Ethiopian wolf
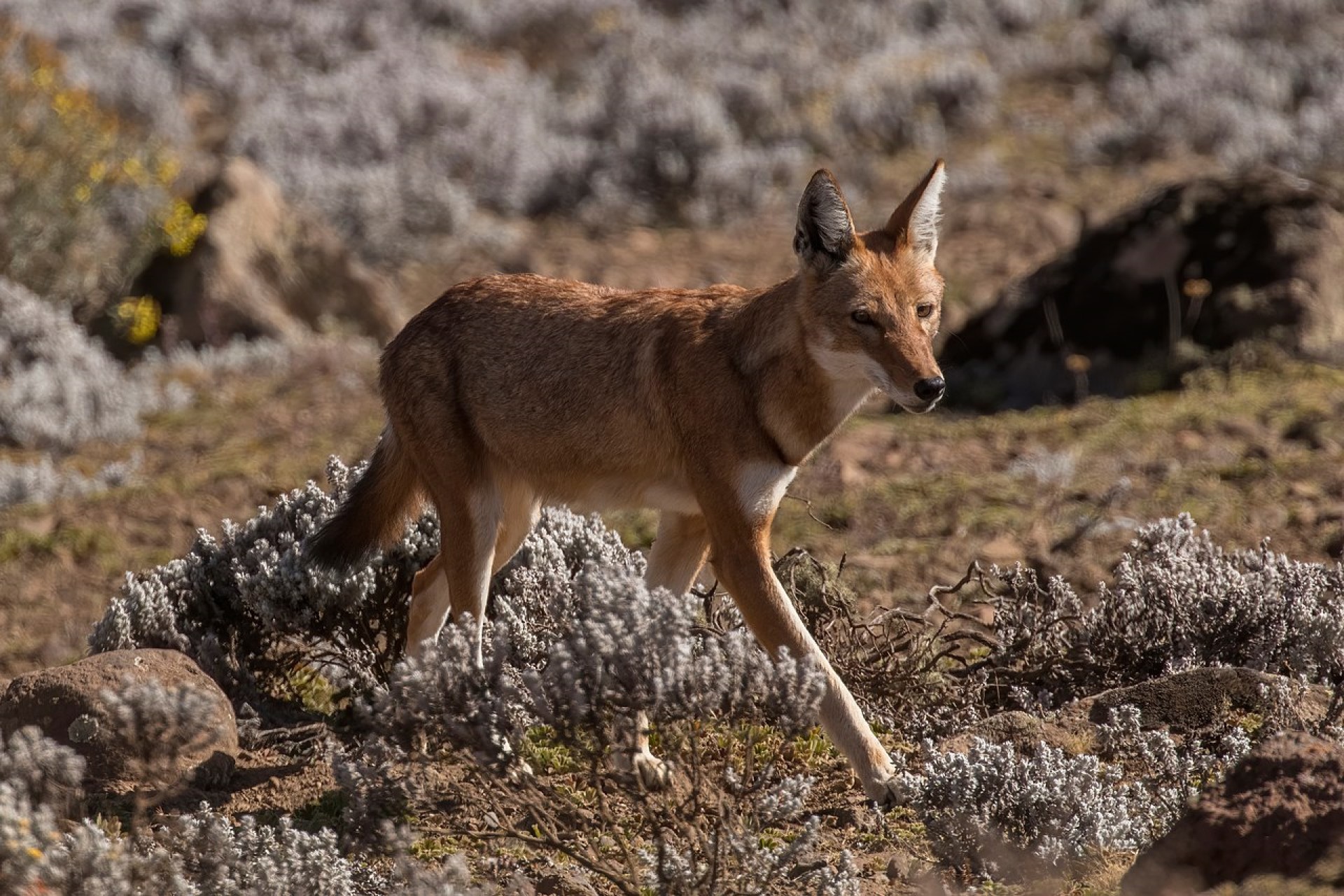
The Ethiopian wolf is a highly endangered canid that is restricted to the highlands of Ethiopia. Other names include the Ethiopian fox, or the Simien wolf.
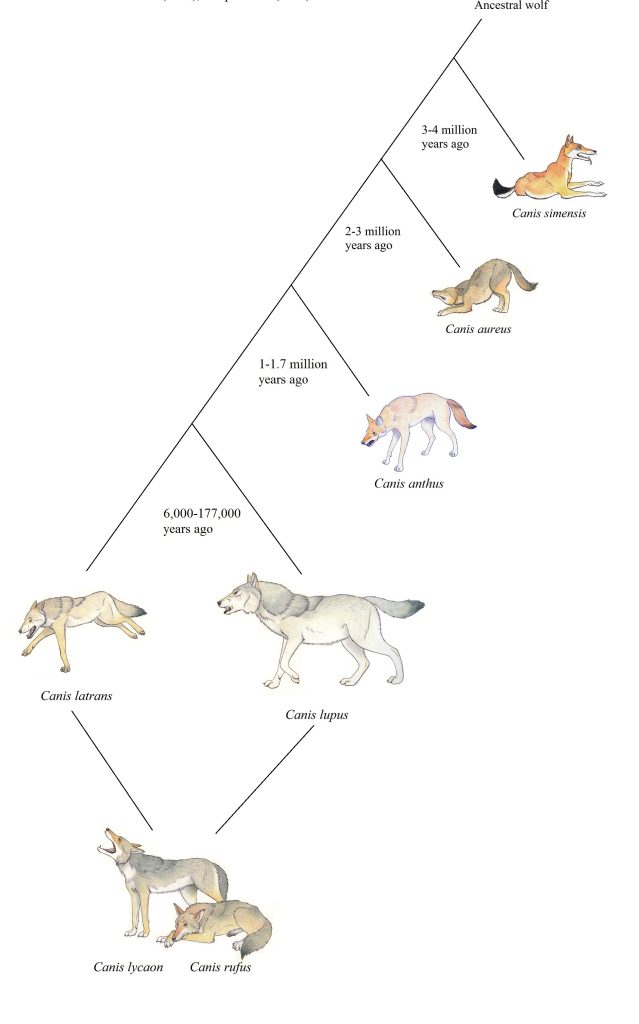
In terms of size, it is about the same size as the Coyote, Genetically, they are more similar to wolves than all jackals (except the Golden jackal). Here, below you can see how closely related each of the wolves are. While they look rather like jackals, their behaviour is far more like wolves – though due to the prey in the area, they do not hunt in packs (though there are regions of earth where grey wolves do not hunt as a pack either.
[smart_post_show id="12227"]













