There is much work around the world, which is going into measuring temperatures as accurately as possible and watching for change. While the British empire routinely took temperature readings on certain trips, and there are various other long records, there is no human record which goes back more than a few centuries. While this is irrelevant for human caused climate change, as we only started releasing large quantities of warmth trapping carbon dioxide in the last few centuries (largely started by the industrial revolution in the UK), we want to be able to both have more records from the last few centuries, and records that go far further back.

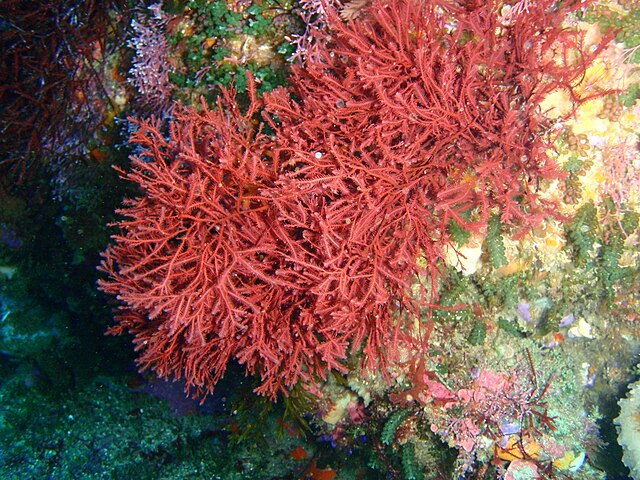
A variety of natural methods have been found, but this new ancient sea sponge method is interesting. This is because, lying 30-90m below the surface of the Mediterranean. In the Mediterranean even in the shallows with the water only changing by around 10 degrees, however, below 12-40 feet (depending on churn etc) the temperature is incredibly constant year round. That is not to say that there is no change in temperature, but it is very small.
So in this instance, these sponges have been recording changing temperature over the years, and according to their tempearture records, the planet has alread warmed by 1.7° C, which is half a degree more than the United Nations climate panel has seen elsewhere.
A number of climate scientists have questioned how wide-ranging a conclusion, you can draw from readings taken from one sponge species in just one location in the world. However, the lead researcher stated “Taking a precautionary principle, our findings show taht global warming is more advanced than we thought and therefore it’s a wake-up call that we have to get on with reducing CO2. He went on to add “We will experience more serious impacts from global warming sooner than we had anticipated”.
6 different speciamins of this sponge species were collected. The sponge can take hundreds of years to grow (to a size only 10cm-15cm). As it grows, it stores strontium and calcium in a ratio which relates directly to the temperature of the water around them. The team reconstructed global water temperatures going back 300 years through this method, and then combined them with land-based temperatures, in order to arrive at global temperatures. Because of the depth, the water temperature changes little from winter to summer, which means that the water tends to match the global average with surprising accuracy.
Incidence like the volcanic eruption in Indonesia in 1815 show up clearly in the record. However, unfortunately, it also confirms that manmade warming started in 1860, and given that global temperature changes are benchmarked against averages of the temperature between 1850 and 1900, it shows that this cannot be considered pre impact by humans.
However, responses are rather more encouraging. Essentially, the point is, that regardless of the sense in taking readings from a moving point, given that both our current position and the warming that we have targeted are against the same wrong number, it is irrelevant – if the start temperature was higher, but all our readings are out by the same quantity, it does not mean we will hit dangerous levels any sooner – these were worked out using the same incorrect measurements.
However, whatever is true, what is clear is that we still need to cut emissions alarmingly fast if we want to escape changes that are likely to kill many people, and displace hundreds of millions more – if not billions.