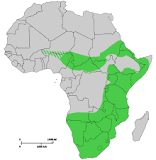
 So the black rhino is one of the two rhino species that survive in Africa. Their last common ancestor was around 6 million years ago (in comparison the Javan and Indian rhino split just 2 million years ago). Being browsers, not grazers, they are far harder to see, as they spend their time deep in the bush, far from the open plains where white rhino are discovered.
So the black rhino is one of the two rhino species that survive in Africa. Their last common ancestor was around 6 million years ago (in comparison the Javan and Indian rhino split just 2 million years ago). Being browsers, not grazers, they are far harder to see, as they spend their time deep in the bush, far from the open plains where white rhino are discovered.
Being solitary, they are also generally found at far lower densities than white rhinos. having said this, in many reserves this is as much as a result of poaching as of a low natural density. Having spent some time based around the Kruger, we have encountered White rhino a huge number of times, but black rhino have eluded us, though their dropping have been encountered on a few occasions.
The black rhino is a younger species than the white rhino having evolved from it, 4-5 million years ago.
They both have 2 horns, made of keratin, the same as our fingernails, with the front one being longer than the back one. The front horn has an average length of 50cm, though this is not a set thing. Plenty of black rhino have been measured with a horn 135cm long, and the world record was a horn 150cm long.
Regions of their range have been lost at various times, though in recent times, there has been an effort to turn back time In May 2017, 18 eastern black rhinos were translocated from South Africa to the Akagera National Park in Rwanda. The park had around 50 rhinos in the 1970s but had lost them all by 2007. In September 2017 18 were reintroduced, and 1 has been born since. The park employs a team to protect the rhinos and so far this has worked. In October 2017, This transfer took place in 2018. The governments of Chad and South Africa reached an agreement in October 2017, to transfer six black rhinos from South Africa to Zakouma National Park in Chad; this was complete by May 2018. Once established, this will be the northernmost population of the species. The species was wiped out from Chad in the 1970s and is under severe pressure from poaching in South Africa. The agreement calls for South African experts to assess the habitat, local management capabilities, security and the infrastructure before the transfer can take place.
Historically there have been a wide range of subspecies suggested for this species: The most accepted position considers seven or eight subspecies, of which three became extinct in historical times and one is on the brink of extinction. I have listed all these below
- Southern black rhinoceros also known as Cape black rhinoceros (D. b. bicornis) – Extinct. Once abundant from the Cape of Good Hope to Transvaal, South Africa and probably into the south of Namibia, this was the largest subspecies. It became extinct due to excessive hunting and habitat destruction around 1850.
- North-eastern black rhinoceros (D. b. brucii) – Extinct. Formerly central Sudan, Eritrea, northern and south-eastern Ethiopia, Djibouti and northern and south-eastern Somalia. Relict populations in northern Somalia vanished during the early 20th century.
- Western black rhinoceros (D. b. longipes) – Extinct. Once lived in South Sudan, northern Central African Republic, southern Chad, northern Cameroon, north-eastern Nigeria and south-eastern Niger. The range possibly stretched west to the Niger River in western Niger, though this is unconfirmed. The evidence from Liberia and Burkina Faso mainly rests upon the existence of indigenous names for the rhinoceros. A far greater former range in West Africa as proposed earlier is doubted by a 2004 study. The last known wild specimens lived in northern Cameroon. In 2006 an intensive survey across its putative range in Cameroon failed to locate any, leading to fears that it was extinct in the wild. On 10 November 2011 the IUCN declared the western black rhinoceros extinct.
- Chobe black rhinoceros (D. b. chobiensis) – A local subspecies restricted to the Chobe Valley in southeastern Angola, Namibia (Zambezi Region) and northern Botswana. Nearly extinct, possibly only one surviving specimen in Botswana.
- Uganda black rhinoceros (D. b. ladoensis) – Former distribution from South Sudan, across Uganda into western Kenya and south-westernmost Ethiopia. Black rhinos are considered extinct across most of this area and its conservational status is unclear. Probably surviving in Kenyan reserves.
- Eastern black rhinoceros (D. b. michaeli) – Had a historical distribution from South Sudan, Uganda, Ethiopia, down through Kenya into north-central Tanzania. Today, its range is limited primarily to Kenya and Tanzania.
- South-central black rhinoceros (D. b. minor) – Most widely distributed subspecies, characterised by a compact body, proportionally large head and prominent skin-folds. Ranged from north-eastern South Africa (KwaZulu-Natal) to north-eastern Tanzania and south-eastern Kenya. Preserved in reserves throughout most of its former range but probably extinct in eastern Angola, southern Democratic Republic of Congo and possibly Mozambique. Extinct but reintroduced in Malawi, Botswana, and Zambia. It also ranges in parts of Namibia and inhabit national parks in South Africa.
- South-western black rhinoceros (D. b. occidentalis) – A small subspecies, adapted to survival in desert and semi-desert conditions. Originally distributed in north-western Namibia and southwestern Angola, today restricted to wildlife reserves in Namibia with sporadic sightings in Angola. These populations are often referred to D. b. bicornis or D. b. minor, but some experts consider them a subspecies in their own right.
The most widely adopted alternative scheme only recognizes five subspecies or “eco-types”: D. b. bicornis, D. b. brucii, D. b. longipes, D. b. michaeli, and D. b. minor. This concept is also used by the IUCN, listing three surviving subspecies and recognizing D. b. brucii and D. b. longipes as extinct. The most important difference to the above scheme is the inclusion of the extant southwestern subspecies from Namibia in D. b. bicornis instead of in its own subspecies, whereupon the nominal subspecies is considered extant.
Seeing Black rhino is hard, but they are in most African reserves that we list
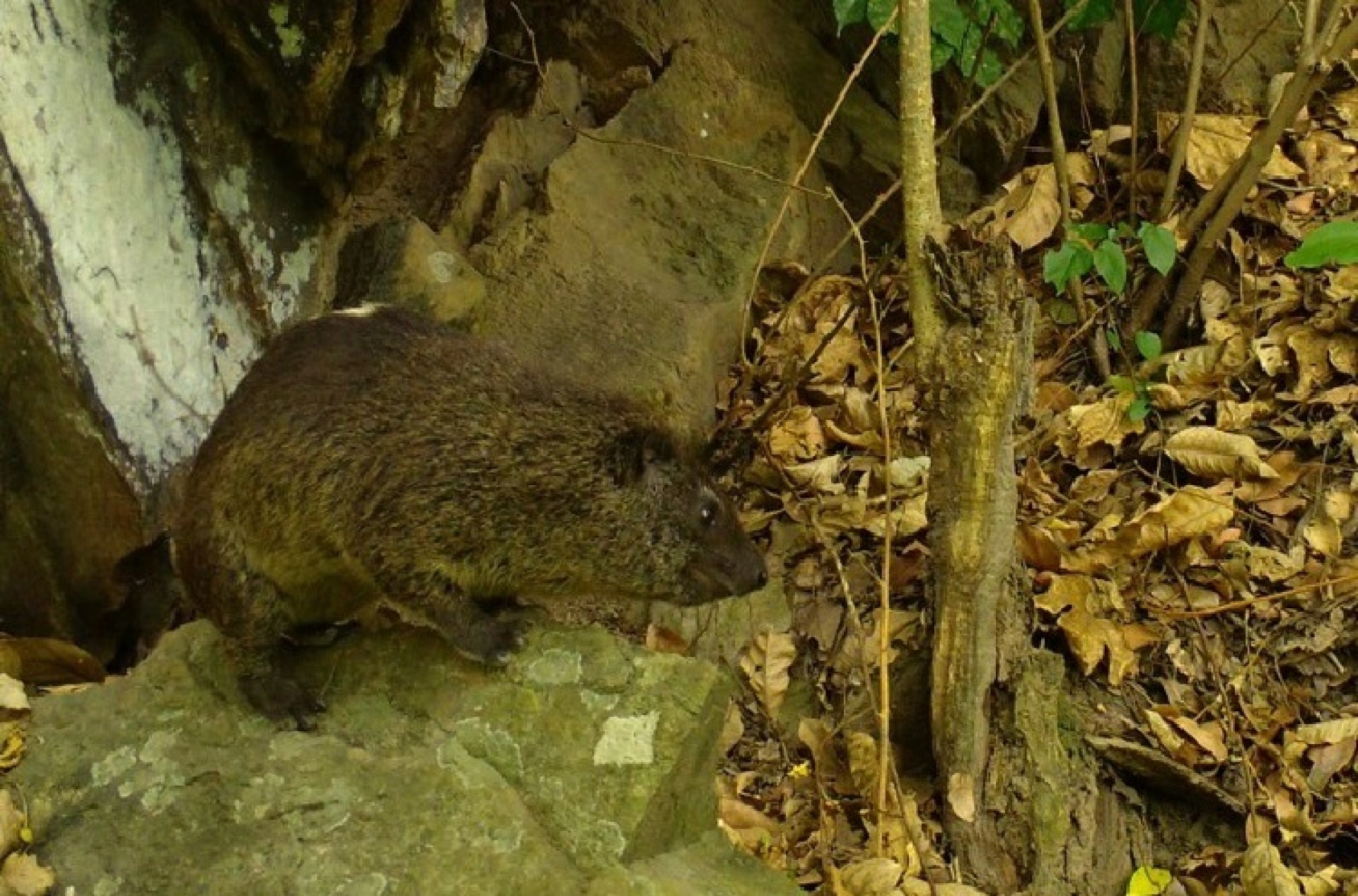



 Southern tree hyrax It is found in temperate forests, subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, moist savanna, and rocky areas.
Southern tree hyrax It is found in temperate forests, subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, moist savanna, and rocky areas.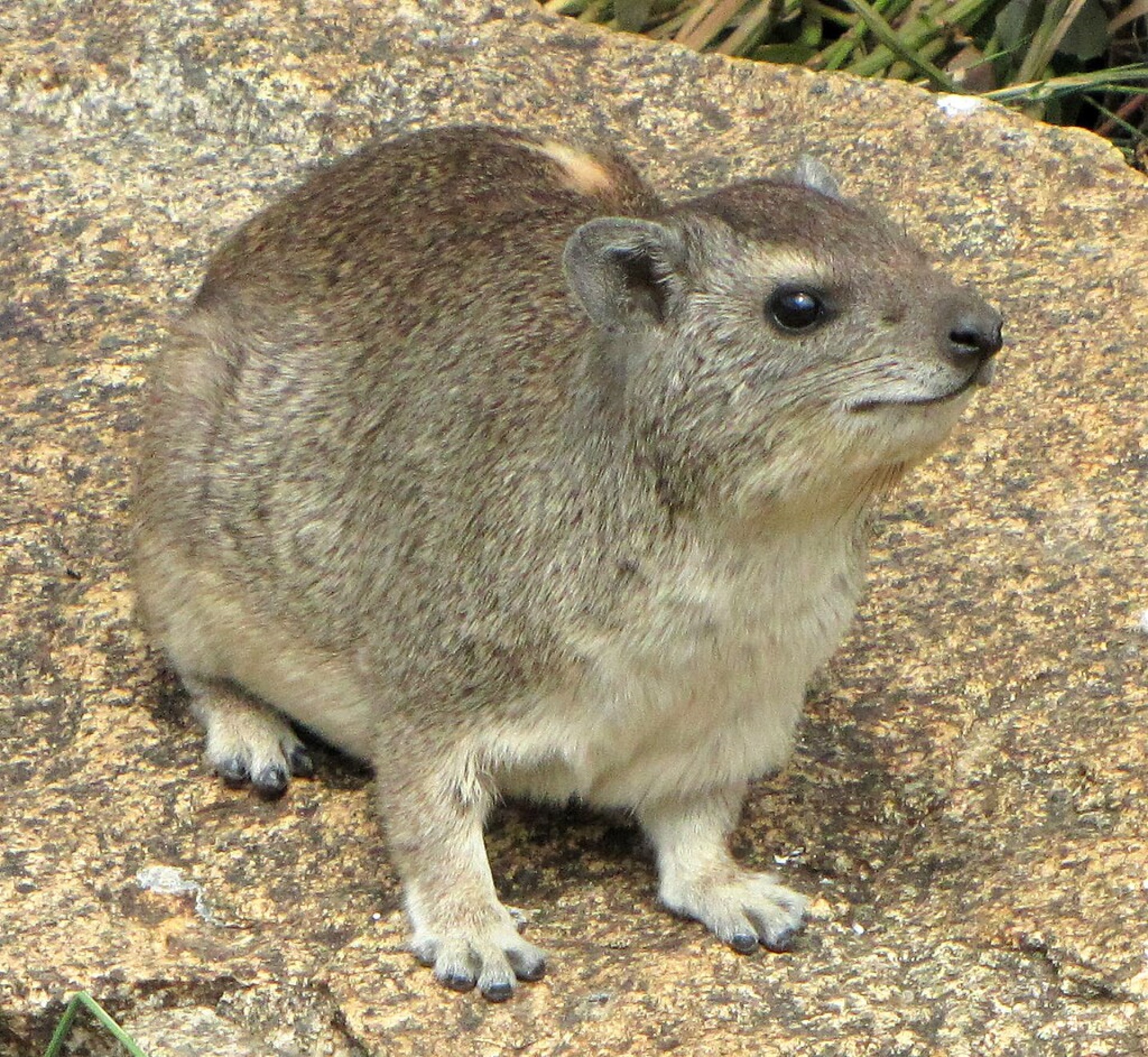
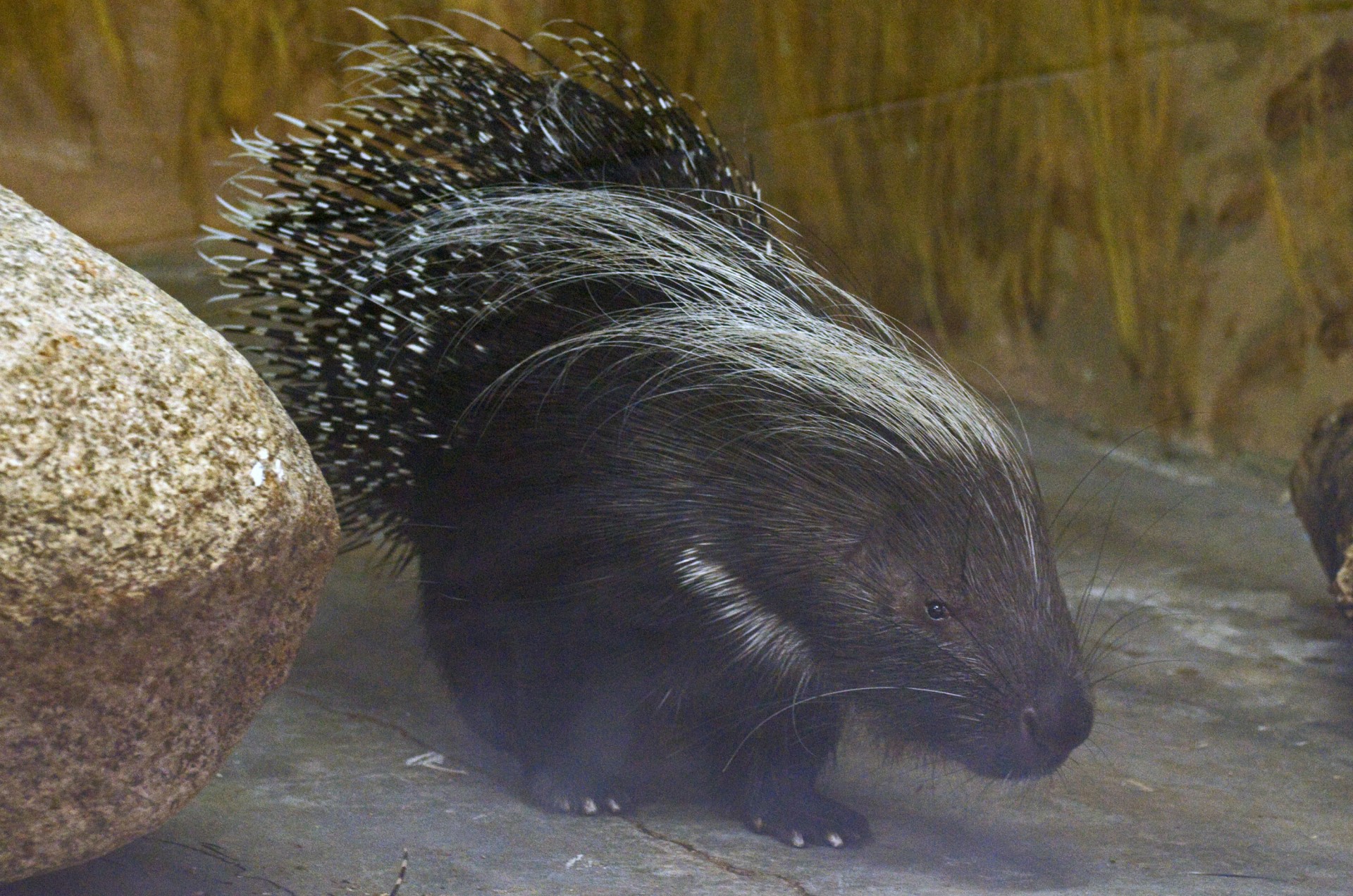
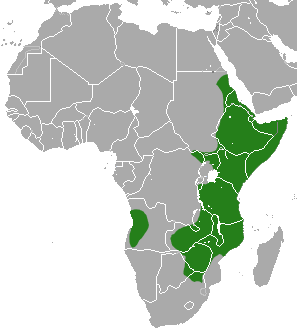

 This is a species of rat-like porcupine, found in a broad belt of Equatorial Africa, right across the continent from Guinea to Kenya.
This is a species of rat-like porcupine, found in a broad belt of Equatorial Africa, right across the continent from Guinea to Kenya. 

 porcupine, (also called the African crested porcupine) is native to North Africa (though it may be locally extinct in Egypt) and sub-Saharan Africa. It is also found in Italy, where the romans introduced it as an extra food source. While accurate estimates on the population size are not seemingly easy to find, Tuscany has a large enough population for it to be one of the more often sighted species when active (at night). Below, I have embedded some footage of an Italian Porcupine
porcupine, (also called the African crested porcupine) is native to North Africa (though it may be locally extinct in Egypt) and sub-Saharan Africa. It is also found in Italy, where the romans introduced it as an extra food source. While accurate estimates on the population size are not seemingly easy to find, Tuscany has a large enough population for it to be one of the more often sighted species when active (at night). Below, I have embedded some footage of an Italian Porcupine porcupine is a rodent species native to southern Asia and the Middle East. It weighs 11-18kg and is 70-90cm long. It has similar looking quills to the African Porcupine, and has a similar diet.
porcupine is a rodent species native to southern Asia and the Middle East. It weighs 11-18kg and is 70-90cm long. It has similar looking quills to the African Porcupine, and has a similar diet. porcupine or Himalayan porcupine is a species of rodent. The head and body measurement are around 56-74 cm and the tail is about 6–11 cm. They weigh around 10 kg-18 kg. They normally feed on roots, tubers, bark and fallen fruits. They also eat carrion, insects, and large tropical seeds. They forage at night and rests during the day. It may be found singly or in pairs. It can also swim and gnaw. The sow usually has one, but twins have also been recorded.
porcupine or Himalayan porcupine is a species of rodent. The head and body measurement are around 56-74 cm and the tail is about 6–11 cm. They weigh around 10 kg-18 kg. They normally feed on roots, tubers, bark and fallen fruits. They also eat carrion, insects, and large tropical seeds. They forage at night and rests during the day. It may be found singly or in pairs. It can also swim and gnaw. The sow usually has one, but twins have also been recorded.
 porcupine is a species of rodent. It is endemic to Indonesia. Due to the popularity of the hunting and consumption of the Sunda porcupine as an aphrodisiac, the Ministry of Environment and Forestry in Indonesia has listed this species as a protected animal as of June 2018.
porcupine is a species of rodent. It is endemic to Indonesia. Due to the popularity of the hunting and consumption of the Sunda porcupine as an aphrodisiac, the Ministry of Environment and Forestry in Indonesia has listed this species as a protected animal as of June 2018. porcupine
porcupine  (also called Palawan porcupine) is a species of rodent endemic to the island of Palawan in the Philippines. It is known locally as durian or landak.
(also called Palawan porcupine) is a species of rodent endemic to the island of Palawan in the Philippines. It is known locally as durian or landak. or Quichua porcupine is a species of rodent. It is found in the Andes of northern Ecuador and Colombia as well as in Panama. This porcupine is little known, but is probably arboreal, nocturnal and solitary like its relatives. The species is thought to be uncommon to rare and the population decreasing. It is threatened by deforestation, habitat fragmentation and agriculture. It is 60-80cm long (including tail), and weighs 2kg when fully grown. The ecology of this species is little known. Its behaviour is likely to resemble that of its close relatives in being nocturnal and arboreal, and feeding on fruit and leaves.
or Quichua porcupine is a species of rodent. It is found in the Andes of northern Ecuador and Colombia as well as in Panama. This porcupine is little known, but is probably arboreal, nocturnal and solitary like its relatives. The species is thought to be uncommon to rare and the population decreasing. It is threatened by deforestation, habitat fragmentation and agriculture. It is 60-80cm long (including tail), and weighs 2kg when fully grown. The ecology of this species is little known. Its behaviour is likely to resemble that of its close relatives in being nocturnal and arboreal, and feeding on fruit and leaves. porcupine (Coendou bicolor) is a species of nocturnal and arboreal rodent in the family Erethizontidae.
porcupine (Coendou bicolor) is a species of nocturnal and arboreal rodent in the family Erethizontidae. also called Koopman’s porcupine, is a porcupine species from the New World and is endemic to northern Brazil. It occurs in the Amazon rainforest east of the Madeira River and south of the Amazon River. It inhabits primary forest and possibly second growth. It was described as Coendou koopmani by Charles O. Handley Jr. and Ronald H. Pine in 1992, but was subsequently found to be identical to a species described in 1818. It is nocturnal and herbivorous.
also called Koopman’s porcupine, is a porcupine species from the New World and is endemic to northern Brazil. It occurs in the Amazon rainforest east of the Madeira River and south of the Amazon River. It inhabits primary forest and possibly second growth. It was described as Coendou koopmani by Charles O. Handley Jr. and Ronald H. Pine in 1992, but was subsequently found to be identical to a species described in 1818. It is nocturnal and herbivorous.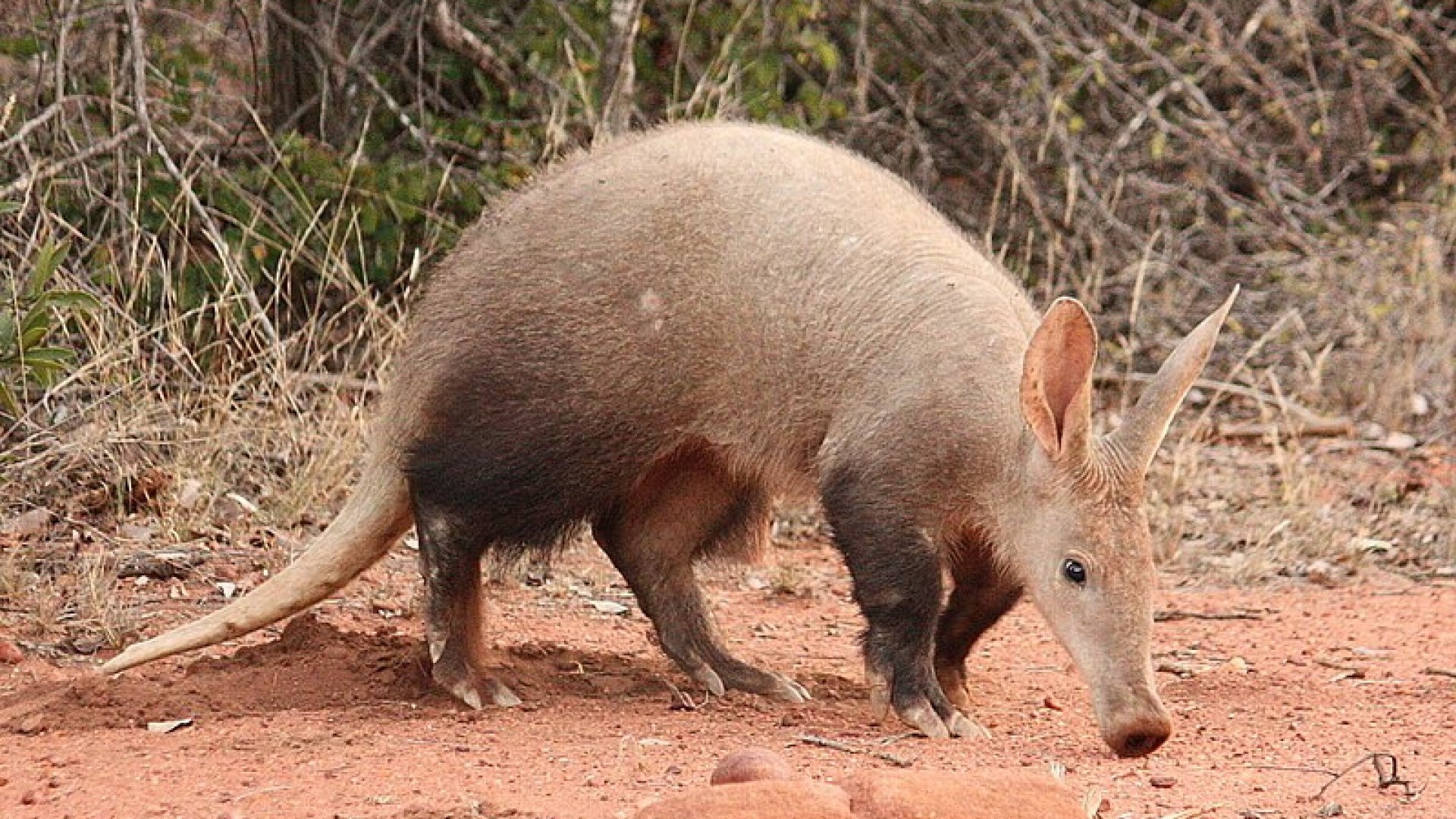
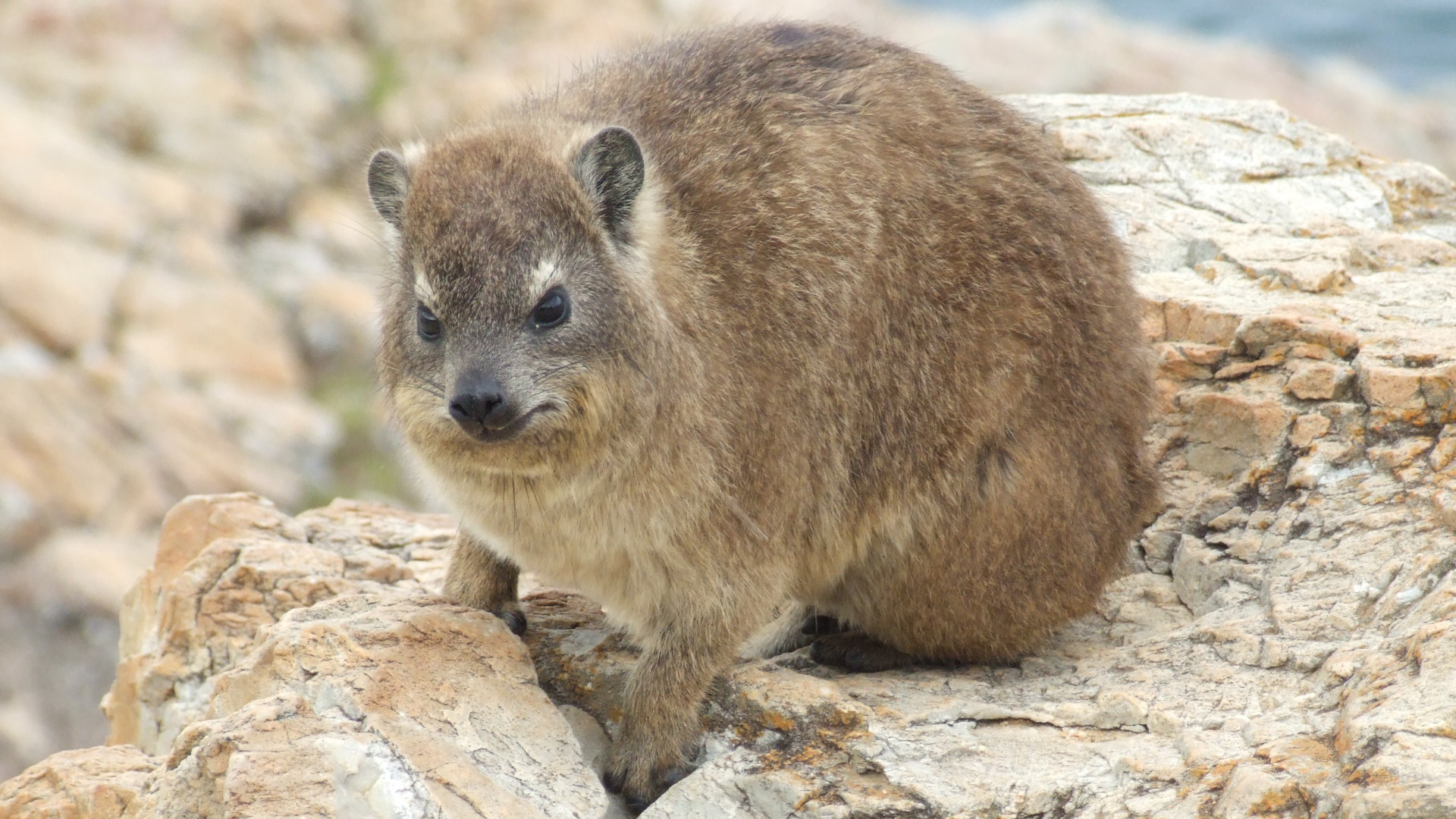




 Western tree hyrax, also known as the western tree dassie or Beecroft tree hyrax
Western tree hyrax, also known as the western tree dassie or Beecroft tree hyrax Rock or cape hyrax has 5 recognized subspecies, again, unsurprising given its vast range. Generally having a hide within a natural rock cavity, Rock hyraxes are social animals that live in colonies of up to 50 individuals. They sleep in one group, and start the day, warming up in the sun
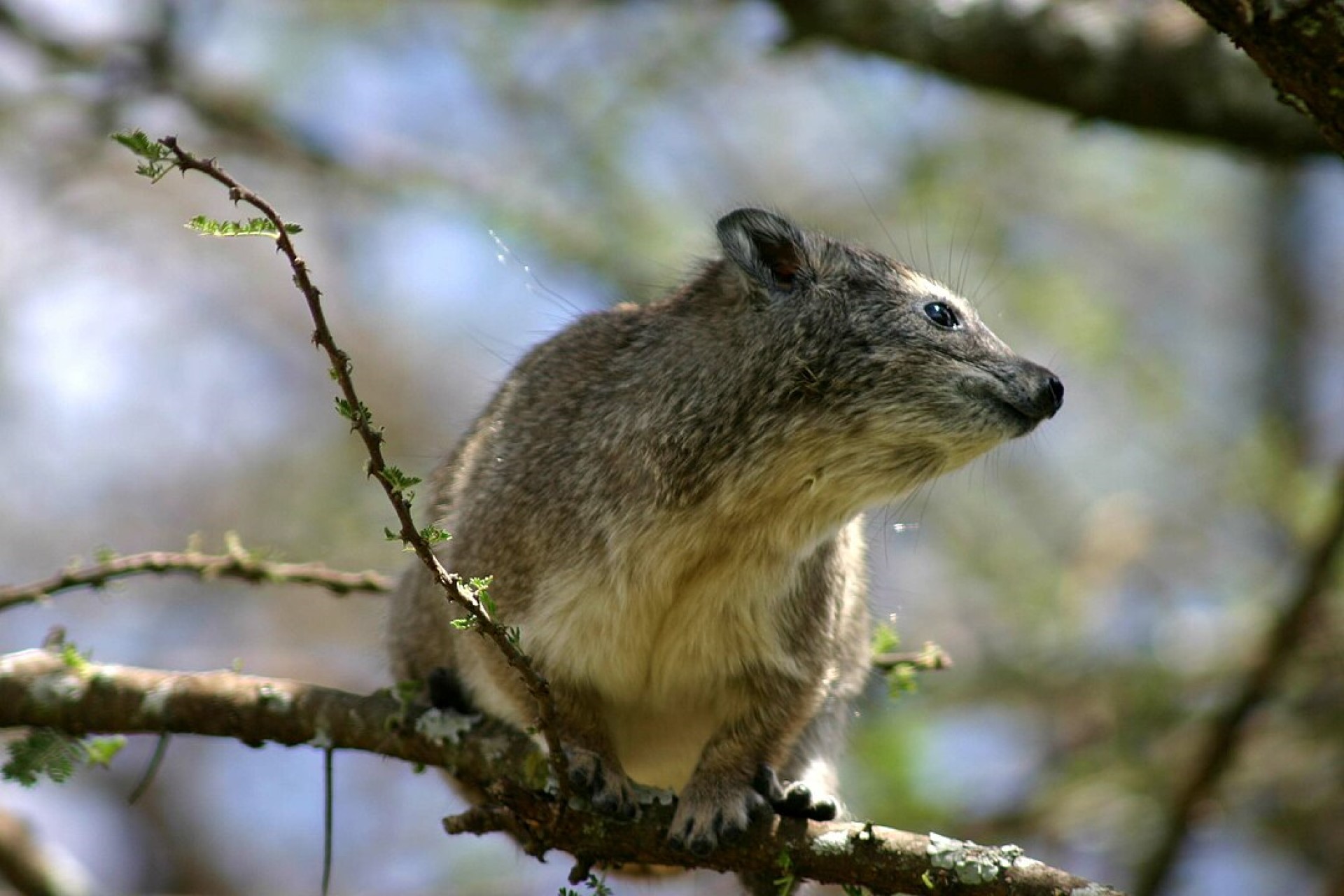
Rock or cape hyrax has 5 recognized subspecies, again, unsurprising given its vast range. Generally having a hide within a natural rock cavity, Rock hyraxes are social animals that live in colonies of up to 50 individuals. They sleep in one group, and start the day, warming up in the sun Eastern tree hyrax is the most localized of the tree hyrax species, only found in places within a narrow band of lowland and montane forests in Kenya and Tanzania and close-by islands. A solitary species, it lives in tree cavities, and communicates with others, through scent marking and high pitched calls.
Eastern tree hyrax is the most localized of the tree hyrax species, only found in places within a narrow band of lowland and montane forests in Kenya and Tanzania and close-by islands. A solitary species, it lives in tree cavities, and communicates with others, through scent marking and high pitched calls. 
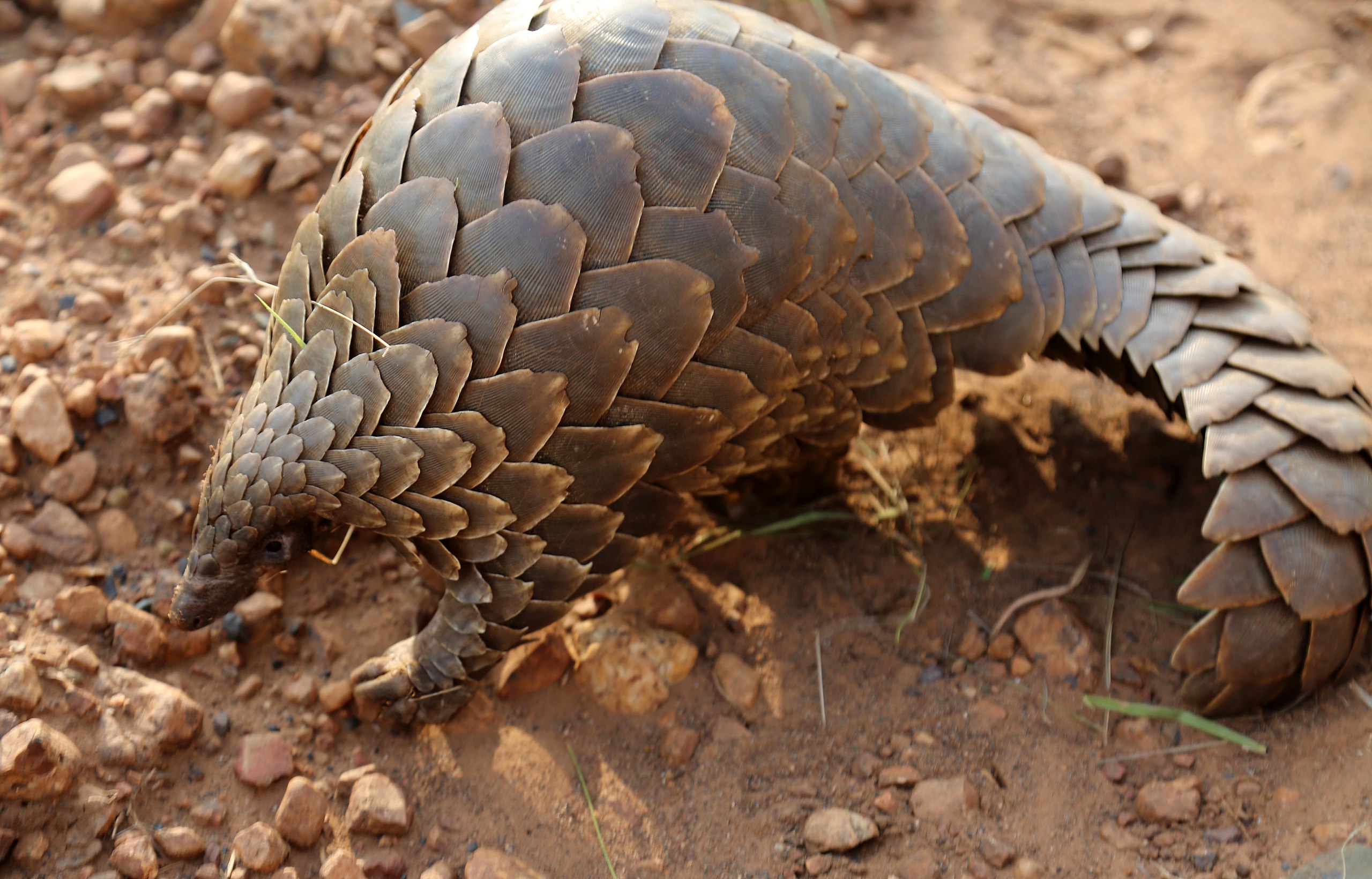
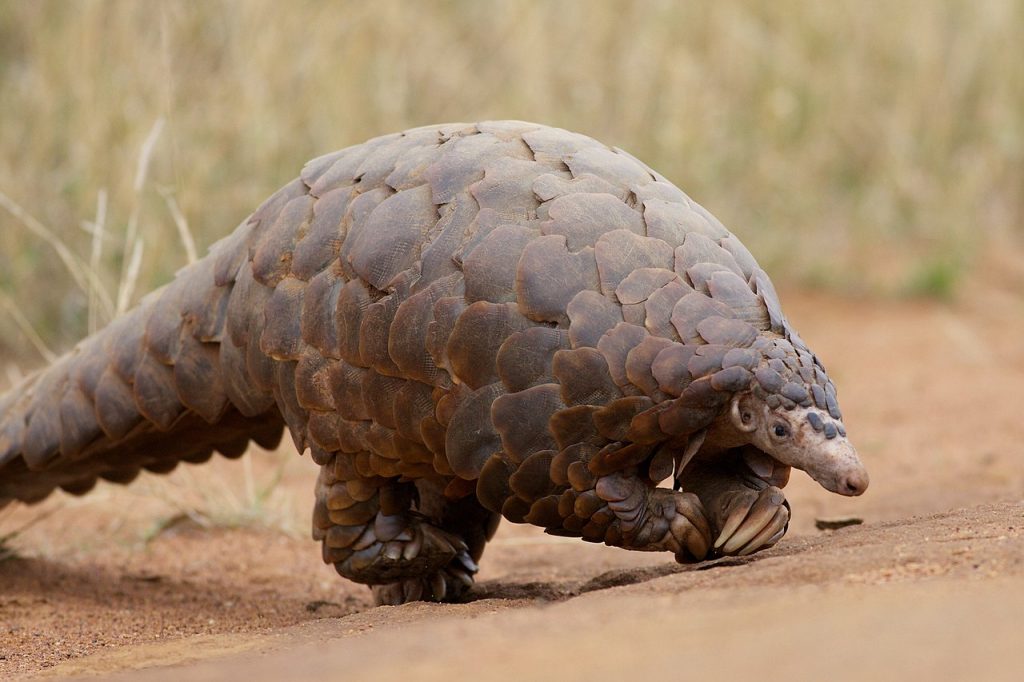






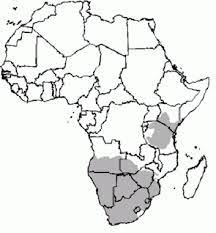
 The HIrola ( also known as the Hunters hartebeest or hunters antelope) is a critically endangered species. It was named by H.C.V Hunter (a big game hunter and zoologist) in 1888. It is the only member of the genus Beatragus, and it currently has 300-500 individuals living in the wild (there are none in captivity).
The HIrola ( also known as the Hunters hartebeest or hunters antelope) is a critically endangered species. It was named by H.C.V Hunter (a big game hunter and zoologist) in 1888. It is the only member of the genus Beatragus, and it currently has 300-500 individuals living in the wild (there are none in captivity).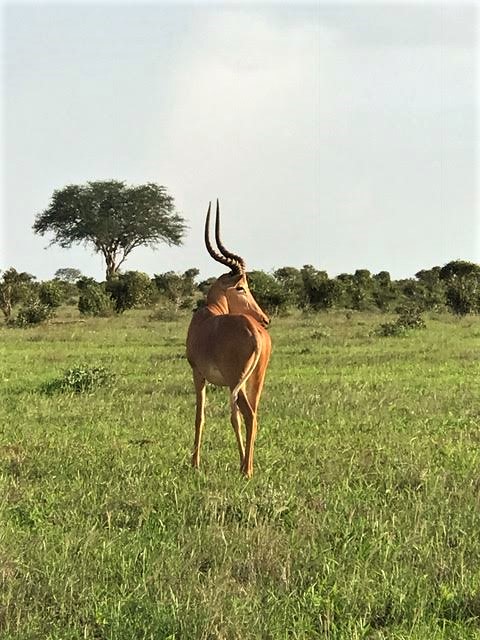
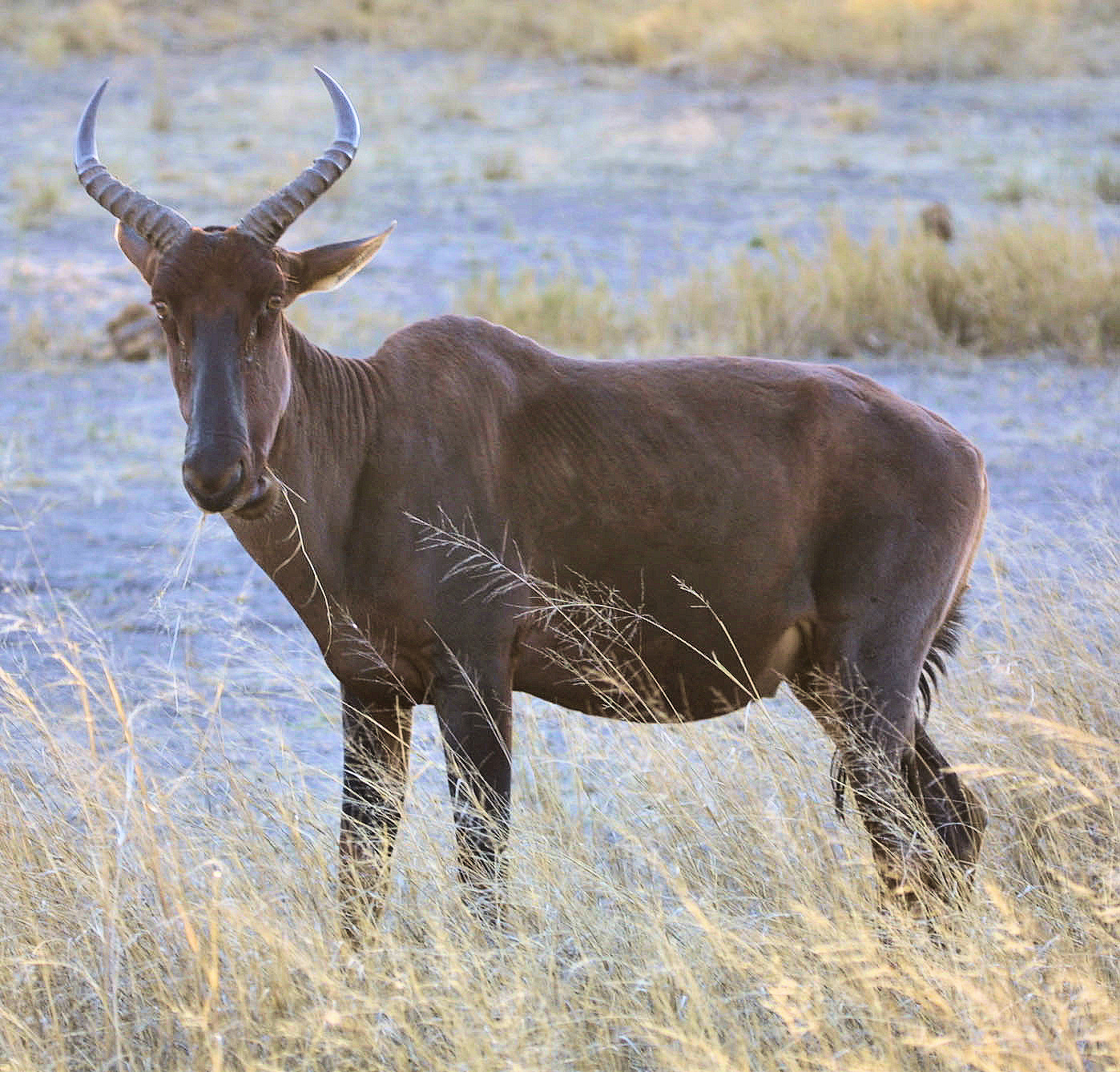
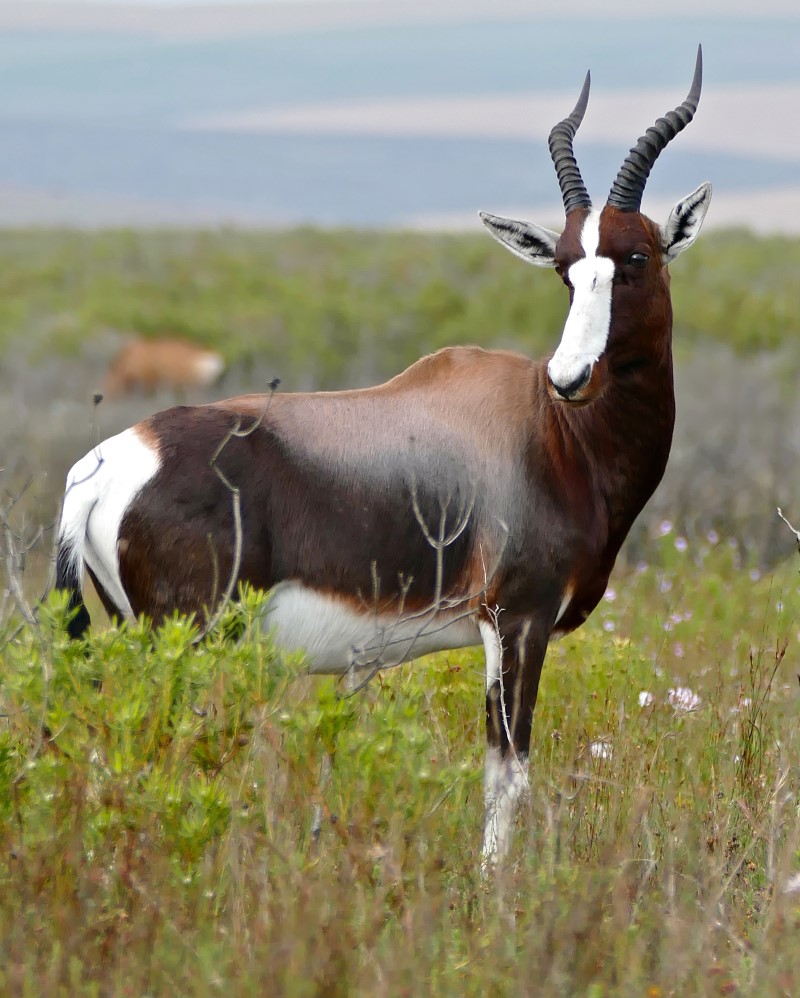




 many as 70 subspecies, local variants and similar have been suggested, however there is only one currently recognized species.
many as 70 subspecies, local variants and similar have been suggested, however there is only one currently recognized species. common wildebeest, white-bearded gnu or brindled gnu.
common wildebeest, white-bearded gnu or brindled gnu.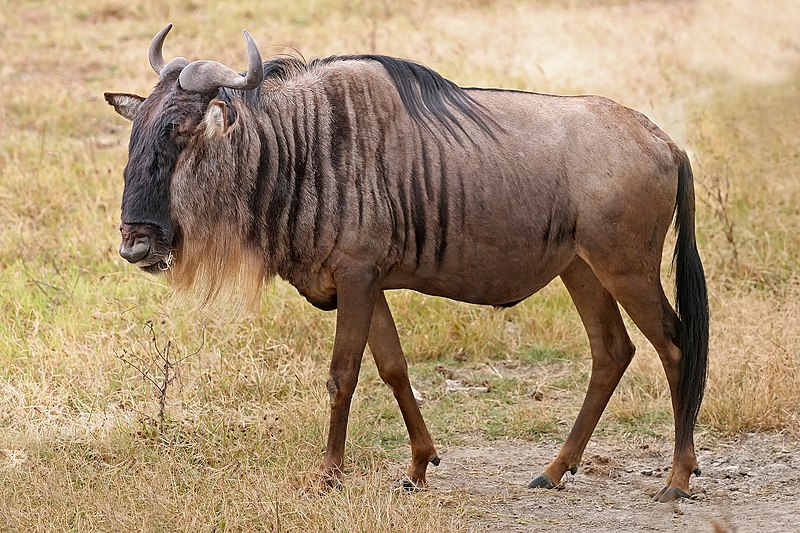
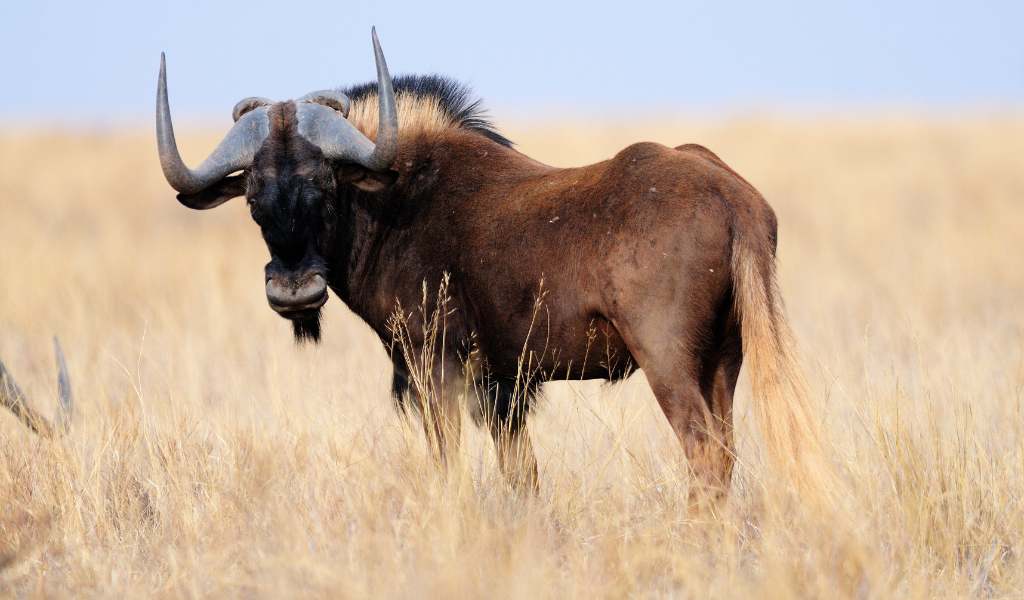
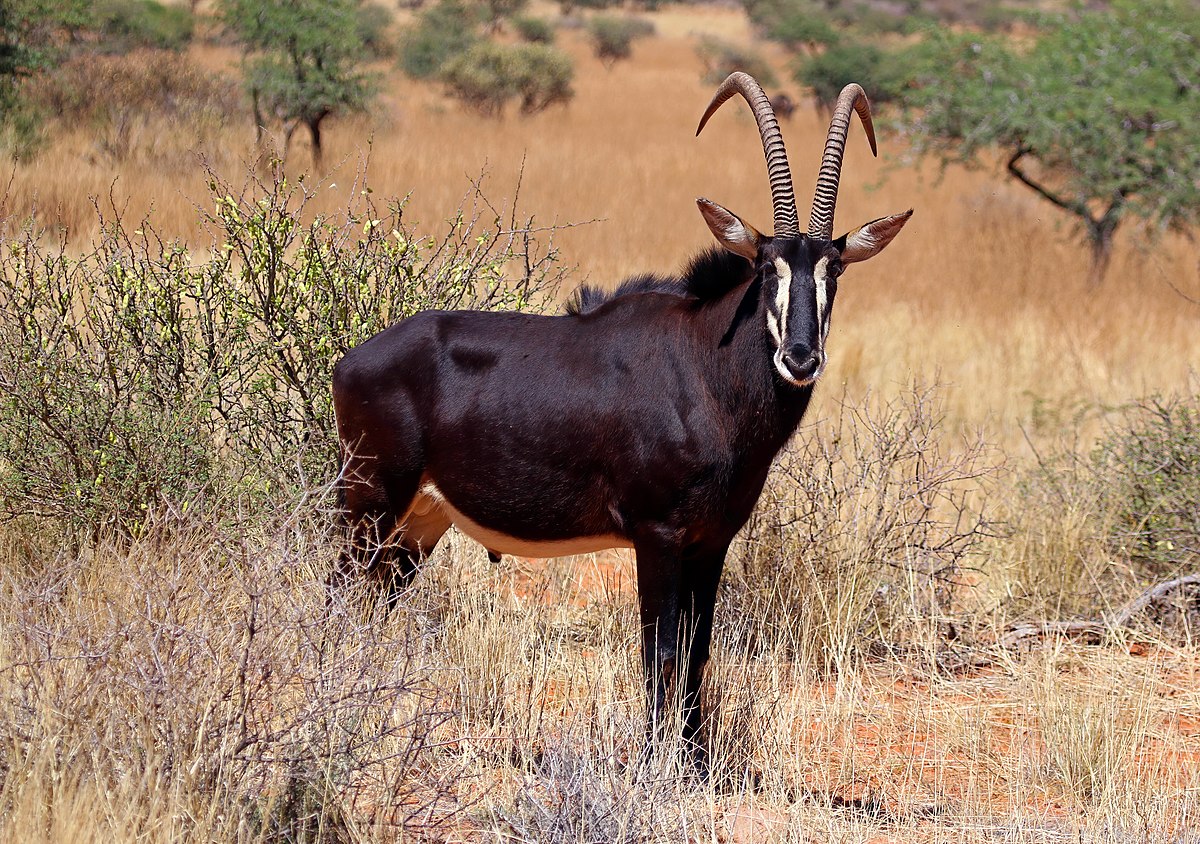






 are found in a band across Africa, including areas of Eastern, Central and Western Africa.
are found in a band across Africa, including areas of Eastern, Central and Western Africa.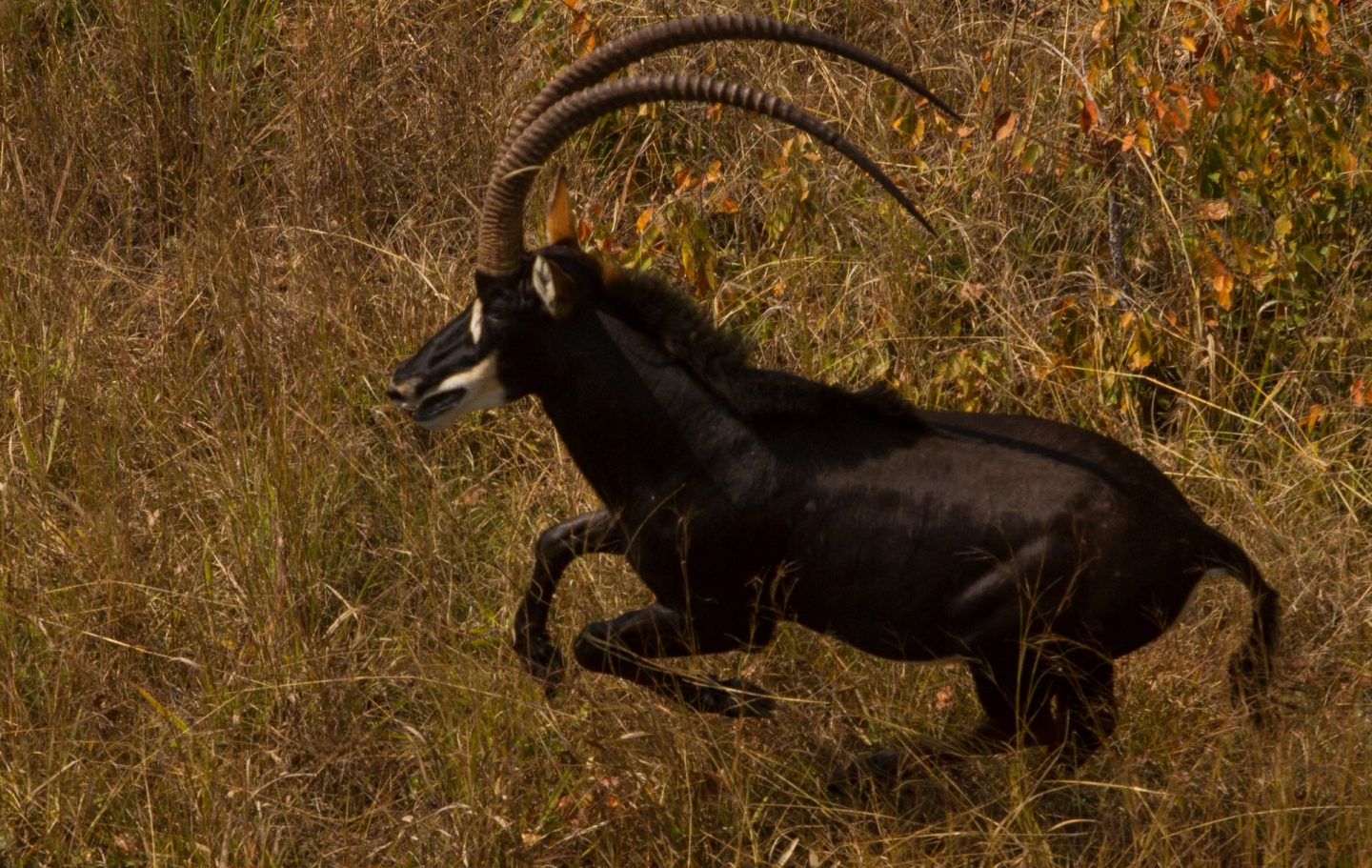
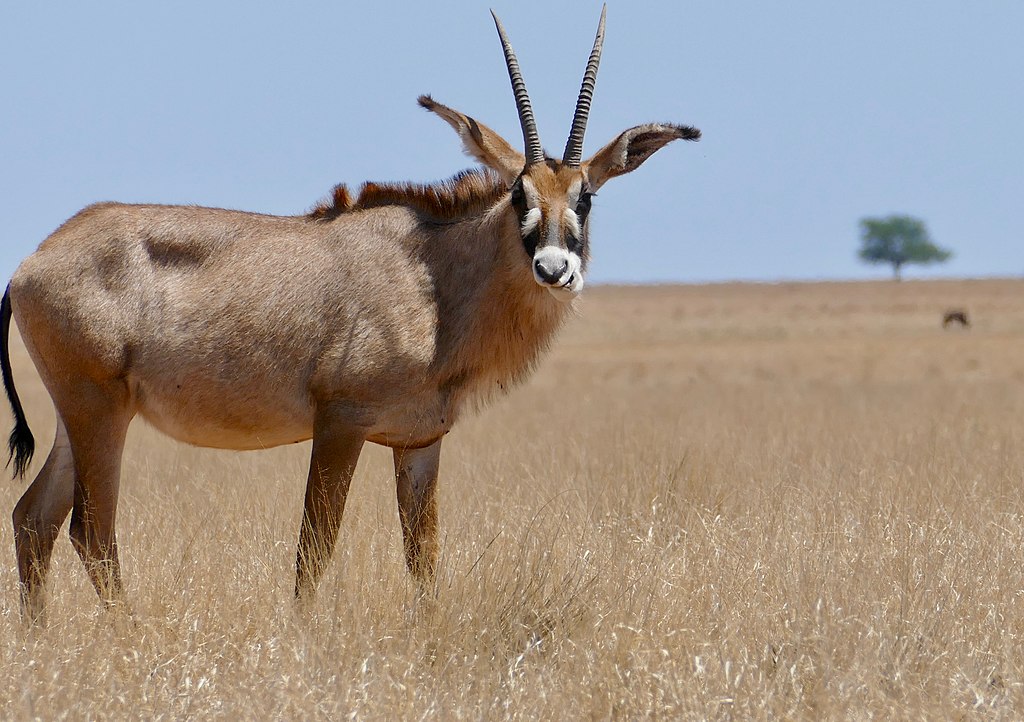
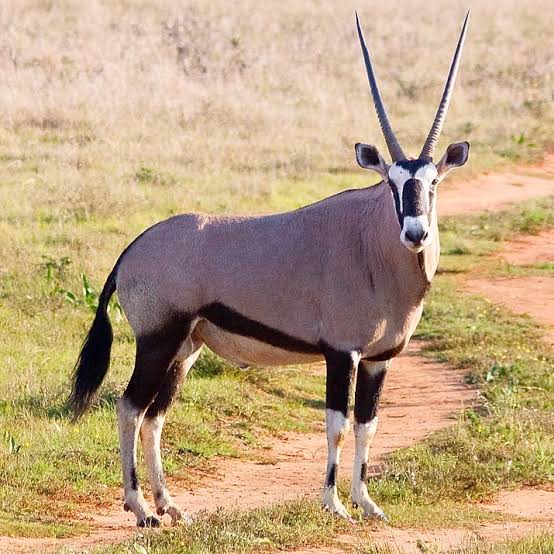
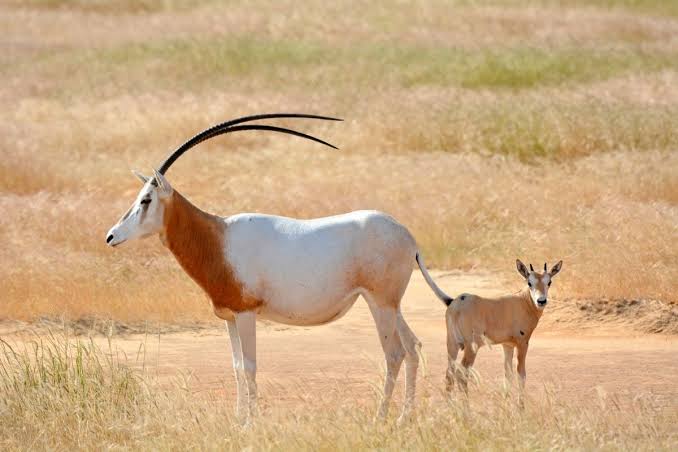





 Impala
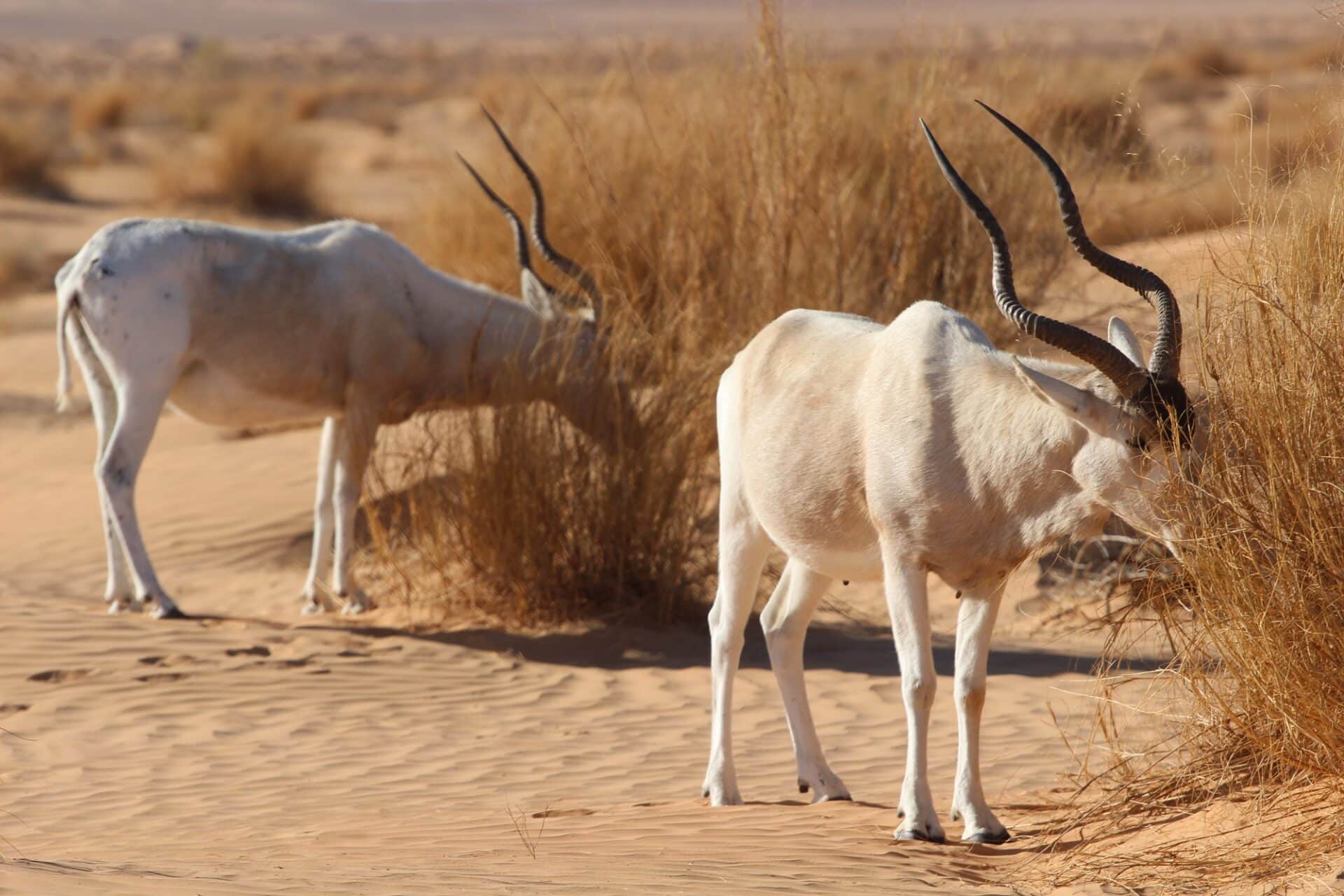
Impala antelope, species with a handful of small populations acros central and western north Africa. It lives in the Sahara and the Sahel desert.
antelope, species with a handful of small populations acros central and western north Africa. It lives in the Sahara and the Sahel desert.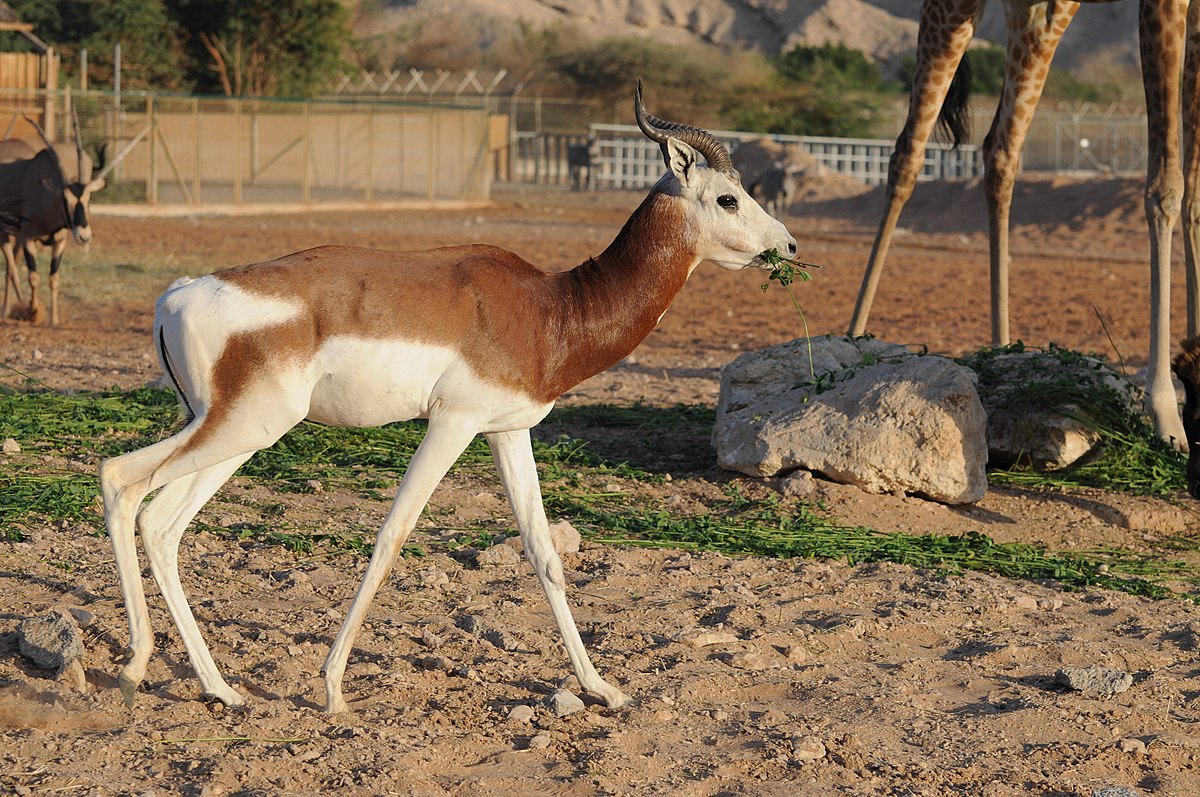 
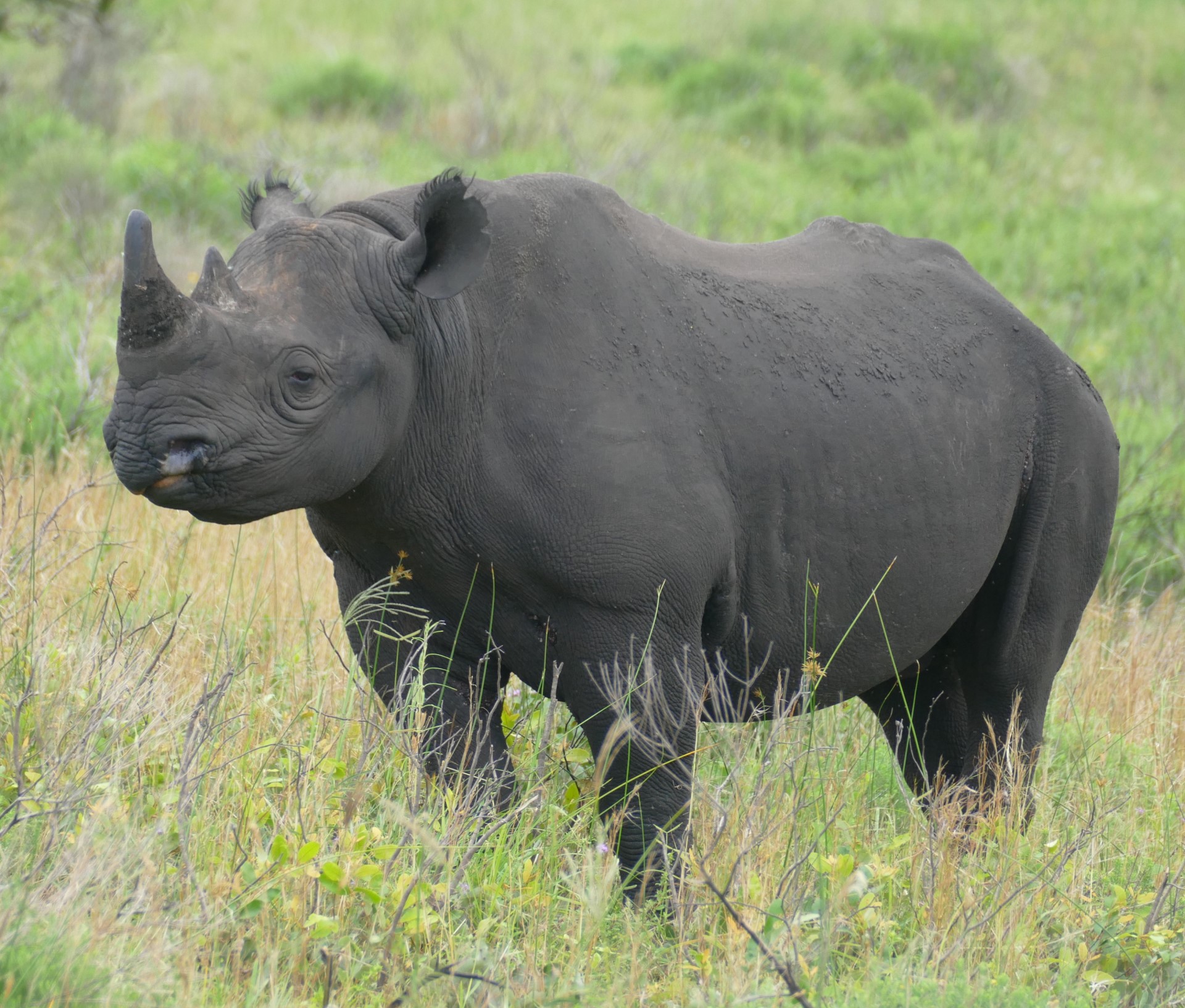

 So the black rhino is one of the two rhino species that survive in Africa. Their last common ancestor was around 6 million years ago (in comparison the Javan and Indian rhino split just 2 million years ago). Being browsers, not grazers, they are far harder to see, as they spend their time deep in the bush, far from the open plains where white rhino are discovered.
So the black rhino is one of the two rhino species that survive in Africa. Their last common ancestor was around 6 million years ago (in comparison the Javan and Indian rhino split just 2 million years ago). Being browsers, not grazers, they are far harder to see, as they spend their time deep in the bush, far from the open plains where white rhino are discovered.