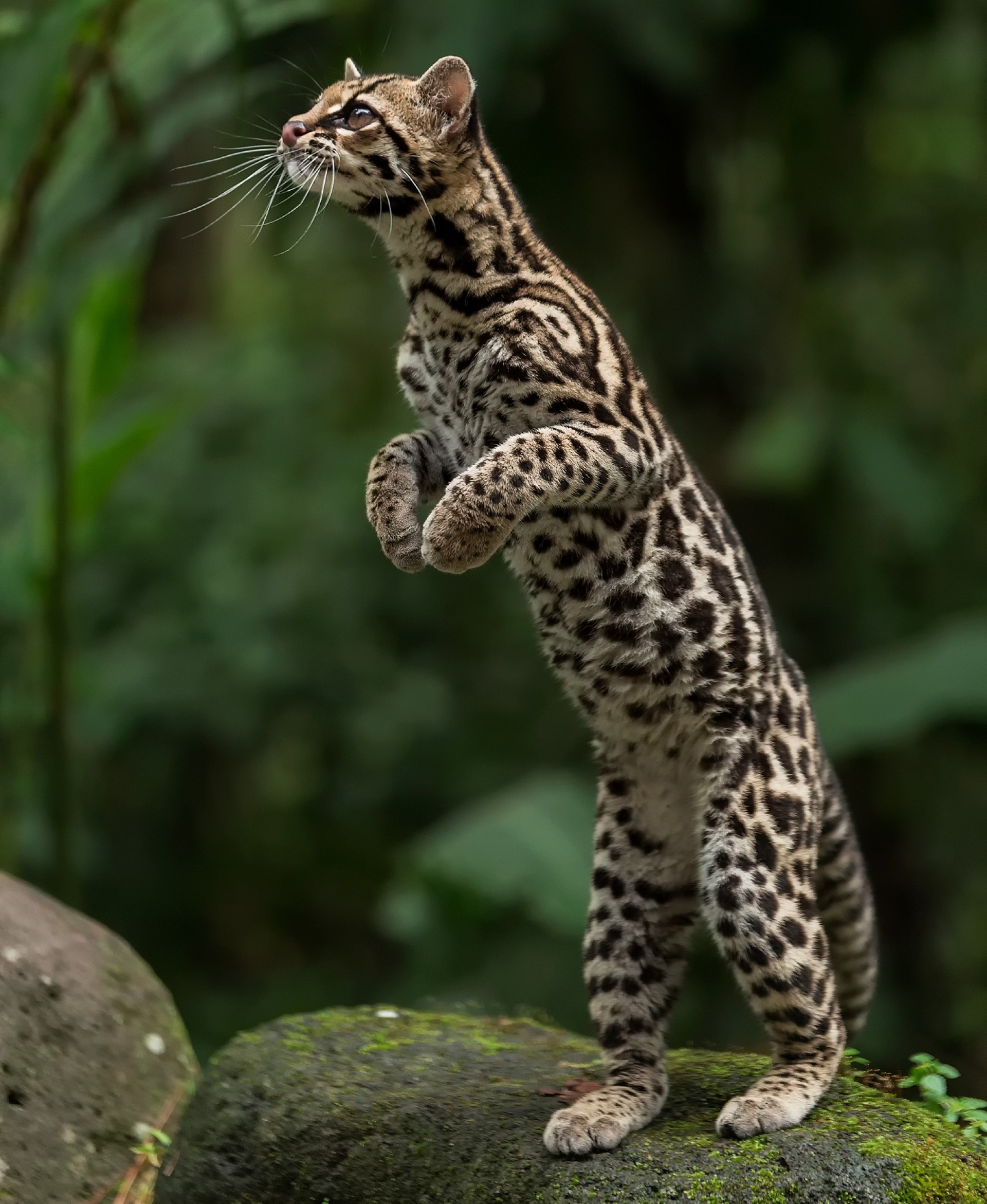
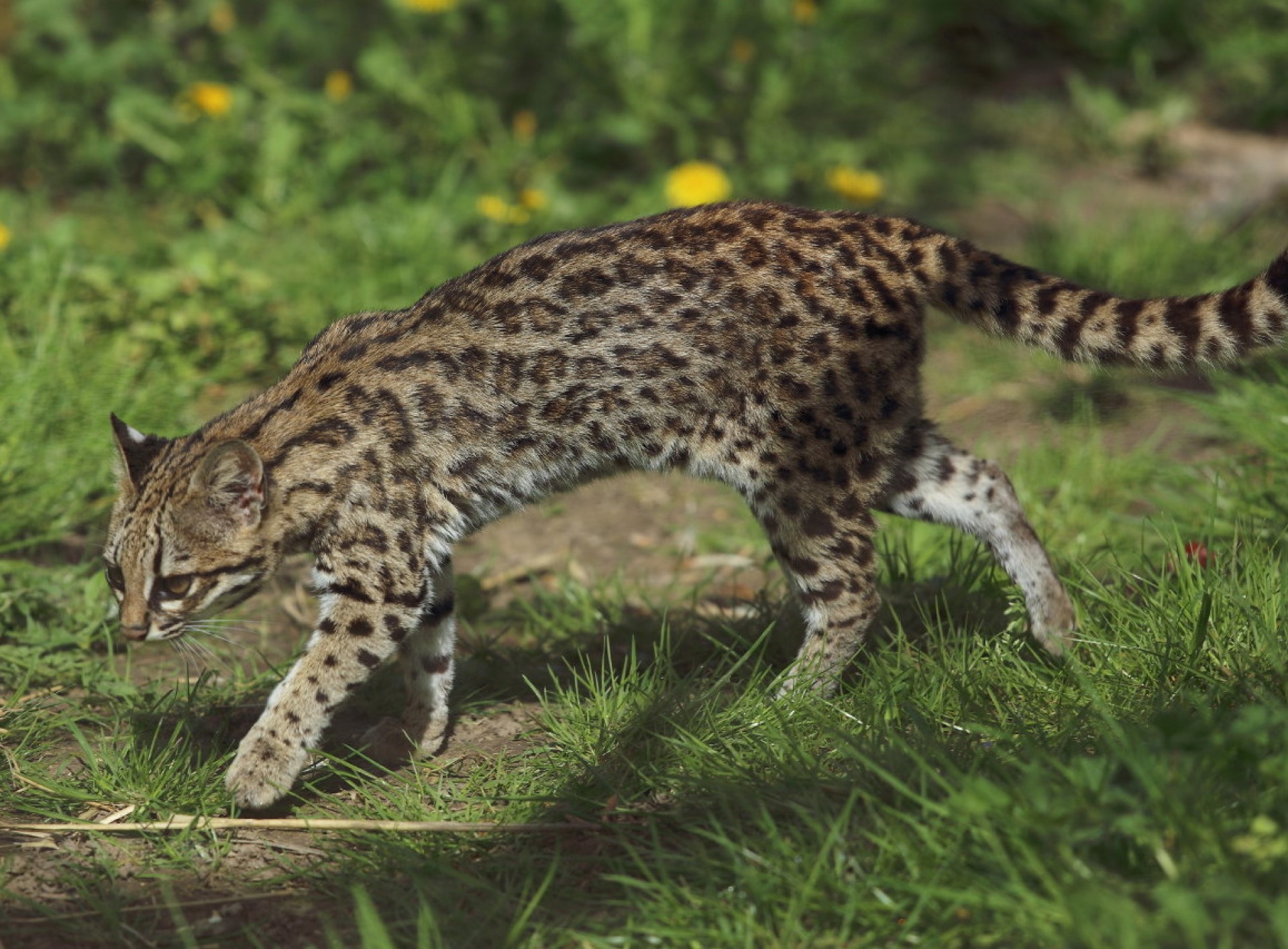
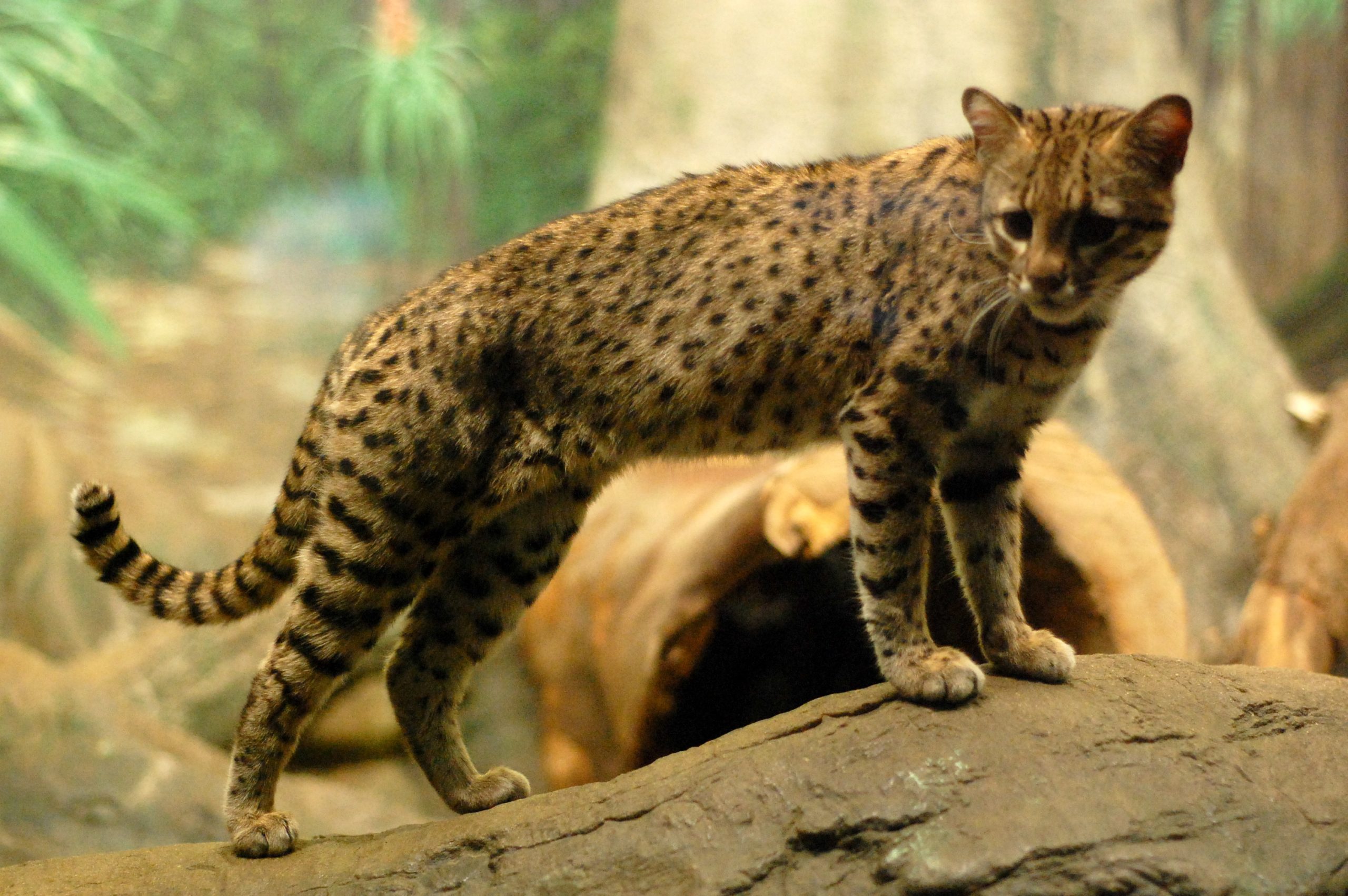
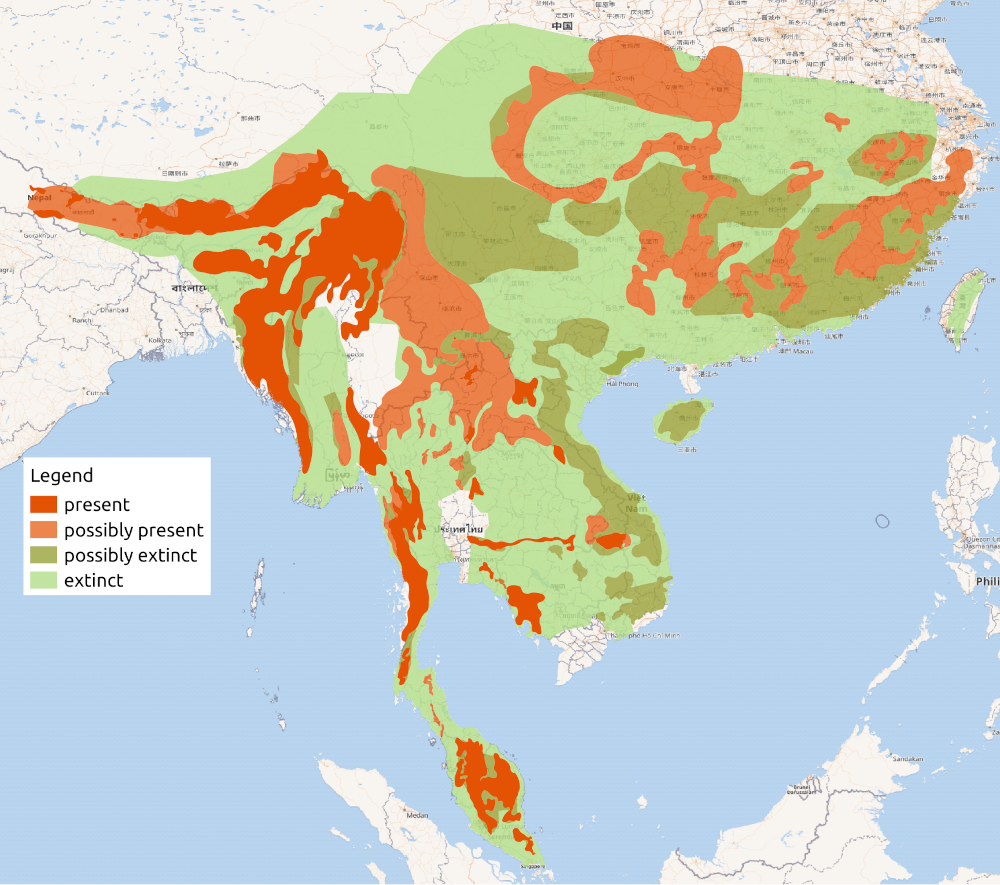
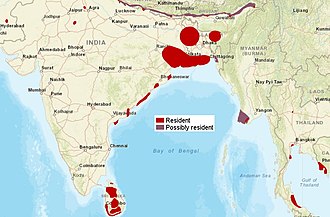
The common raccoon dog (also known as the (Chinese or Asian racoon dog, to distinguish it from the Japanese racoon dog)is a species which is found in east Asia. Although named for its facial markings, it is not closely related to raccoons and, although part of the dog family, it is more closely related to the fox.
This animal has been widely introduced in Europe due to regular escapes from fur farms.
Common raccoon dogs are omnivores that feed on insects, rodents, amphibians, birds, fish, reptiles, molluscs, crabs, sea urchins, human garbage, carrion, and eggs, as well as fruits, nuts, and berries.
Wolves predate them, and eat many in the spring. In Russia, wolves can account for as much as 2/3 of the deaths. Other animals like badgers and lynx will kill them, but generally do not go out of the way to do so. A range of birds of prey also target them.
They are the only canid to hibernate. There are around 4 subspecies. The Japanese racoon dog was thought to be a subspecies until recently when it was elevated to being its own species. They are one of the species that is thought to be have spread covid, and there are other illnesses that their introduction has caused to arrive in new countries.