At various times over the last century, the elephant population has been decimated. Between 1979 and 1989 the elephant population halved. Even recently, between 2007 -2014 30% of Africa elephants were lost.
Yet this is only the top of the iceberg. In 1930 there were an estimated 10,000,000 African elephants roaming the continent -today just 415,000 remain 96% decline. That means a sustained loss of almost 1%a year for almost a century.
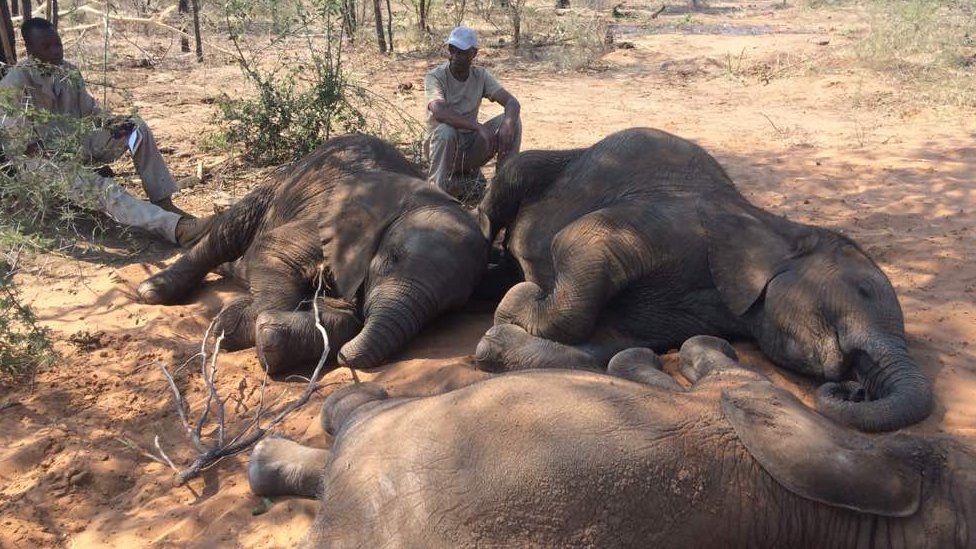

Now, there is another problem with this. These elephants belong to 2 species, the African forest elephant and the African Bush (or Savannah elephant). It is estimated just 40,000-50,000 African forest elephants remain; and it has to be remembered that the differences between the African forest and Savannah elephants are not small – they are not sub species, they are separate species.
The African forest elephant, overlooked by poachers for a long time, had had precipitous collapse in numbers, from over 700,000 to likely under 100,000. More than half of the remaining population lives in Gabon – which makes them susceptable to any change in policy in this small African country.
All this, is a rather long winded way to say that African elephants have suffered over the last century.
The British government has banned the import of ivory. Now they are closing the loophole, by banning other body parts from elephants – why stop ivory import, if the elephant will be driven to extinction for is ears or feet anyway.
Now, it is true that there is some legal hunting. In some places this does make sense, and I would suggest rules to allow import from these places – however these are few and far between, and many are not currently healthy enough to allow hunting. I am thinking of places like the Selous – 20,000 square miles. At one point housing more than 110,000 elephants, successive round of devestating poaching has reduced that to 10,000 or less.
While a take of 50-100 (even 500) from 110,000 is a founding error, this big a take from 10,000 is quite different. In a healthy ecosystem, this take of 1% or less would be fine, but it is likely that animals are still being lost to the poachers. Furthermore, given such a precipitous decline much of the population knowledge will have been lost – making survival through tough times far harder already.
My feeling, is that hunting should only happen if there is no other option. Sure, a hunted elephant brings in a lot of money, however, the Selous could support a vast photographic Safari destination, if the tsetse fly could be eliminated. This would give well passing jobs to the many poor communities living around it’s fringes. Certainly, I would argue with Africa has no need to trophy hunting of elephants, or most other species – never mind the fact that someone going on a canned lion hunt does not risk his life, and is guaranteed to kill. Essentially a canned lion hunt, is killing an animal in a large zoo.