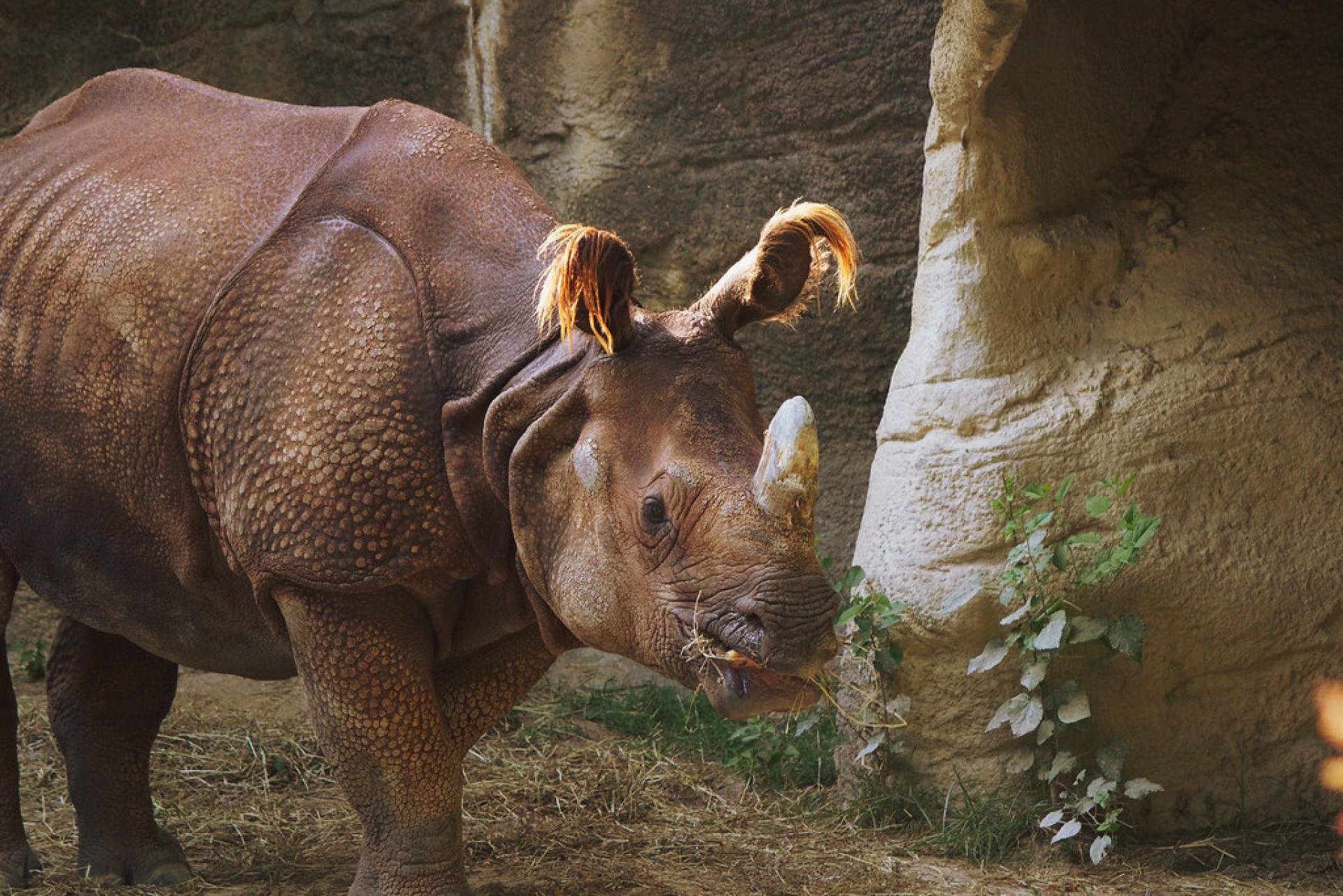
Sumatran Rhinoceros
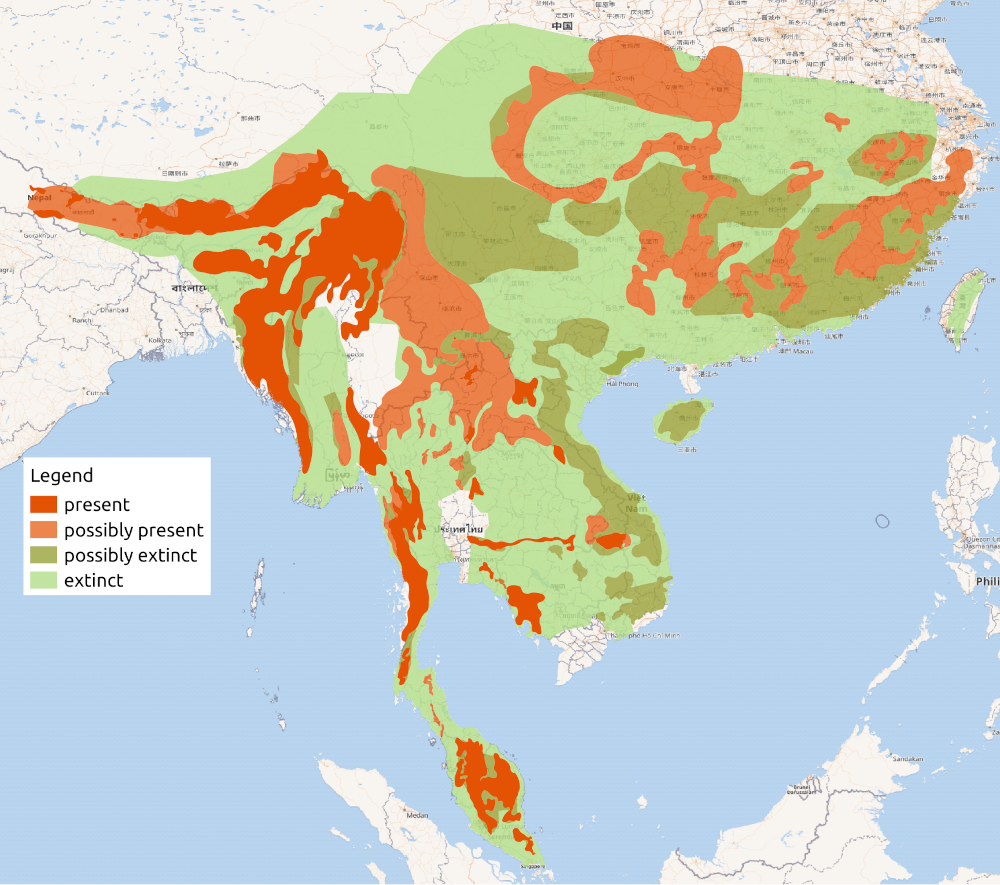
 Sumatran rhino is also known as a hairy rhinoceros or Asian two-horned rhinoceros. Like the Javan rhino, the Sumatran rhino once had a range which covered a far larger area: rainforests, swamps and cloud forests in India, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and southwestern China, particularly in Sichuan.
Sumatran rhino is also known as a hairy rhinoceros or Asian two-horned rhinoceros. Like the Javan rhino, the Sumatran rhino once had a range which covered a far larger area: rainforests, swamps and cloud forests in India, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and southwestern China, particularly in Sichuan.
There are still 3 on the island of Borneo, as you can see, the map still lists a population on the Malay peninsula though it is thought that this group is extinct. The 3 subspecies are:
- The Sumatran island population: Western (34-47 individuals). This is unfortunately split in to 4 populations
- The Borneo island population: Eastern (may be as low as 3). This was only discovered in 2016 in East Kalimantan, after the population in Sabah, Malaysia (northern part of the island) was declared extinct in 2015
- The mainland population: Northern (this is thought to be extinct as of 2010, but it is possible that a small group remain.
Only four areas are known to contain Sumatran rhinoceros: Bukit Barisan Selatan National park, Gunung Leuser national park, and Way Kambas National park on Sumatra, and on Borneo west of Samarindah.
We hope to be able to list trekking for seeing animals like this in the future, do get in touch if you work in this field.
New baby girl! Sumatran rhino born in captivity in a breeding centre in Sumatra
- Tim
- March 29, 2022
Today the Sumatran rhino is critically endangered. It is thought that not more than 80 exist in the wilds of Sumatra. Not particularly closely related to the Javan rhino, the...
Third Sumatran rhino sanctuary moving forwards
- Tim
- July 1, 2021
The Sumatran rhino is critically endangered. Just a few years ago, the last of the mainland Sumatran rhino died, leaving only the population on Sumatra itself.

Snares set by poaching are still threatening Sumatran Rhino, now with only about 80 left
- Tim
- November 25, 2020
The leuser ecosystem on the island of Sumatra, is home to a fascinating range of animals, not found together anywhere else. In particular, this ecosystem supports tigers orangutans elephants and...
The last Sumatran rhino living in Malaysia has died
- Tim
- December 10, 2019

The Sumatran rhino was once found throughout out much of Southeast Asia including parts of India, Vietnam, China, Myanmar, Thailand as well as Borneo.
Now...
Saving the Sumatran rhino
- Tim
- June 19, 2018
Javan rhinos: is the Indonesian government lying? misleading? or being straight with the world.
- Tim
- May 1, 2024
It appears that the counters of the Javan rhino, have continued to count animals which have not been seen for years. Given how much poaching has been going on, this...
Can simple changes help the Javan rhino recover?
- Tim
- January 24, 2024
Above is a fascinating video about a photographers journey to try to see this rhinos in the wild (spoiler alert, it was a success, as you can see from...
The Indonesian rhinos that once roamed across much of Asia
- Tim
- April 30, 2023
The wildlife of Indonesia now often looks like relatively unique to those islands. This is not the natural state of affairs. 60,000 years ago, a cousin of the orangutan lived...
Two baby rhino born in Java in the species last remaining habitat
- Tim
- February 17, 2022
There are only around 60 rhino left in the wild. They live in Ujung Kulon National Park. To put that in perspective, that is an increase of 3.3%.

The rise of rhino poaching within South Africa
- Tim
- April 2, 2018
Species watch
- Tim
- May 11, 2022
I am intending to make this into a new set of articles that will appear on this website. Obviously, these species will not be the only ones that are covered...
Positive news from Borneo – reconnecting wilderness
- Tim
- July 20, 2023
One of the problems with cutting down rainforest, it often what is left is so fragmented that it is useless for conservation. Remaining blocks of forest must allow a viable...
Indonesias leading University has proposed classifying Palm oil as a forest crop – This is insane, read on to find more – urgent condemnation needed
- Tim
- January 11, 2022
This proposal would mean that Indonesia could cut down all its rainforest and replace them with Palm Oil, and would have engaged in zero deforestation.

This...