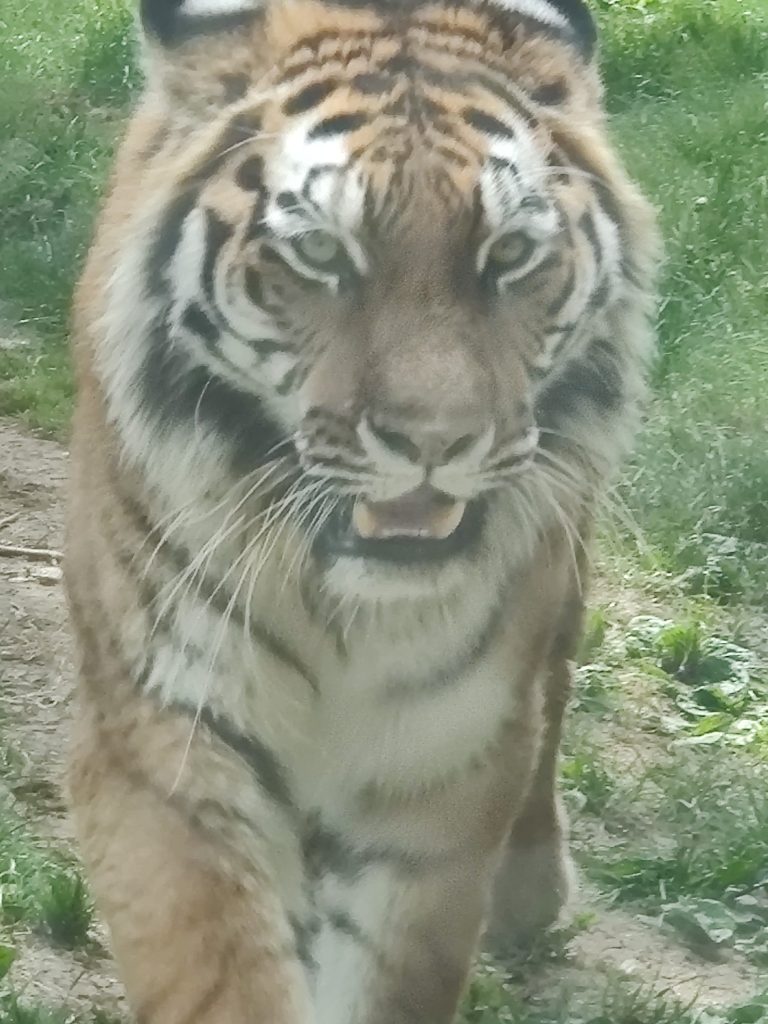
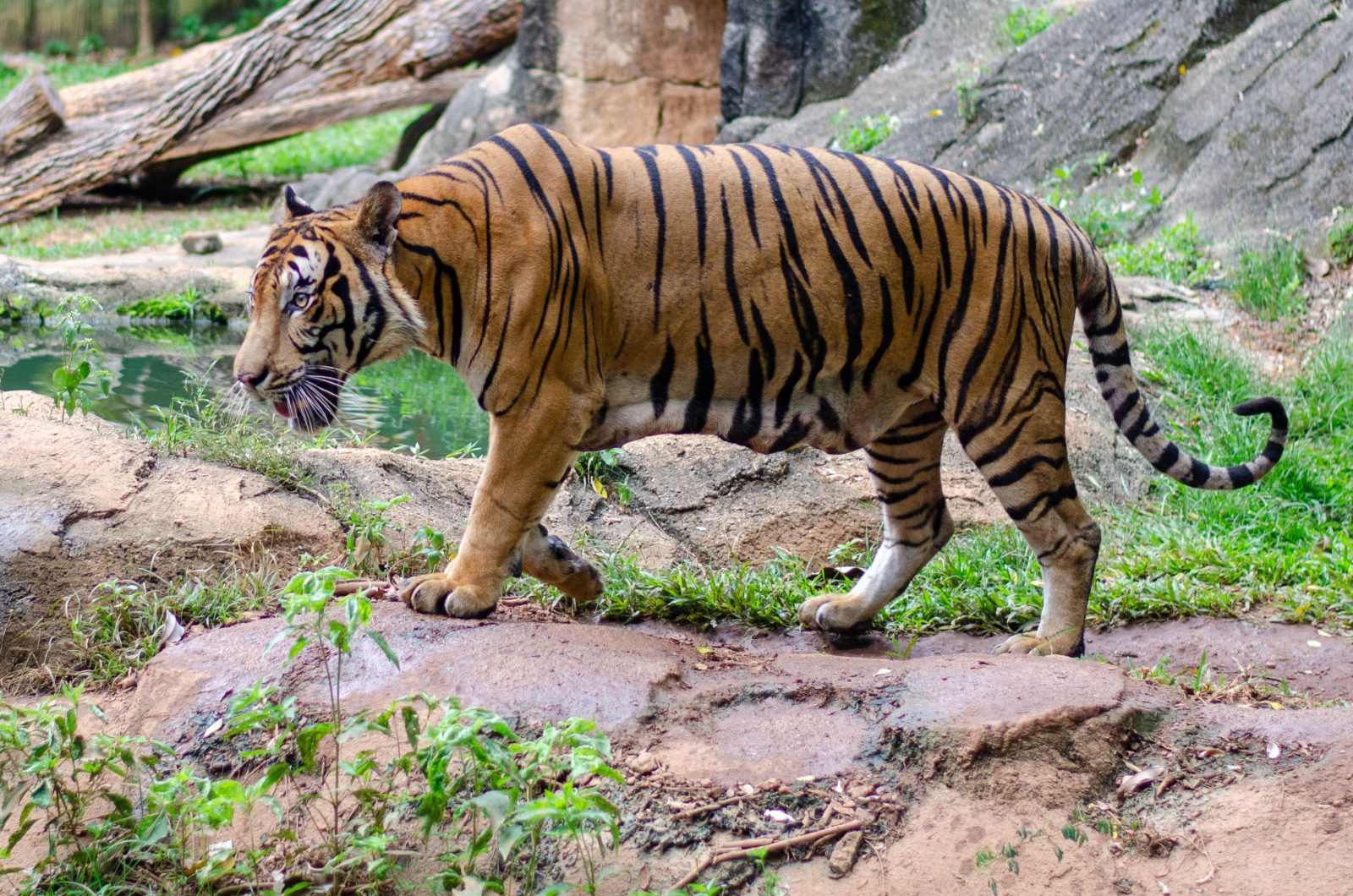
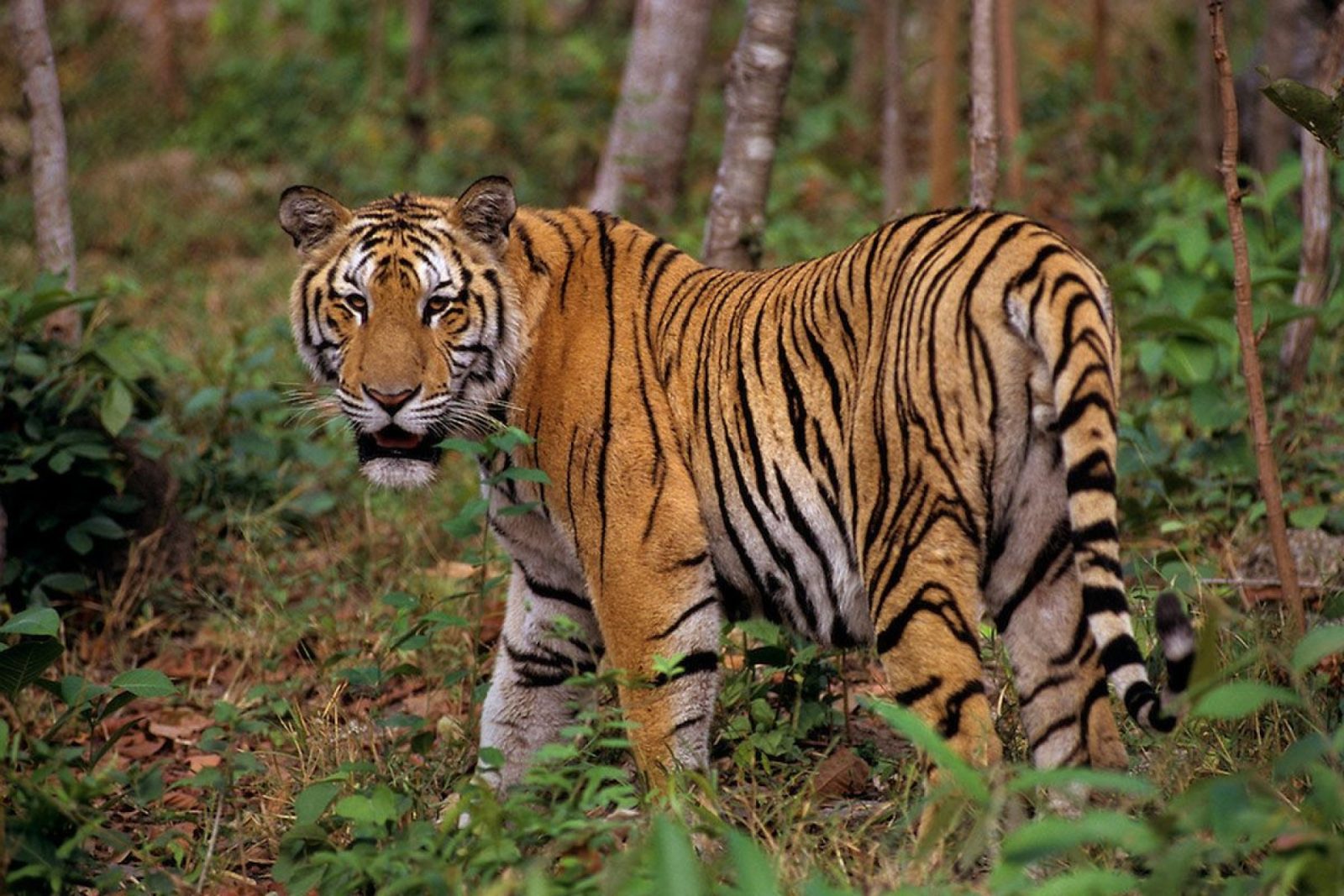
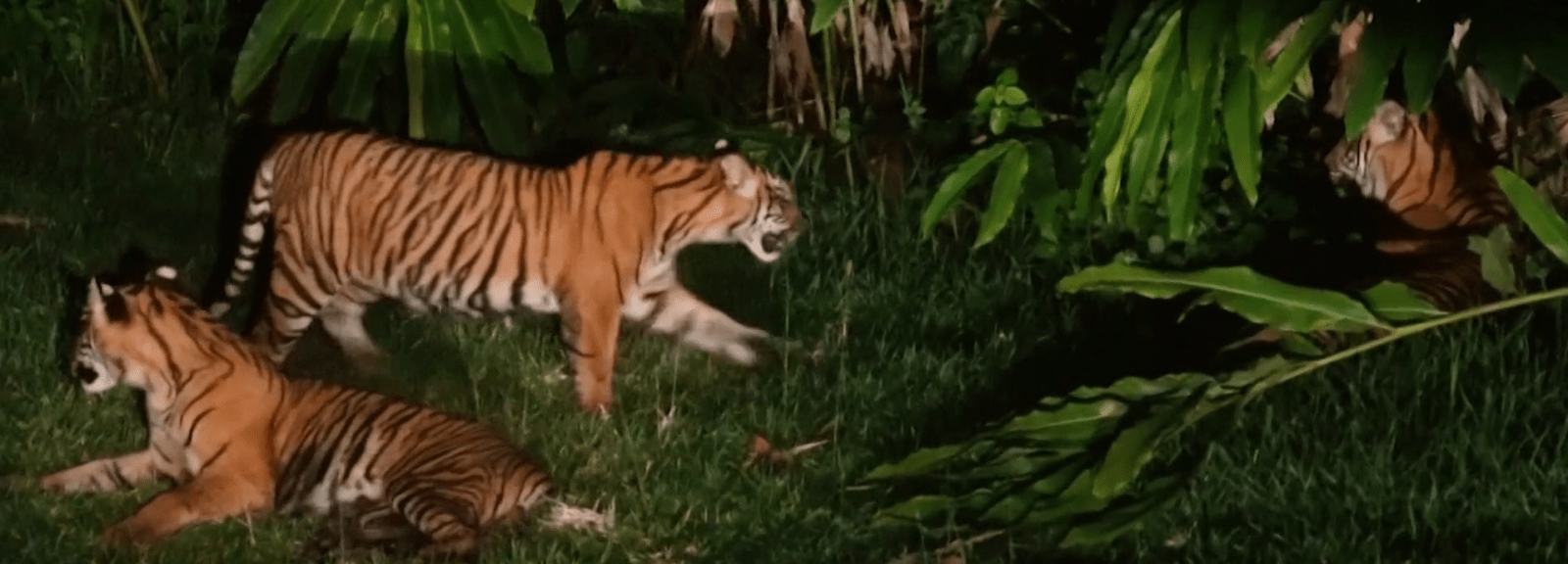
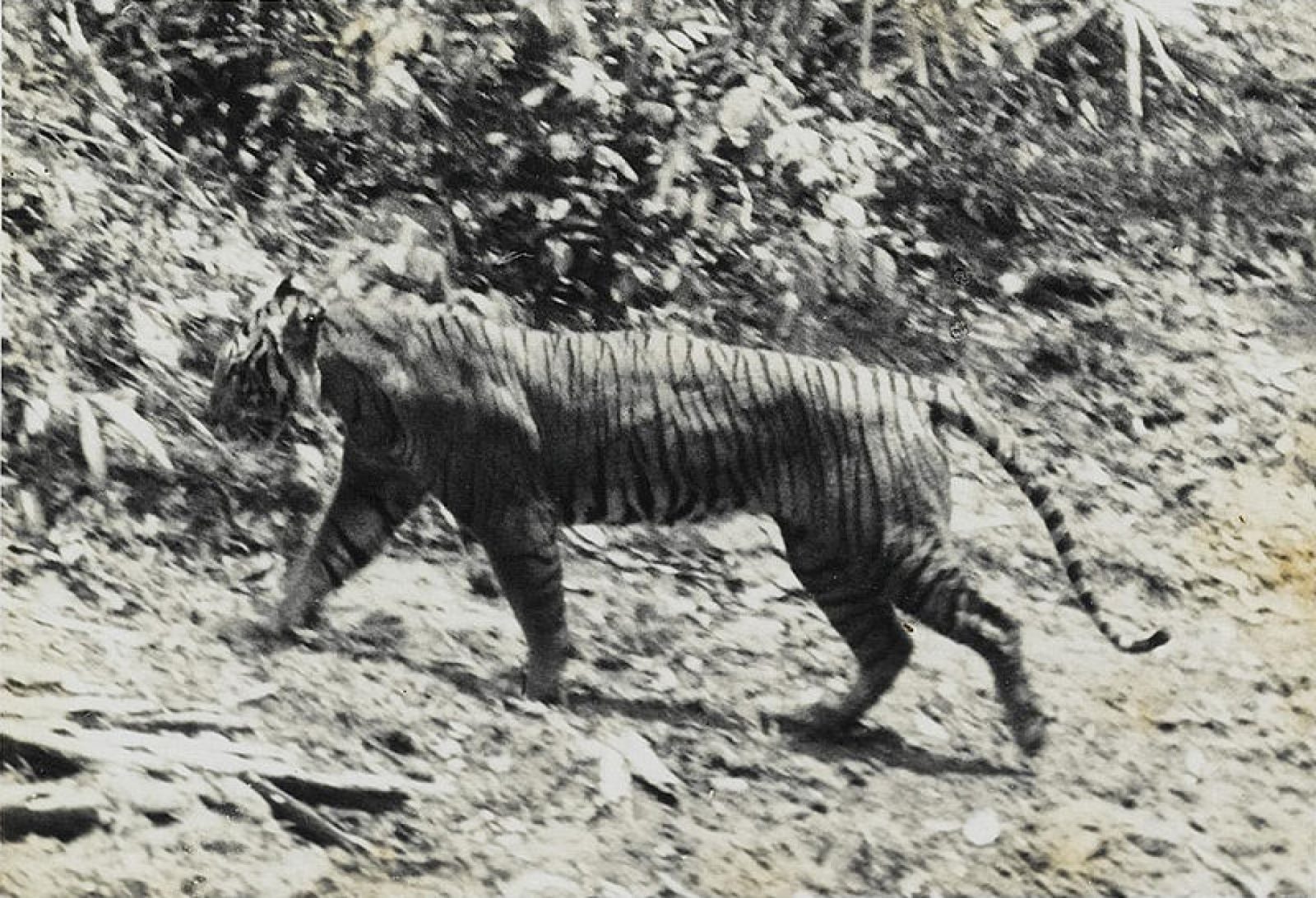
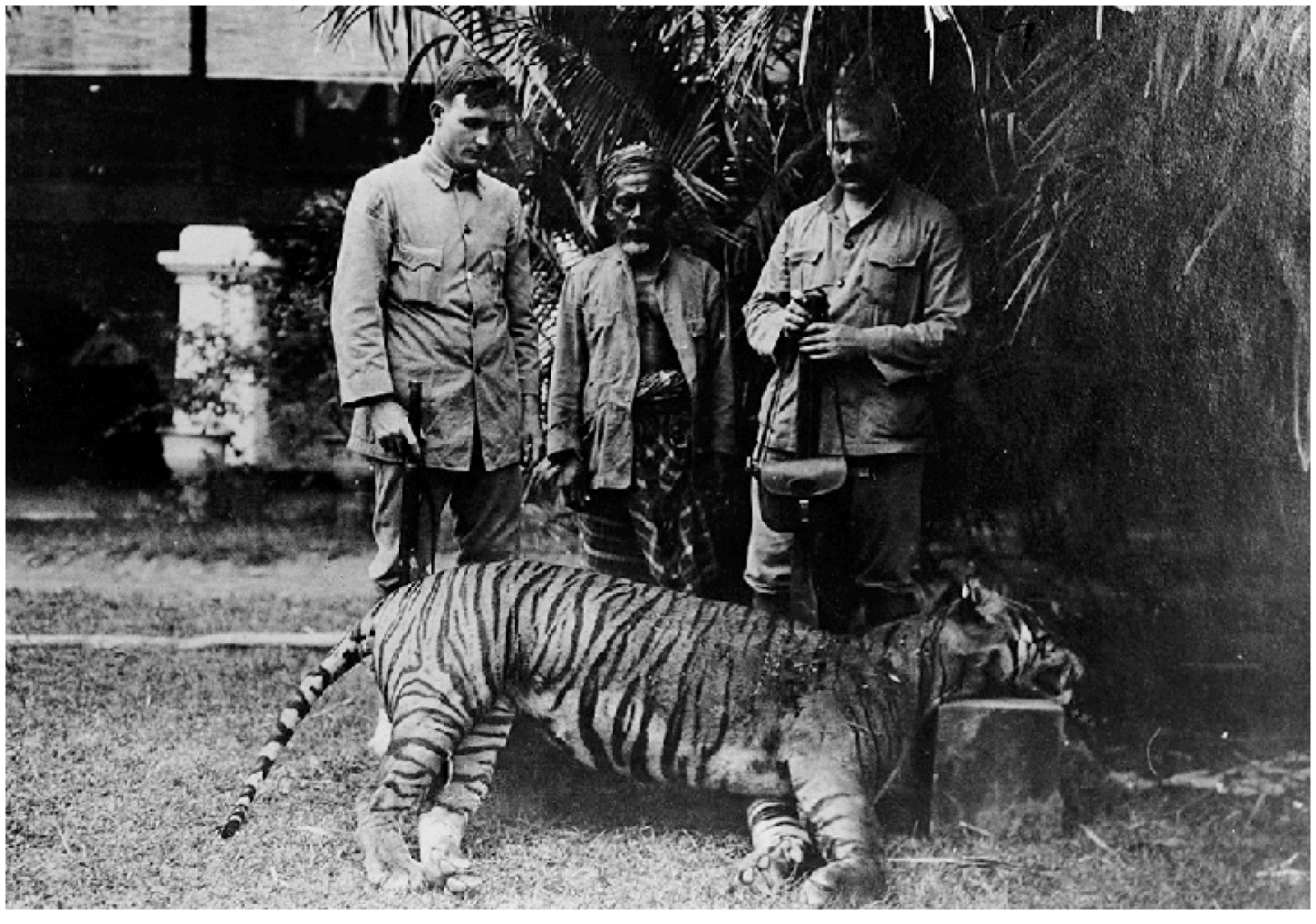
Historically found in Cambodia, China, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam, this species decline is large. In 2010, the assessment was that there were 250 left in Thailand, with around 85 in Myanmar and perhaps 20 hanging on in Vietnam. It is thought that the population is now just 250. This sub-species is found in Myanmar(85)) and Thiland(237), with a total population of an estimated 342 individuals. Back in 2009-2014 the population was thought to be between 189-252 in this period. Vietnam is only thought to have 5 remaining, while Laos is thought to have 2. Historically, it was also found in Cambodia and China. Historically, it is thought that this species range would have gone further North, potentially up to Chittagong Hill Tracts and Brahmaputra River basin, where the Bengal tiger populations range ended.
In Myanmar, surveys were conducted between 1999 and 2002, confirming the presence of tigers in the Hukawng Valley, Htamanthi Wildlife Sanctuary and in two small areas in the Tanintharyi Region. The Tenasserim Hills is an important area, but forests are harvested there (which means that they may be too much disruption for the tiger to survive here). In 2015, a camera trap took an image of a tiger in the hill forests of Kayin State. Camera trap surveys between 2016 and 2018 revealed about 22 adult individuals in three sites that represent 8% of the potential tiger habitat in the country. How many the rest of the country could support even if they had to be reintroduced is beyond the scope of this.
More than half of the total Indochinese tiger population survives in the Western Forest Complex in Thailand (Covering an area of about 18,000 sq. km. extended into Myanmar border along the Tennaserim Range and abreviated to (WEFCOM)) is considered as the largest remaining forest track in the mainland Southeast Asia that is made up of 17 protected areas (without gaps between them; 11 national parks and 6 wildlife sanctuaries.), especially in the area of the Huai Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary. This habitat consists of tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests. Camera trap surveys from 2008 to 2017 in eastern Thailand detected about 17 adult tigers in an area of 4,445 km2 (1,716 sq mi) in Dong Phayayen–Khao Yai Forest Complex. Several individuals had cubs. The population density in Thap Lan National Park, Pang Sida National Park and Dong Yai Wildlife Sanctuary was estimated at 0.32–1.21 individuals per 100 km2 (39 sq mi). Three subadult tigers were photographed in spring 2020 in a remote region of Thailand that are thought to be dispersing – moving out of areas which they were born into, and trying to find territory of their own.
In Laos, 14 tigers were documented in Nam Et-Phou Louey National Protected Area during surveys from 2013 to 2017, covering four blocks of about 200 km2 (77 sq mi) semi-evergreen and evergreen forest that are interspersed with some patches of grassland. Surveys that have been carried out since, have failed to detect any tigers, and the likelihood is that they have been extirpated as a result of poaching. Given the huge value of dead tigers in Chinese medicine, this is not a big surprise, as the current value for a carcass of a dead tiger is around £67,000 before doing anything with it, the value of it after extracting everything used in Chinese medicine (no evidence that it does anything) is around 5 times higher or £335,000. That is a huge windfall, but given that the average salary in Thailand is about £2200 a year (meaning that while many earn a great deal more than this, also many earn much less). 335,000, therefore represents perhaps 150 years of average salary. This is another place, where tourism can help. A thriving tourism industry will bring well paid jobs to many, and will therefore, not only preserve the tiger, but has the capacity of lifting many communities out of destitution.
In eastern Cambodia, tigers were last recorded in Mondulkiri Protected Forest and Virachey National Park during surveys between 1999 and 2007. In 2016, the Cambodian government declared that the tiger was “functionally extinct”. In April 2023, India signed a memorandum of understanding with Cambodia to assist the country with the tiger’s reintroduction. At least 90 acres (36 ha) of the Cardamom Mountains of Tatai Wildlife Sanctuary could be used to host Bengal tigers (though this if a correct number is not going to do much for a wild tiger).
From the 1960s and earlier, the Indochinese tiger occurred throughout the mountains in Vietnam, even in the midlands and Islands. In the report of the Government of Vietnam at the Tiger Forum in 2004, there would be tigers in only 17 provinces and they were living in fragmented and severely degraded forest areas. Tigers were still present in 14 protected areas in the 1990s, but none have been recorded in the country since 1997. There is news of its extinction in both countries. In Laos, no tiger has been seen since 2013, when its populations were estimated at only two, and these two individuals simply vanished shortly after 2013 from Nam Et-Phou Louey National Protected Area, denoting they were most likely killed either by snare or gun. In Vietnam, a 2014 IUCN Red List report indicated that tigers were possibly extinct in Vietnam.
In China, it occurred historically in Yunnan province and Mêdog County, where it probably does not survive today. Thus, probably the Indochinese tiger now only survives in Thailand and Myanmar. In Yunnan’s Shangyong Nature Reserve, three individuals were detected during surveys carried out from 2004 to 2009.
In Thailand’s Huai Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary, 11 individual tigers were equipped with GPS radio collars between June 2005 and August 2011. Females had a mean home range of 70.2km2 (27.1 sq mi) and males of 267.6km2 (103.3sq mi).
Between 2013 and 2015, 11 prey species were identified at 150 kill sites. They ranged in weight from 3 to 287 kg. Sambar deer, banteng, gaur, and wild boar were most frequently killed, but also remains of Asian elephant calves, hog badger, Old World porcupine, muntjac, serow, pangolin, and langur species were identified.
The primary threat to the tiger is poaching for the illegal wildlife trade. Tiger bone has been an ingredient in traditional Chinese medicine for more than 1,500 years and is either added to medicinal wine, used in the form of powder, or boiled to a glue-like consistency. More than 40 different formulae containing tiger bone were produced by at least 226 Chinese companies in 1993. Tiger bone glue is a popular medicine among urban Vietnamese consumers.
Between 1970 and 1993, South Korea imported 607 kg of tiger bones from Thailand and 2,415 kg from China between 1991 and 1993. Between 2001 and 2010, wildlife markets were surveyed in Myanmar, Thailand, and Laos. During 13 surveys, 157 body parts of tigers were found, representing at least 91 individuals. Whole skins were the most commonly traded parts. Bones, paws, and penises were offered as aphrodisiacs in places with a large sex industry. Tiger bone wine was offered foremost in shops catering to Chinese customers. Traditional medicine accounted for a large portion of products sold and exported to China, Laos, and Vietnam. Between 2000 and 2011, 641 tigers, both live and dead, were seized in 196 incidents in Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, Cambodia, and China; 275 tigers were suspected to have leaked into trade from captive facilities. China was the most common destination of the seized tigers.
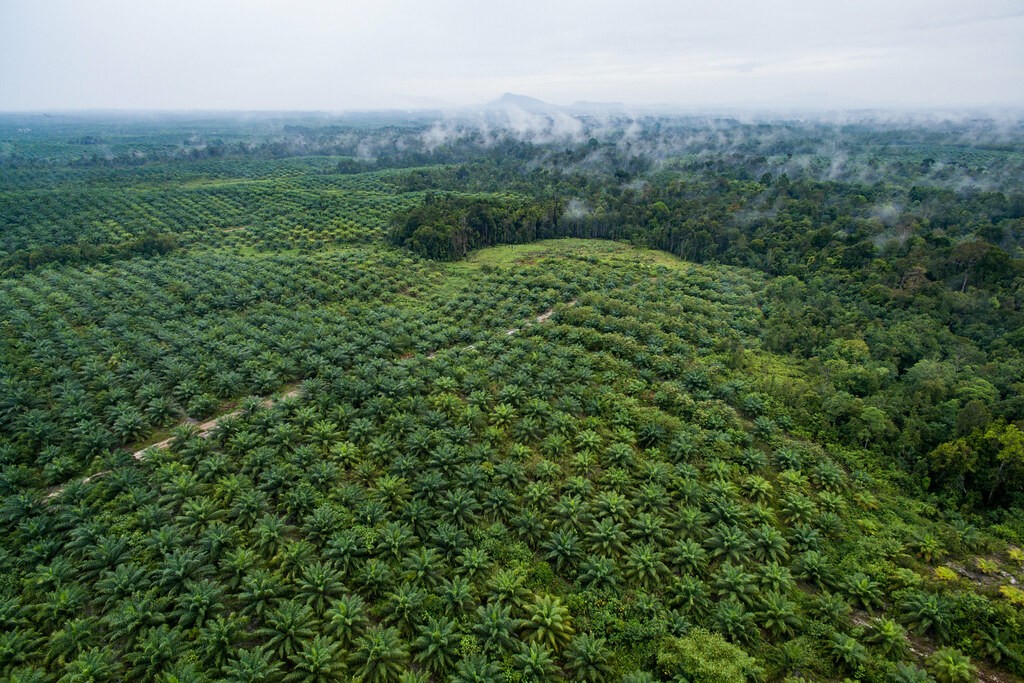
In Myanmar’s Hukaung Valley, the Yuzana Corporation, alongside local authorities, has expropriated more than 200,000 acres (81,000 ha) of land from more than 600 households since 2006. Much of the trees have been logged, and the land has been transformed into plantations. Some of the land taken by the Yazana Corporation had been deemed tiger transit corridors. Without this land, smaller reserves can instantly become incapable of supporting tigers longterm. These are areas of land that were supposed to be left untouched by development in order to allow the region’s Indochinese tigers to travel between protected pockets of reservation land.
Since 1993, the Indochinese tiger has been listed on CITES Appendix I, making international trade illegal. China, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, and Taiwan banned trade in tigers and sale of medicinal derivatives. Manufacture of tiger-based medicine was banned in China, and the open sale of tiger-based medicine reduced significantly since 1995.
Patrolling in Thailand’s Huai Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary has been intensified since 2006 so that poaching appears to have been reduced, resulting in a marginal improvement of tiger survival and recruitment. By autumn 2016, at least two individuals had dispersed to adjacent Mae Wong National Park; six cubs were observed in Mae Wong and the contiguous Khlong Lan National Park in 2016, indicating that the population was breeding and recovering.[43]
In Thailand and Laos, this tiger is considered Endangered, while it is considered Critically Endangered in Vietnam and Myanmar. Of course, if all this is correct, then some of these countries should amend their listing to extinct.
The Indochinese tiger is the least represented in captivity and is not part of a coordinated breeding program. As of 2007, 14 individuals were recognized as Indochinese tigers based on genetic analysis of 105 captive tigers in 14 countries. This is no where near enough to be able to do a reintroduction.
I will hope to add links to help arrange travel to see this species, do get in touch if you can help
More than half of the total Indochinese tiger population survives in the Western Forest Complex in Thailand, especially in the area of the Huai Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary.
They are considered endangered in Thailand and critically endangered in Myanmar and Vietnam
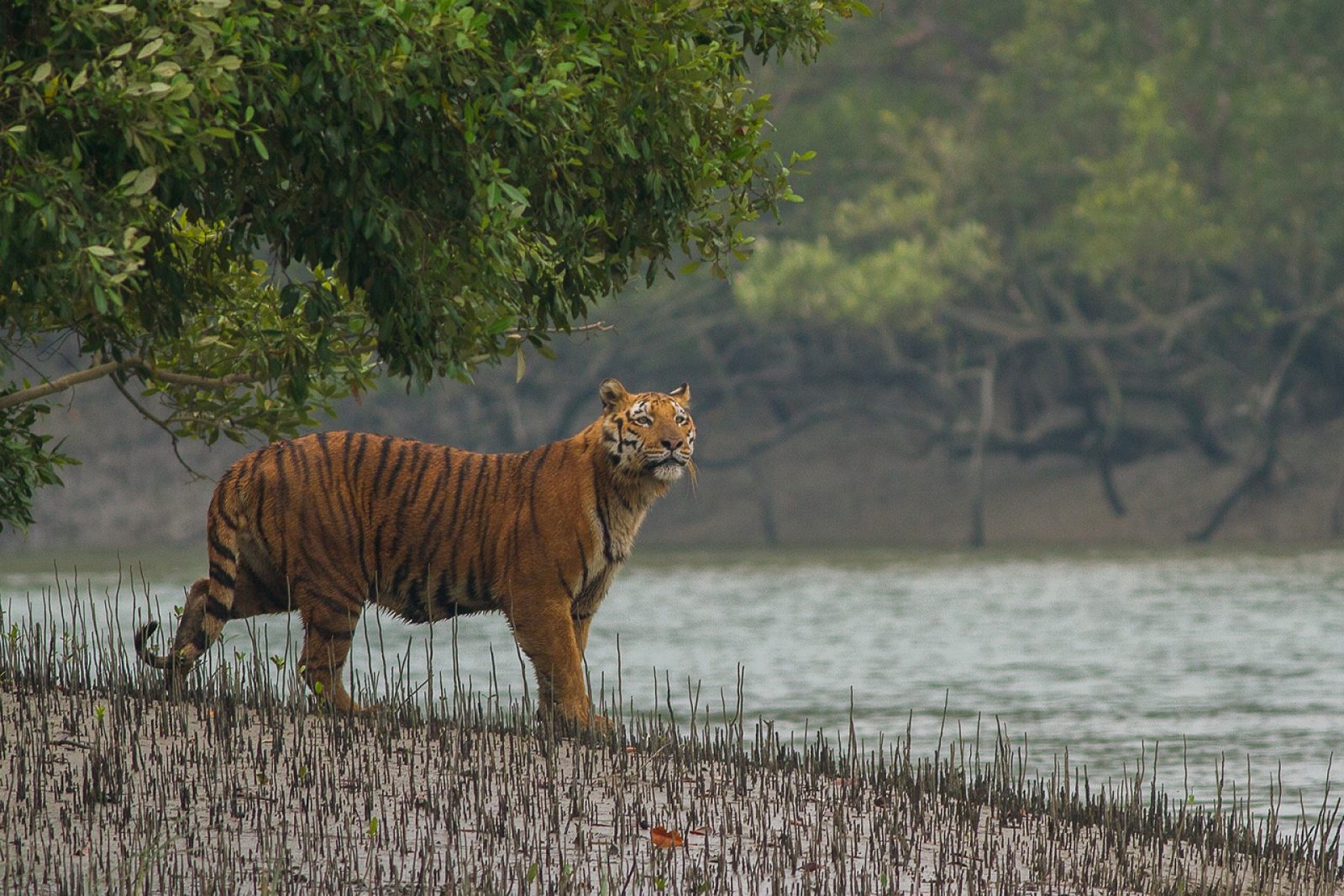



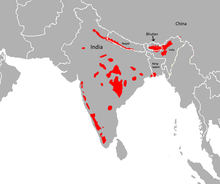 The country with the most tigers is India, hosting around 70% of the remaining tigers, or a little over 3000. However, this is down from 100,000 in 1900. In 2006 the Indian tiger population was as low as just 1411 – there are individual reserves in Africa with more lions in than this number. Given that there are 54 tiger reserves in India, that leaves an average population of just 30 per reserve – translocation will be required to maintain genetically healthy tigers. Formerly working on pug-marks, counting has been replaced with photo identification, as pug marks were overestimating the population (Simlipal reserve in Orissa state claimed 101 tigers in 2004, yet in 2010 a photo count stated 61, and this is thought a a huge over estimate, as the same state government claims just 45 tigers across the state. Sariska and Panna reserves in India are worse with the government having to admit that there are no tigers left (2 reserves of at least 5 so called tiger reserves with none left).
The country with the most tigers is India, hosting around 70% of the remaining tigers, or a little over 3000. However, this is down from 100,000 in 1900. In 2006 the Indian tiger population was as low as just 1411 – there are individual reserves in Africa with more lions in than this number. Given that there are 54 tiger reserves in India, that leaves an average population of just 30 per reserve – translocation will be required to maintain genetically healthy tigers. Formerly working on pug-marks, counting has been replaced with photo identification, as pug marks were overestimating the population (Simlipal reserve in Orissa state claimed 101 tigers in 2004, yet in 2010 a photo count stated 61, and this is thought a a huge over estimate, as the same state government claims just 45 tigers across the state. Sariska and Panna reserves in India are worse with the government having to admit that there are no tigers left (2 reserves of at least 5 so called tiger reserves with none left).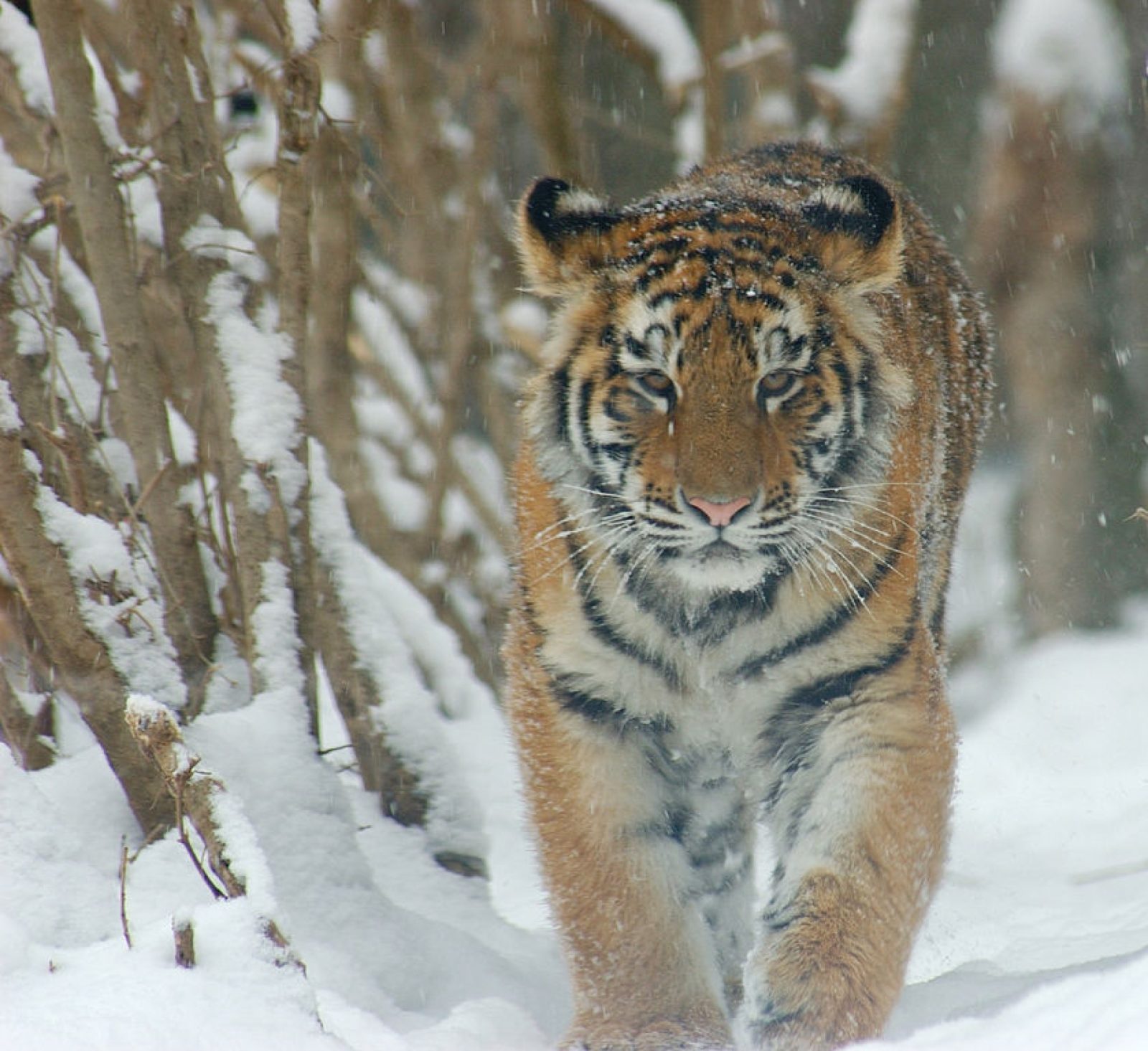 
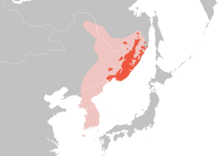 Russia hosts one of the hardest tigers to see. However, there are now around 500 Amur tigers roaming the remote far east of Russia, up from less than 40 in the 1940s, this population has also had great gains.
Russia hosts one of the hardest tigers to see. However, there are now around 500 Amur tigers roaming the remote far east of Russia, up from less than 40 in the 1940s, this population has also had great gains. 












