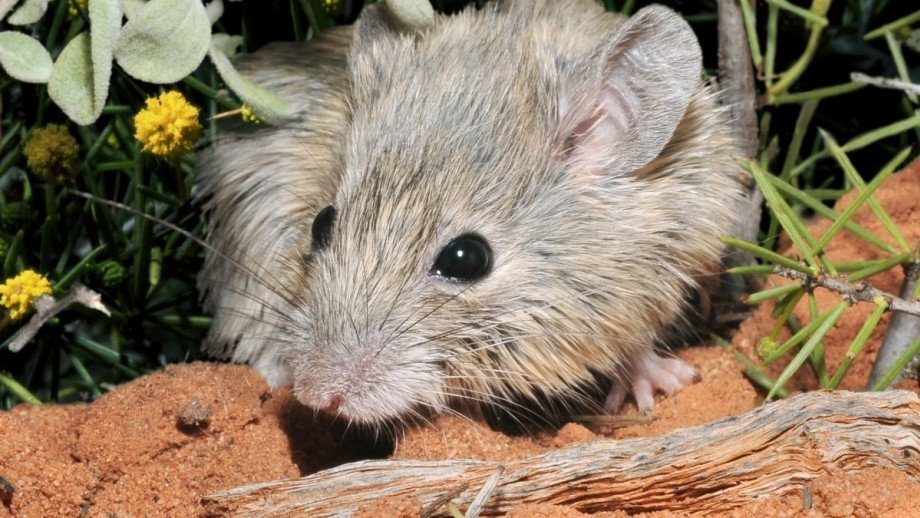
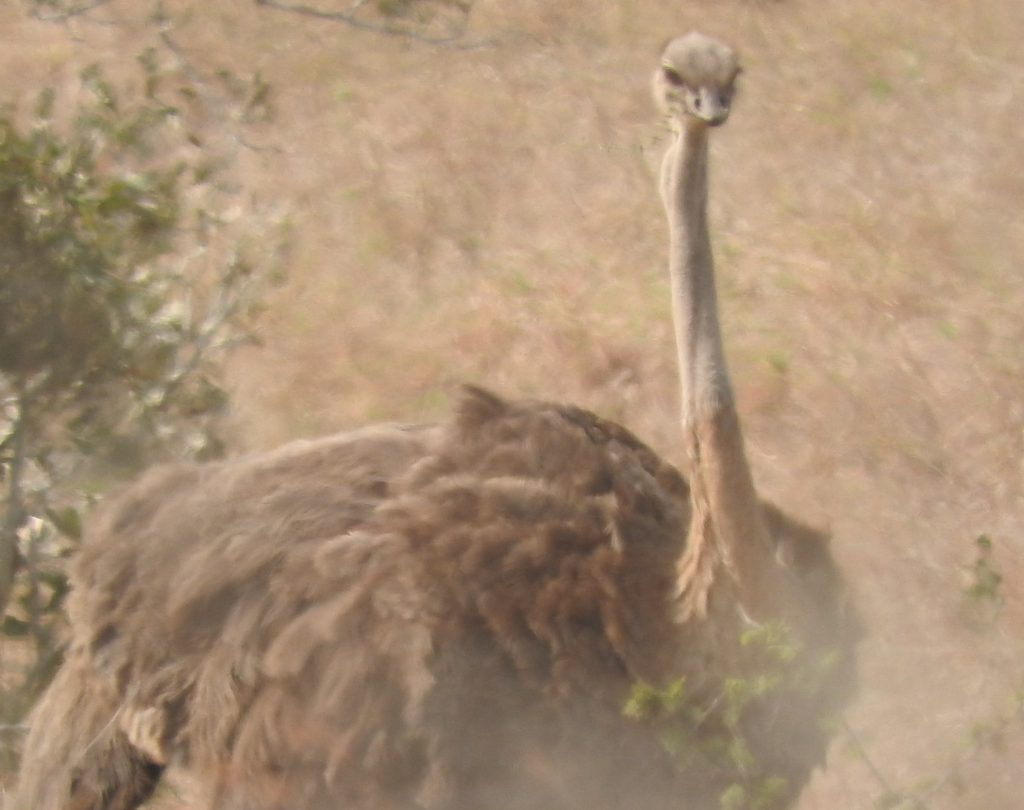
Rhea
Greater Rhea
Lesser Rhea

Found in Eastern South America, it is also known as the America, Common or Grey Rhea. In Portugese it is known as Ema. It is found in grasslands, Savanna or wet grasslands. When fully grown it weighs 20-27kg, and can live to around 10.5 years. It is listed as near threatened with a population of unknown size. Its range in South America is large, covering 6.5 million square km (2.5 million square miles).
Back in the 90s 6-8 individuals escaped from a private zoo in Germany, and this population has grown to around 550 birds.
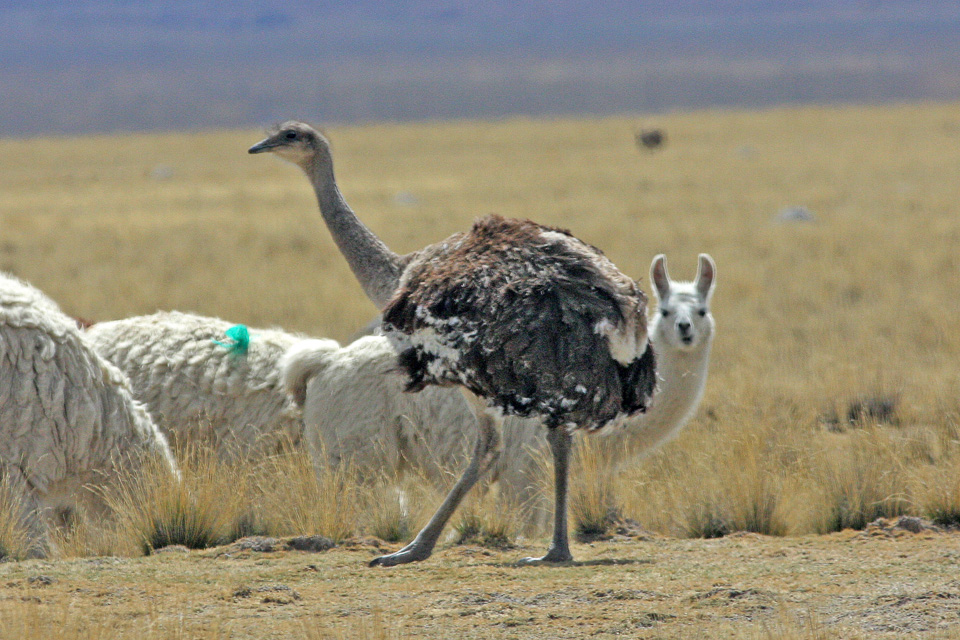
Also known as the Darwins rhea. Its found on the Andean plateau as well as Patagonia.
Darwins rhea. Its found on the Andean plateau as well as Patagonia.
Mostly a herbivore, it will take lizards and animals such as grasshoppers when the opportunity arises. They are listed as least concern and there are two subspecies (see the map to the right). While the main subspecies still has a range of 850,000 square km, and a population that is healthy, both other subspecies (found further north) have populations of only several hundred.
Should either of these species get mentioned in the blog, they will appear below (though it is possible with a short name, the letters may appear in other articles).
As we make contacts which will allow you to see these species in the wild, they will be added below the news carrousel – do get in touch with the form at the top of the home page, we would love to help people fiind you
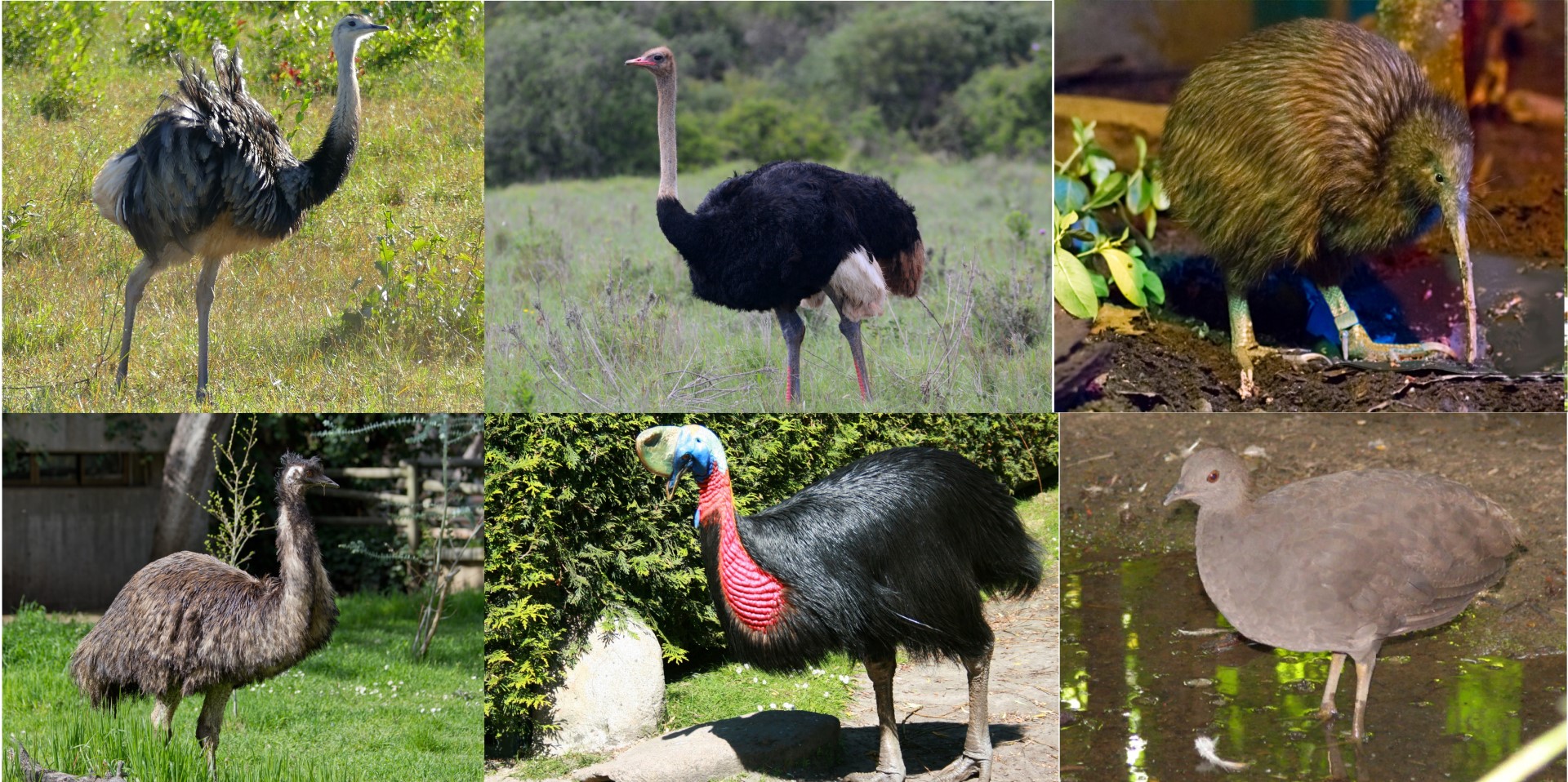
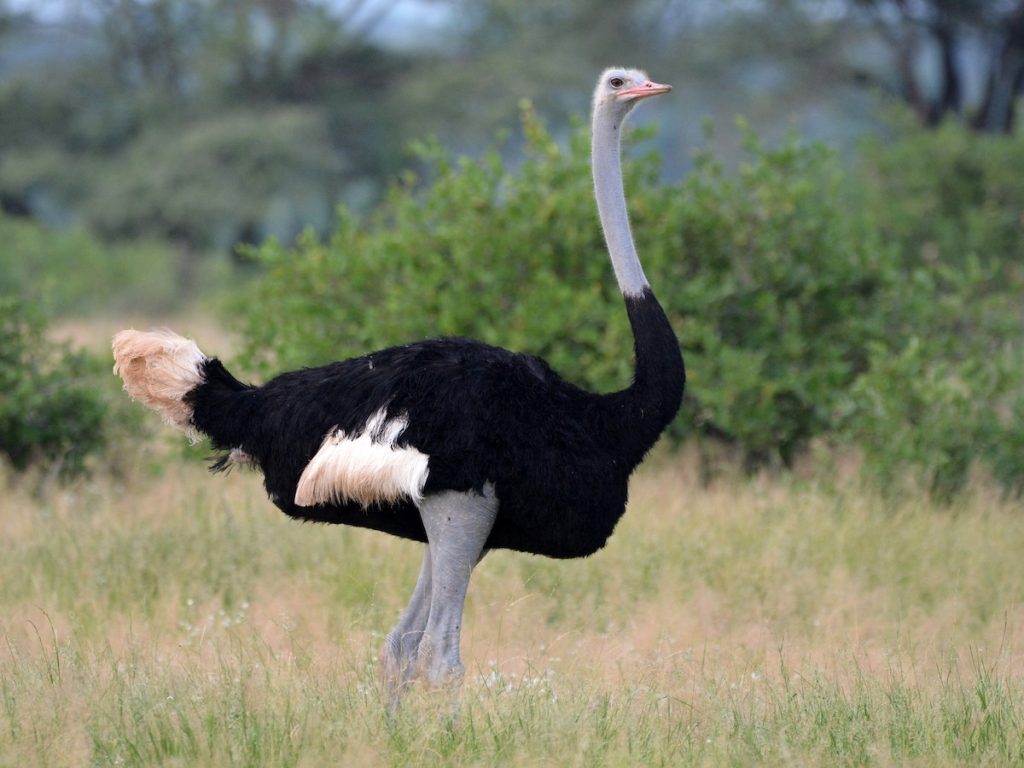
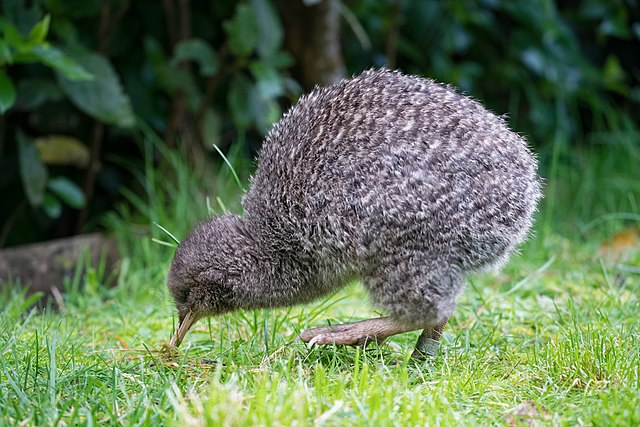
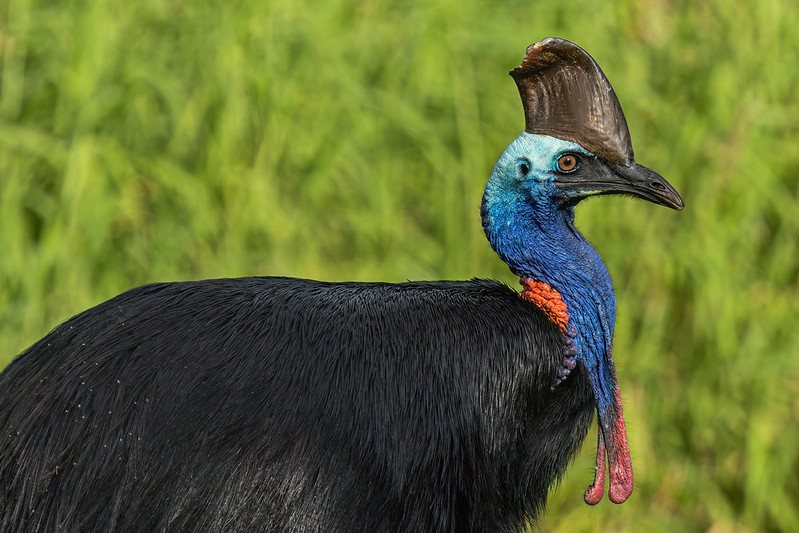









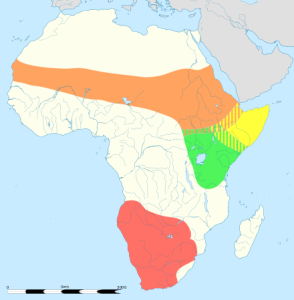 This is a map of the different Ostrich species and subspecies range
This is a map of the different Ostrich species and subspecies range

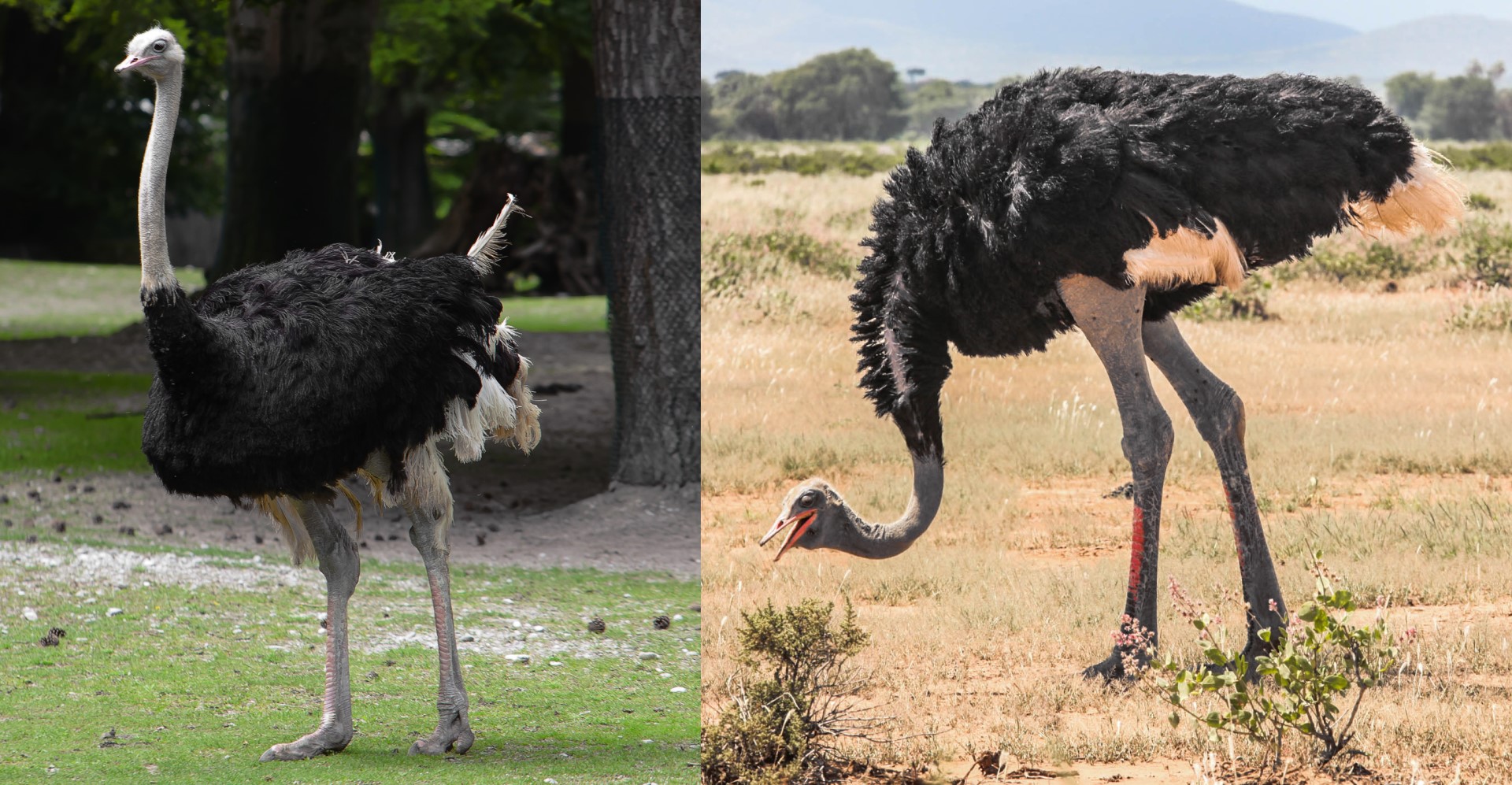
 As this is all of the Struthionimorphae family, you will be able to visit the Osterich page by clicking on either image.
As this is all of the Struthionimorphae family, you will be able to visit the Osterich page by clicking on either image.



















