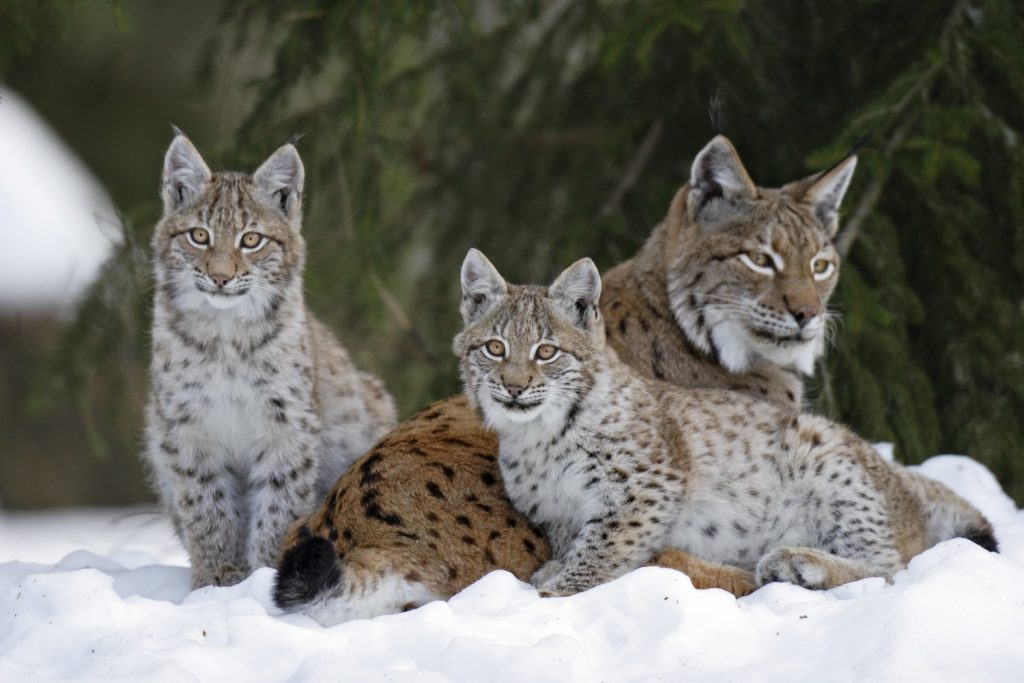
The recovery of wolves bears and lynx over the last several generations in western Europe has been nothing short of astounding.
In the 1960s the population of the iberian wolf did not number more than a few hundred, yet now there are 2500. Similarly, bears got very low but now more than 300 roam – though this still has some way to go. The Iberian lynx was not heavily hunted, yet was still almost wiped out due to human introduced diseases wiping out most of the rabbits in Spain.
France destroyed its wolf population completely, though they are back, having crossed from Italy about 20-30 years ago. Bears were similarly almost wiped out, except a tiny relict population in the Pyrenes. Unfortunately, this population has not done well and is essentially only there because of bear translocations from further east. Similarly, Lynx were eradicated by 1900 though this has been reversed by reintroduction projects. There are a couple of zones where lynx are found (a reintroduction project in Switzerland returned them to part of france), However, there is not going to be more than 130 lynx in the whole country and the population does not seem to be growing.
Italy retained a wolf population, though in the 1970s there was only 70-100 left. Nowadays, 1000-2000 wolves roam the country, and it is roaming members of this population that seeded the population in France. 80-90 bears remain in Italy (the Marsican bear), and while this is a more healthy population than that in France, it is still not enough to be secure. Lynx were eradicated but have been reintroduced, though they are not thought to have established a population that would be secure longterm without continued translocations.
Scandinavia could in some ways be thought of as a strong-point for all three animals in western-Europe, though there are still views that are not helpful. The encouraging thing here, is that the wolf is able to return from Russia. There are no more than 500 wolves in this area, and Norway has a relatively strange view of the wolf, with human hunting elk very popular, wolves are seen as a nuisance and kept at a minimum. Norway has a similar view of the bear, with them being far more common in Sweden. Lynx are widespread in this part of the world.
Why should we champion the return of these animals? They have the capacity to rebalance environments, as well as allowing forests to operate properly – in the UK, as we are missing these predators, replanting forests are often hindered by deer grazing them to much. There are other reasons though. These animals can be a big tourist draw, allowing people to make a good income, often in places where there is little other economic potential. In the UK, return of wolves and lynx would save hundreds of human lives each year by reducing deer collisions on our roads.
Will their recovery continue? I hope so, though it seems to very much be an area where progress is two steps forwards and one step back.