Amazon Dolphin
The Amazon river dolphin, (other names include boto, bufeo or pink river dolphin), is a species of toothed whale endemic to South America and is classified in the family Iniidae. Three subspecies are currently recognized: Amazon river dolphin,, Bolivian river dolphin and the Orinoco river dolphin while position of Araguaian river dolphin within the clade is still unclear The three subspecies are each found in a separate river basin (in order) the Amazon basin, the upper Madeira River in Bolivia, and the Orinoco basin.
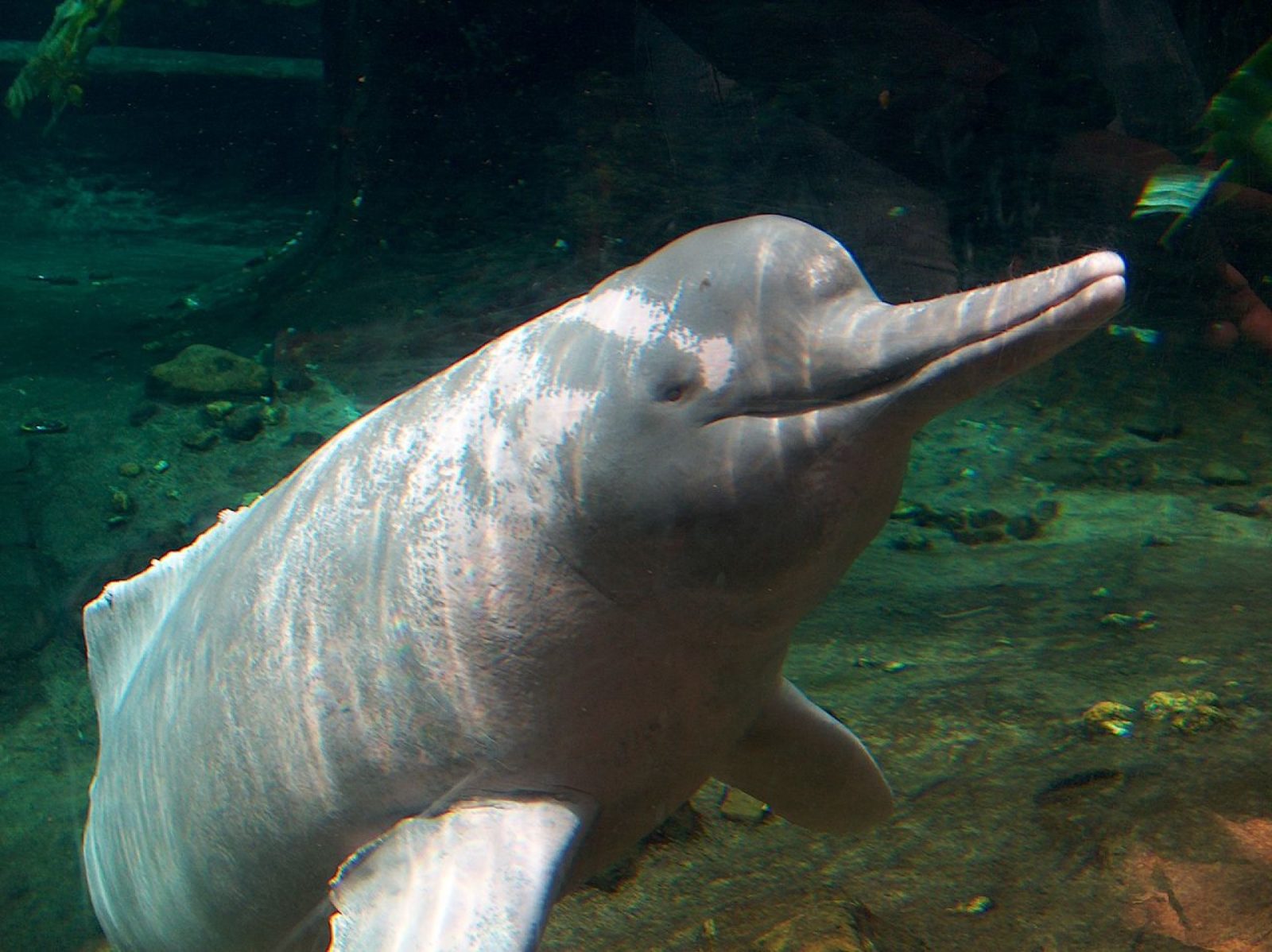
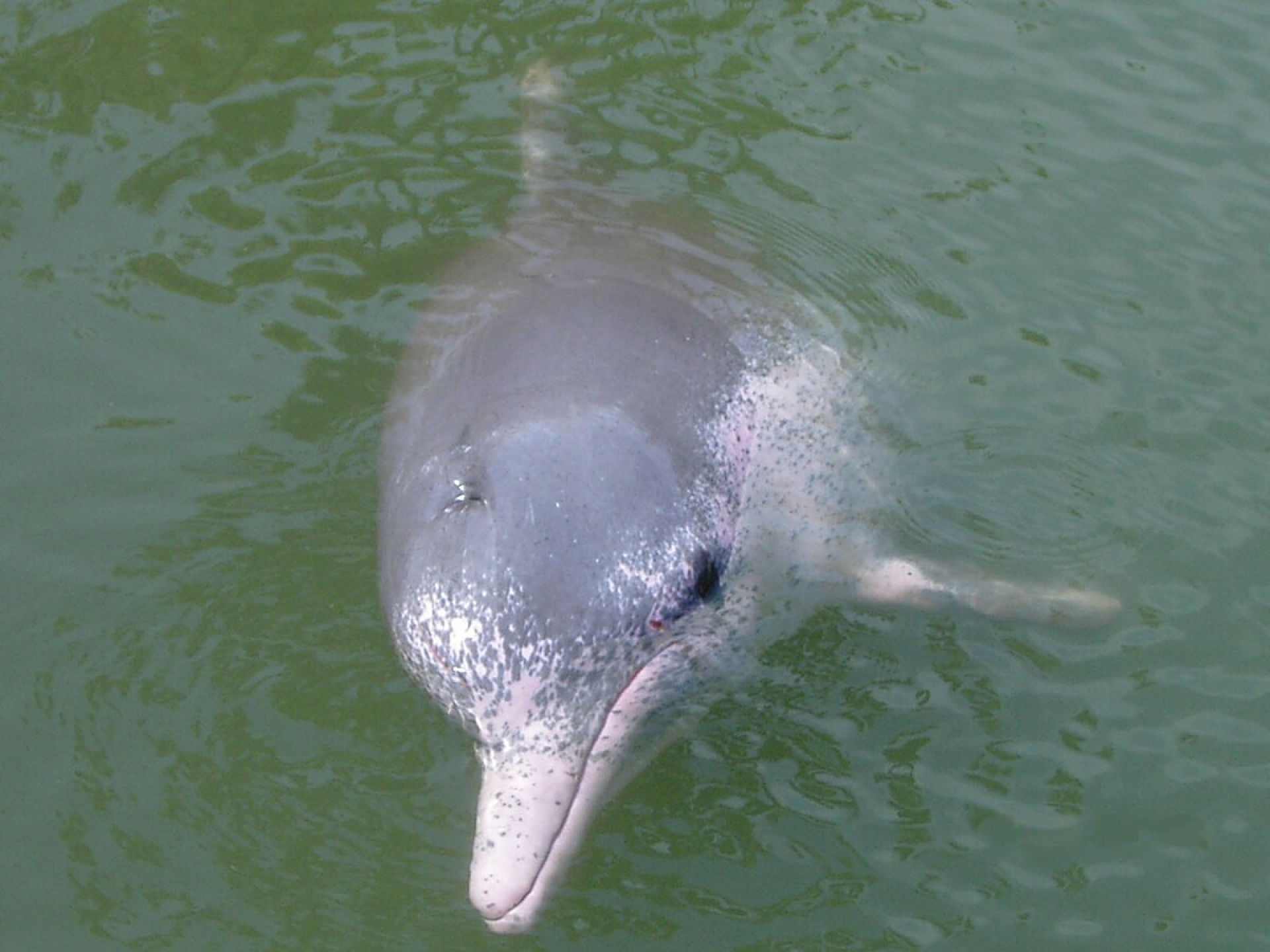
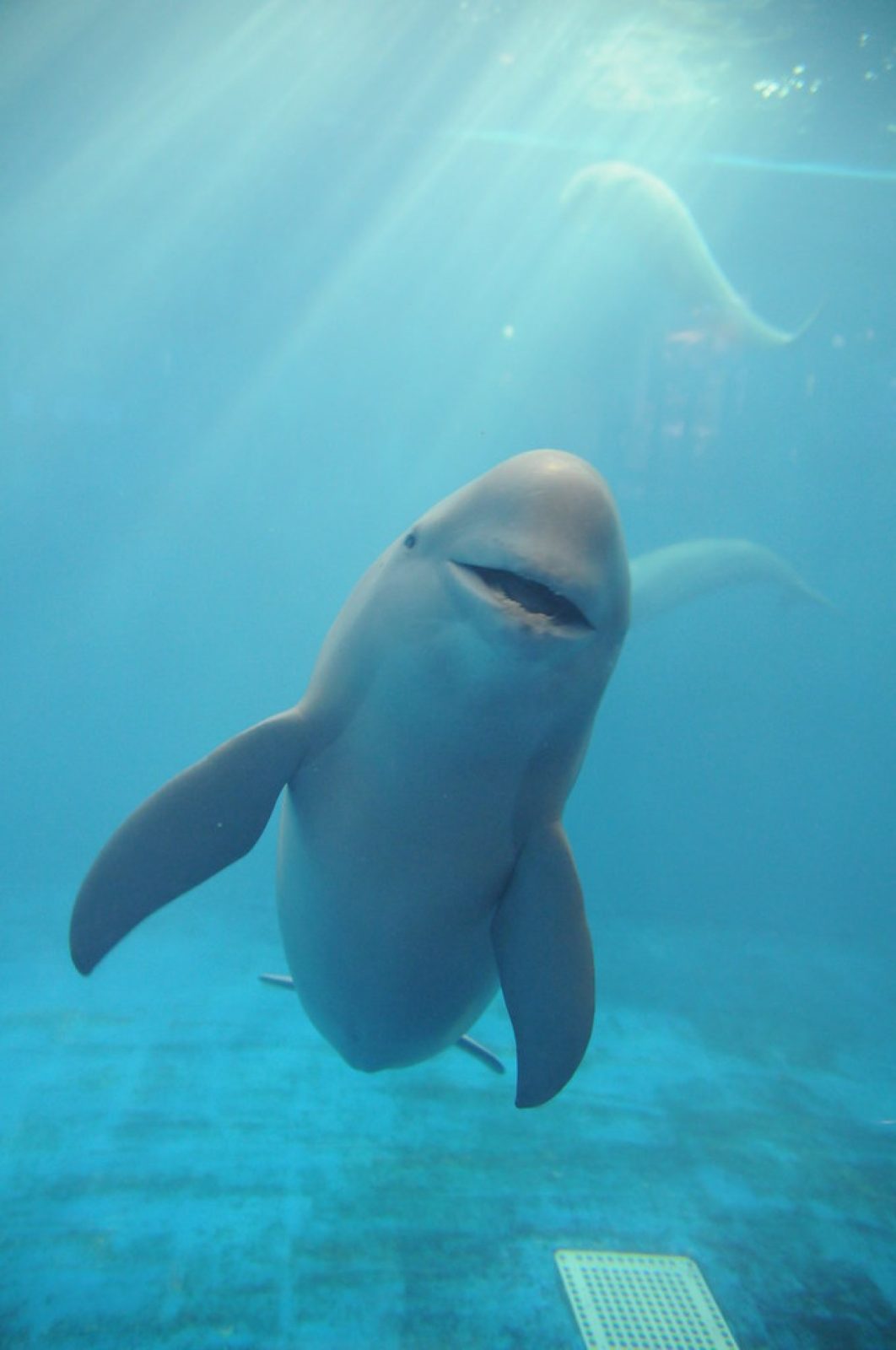
The Amazon river dolphin is the largest species of river dolphin, with adult males reaching 185 kilograms (408 lb) in weight, and 2.5 metres (8.2 ft) in length. Adults acquire a pink colour, more prominent in males, giving it its nickname “pink river dolphin”. Sexual dimorphism is very evident, with males measuring 16% longer and weighing 55% more than females.
Like other toothed whales, they have a melon, an organ that is used for bio sonar. The dorsal fin, although short in height, is regarded as long, and the pectoral fins are also large. The fin size, unfused vertebrae, and its relative size allow for improved manoeuvrability when navigating flooded forests and capturing prey.
They have one of the widest ranging diets among toothed whales, and feed on up to 53 different species of fish, such as croakers, catfish, tetras and piranhas. They also consume other animals such as river turtles, aquatic frogs, and freshwater crabs. However, this is not particularly surprising, as there are so many forms of life in the Amazon rainforest, and plenty is likely to occasionally find themselves in the river.
In 2018, this species was classed as endangered, by the IUCN with a declining population. Threats include incidental catch in fishing lines, direct hunting for use as fish bait or predator control, damming, and pollution; as with many species, habitat loss and continued human development is becoming a greater threat.
While it is the only species of river dolphin kept in captivity, almost exclusively in Venezuela and Europe, it is difficult to train and often die very young, when kept in captivity..
Life expectancy of the Amazon river dolphin in the wild is unknown, but in captivity, the longevity of healthy individuals has been recorded at between 10 and 30 years. However, a 1986 study of the average longevity of this species in captivity in the United States is only 33 months. An individual named Baby at the Duisburg Zoo, Germany, lived at least 46 years, spending 45 years, 9 months at the zoo.
Below you will find any news articles on Amazon dolphin (though articles with both words also get sucked in). Also we will add any information on where you can go to see these in the wild, beneath both of these.