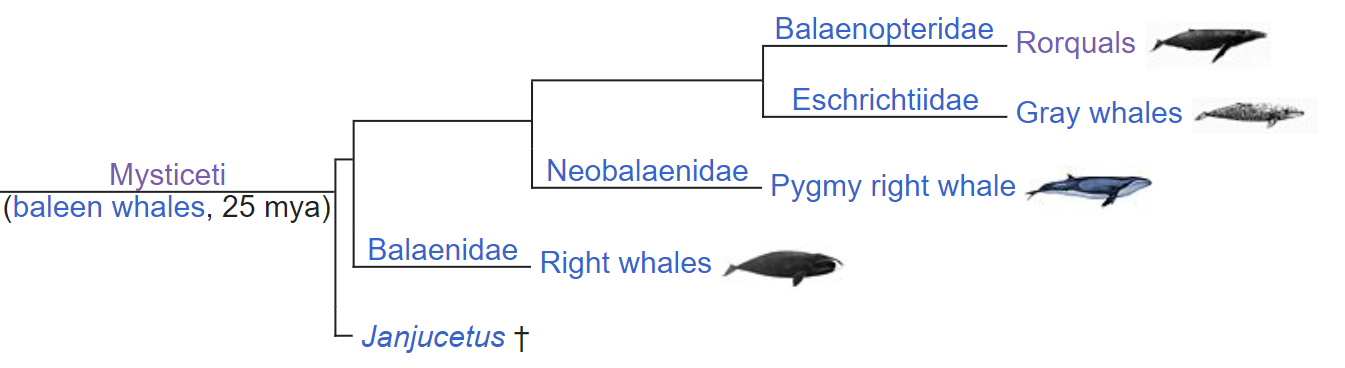
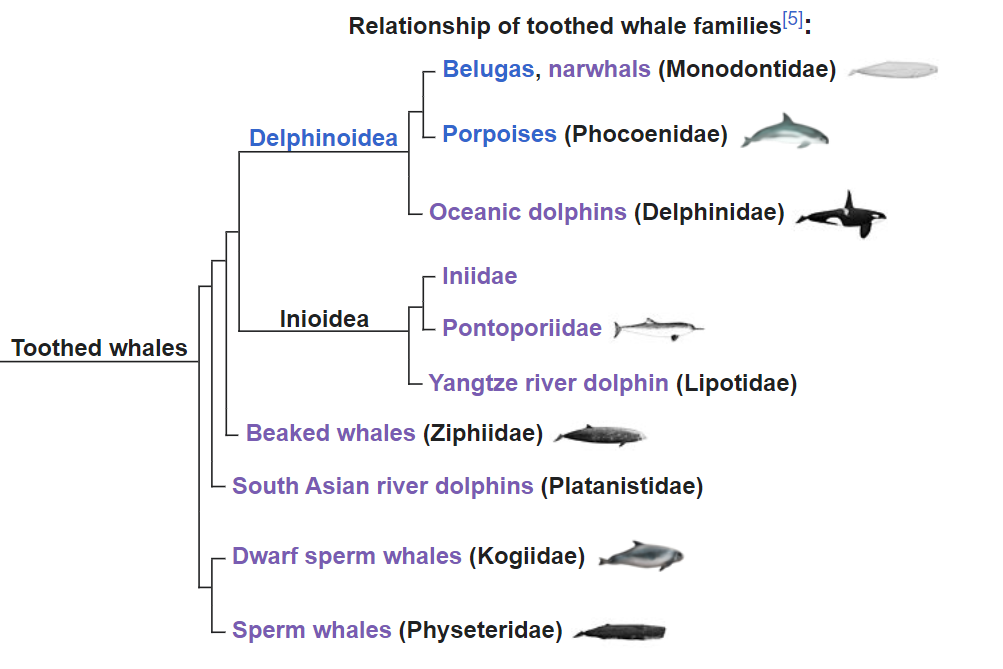
Beaked whales
Beaked whales are a fascinating wide-ranging family. There are 24 species, but they spend much of their time in the ocean depths, and are capable of holding their breath for up to 3 hours.
More amazingly, it appears that some species might only spend several minutes at the surface before returning to the depths. Now, while this 3 hours record dive is repeatable is a big question. Assuming the beaked whale was capable of repeating this 8 times in a 24 hour period, we would be talking about a species which spends only 1% of its time at the surface. Given their shape also allows them to keep an incredibly low profile, even at the surface – and we do not know how many of them there are, it makes it clear how hard it would be to spot one.
If you could sit in one place, in the ocean for 24 hours, and have a whale repeatedly return to the surface for 2 minutes, half a mile away, it would not be hard to miss the animal.
Please note, where I have found a video, it is in line with the correct image. Before you reach all these species, there is an amalgamated news section for all beaked whales.
We are eager to support tourism of these species, but given they are seen so rarely, there is not a great deal of tourism connected to them. However, we will happily list anyone who does work in tourism and sees one of these even once (we will also list you on pages for cetaceans that you see more regularly.
Record length for a mammal to hold its breath has been smashed
- Tim
- October 3, 2020
Beaked whales are a relatively little known about family of species.they are known to be able to hold their breath for incredibly long periods of time, but a recent study...

Arnoux beaked whale Genus Beradius
Also known as the southern 4 toothed whale, southern beaked whale, New Zealand beaked whale, southern giant bottlenose whale and southern porpoise whale is one of the species of Berardius. This species and the one below, is so similar that only genetic evidence and the huge distance between them convinced people they were separate species.
Little is known about them, because they are encountered so rarely
Baird Beaked whale Genus Beradius
Also known as the northern giant bottlenose whale, North Pacific bottlenose whale, giant four-toothed whale, northern four-toothed whale and the North Pacific four-toothed whale, is a species of whale from the genus Beradius. It is the second largest toothed whale after the Sperm Whale


Sato Beaked whale Genus Beradius
This whale was only recognized as a separate species on the basis of mtDNA. Its beak is usually only around 4% of body length. The name comes from the researcher who defined it (from pictures on land.
They generally have many scars, which are easy to see, as their skin is dark and the scars light to white.
Its classed as near threatened, though its hard to know.


Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Hyperoodon – bottlenose whales, Southern bottlenose whale
The southern bottlenose whale is a species of whale, in the Ziphiid family, one of two members of the genus Hyperoodon. Seldom observed, the southern bottlenose whale is resident in Antarctic waters. The species was first described by English zoologist William Henry Flower in 1882, based on a water-worn skull from Lewis Island, in the Dampier Archipelago, Western Australia. They live in deep ocean waters over 1000 meters.
Gnerally their dives last 15-40 minutes, but it is unclear if they would be capable of diving for as long as the northern species. There are no population estimates, though they make up 90% of ziphiid sightings in Antarctic waters.
Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Indopacetus, Tropical bottlenose whale
The tropical bottlenose whale, also known as the Indo-Pacific beaked whale or Longman’s beaked whale, was considered to be the world’s rarest cetacean until recently, but the spade-toothed whale now holds that position. As of 2010, the species is now known from nearly a dozen strandings and over 65 sightings. This is the only species in its genus.
Given how rarely they are sighted, they have not been hunted, though they have been killed accidently.

Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Mesoplodon, mesoplodont whales, Andrews Beaked whale
Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Mesoplodon, mesoplodont whales Blainvilles beaked whale

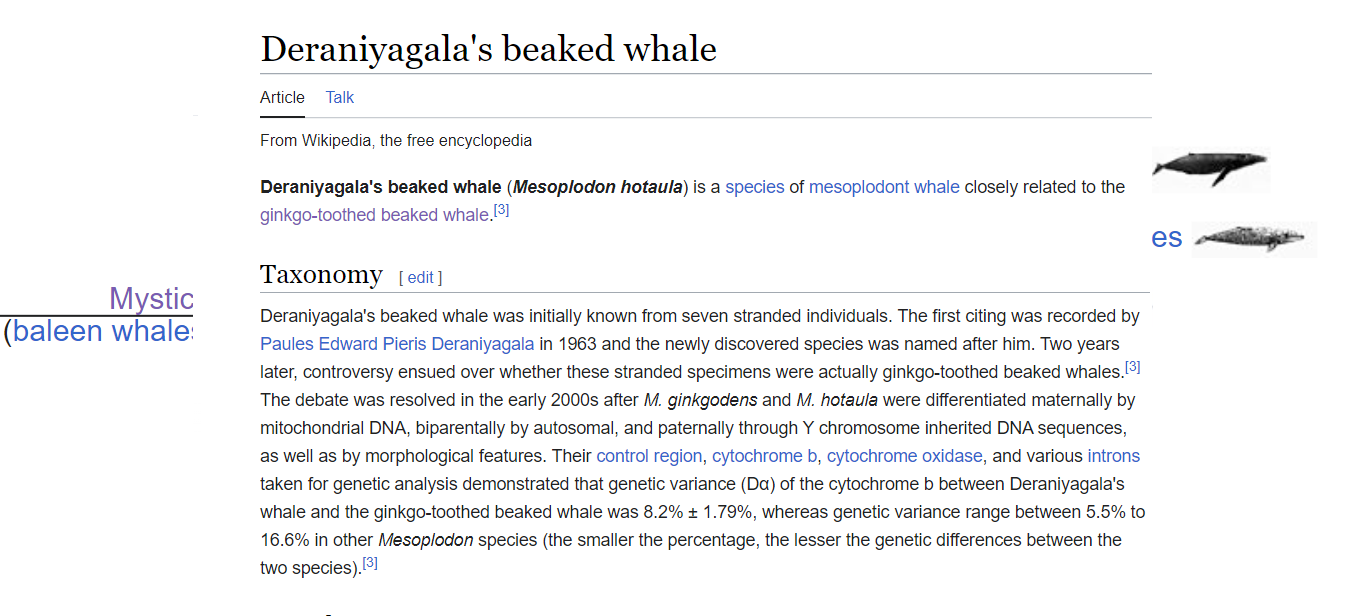
Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Mesoplodon, mesoplodont whales Deraniyagala beaked whale
The Deraniyagala beaked whale is so rare, I have been unable to find a video to place here
.
.
.
.
Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Mesoplodon, mesoplodont whales, Gervaiss beaked whale


Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Mesoplodon, mesoplodont whales,
Ginkgo-toothed beaked whlae
Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Mesoplodon, mesoplodont whales, grey beaked whale

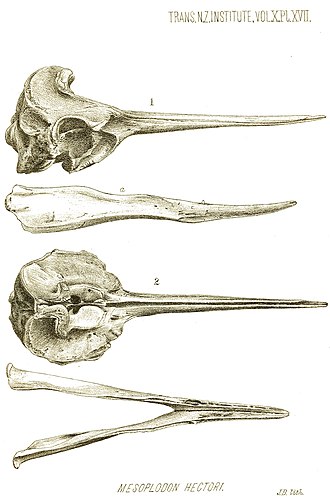
Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Mesoplodon, mesoplodont whales, Hectors beaked whale
Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Mesoplodon, mesoplodont whales, Hubbs Beaked whale

Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Mesoplodon, mesoplodont whales, Perrins beaked whale
Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Mesoplodon, mesoplodont whales, Pygmy beaked whale
Subfamily Hyperodontinae, Genus Mesoplodon, mesoplodont whales
Subfamily Hyperodontinae

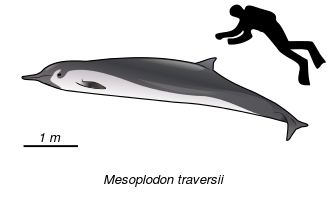
Subfamily Hyperodontinae
Subfamily Hyperodontinae


Subfamily Hyperodontinae
Subfamily Hyperodontinae