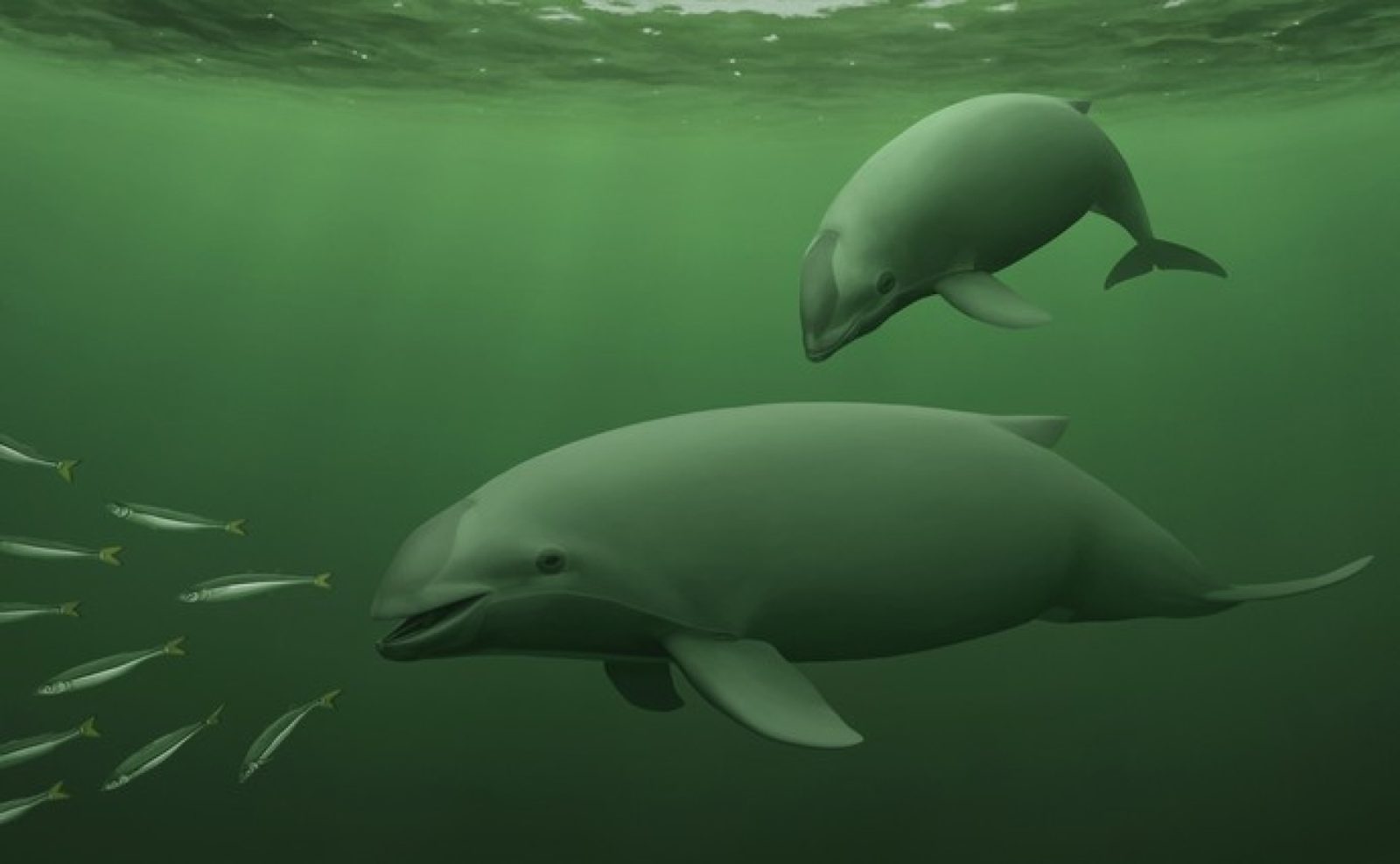
Bermeister Porpoise
First described by Hermann Burmister in 1865, they are thought to have a population that numbers at least in the 10,000s. Found from Peru in the Pacific to Brazil in the Atlantic, while usually found in shallow coastal waters, they have been located 1000m down.
Most photos of this species are of a dead individual. It is black which explains its other name – the black porpoise, though it is thought that they turn black after death and are dark grey beforehand. The underside is lighter, though this is common as it helps with camouflage against the light surface of the water. Usually 1.5m in length and with a weight of 50-75kg, they can be mistaken for the Chilean dolphin, which is a similar size. Their dorsal fin is more triangular and points back rather than up so should not be confused.
They are shy, usually moving away from boats at a high speed. Usually seen in pairs or alone. However, they have been seen in larger groups, with a group spotted off the coast of Chile numbering 50.
Eating Hake, Maceral and Anchovies, which are all species impacted greatly by el nino. Many of the marine mammals in the area starved or struggled until the fish returned.
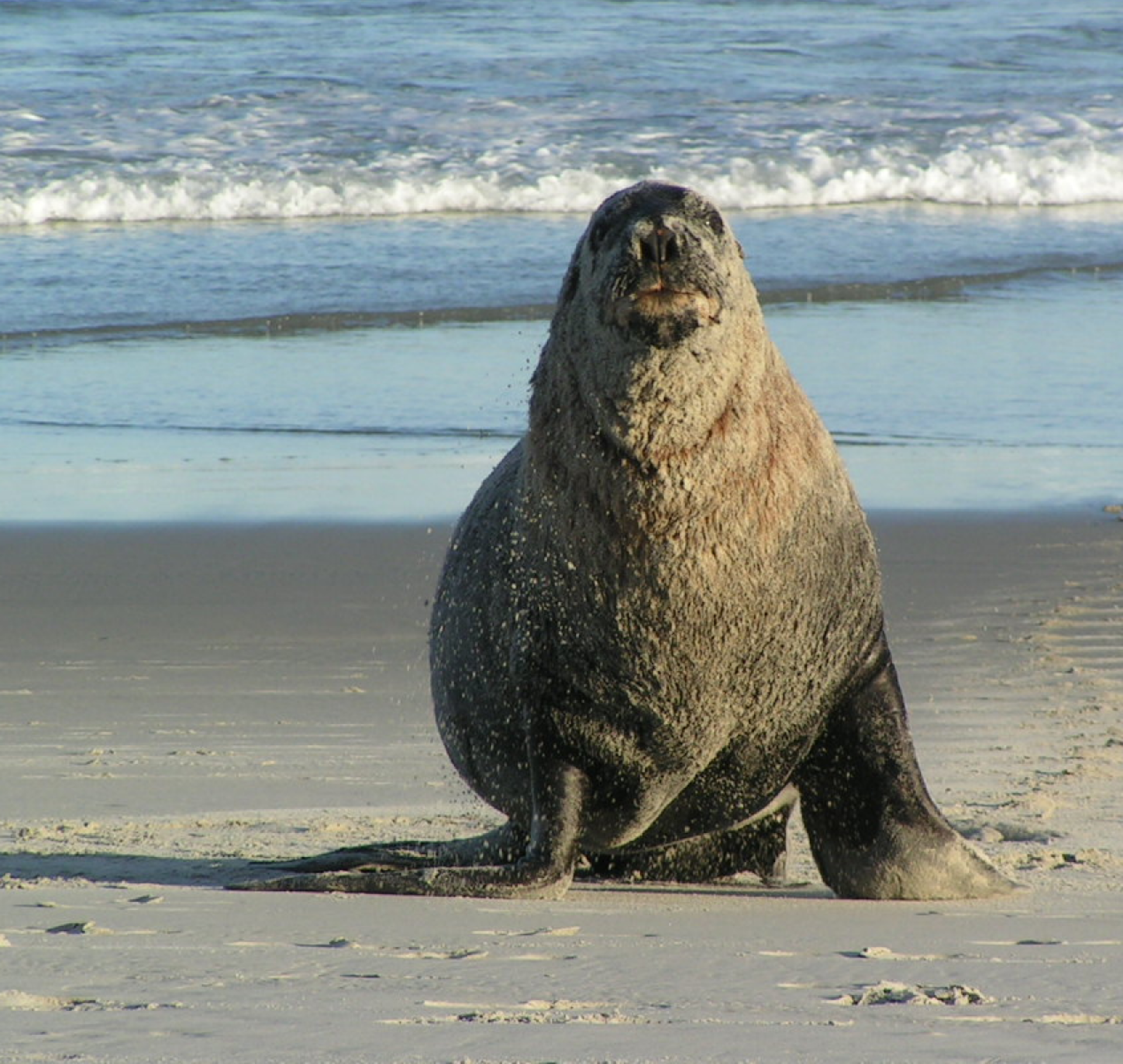



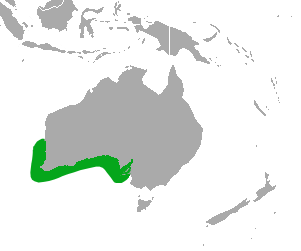 only endemic pinniped found in Australia.
only endemic pinniped found in Australia.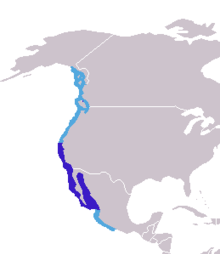 the west coast of north America. On this map, the navy blue marks the breeding rance, while the light blue shows the total range that they can be found in. It should be noted, that previously the Japanese and Galapagos sealion were both considered subspecies of the Californian species, but no longer. They can stay healthy, for a time, in fresh water, and have been seen living for a while in Bonneville dam – 150 miles inland.
the west coast of north America. On this map, the navy blue marks the breeding rance, while the light blue shows the total range that they can be found in. It should be noted, that previously the Japanese and Galapagos sealion were both considered subspecies of the Californian species, but no longer. They can stay healthy, for a time, in fresh water, and have been seen living for a while in Bonneville dam – 150 miles inland.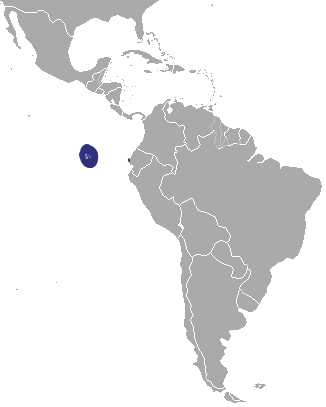 on all of the Galapagos Islands, as well as (in smaller numbers) on Isla de la Plata, which is just 40km from Puerto López a village in Ecuador. There have also been recorded sightings on the Isla del Coco which is 500km southwest of Costa Rica (and 750km from the Galapagos). These are not regular, and so have been considered vagrant. It is of course possible that historically they roamed here, but we cannot say.
on all of the Galapagos Islands, as well as (in smaller numbers) on Isla de la Plata, which is just 40km from Puerto López a village in Ecuador. There have also been recorded sightings on the Isla del Coco which is 500km southwest of Costa Rica (and 750km from the Galapagos). These are not regular, and so have been considered vagrant. It is of course possible that historically they roamed here, but we cannot say. known as the Hooker sealion) is native to south island, though before 1500 it is thought that it was also found on north island. They tend to breed on Subarctic islands of Auckland and Campbell (99% of the pups are born in these islands). In 1993, sealions started breeding on South Island again for the first time in 150 years.
known as the Hooker sealion) is native to south island, though before 1500 it is thought that it was also found on north island. They tend to breed on Subarctic islands of Auckland and Campbell (99% of the pups are born in these islands). In 1993, sealions started breeding on South Island again for the first time in 150 years.







