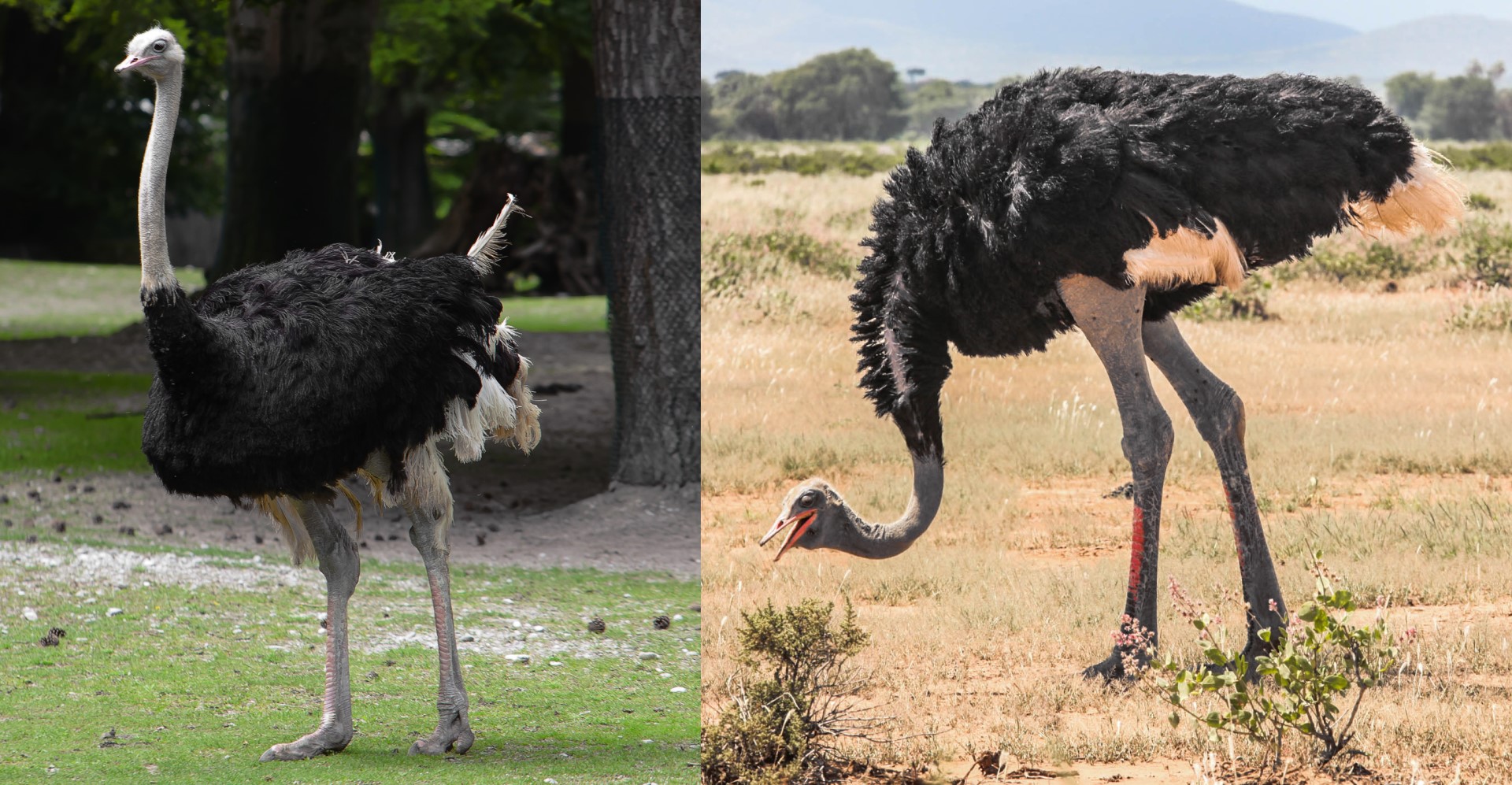
Both ostrich species Combined PaleoNeolithic photo credit Diego Delso&Ninara
Ostrich
Common Ostrich
Somali Ostrich
The common ostrich is found across a large part of the African Continent. Until 1919 there was a fourth subspecies of the common ostrich which was found across much of the Arabian Peninsular. It was completely extinct in the wild by 1972. They have now been reintroduced to Israel, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Jordan and United Arab Emirates – though it is hard to find accurate figures for how many are found there now. (Do get in touch if you operate a reserve with these birds present, we would love to help people find you).
As you can see, the other African subspecies are still going.
The Somali Ostrich was only recognized as a separate species back in 2014, having been thought to be a subspecies until them.
A report to the IUCN in 2006 believed that this ostrich was common in central and southern Somalia until 1970-80. However, following the breakdown in the country, it is not surprising that conservation took back-stage, and it is questionable as to whether any remain (in the horn of africa).
In Kenya it is farmed for meat, feathers and eggs.
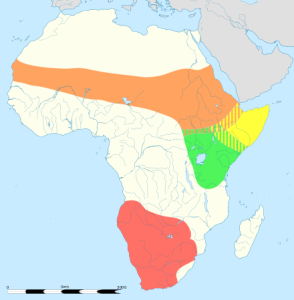 This is a map of the different Ostrich species and subspecies range
This is a map of the different Ostrich species and subspecies range
- The yellow area, shows the range of the Somali Ostrich – Now recognized as a separate species.
- The green area shows the range of the Massai Ostrich – while this population is listed as least concern, its numbers are in decline
- The red is the South African Ostrich, this is generally secure, though only found within reserves.
- The Orange is the range of the North African Ostrich: classed as critically endangered, it is only found in 6 of the 18 countries it originally roamed. It is the largest and heaviest subspecies. The countries it is still found in include fragmented pockets of Cameroon, Chad, Central African Republic and Senegal. They have also been reintroduced into Chad, Morocco and in 2014 (127 years after being lost) Tunisia. They were reintroduced to Saudi Arabia in the Mahazat as-Sayd Protected Area in 1994 and this population has done well with around 90-100 now living within this reserve
There is thought to be approximately 150,000 ostrich left in the wild. Having said this, like other large species, they are prone to local extinction. The best way to see these in the wild are to head to reserves where they still exist.
Unfortunately, they are not easy to look after – in smaller reserves with large predators, they can be hunted and face local extinction. As such, while there are other reserves where they hang on, the majority of their remaining population are split between big reserves like the Kruger and the Serengeti, and small reserves like the Cape point national park in South Africa (this reserve is only 77.5 square km, or around 30 square miles and was in the past a big 5 nature reserve. Now, only the cape leopard is present and this is very rarely seen.
If you wish to see the Ostrich look in our list of wild places. Kruger, Okavango and the Serengeti all have ostrich (in Kruger you need to look in the more sparsely area in the north of the park).
Bringing the Arabian Oryx back from the brink of Extinction
- Tim
- September 26, 2022
With the advent of large numbers of zoos - with healthy collections of animals from around the world, the loss of a species in the wild can sometimes be reversed....
Why are there still do many climate change deniers left, as it effects become impossible to ignore?
- Tim
- August 20, 2020
Despite the fact that the majority of the world's population is increasingly worried by global warming and its effects,and the fact that day by day in year by year we...