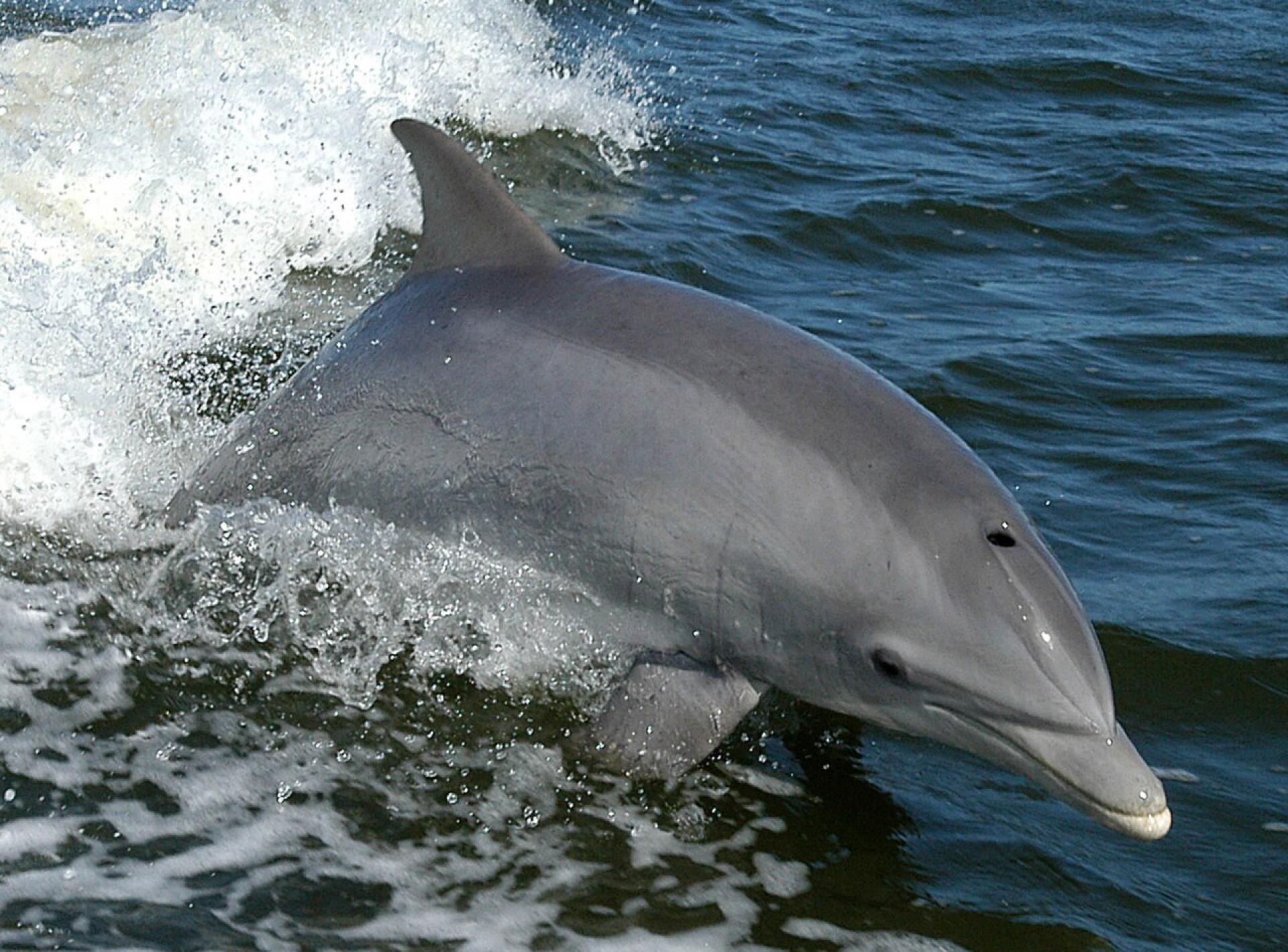
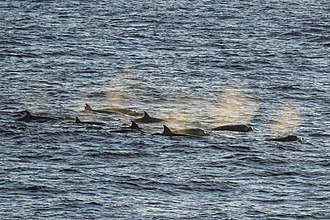- The most abundant cetacean in the world, with around 6 million (it should be noted that there are 1350 humans in the world, for every individual common dolphin).
Despite this fact and its name, the common dolphin is not thought of as the model dolphin (that honour goes to the bottlenose dolphin due to its popular appearances in aquaria and the media). It did, however, feature heavily in Ancient Greek and Roman art and culture, most notably in a mural painted by the Greek Minoan civilization.
It is currently the only member of the genus Delphinus. The common dolphin belongs to the subfamily Delphininae, making this dolphin closely related to the three different species of bottlenose dolphins, humpback dolphins, striped dolphins, spinner dolphins, clymene dolphin, spotted dolphins, fraser’s dolphin and the tucuxi and guiana dolphin.[5] The common dolphin was originally categorized into two different species (now thought to be ecotypes), the short-beaked common dolphin and the long-beaked common dolphin. However, recent evidence has shown that generally long-beaked dolphins of this species have originated from the short-beaked population, and therefore there is no close links between different long-beaked dolphins in any part of the world.
Currently, the common dolphin is divided into four subspecies:
- D. d. delphis, the nominate subspecies
- D. d. bairdii, the Eastern North Pacific long-beaked common dolphin
- D. d. ponticus, the Black Sea common dolphin
- D. d. tropicalis, the Indo-Pacific common dolphin
A number of fossils were erroneously placed in the same genus, but this has since been corrected.
Common dolphins can live in aggregations of hundreds or even thousands of dolphins,though are often seen in groups numbering several hundred individuals (with subgroups consisting of 20-30 individuals). Occasionally, different groups will come together to form mega-pods which can consist of over 10,000 dolphins – quite a site to witness. Genetic studies in the Northeast Atlantic suggest that common dolphin pods generally do not consist of close kin, but rather of members that are not closely related. Unlike many delphinids, common dolphins do not live in a matriarchal society. That being said, closely related individuals are usually found in similar geographical locations fairly consistently, providing evidence that this species displays site fidelity (at least in the North-eastern Atlantic). Male common dolphins display greater site fidelity in relation to their kin than females.
Common dolphin pod structure often consists of nursery pods (which includes females and calves), bachelor pods (consisting of all males) and mixed groups of males and females, including sub-adults and calves. Genetic evidence seems to indicate that common dolphins live in fission-fusion societies, where dolphins form pods that are not necessarily stable and do not necessarily consist of related individuals. It is not known if common dolphins form lifelong bonds with other individuals like the long-term male alliances seen in bottlenose dolphins.
There is some evidence that common dolphins use signature whistles, similar to that of the bottlenose dolphin. These whistles are believed to serve as an acoustic label the dolphin equivalent of a name. It takes approximately 1 year for a calf to learn its signature whistle after which it remains stable for the rest of a dolphin’s life.
In South Africa, as many as 29 common dolphin signature whistle types were detected. However, it was difficult to determine if each dolphin had its own signature whistle due to the vast number of dolphins present (over 1,000) and anthropogenic background noise. Additionally, considering the vast number of dolphins present and taking into account their feeding and diving behaviour, it appears that common dolphin signature whistles are also used for group cohesion. Another hypothesis for the function of signature whistles, is that they serve as a beacon for lost individuals.
Common dolphins sometimes associate with other dolphin species, such as pilot whales (note, not actually whales). In the Gulf of Corinth, common dolphins frequently display mixed species association, especially with striped and Rissos’ dolphins. Over one third of all dolphin sightings in the gulf consisted of mixed species associations that partially consisted of common dolphins. In mixed species associations, the ratio of striped to common dolphins ranged from 6-11:1. When Rissos’ dolphins were present (there would usually be only one or two individuals), it appeared that much of their scars were the result of interactions between striped and spinner dolphins. In much of the interactions, the Rissos’ dolphins would chase and herd the common dolphins toward the boat, while the common dolphins would try and swim under the Rissos’ dolphin. When groups of common and striped dolphins would charge at each other, the Rissos’ dolphin would chase the striped dolphins. Sometimes these interactions appeared to be playful, and at other times aggressive. Synchronized swimming and surfacing was commonly observed. These interactions take place in the deepest part of the Gulf, furthest from shore and usually consist of a total of 60 dolphins from all three species.
There have been 15 cases of common dolphin and striped dolphin hybrids being recorded. Genetic and observational evidence has demonstrated that the hybrids are fertile and are capable of not only reproducing with other hybrids, but are capable of reproducing with each of the parent species. Striped dolphins have been known to mate with other dolphins, as the Clymene dolphin is the result of hybrid speciation between striped and spinner dolphins. However, this is unlikely to happen with common dolphins, as their population in the Gulf of Corinth is too low. Common dolphins and bottlenose dolphins have been known to interbreed in captivity. There is one confirmed case of a hybrid between a bottlenose and common dolphin in Southern Spain, an important feeding ground for both species. The mother was a female bottlenose dolphin (dubbed as Billie) who has spent 10 years within a common dolphin pod. Billie was observed assisting common calves reach the surface at three different intervals and would babysit the calves after the mother went through labour. They have also been observed bow riding on baleen whales, and they also bow ride on boats. They are fast swimmers and breaching behaviour and aerial acrobatics are common with this species. They are also known to display altruistic behaviours to support injured members.
The short-beaked common dolphin is pregnant for 10 to 11 months. The new-born calf has a length of 70 to 100 centimetres (2.3 to 3.3 ft) and weighs about 10 kilograms. For the Black Sea population, weaning occurs at between five and six months, but occurs later (up to about 19 months) in other areas. Typical interbirth interval ranges from one year for the Black Sea population to three years for eastern Pacific Ocean populations. Age of sexual maturity also varies by location, but can range between two and seven years for females and three and 12 years for males. No evidence exists of any major reproductive differences between the two species. In captivity, the long-beaked common dolphin has hybridized with the common bottlenose dolphin . One of the hybrids has been bred back to a bottlenose dolphin, demonstrating such hybrids are fertile.
Find our news section below this video of a megapod of common dolphins