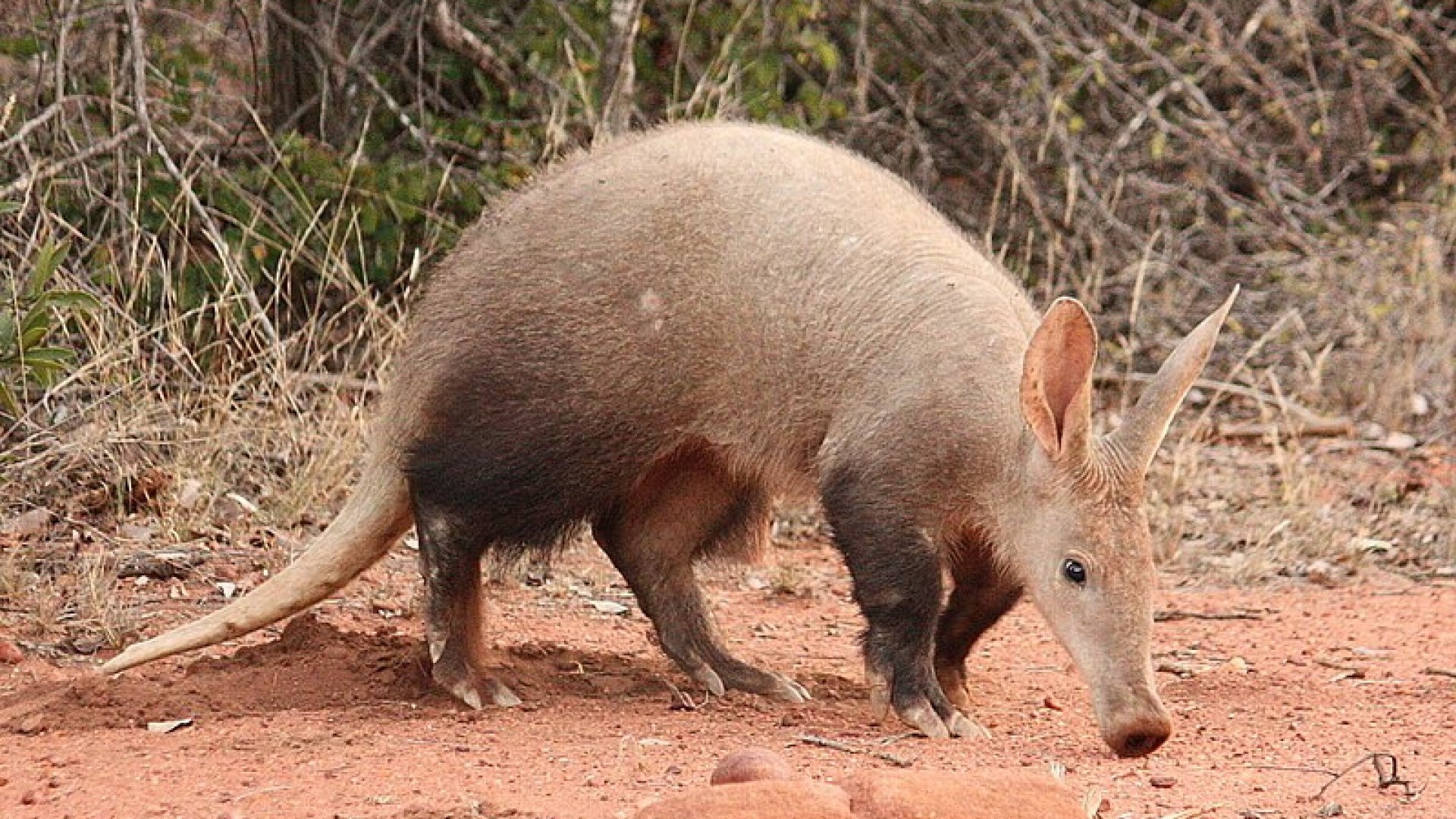

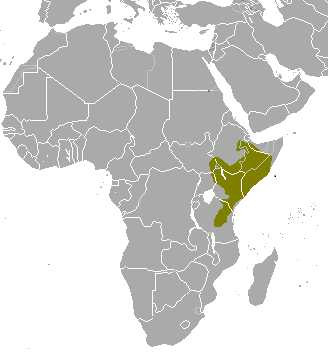
Aardvark
The Aardvark is an incredibly rarely seen animal. It is found on the savannahs of Africa, and generally lives well in and out of protected areas. It is quite a sizable aniimals, and has relatively high densities throughout its range (roughly 1 per square km in habitats that it is best suited to).
So why is it so rare to see this animal? They are one of the most exclusively nocturnal species that you can find. These are animals for which wildlife guides get excited.
The name, translated from Afrikaans means earth-pig. They are incredible diggers, and many of the burrows in the savannah are dug by them, who ever ends up using them.
The are insect eaters, and are well suited. Their claws are strong, allowing them to dig into the incredibly hard termite mounds, it has a long tongue of around 30cm, which they can direct down ant holes to get hold of their food. They have an incredible sense of smell and hearing to allow them to find the animals, and can shut their eyes and nose so as to avoid being attacked back.
Although rarely seen, there are places which have learnt how to watch them, giving you a great chance to see an animal few know about. Over recent decades, they have started appearing in zoos, with Colchester in the UK (should you visit, it is a species that needs patience, otherwise you are likely to just see a pile of aardvarks sleeping in their burrow.
It is at the top of animals I would like to see in the wild. Given, their range both in and out of reserves, I am hoping over time to build up plenty of places to see them out in the human world. Please get in touch if you are a farmer, who has these on your land.
Any of the savannah ecosystems on our wild places list will host these animals, however a great deal of luck will be needed to see them in the wild. However, we will add an special places we find where your odds are higher. For now, click here, if you want to visit a savannah ecosystem in the near future.
Rare sightings, where even a wildlife guide gets excited Aardvarks and Pangolins – and seeing them in the zoo
- Tim
- June 13, 2022
When you go on safari, as with other places there are animals that while fascinating you can be almost certain you will not see.

Brown Hyena hunting Aardvark in the Kruger
- Tim
- November 3, 2020
The Kruger national park is one of the best places to watch wild animals. Indeed on this site I have around 10 destinations spread throughout the Kruger and greater Limpopo...
Are financial institutions around the world supporting pangolin poaching?
- Tim
- December 13, 2020
In the wild there are 8 pangolin species, 4 in Asia and 4 in Africa. The country you that is best known for using pangolin scales in ancient history is...
In Africa the big 5 is famous, what is the UK’s equivalent
- Tim
- August 31, 2020
Apart from b the big 5 and ecotourism big 7 there are a whole host of 5s that have been invented-some are relatively easy, others almost impossible
Big 5: lion...
Review of Kruger National Park
- Tim
- January 6, 2018
- Size [usr 4.5]
- Facilities [usr 5]
- Range of animals [usr 5]
- Road quality [usr 4.5]
- Wildness [usr 3.5]
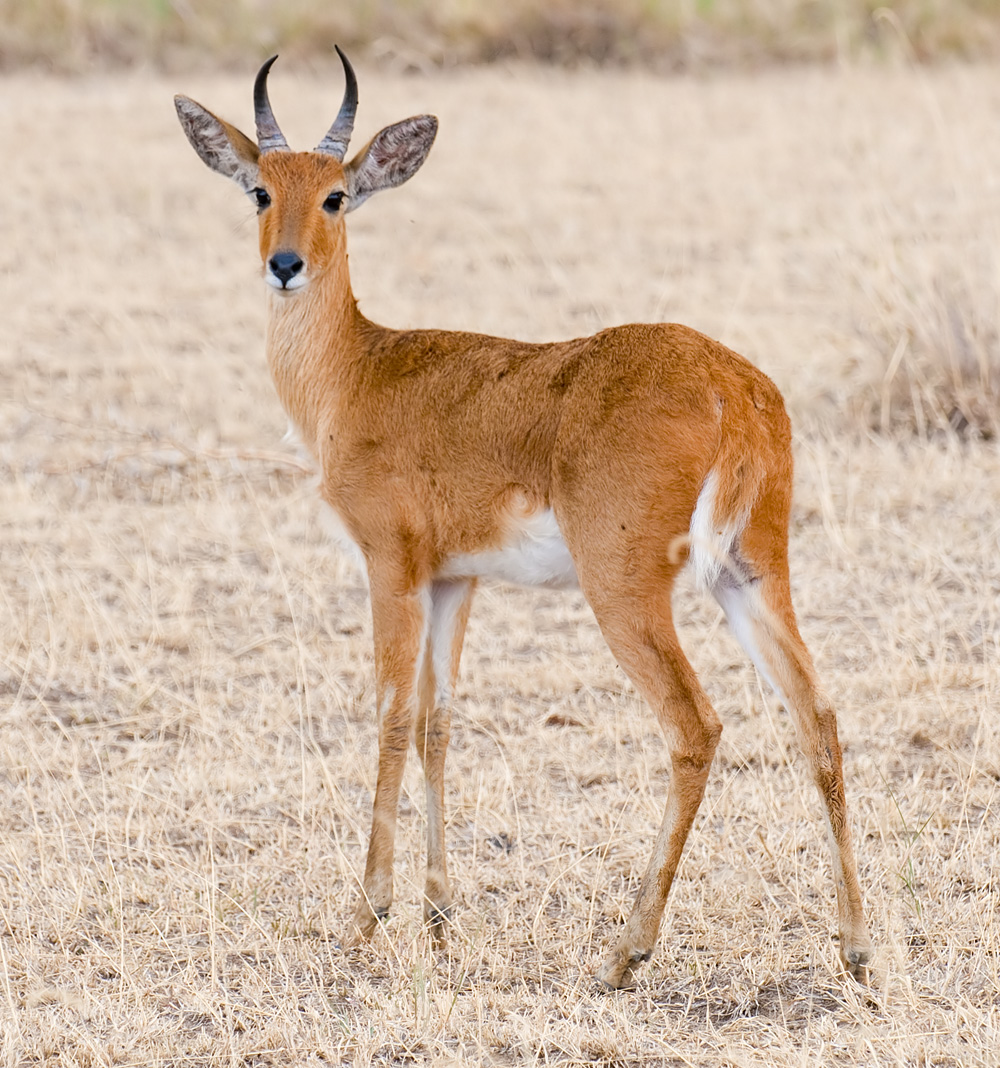
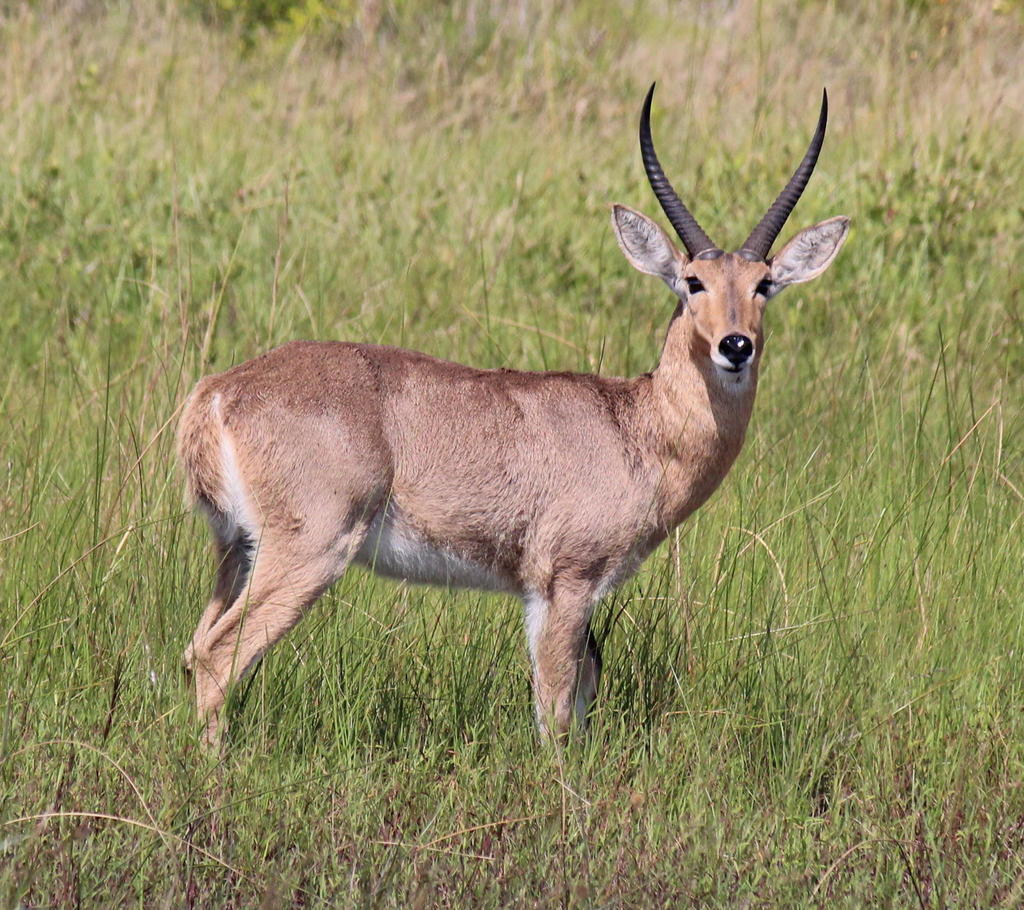





 Reedbuck is found in Southern Africa. It is a midsized
Reedbuck is found in Southern Africa. It is a midsized  are found in a band across Africa, including areas of Eastern, Central and Western Africa.
are found in a band across Africa, including areas of Eastern, Central and Western Africa.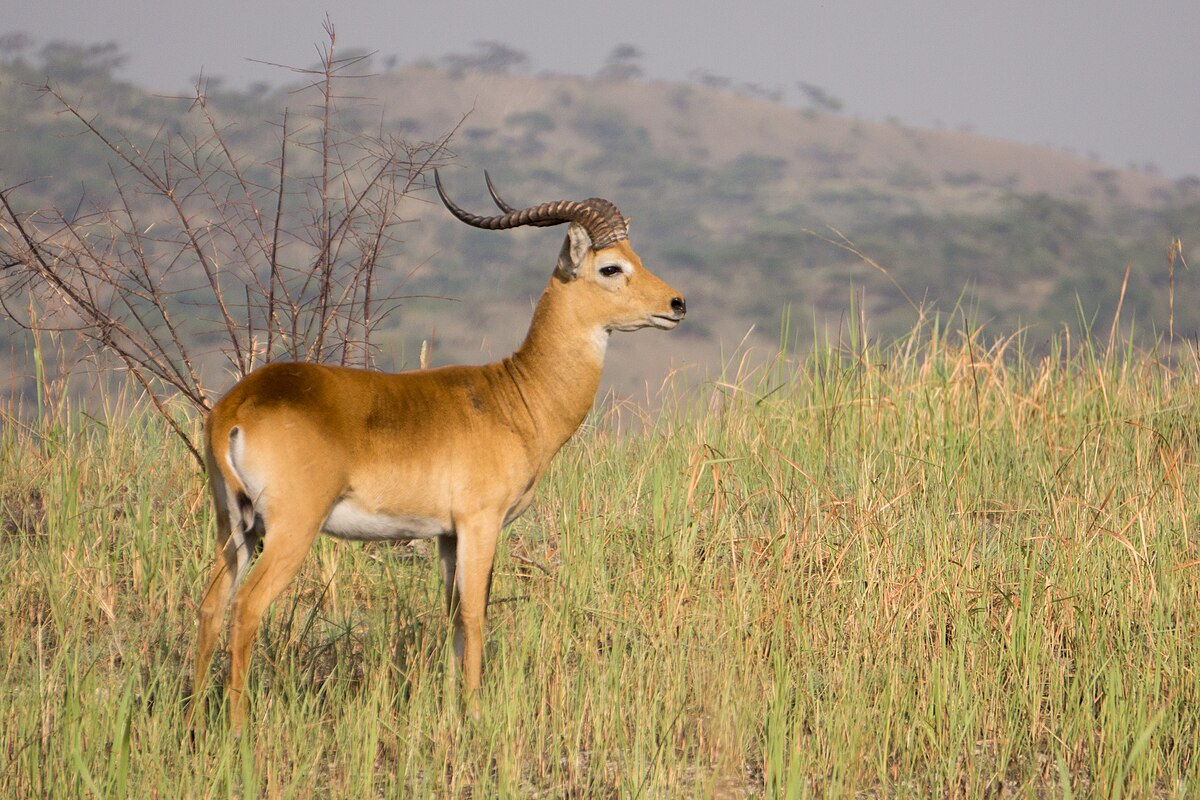
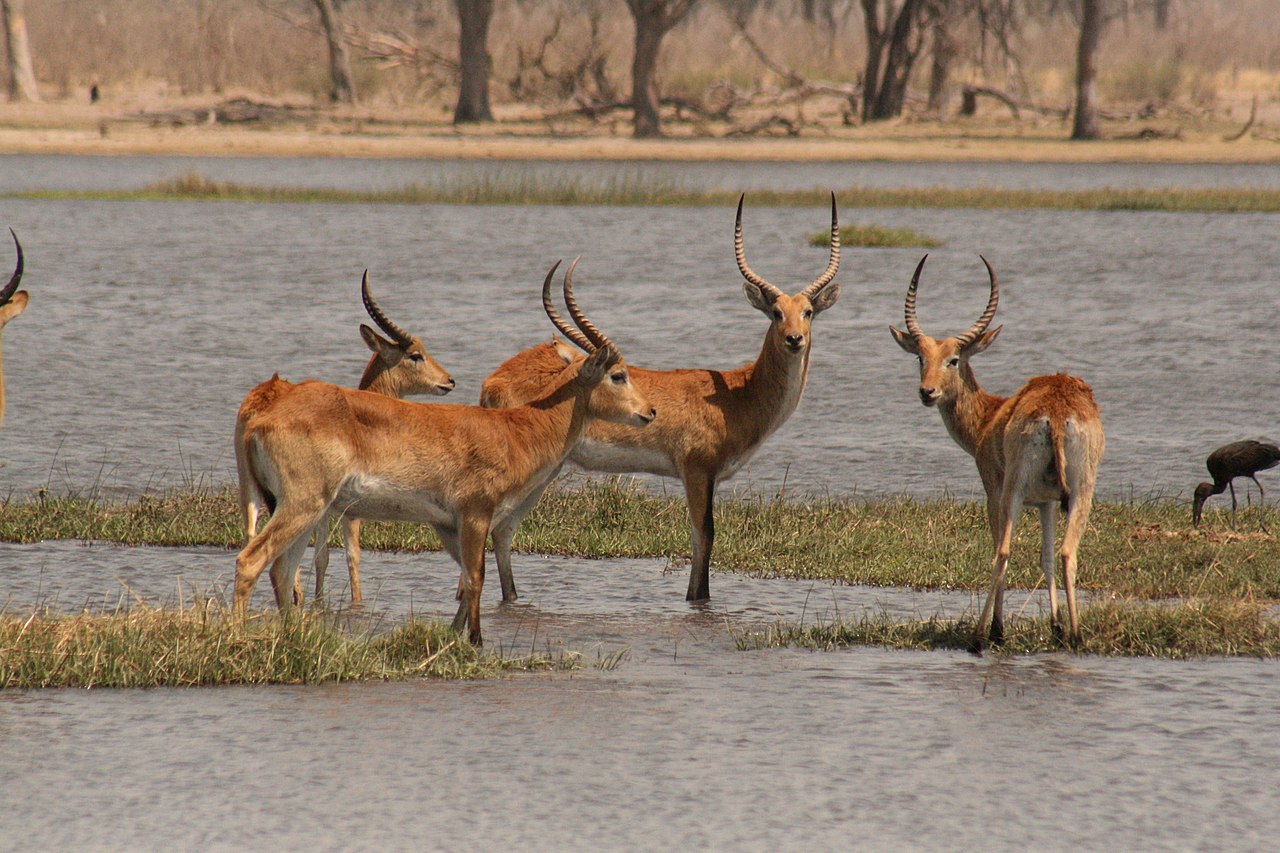

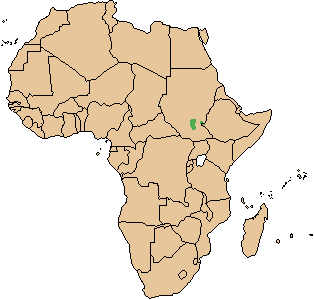 The Nile lechwe or Mrs Gray’s lechwe is an endangered species of antelope found in swamps and grasslands in South Sudan and Ethiopia.
The Nile lechwe or Mrs Gray’s lechwe is an endangered species of antelope found in swamps and grasslands in South Sudan and Ethiopia.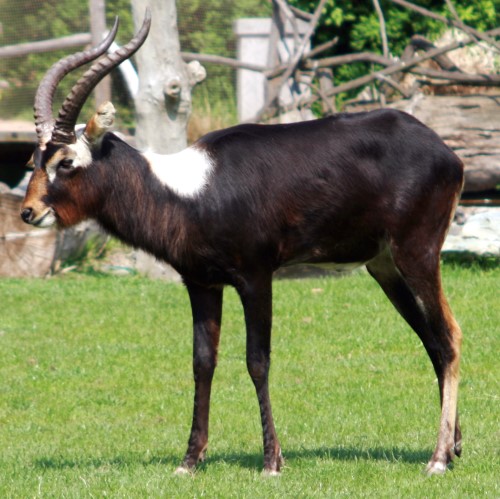
















 Image by
Image by