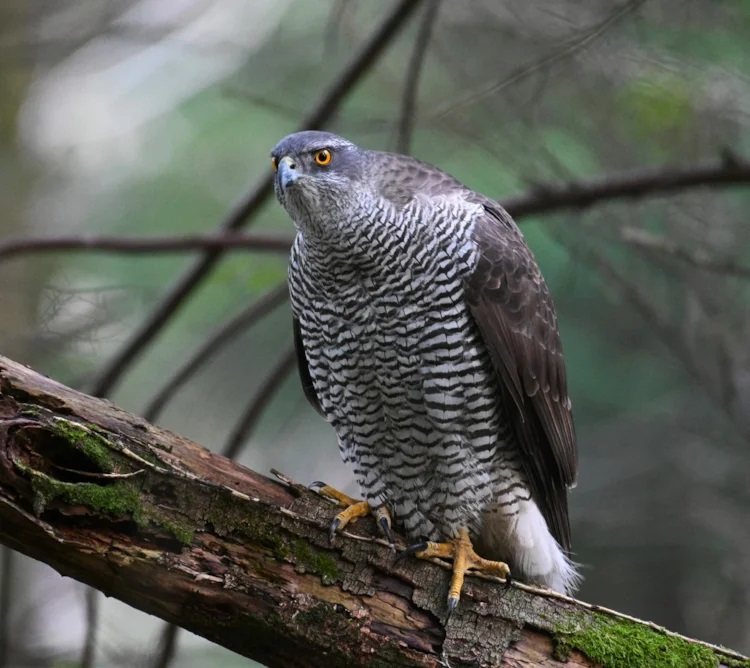
European Goshawks were extinct in Britain at the end of the 19th century (and remained rare for over half a century) but in the last 50 years have made an incredible comeback. In the new forest, in the south of England, there are thought to be hundreds of pairs living wild.
In Thetford forest in Norfolk, an estimated 52% of the goshawks diet was grey squirrel. While it is true that they will also take red squirrels, these are generally better at escaping. More importantly, it is thought that Goshawks could be used to stop the grey squirrels population from growing any further.
As I have written before, the pine marten is also important for the recovery of the red squirrel, as it is far more successful at hunting grey squirrels, and they generally do not cohabit in any part of the country.
This will likely not eliminate the direct need for grey squirrel population to be culled by humans, far from it, but may well help towards the idea of giving red squirrels breathing room.
Continue reading “Could the recovery of the Goshawk save the red squirrel?”